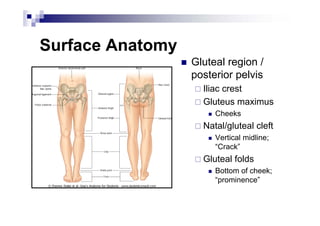
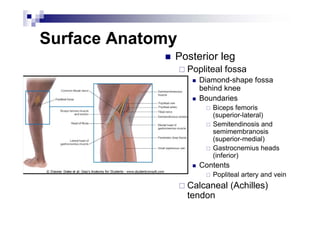
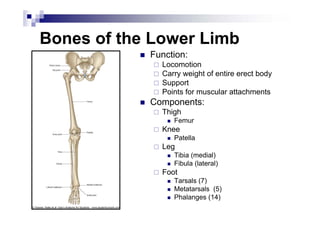
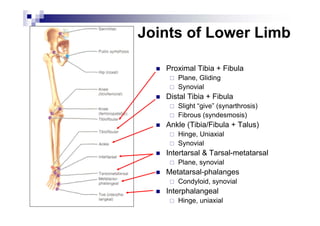
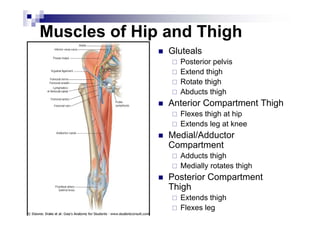
The document provides an overview of the surface anatomy, skeletal composition, joints, muscles, innervation, and vasculature of the lower limb, including the pelvis, thigh, leg, and foot. Key details include the bones of the femur, tibia, fibula, and foot; muscles like the gluteals, quadriceps, hamstrings, and gastrocnemius; major nerves from the lumbar and sacral plexuses including the femoral, obturator, sciatic, and tibial nerves; and arterial blood supply from the femoral, popliteal, anterior tibial, and posterior tibial arteries.