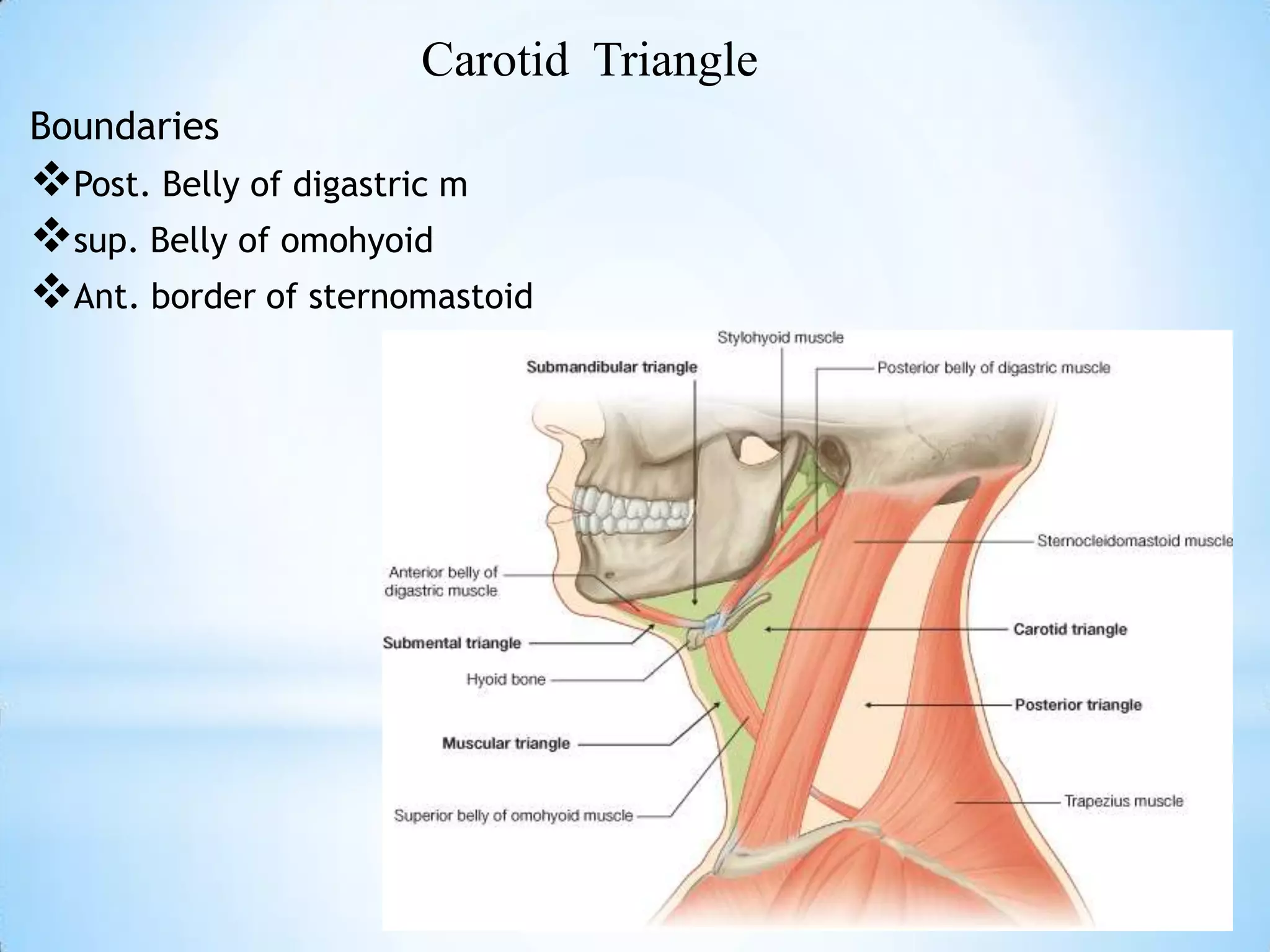
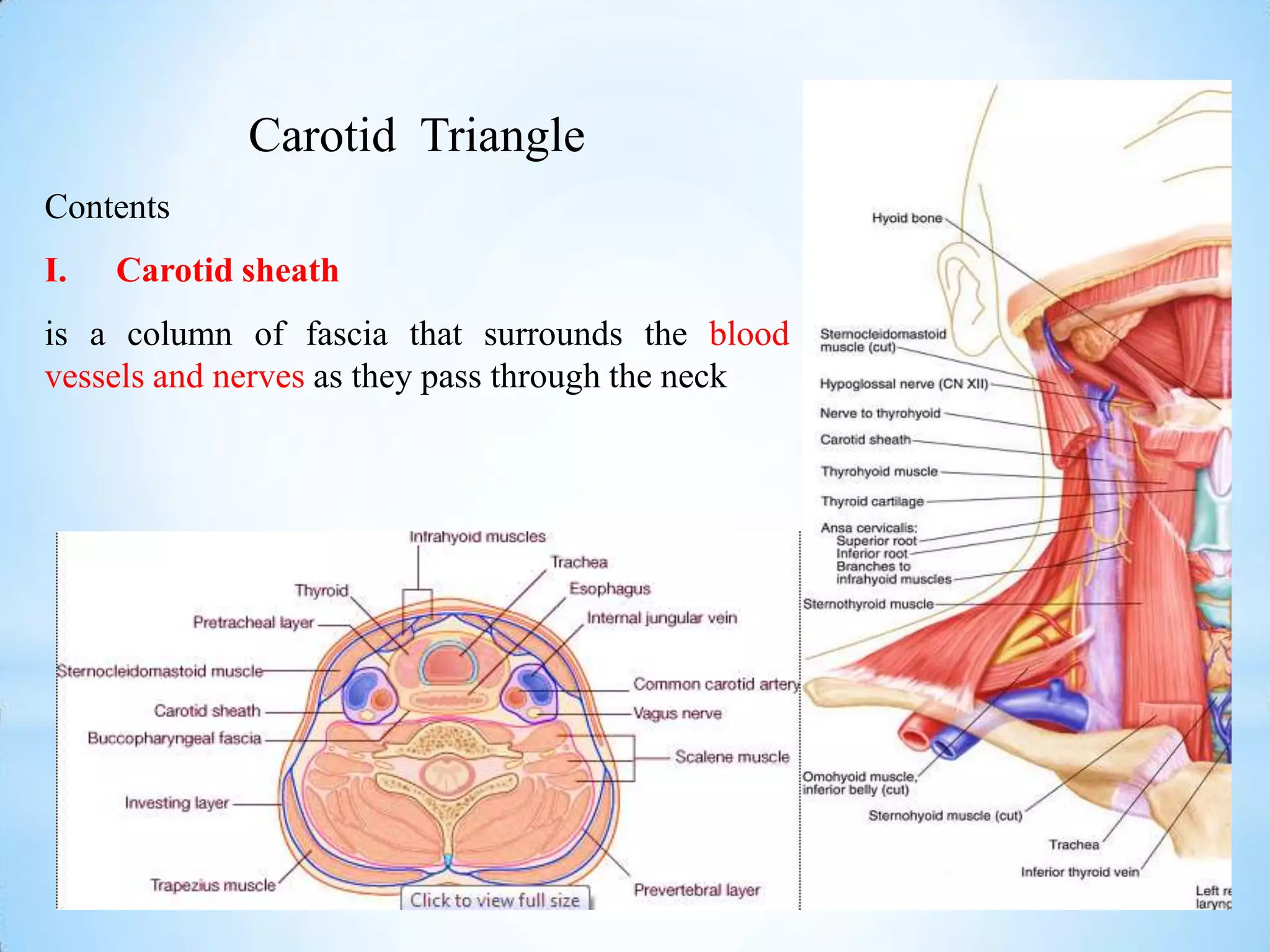
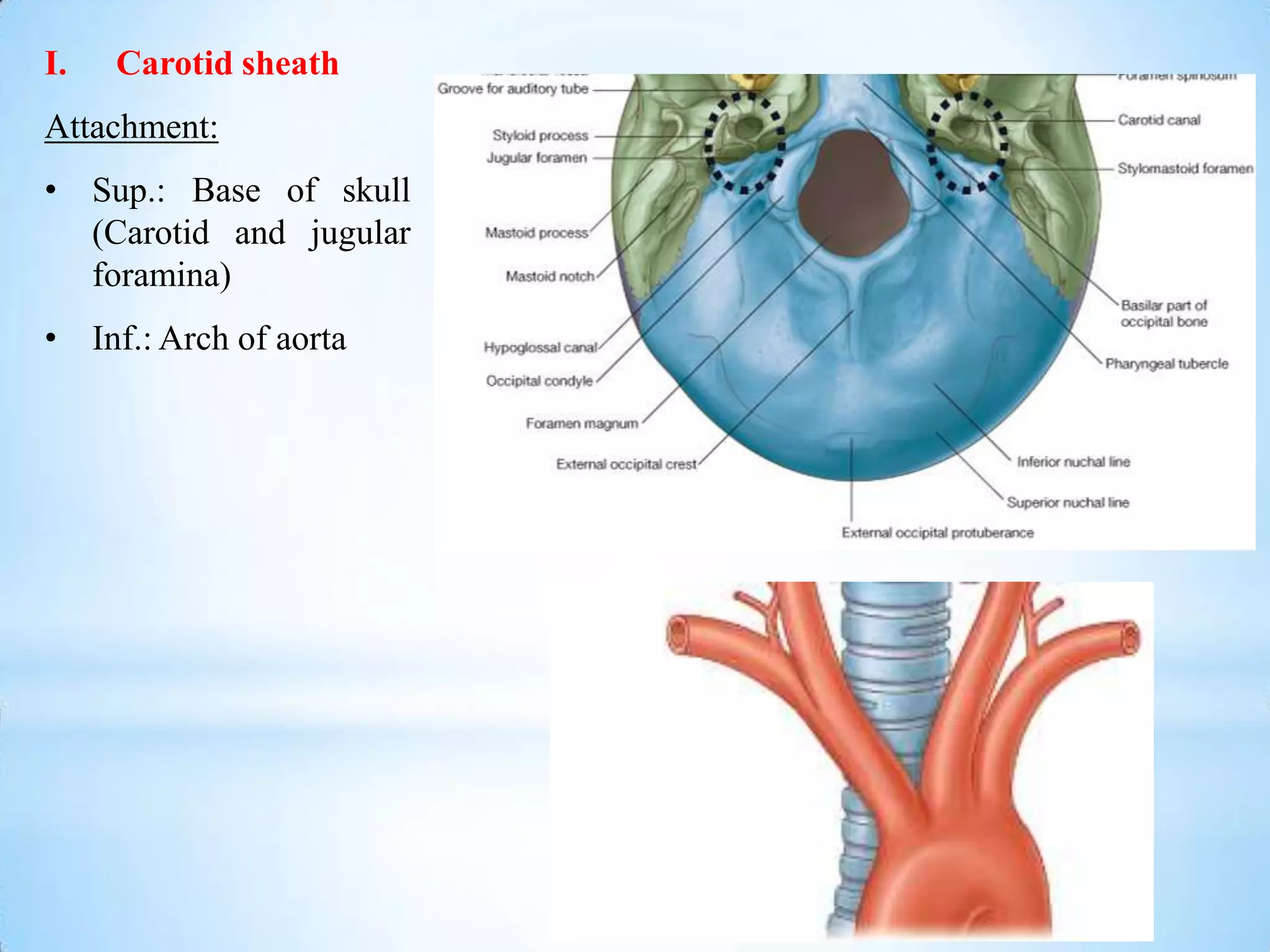
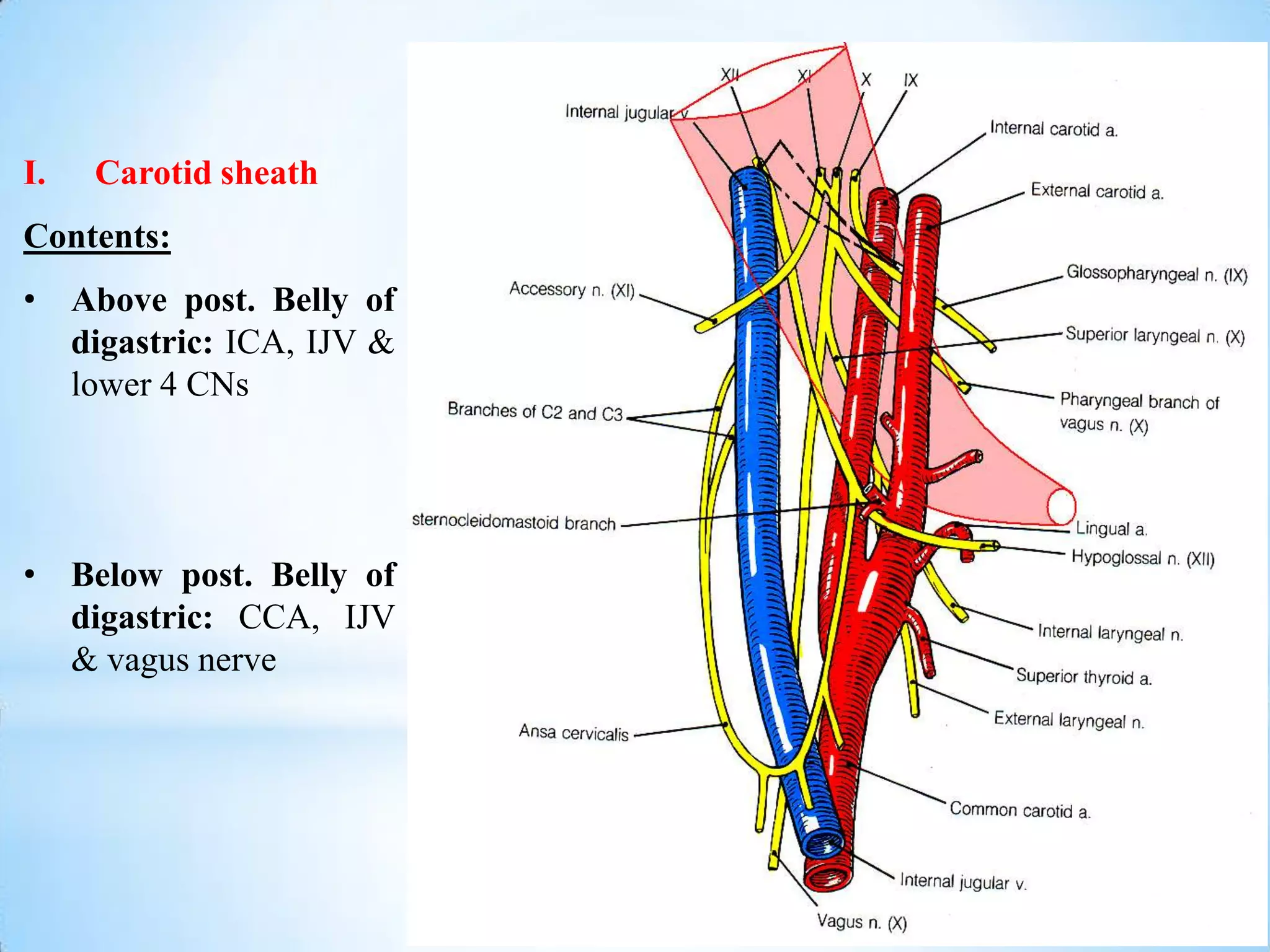
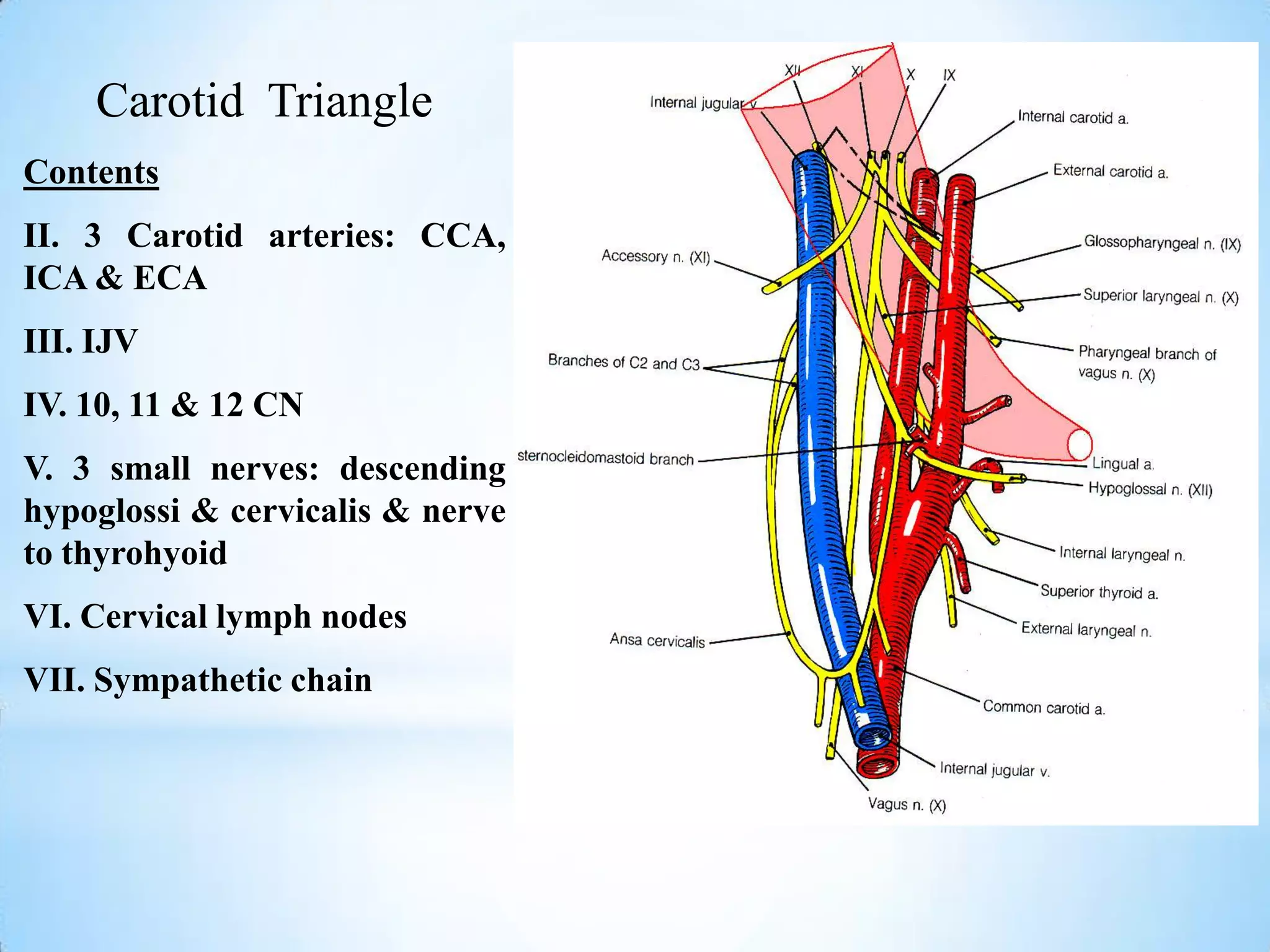
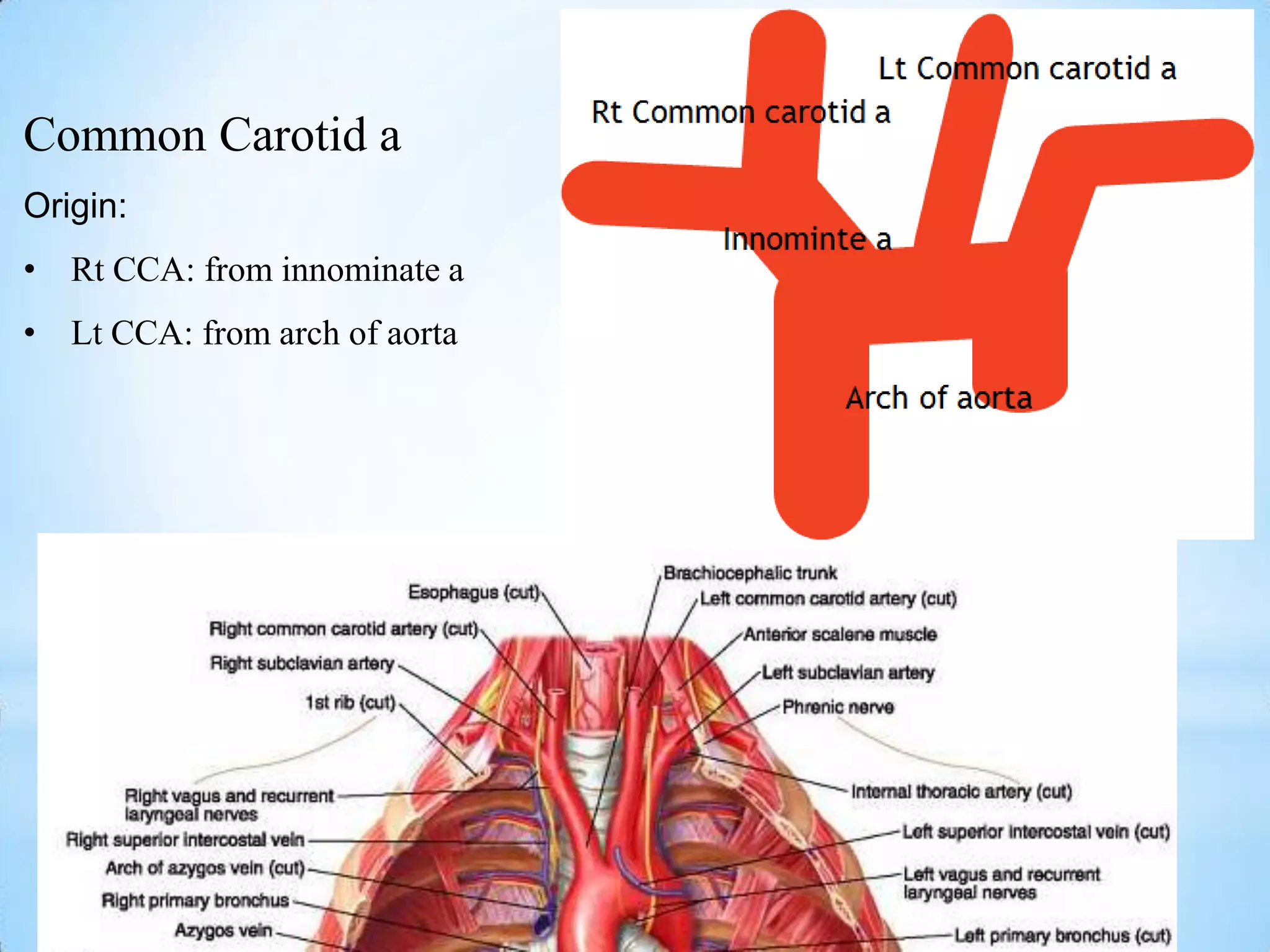
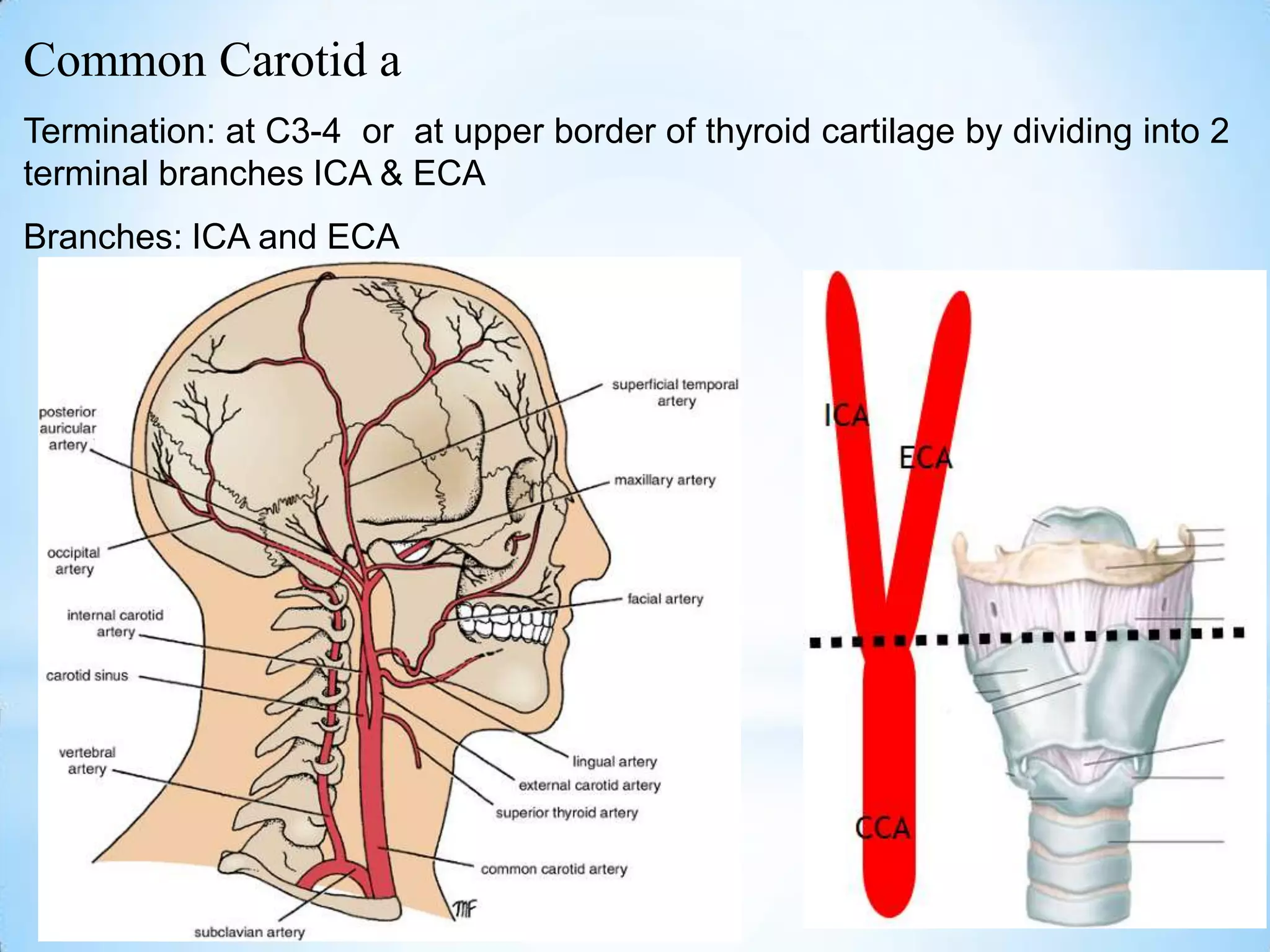
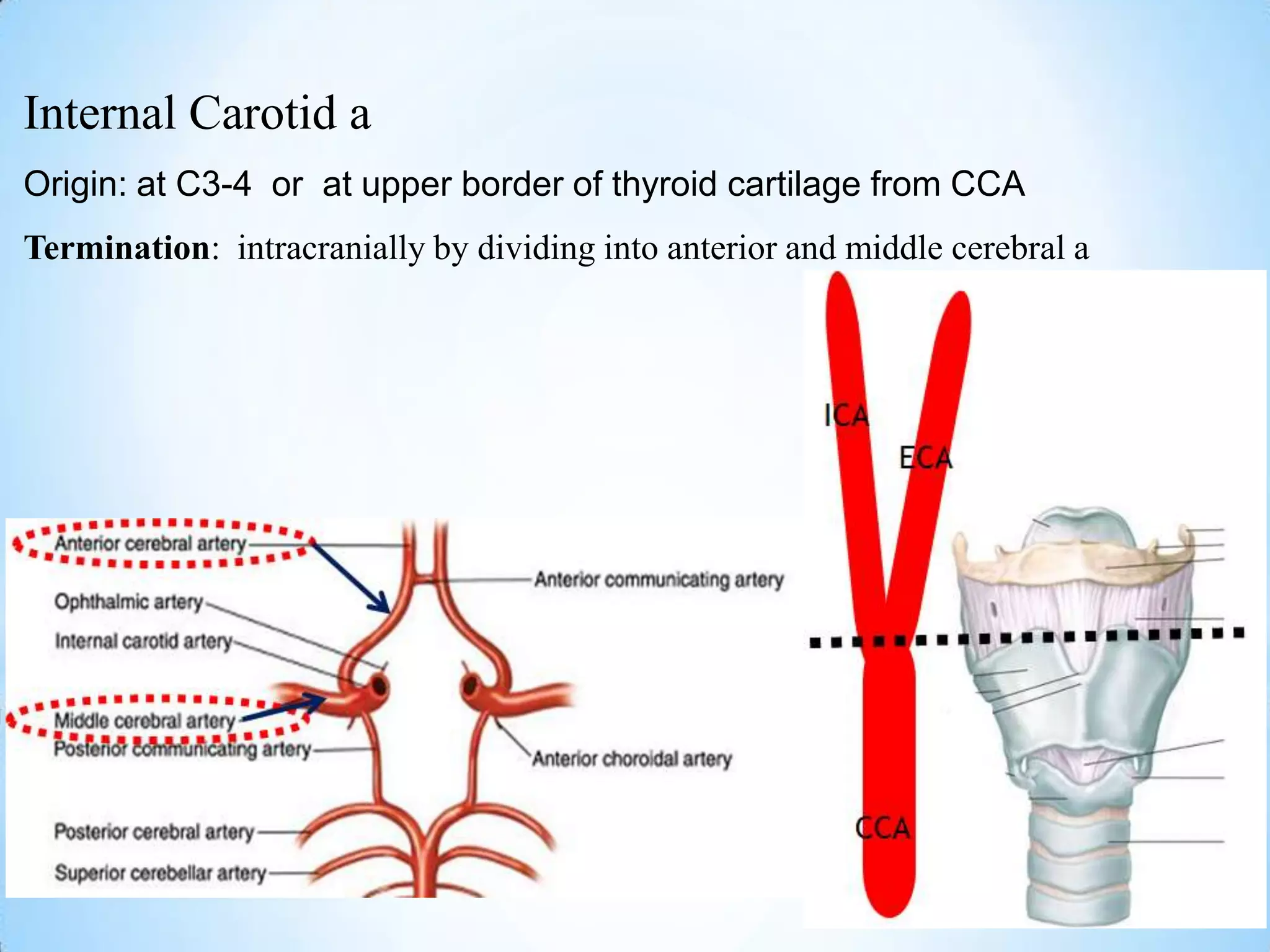
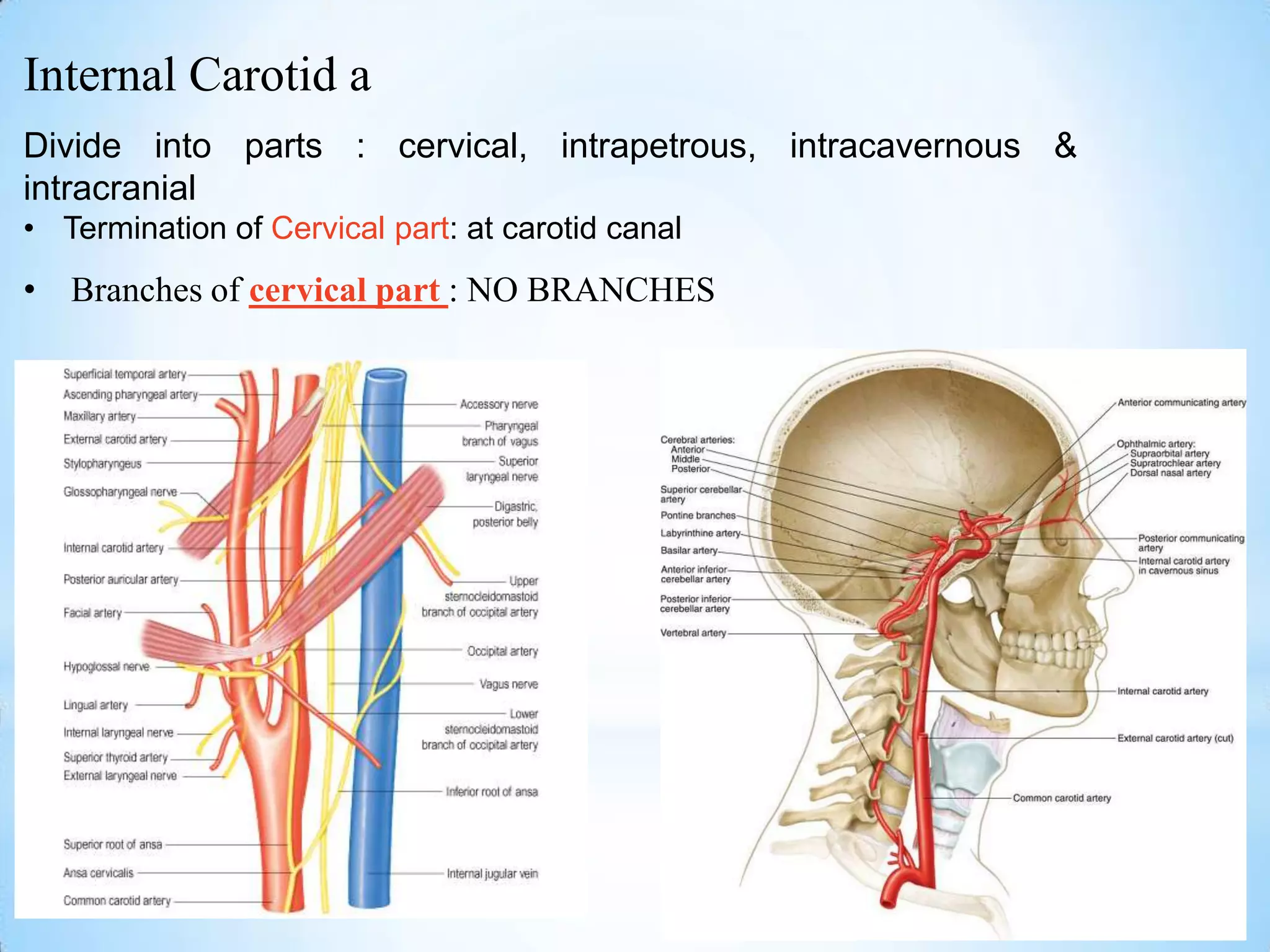
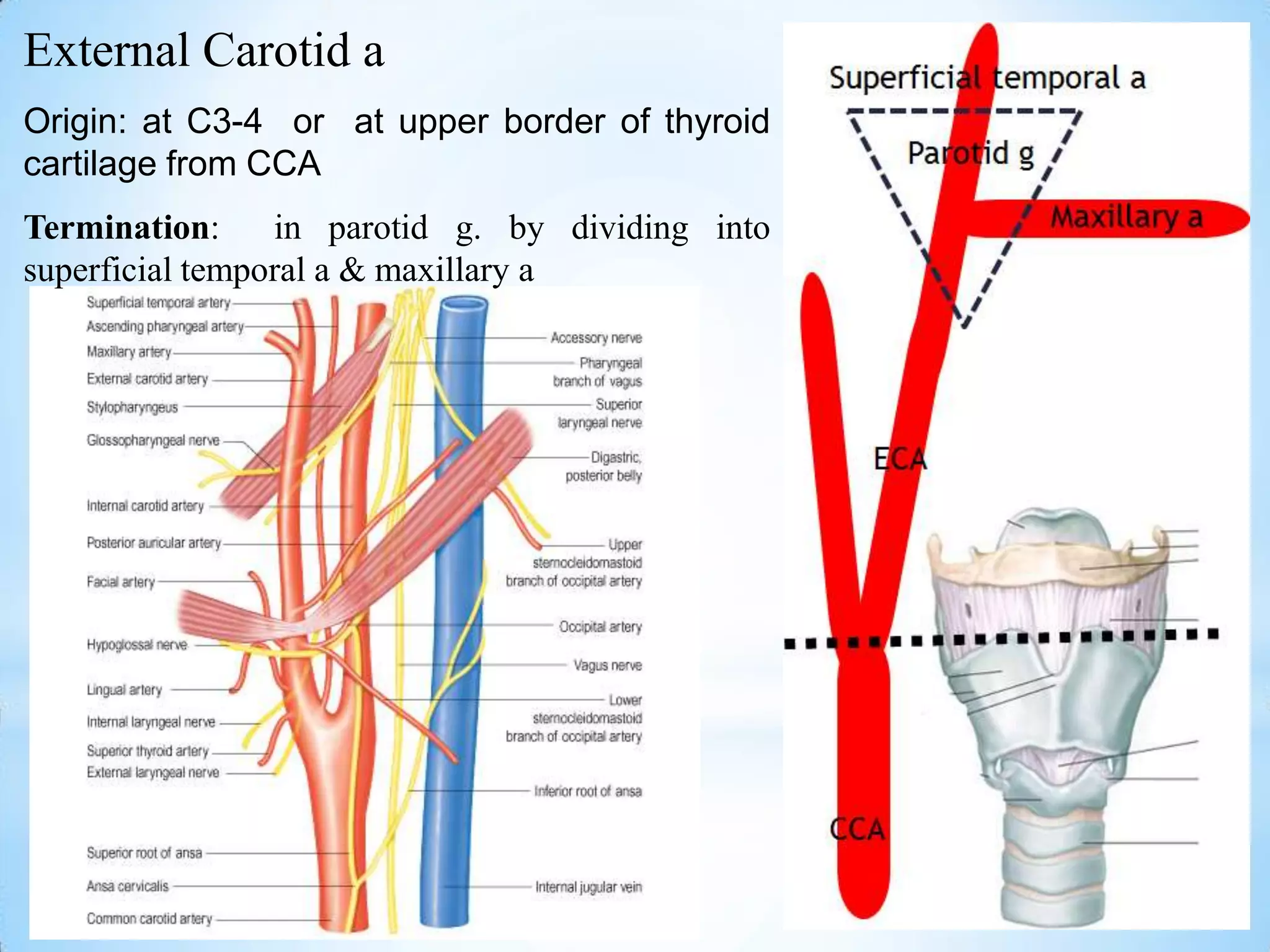
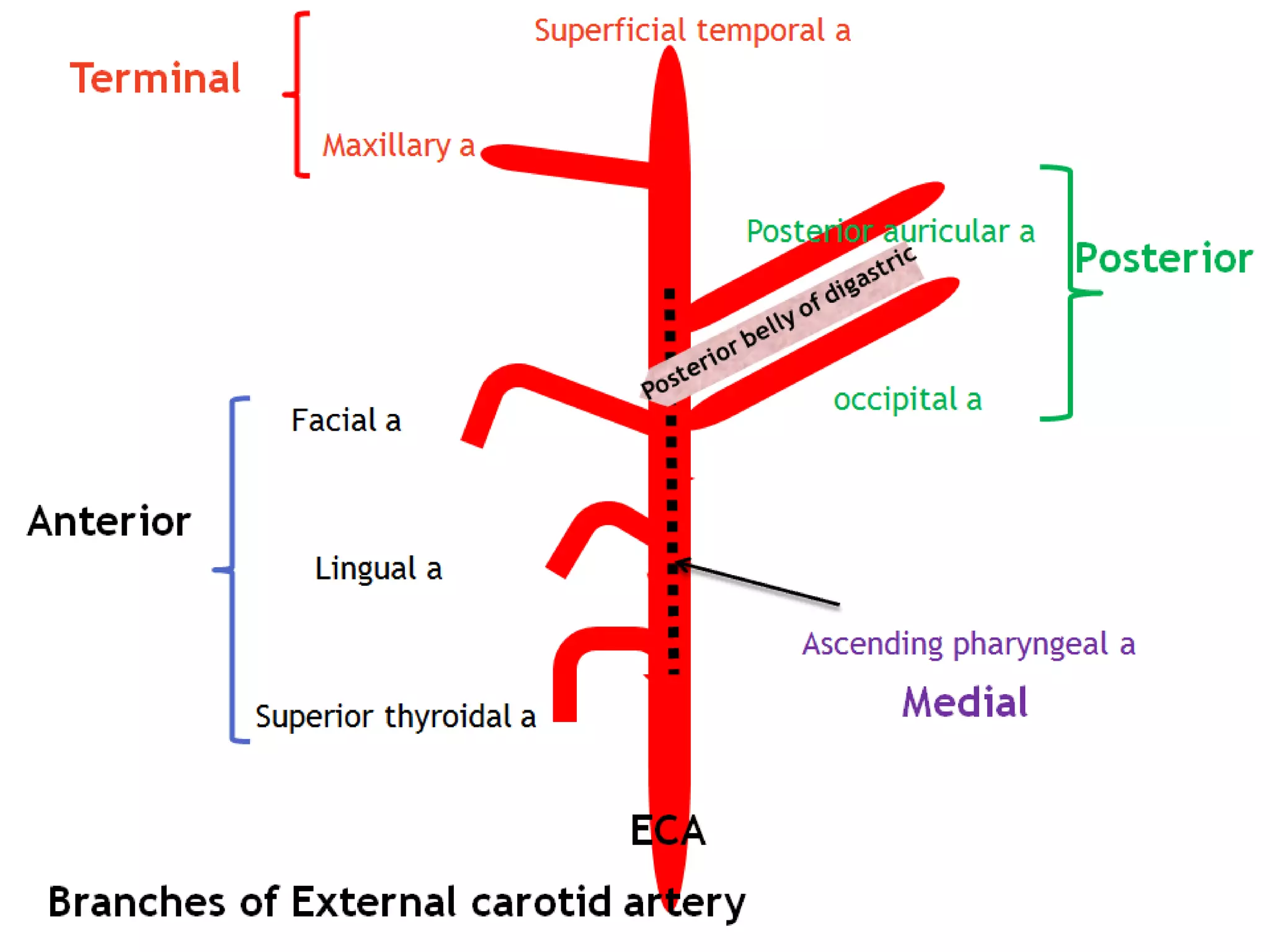
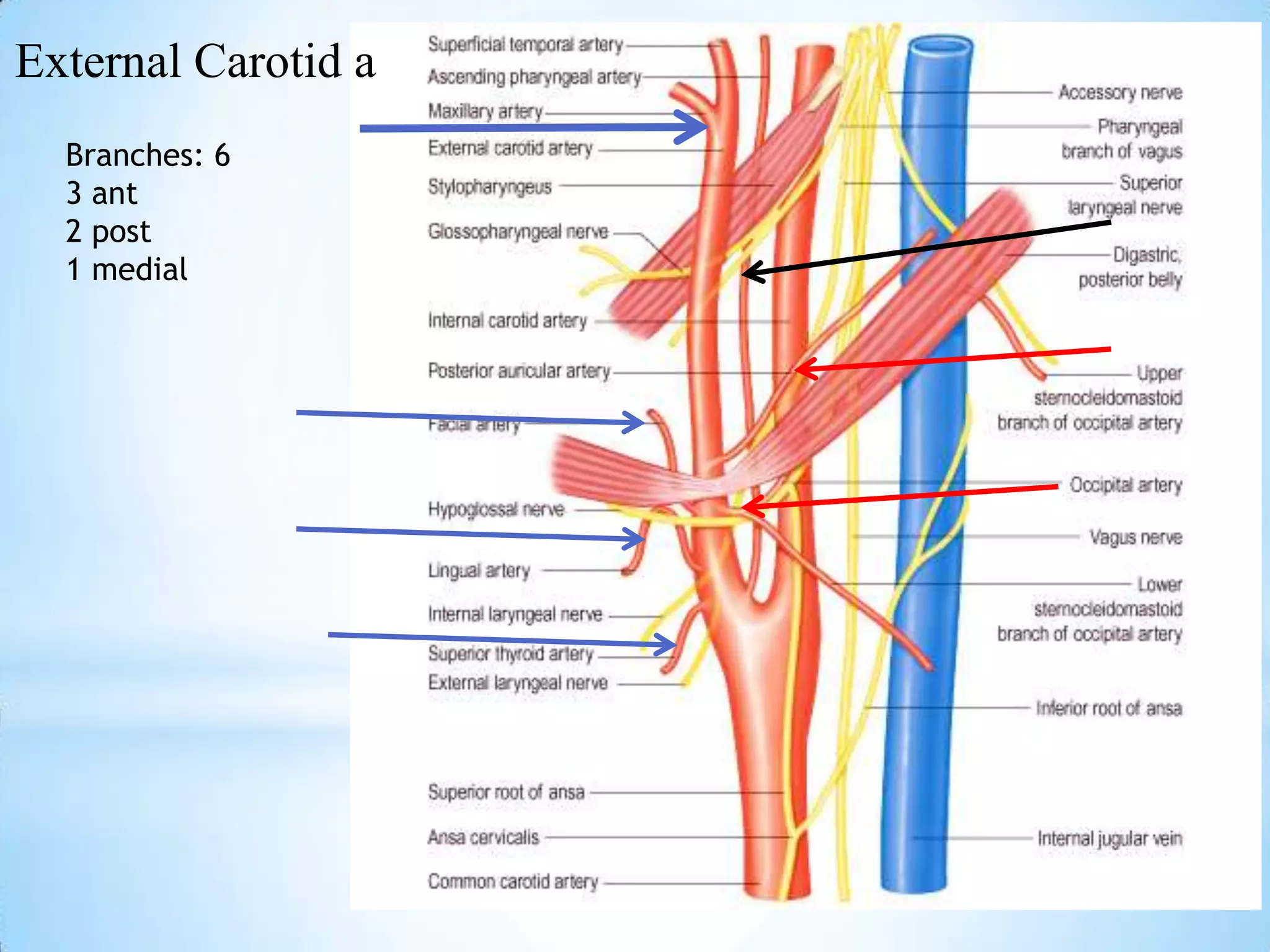
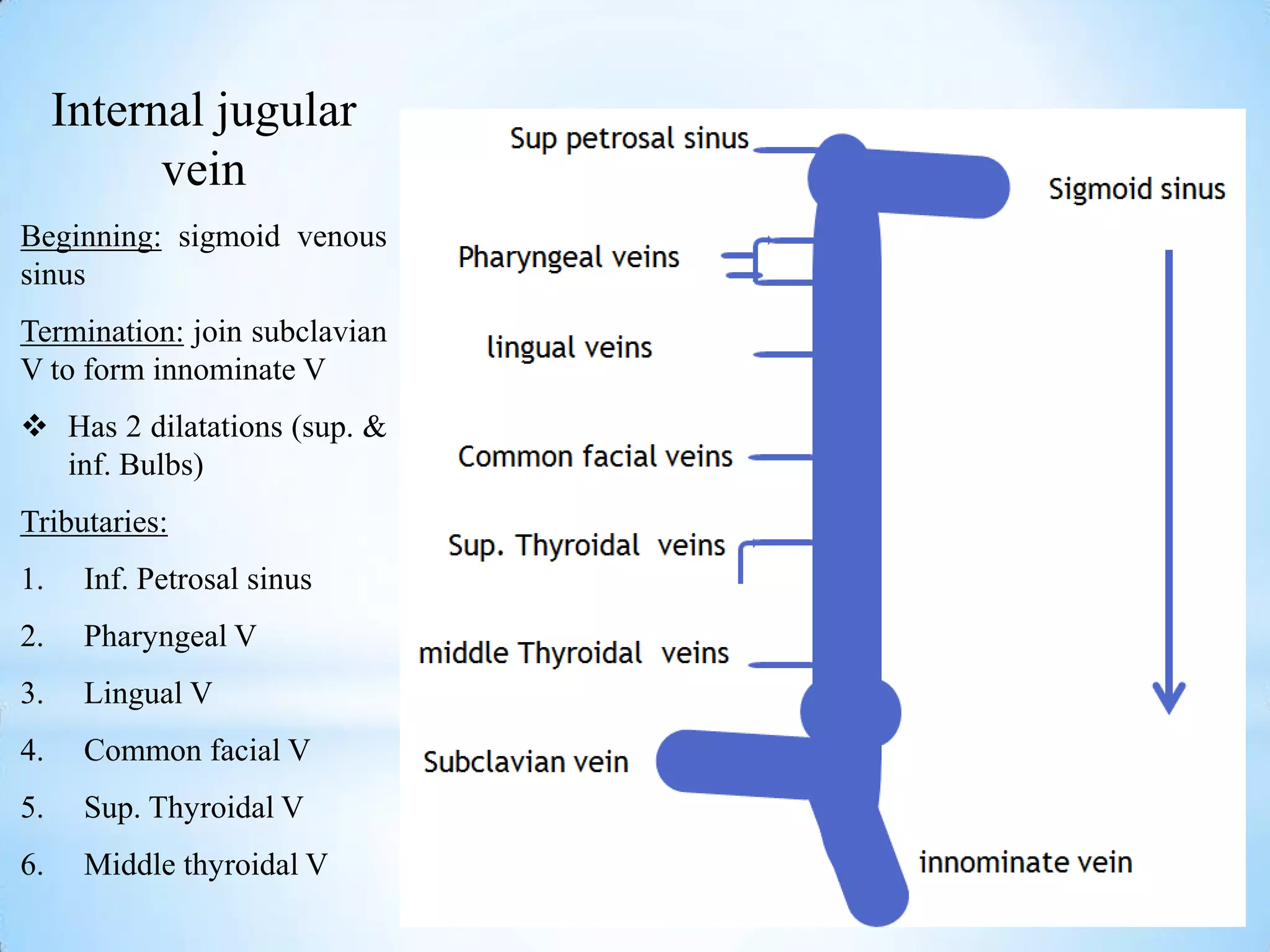
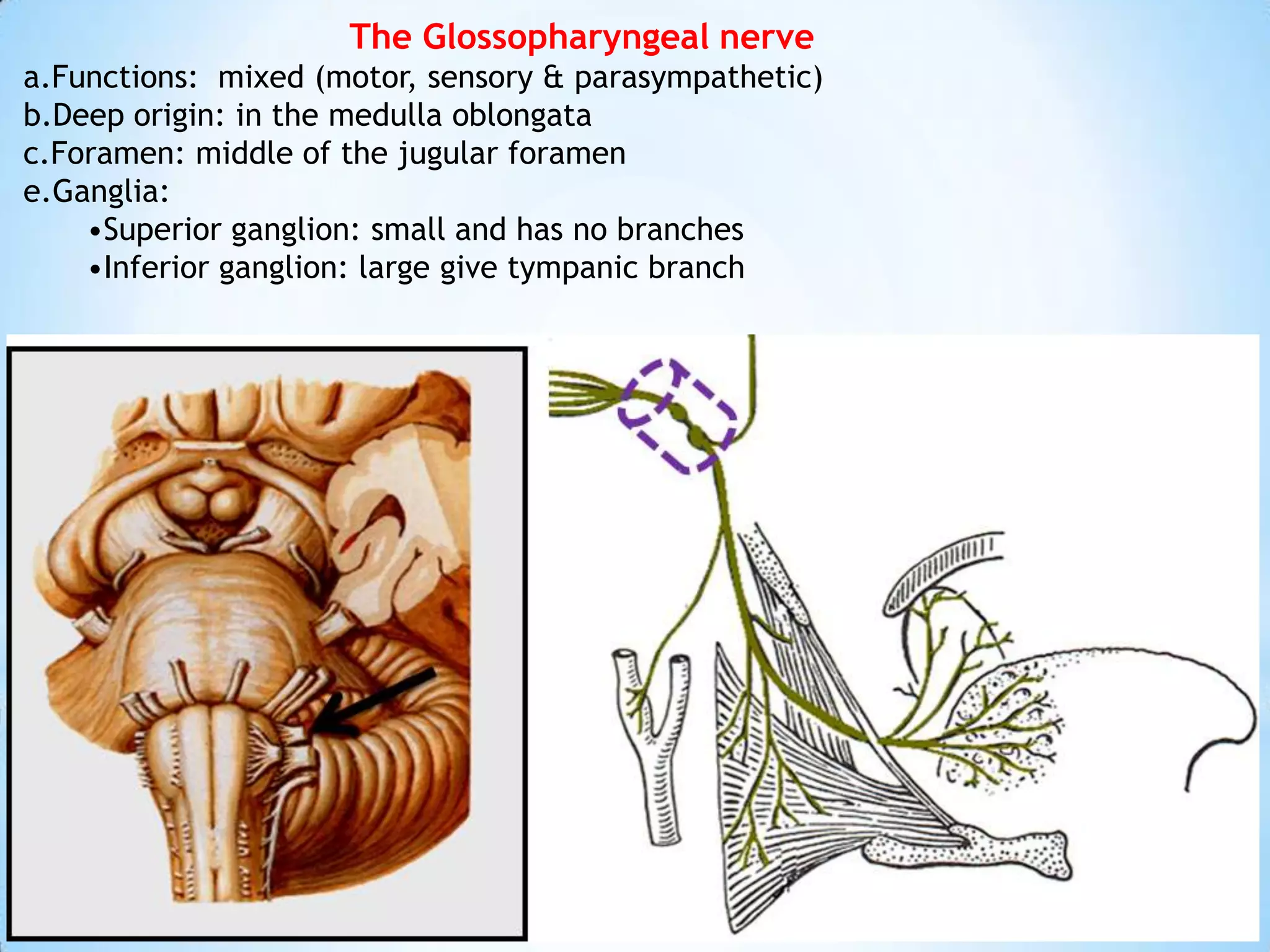
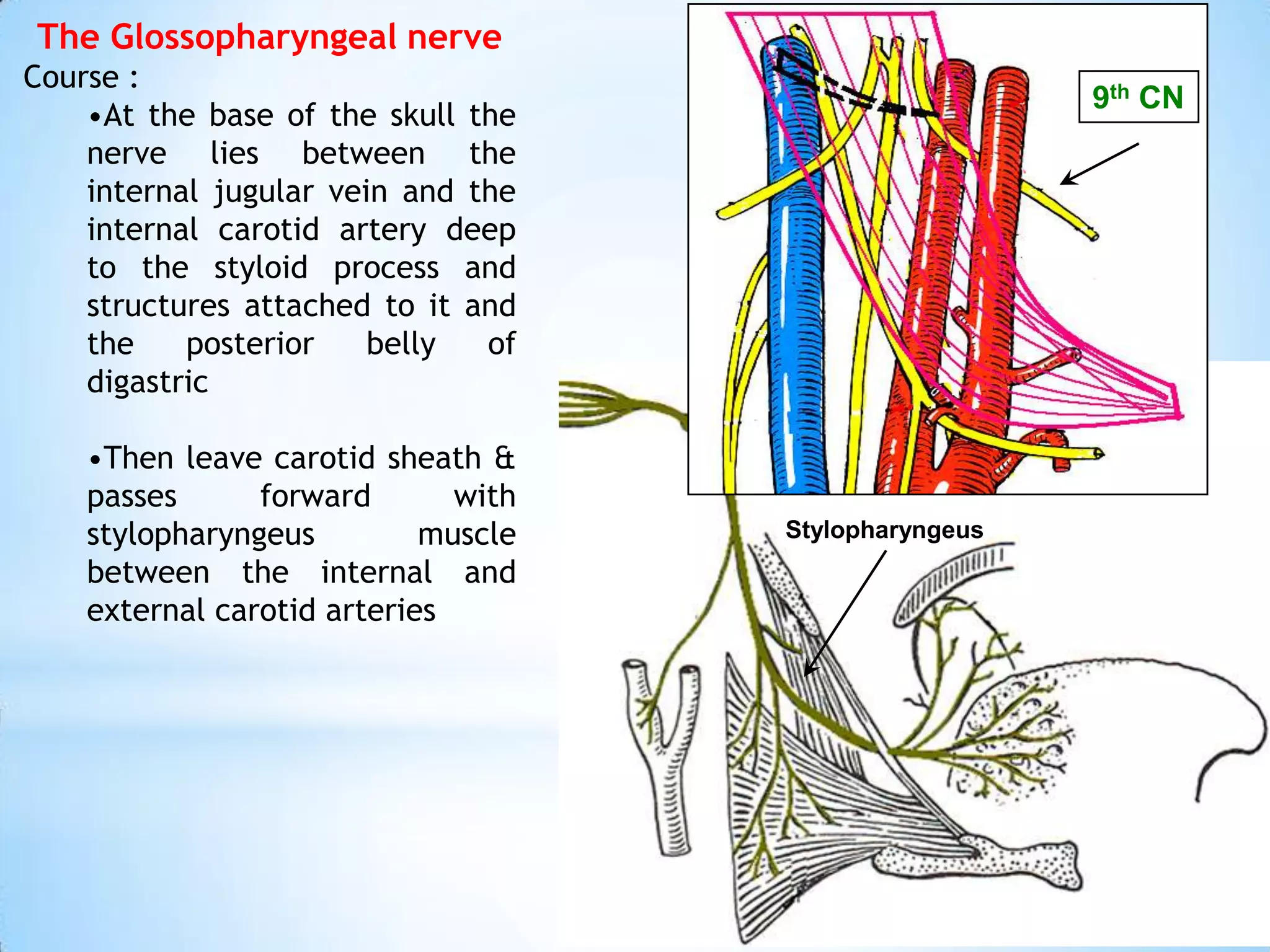
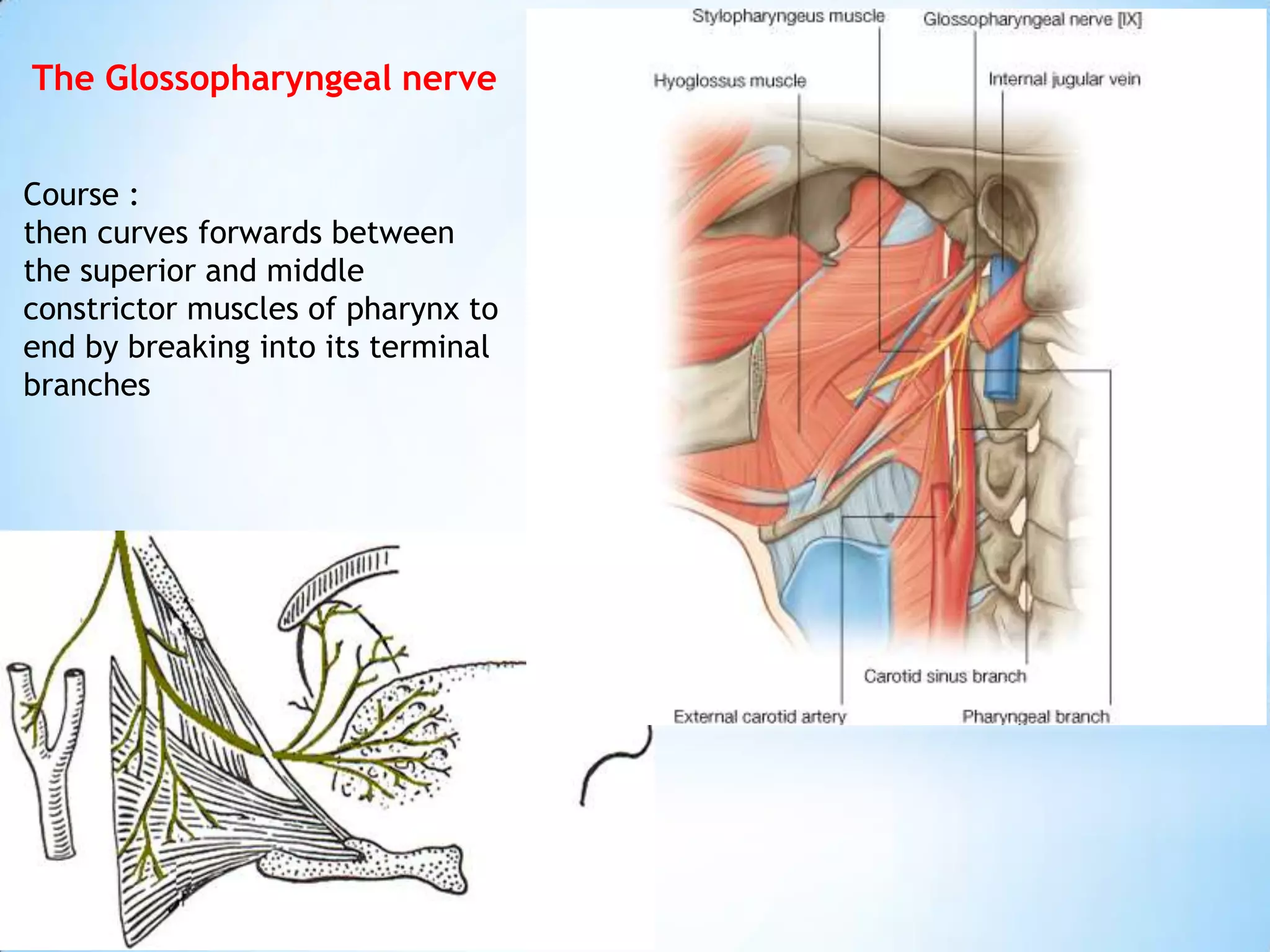
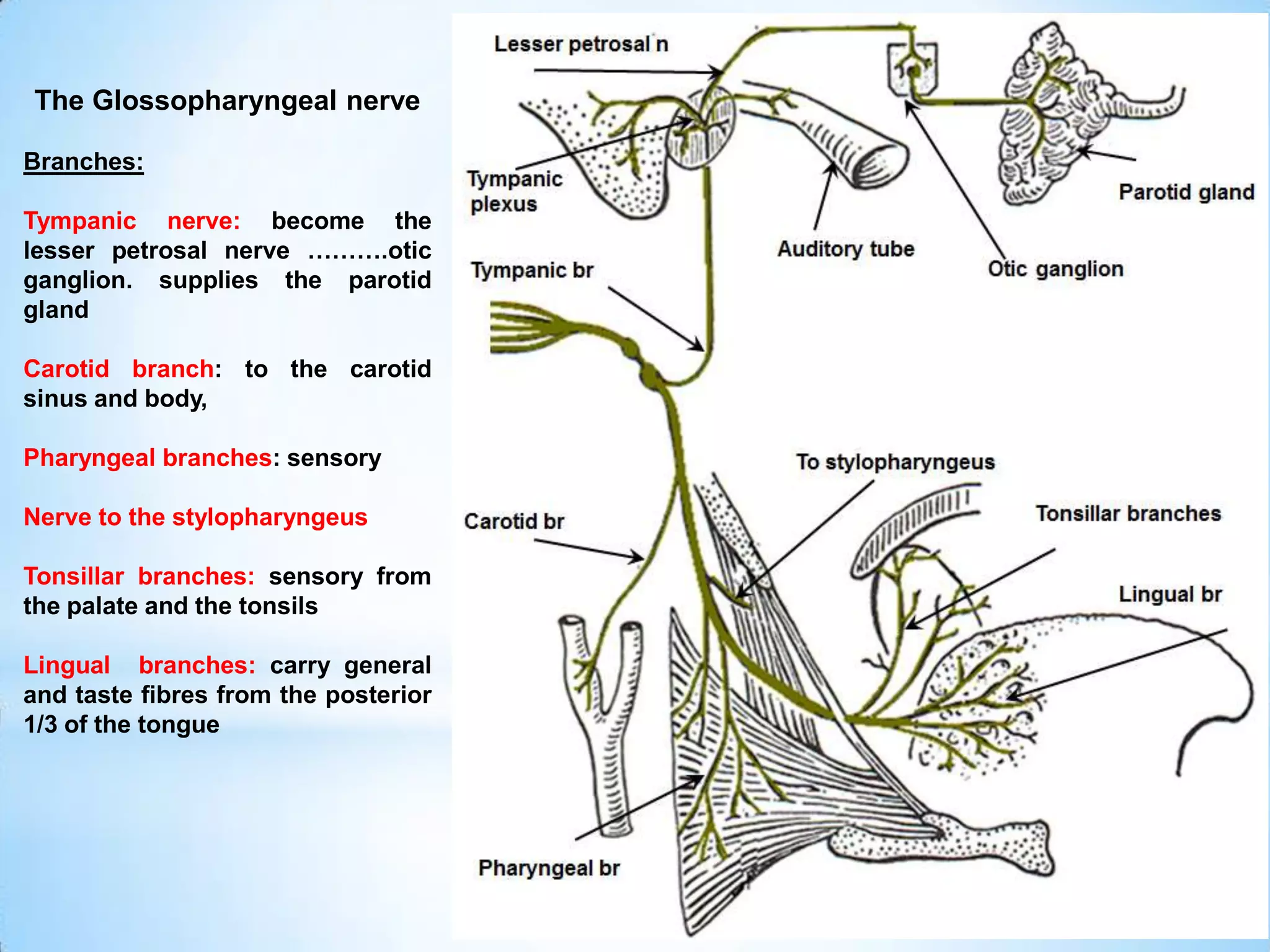
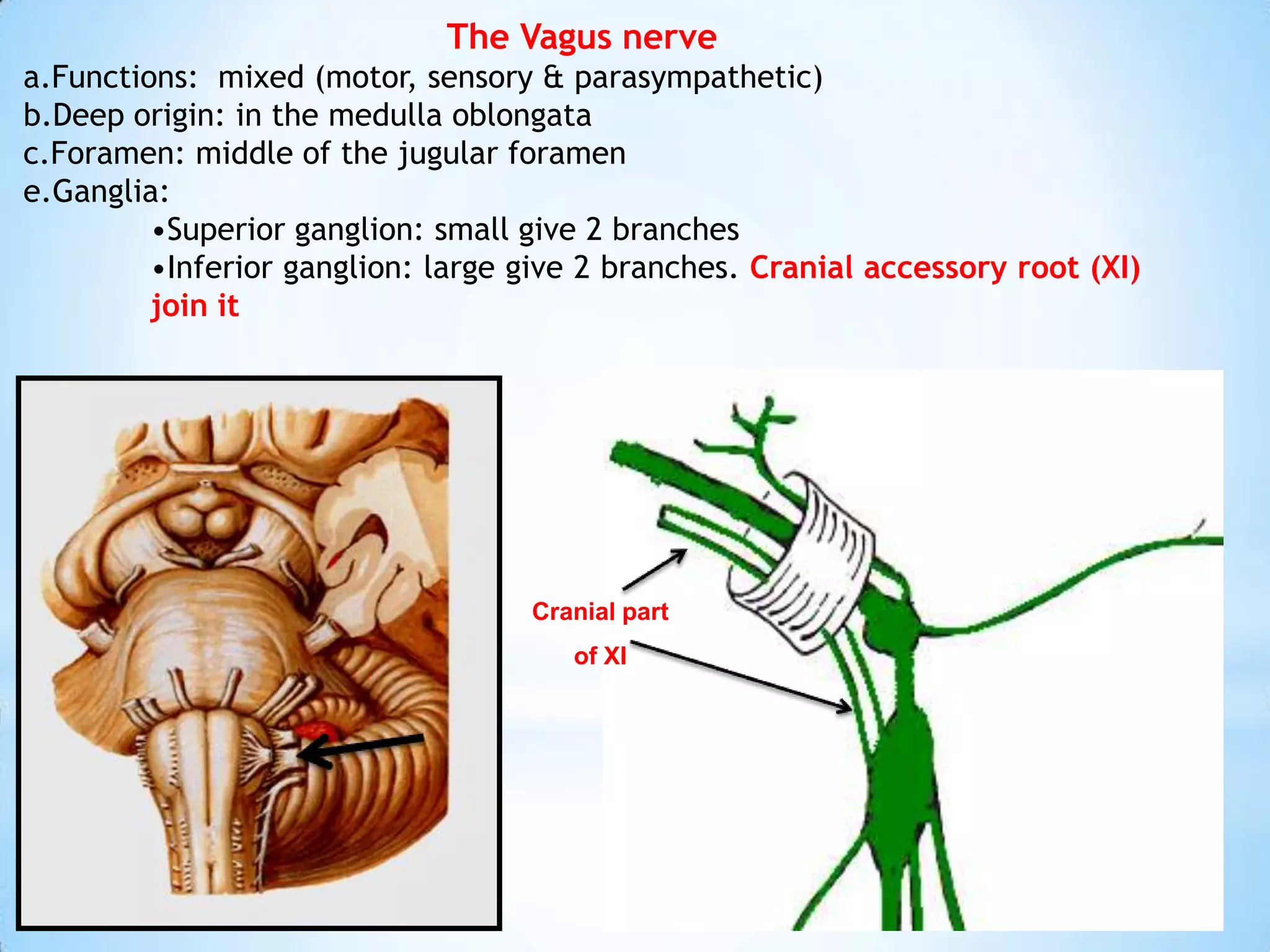
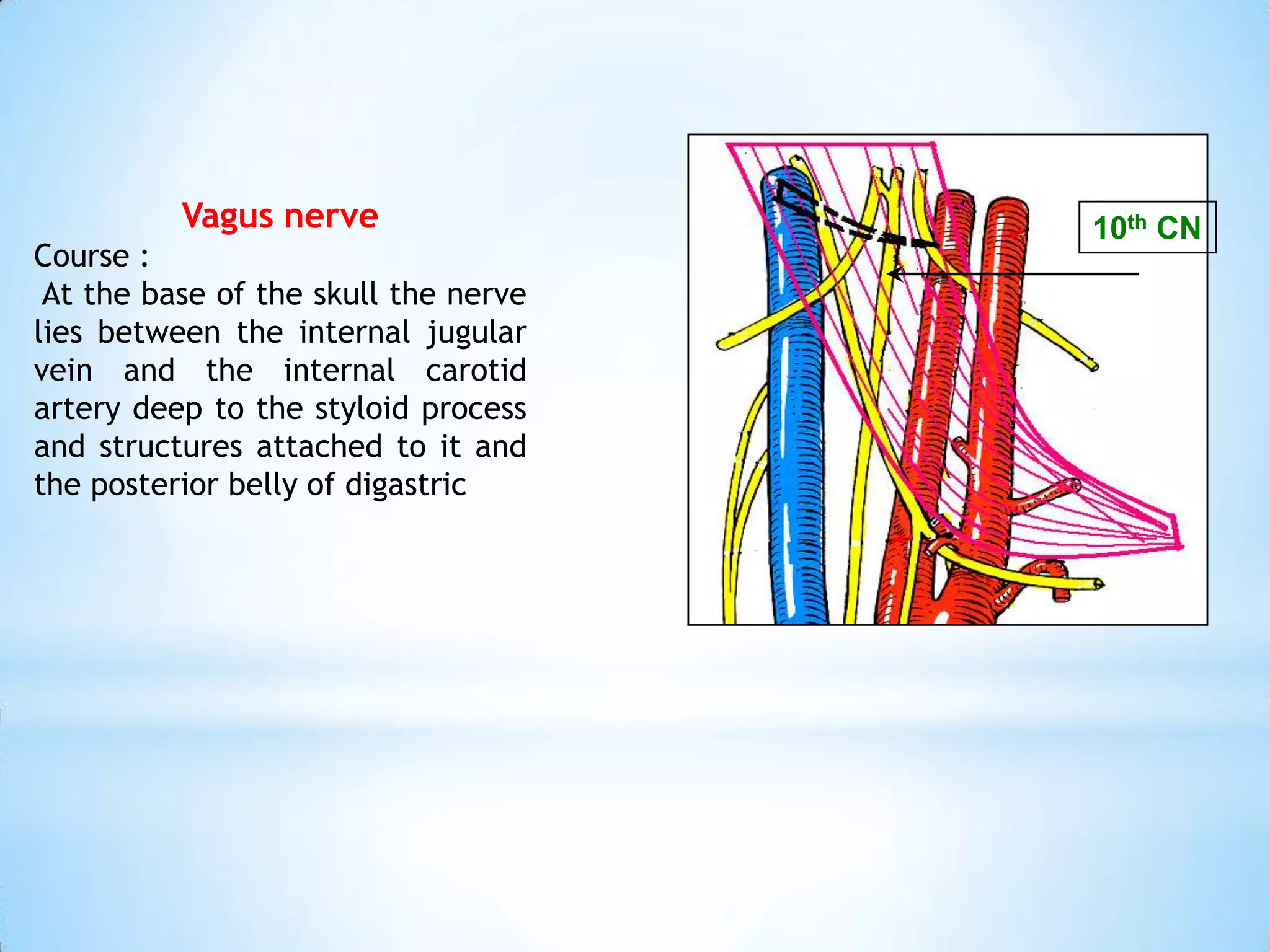
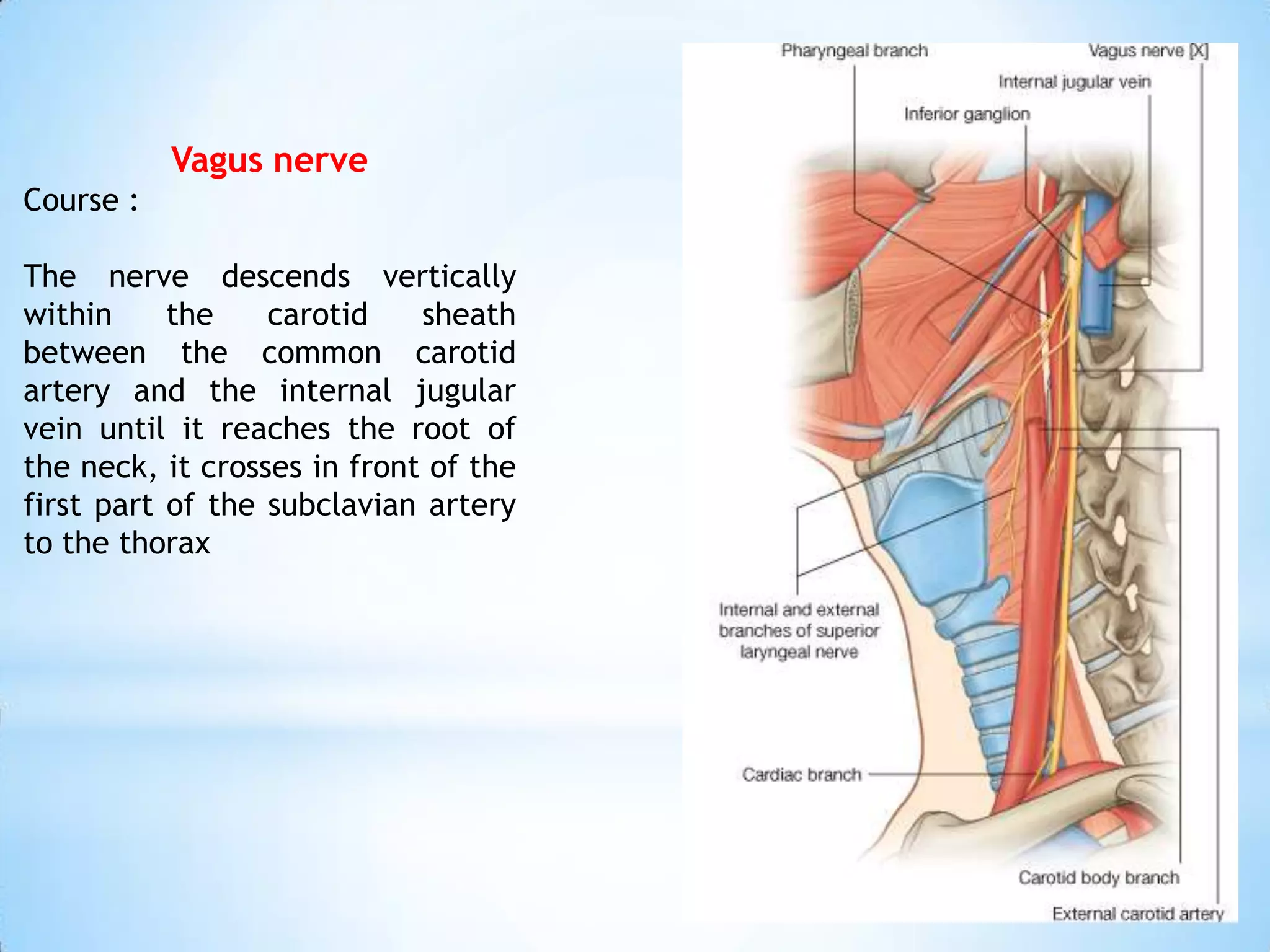
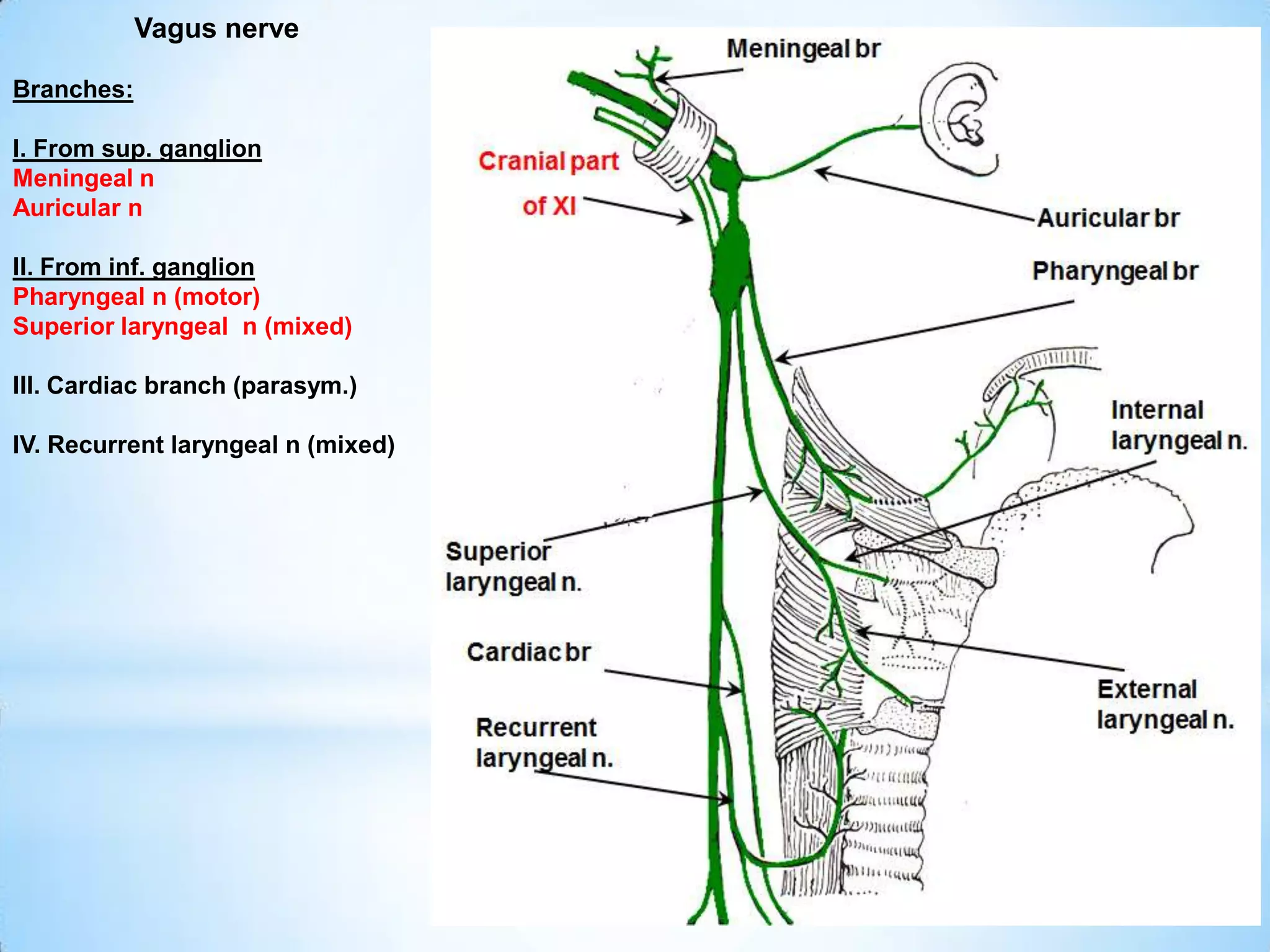
The carotid triangle contains the carotid arteries, internal jugular vein, and cranial nerves X, XI, and XII. It is bounded by the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, the omohyoid muscle, and the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The carotid sheath surrounds the major blood vessels and nerves as they pass through the neck. The glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves pass through the carotid triangle, giving off branches innervating nearby structures before descending in the neck.