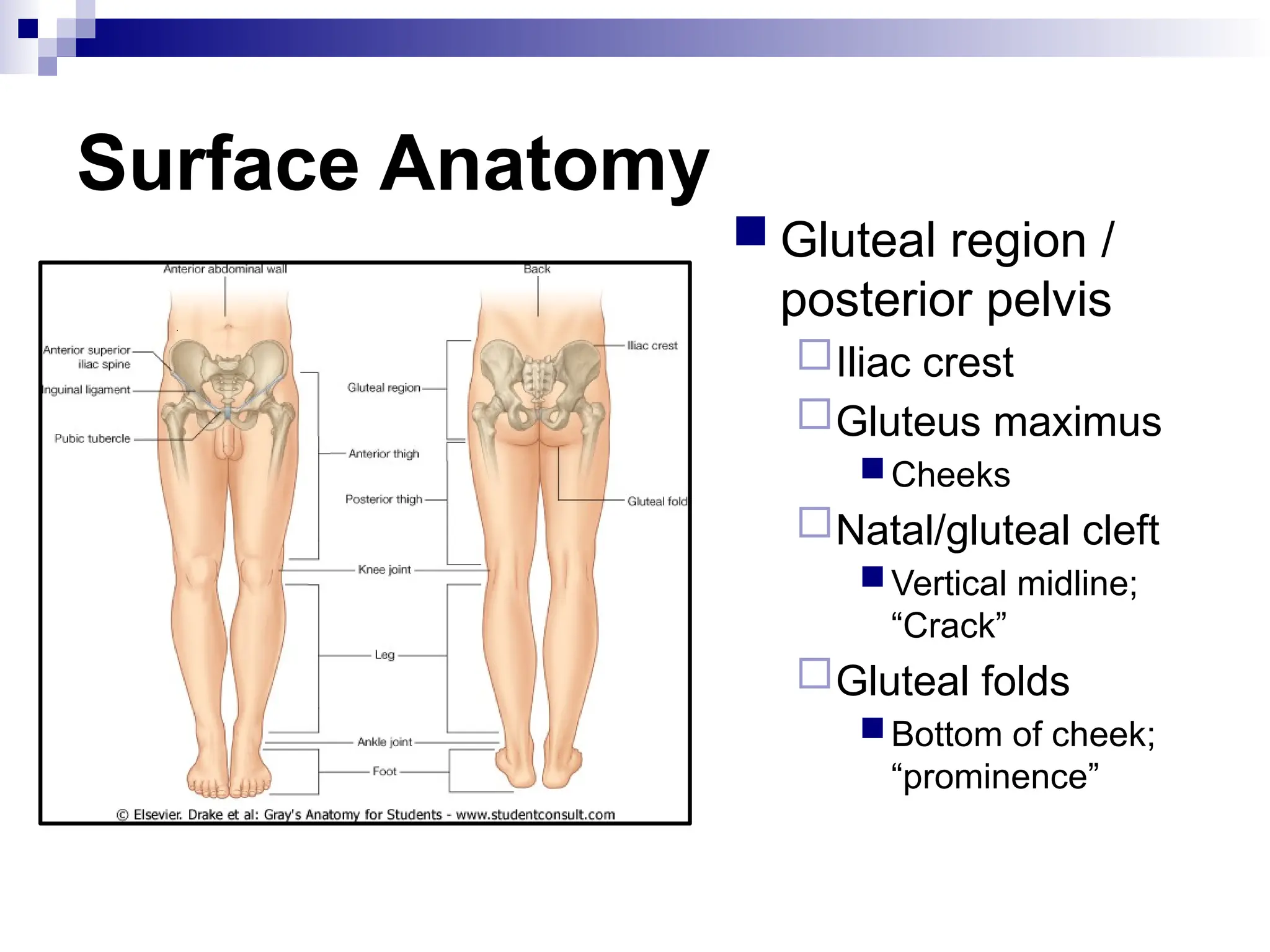
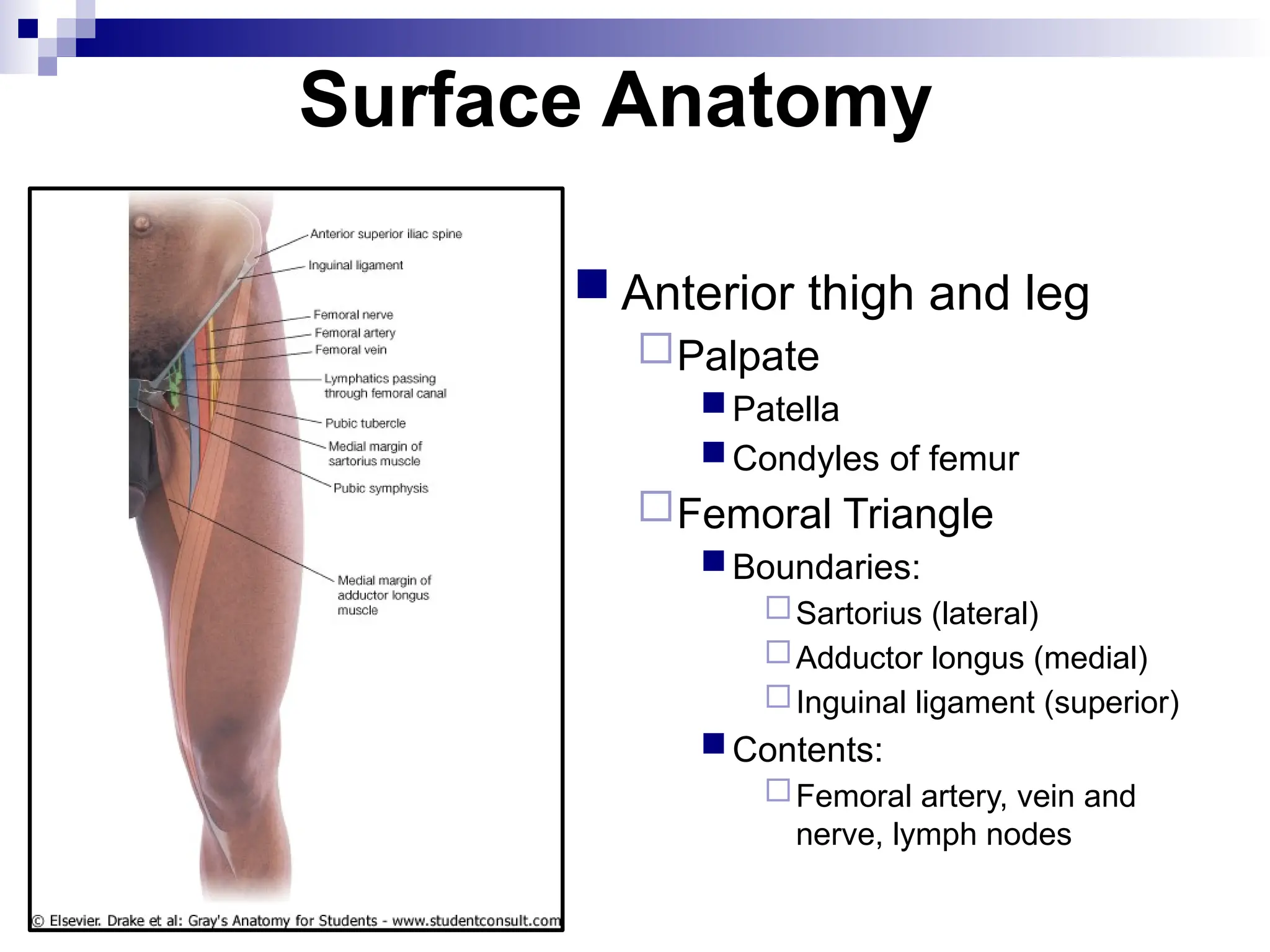
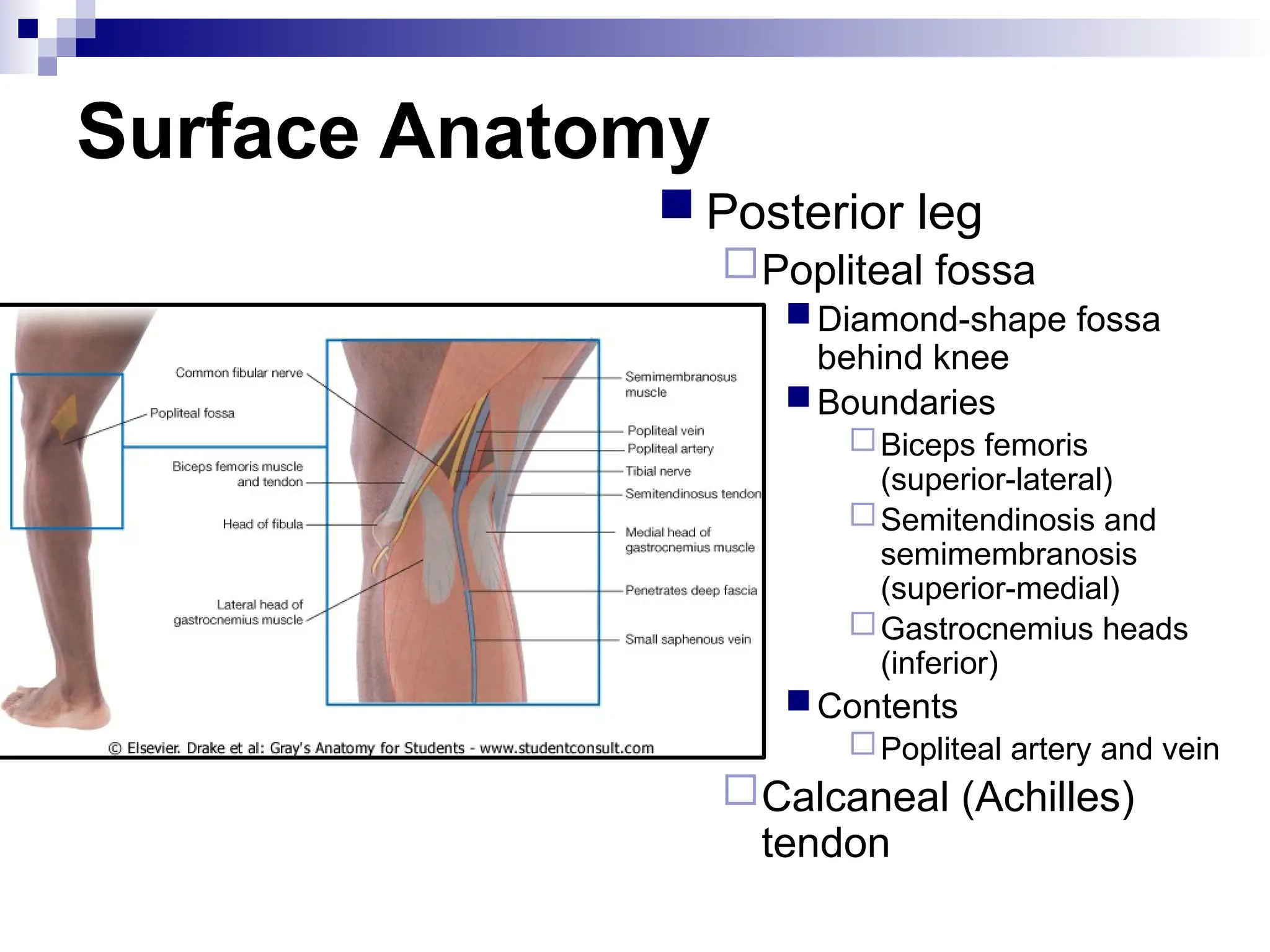
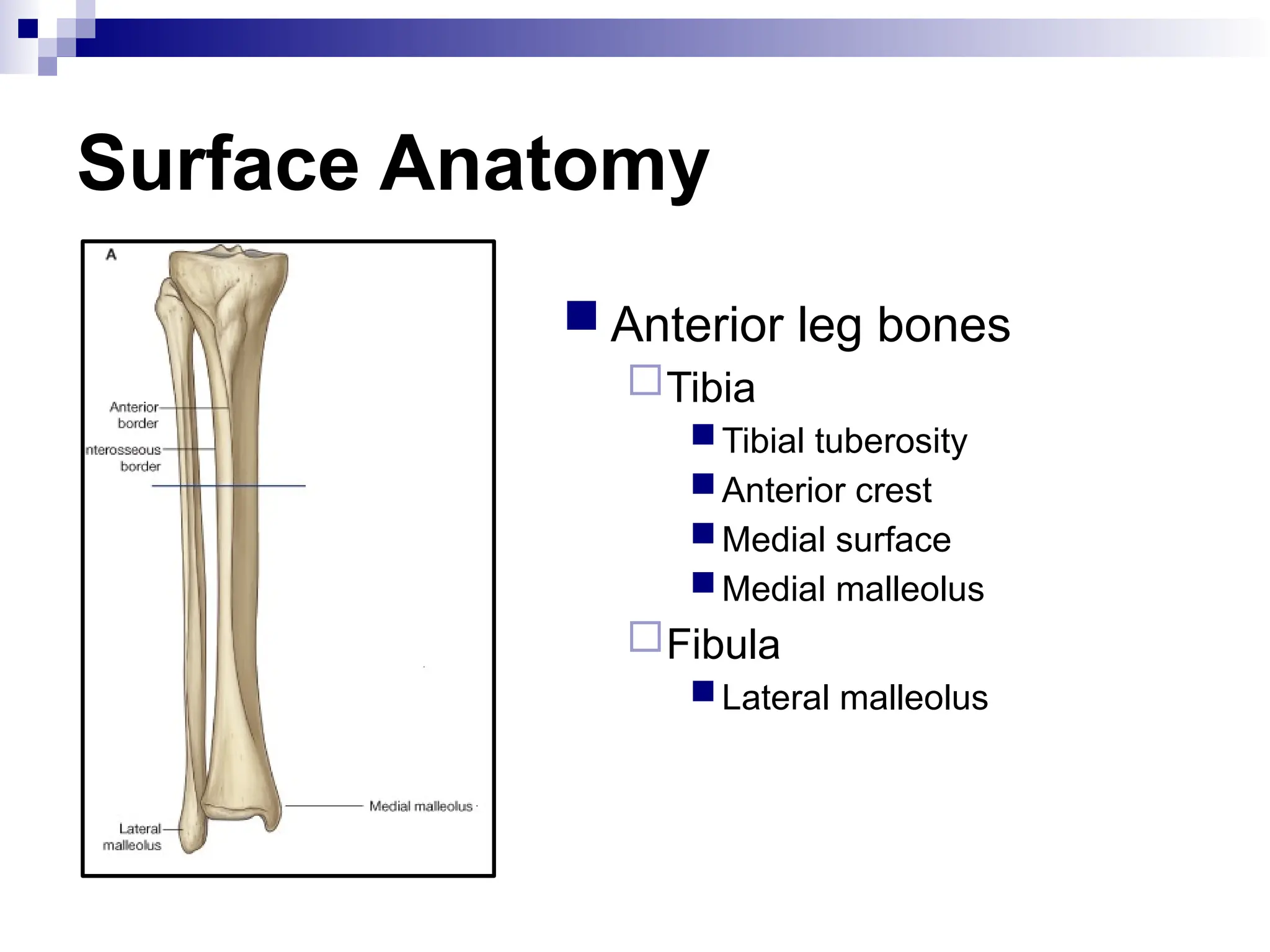
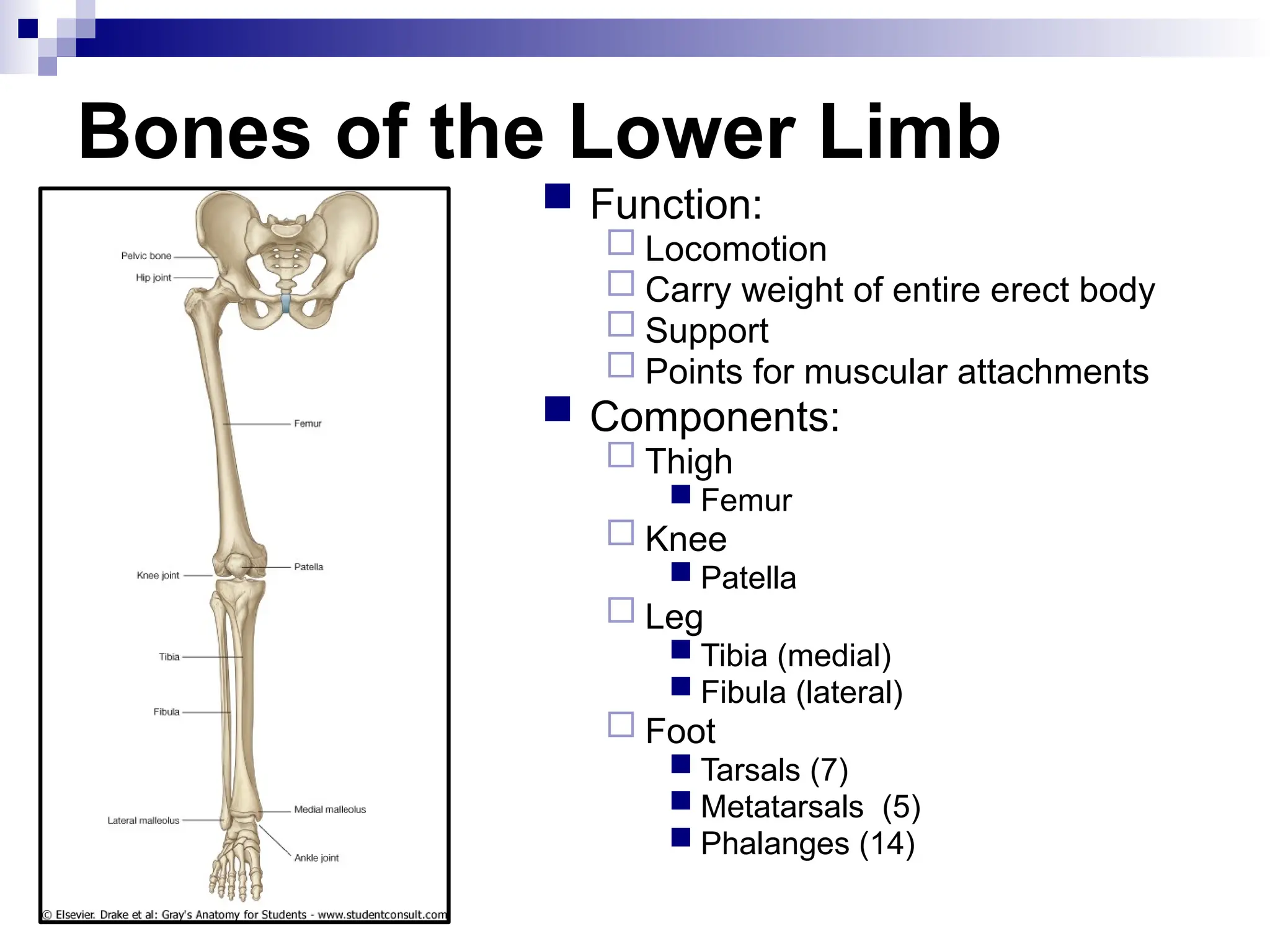
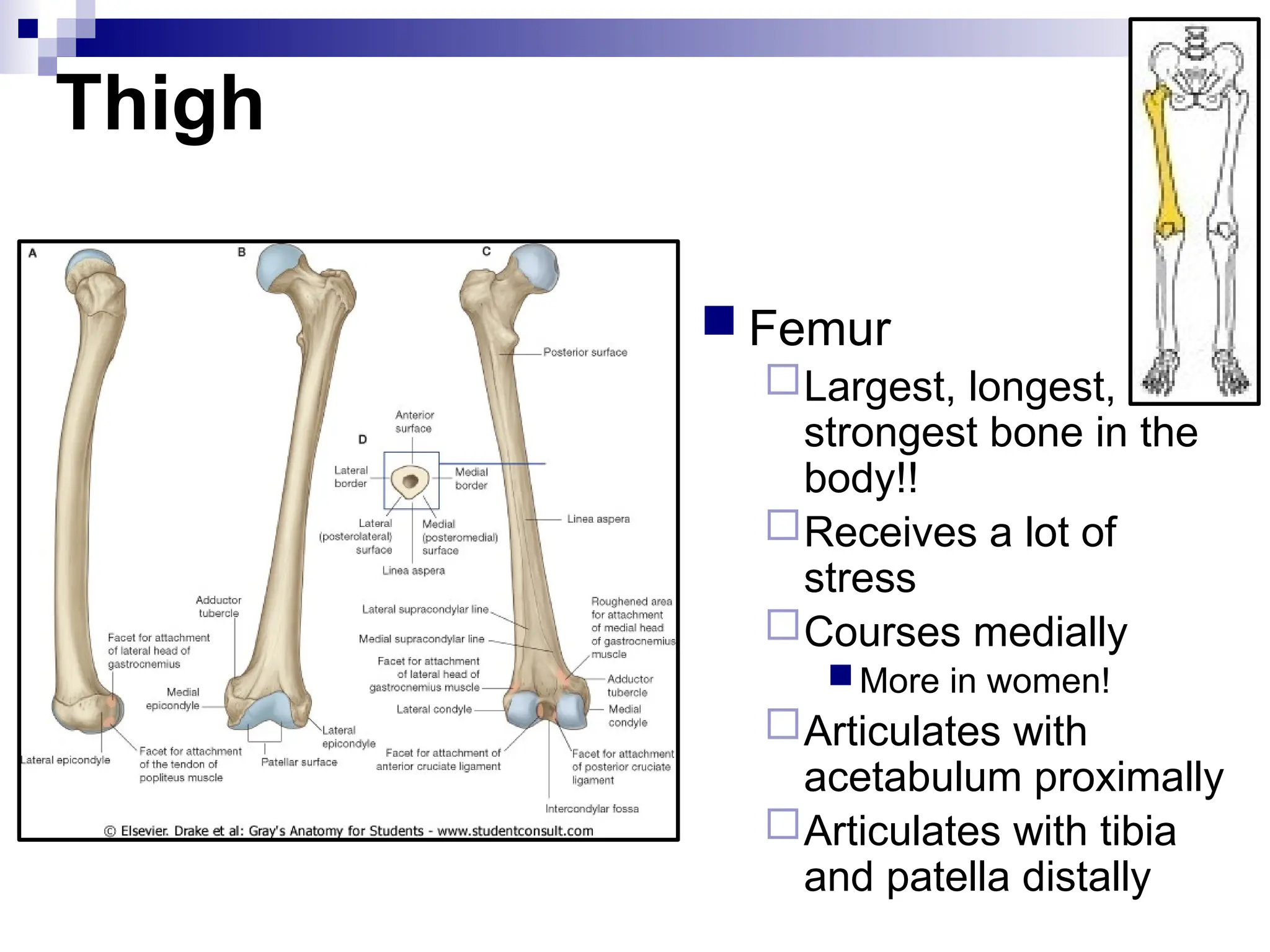
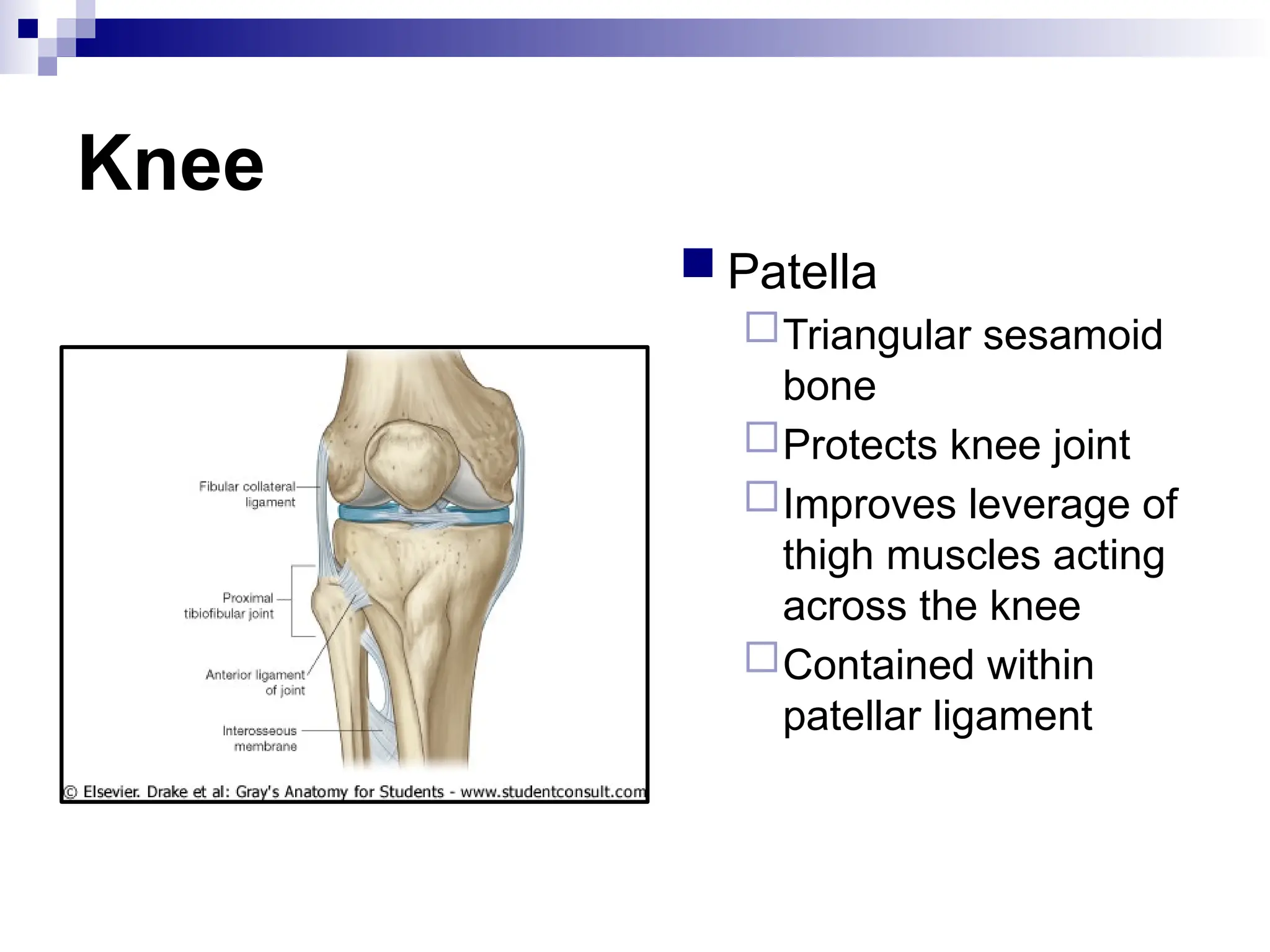
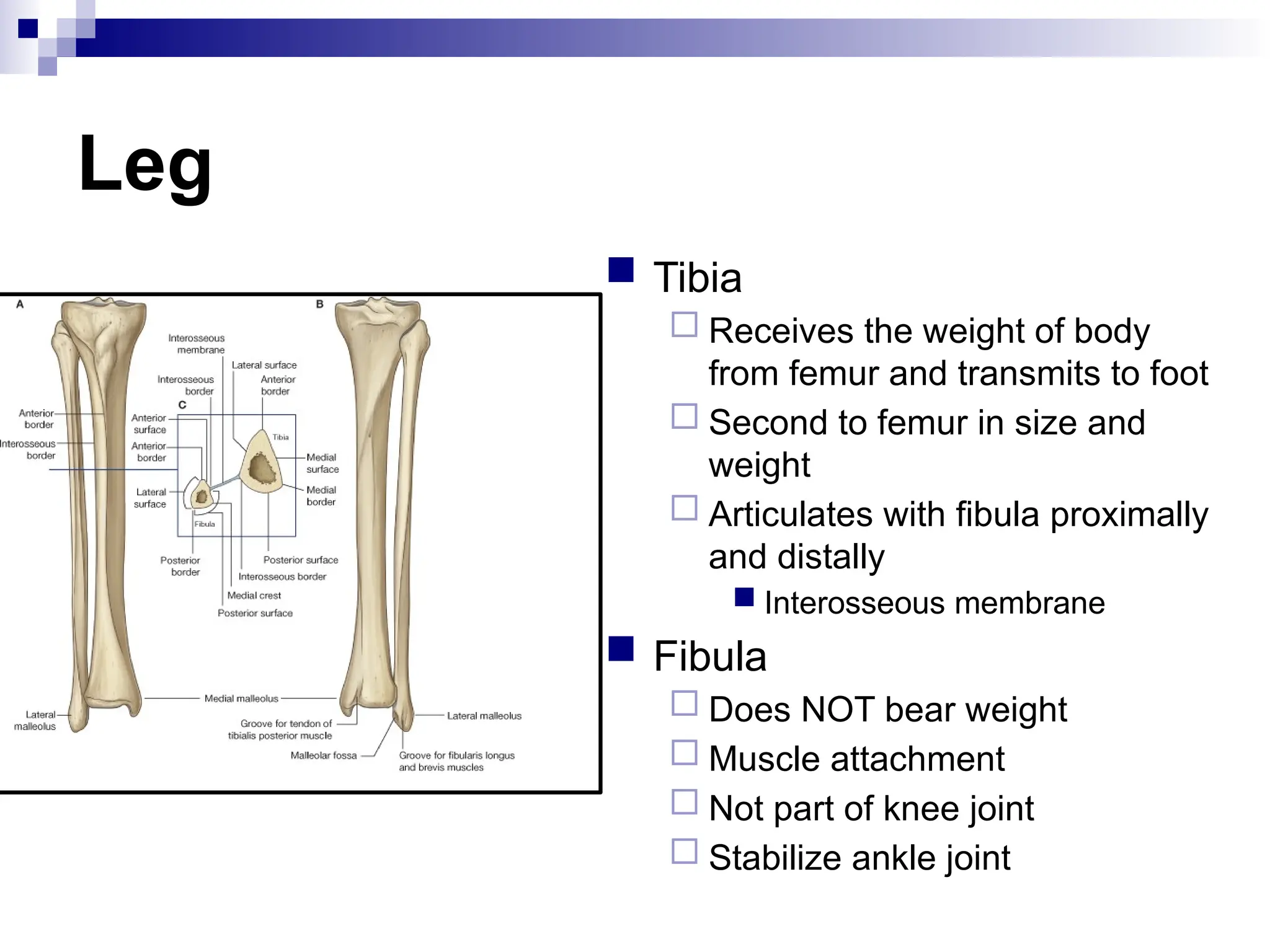
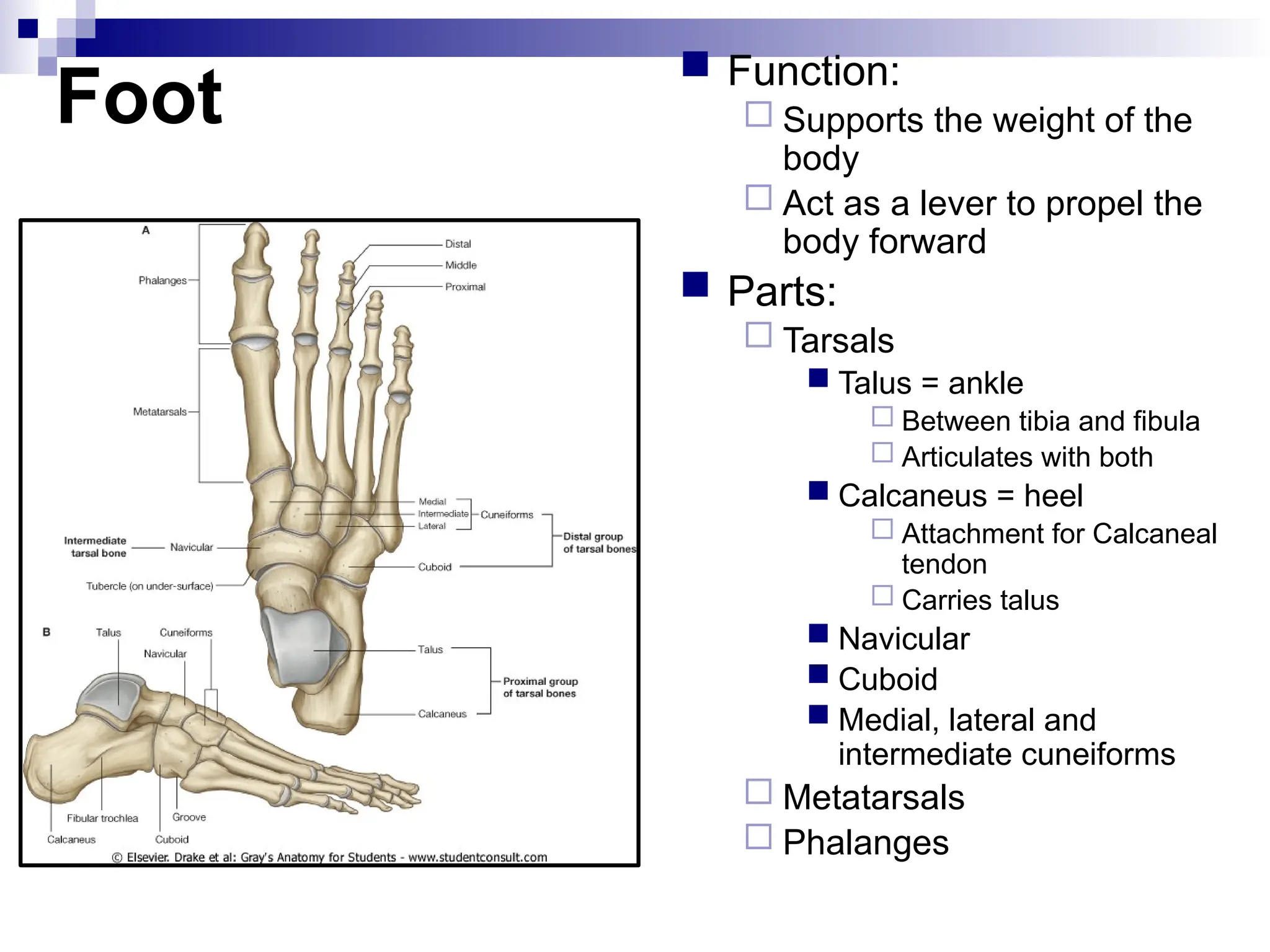
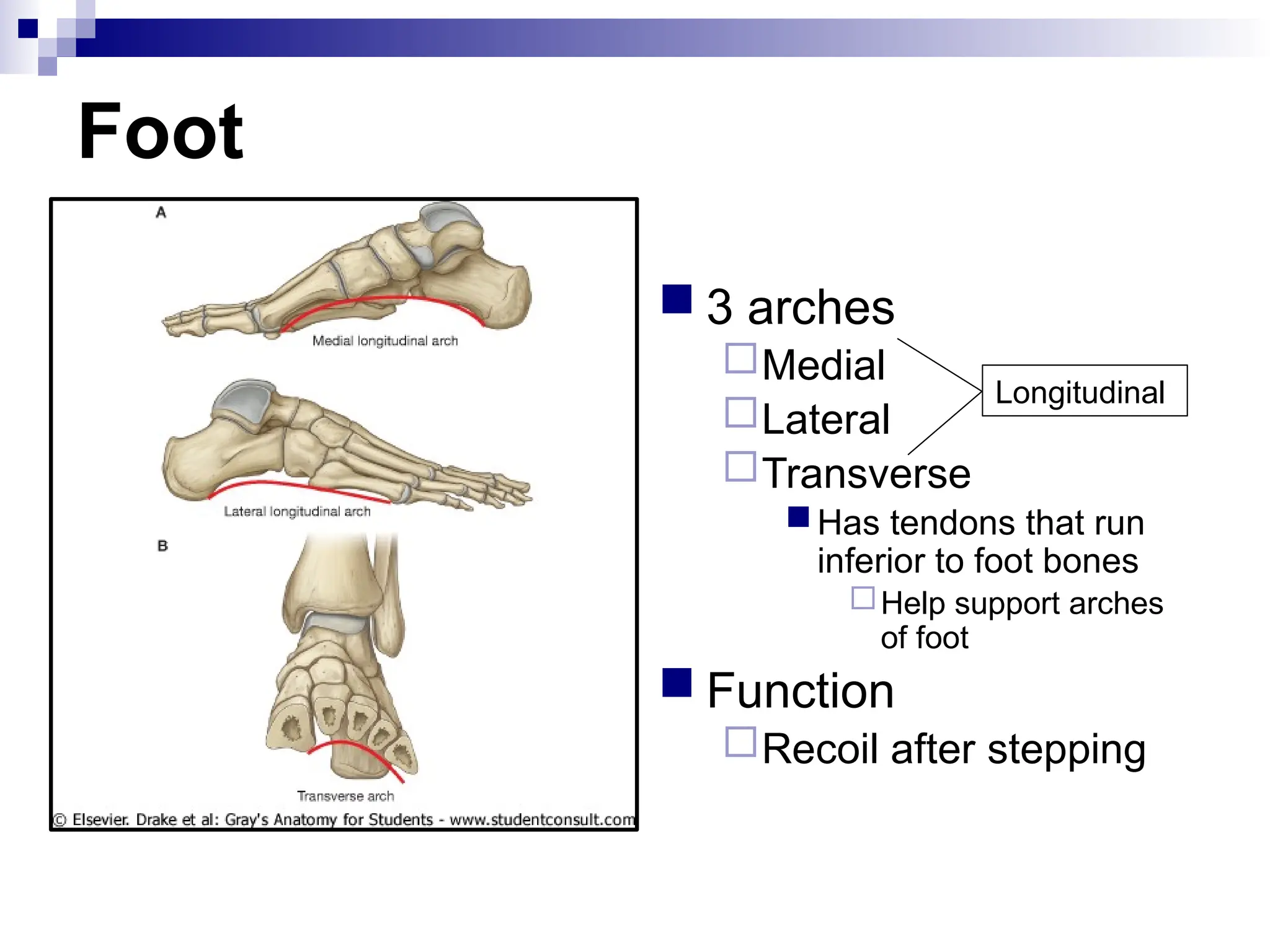
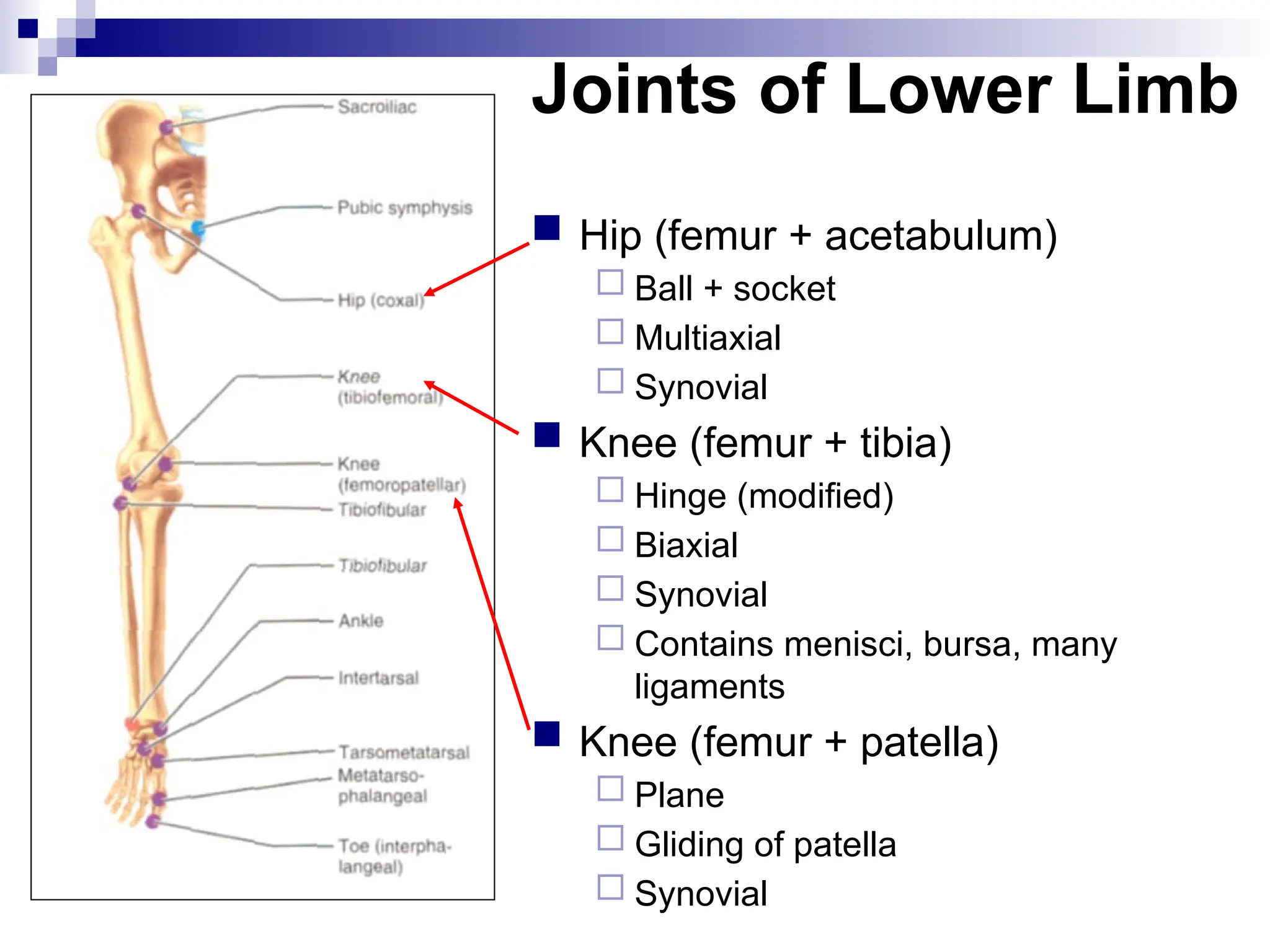
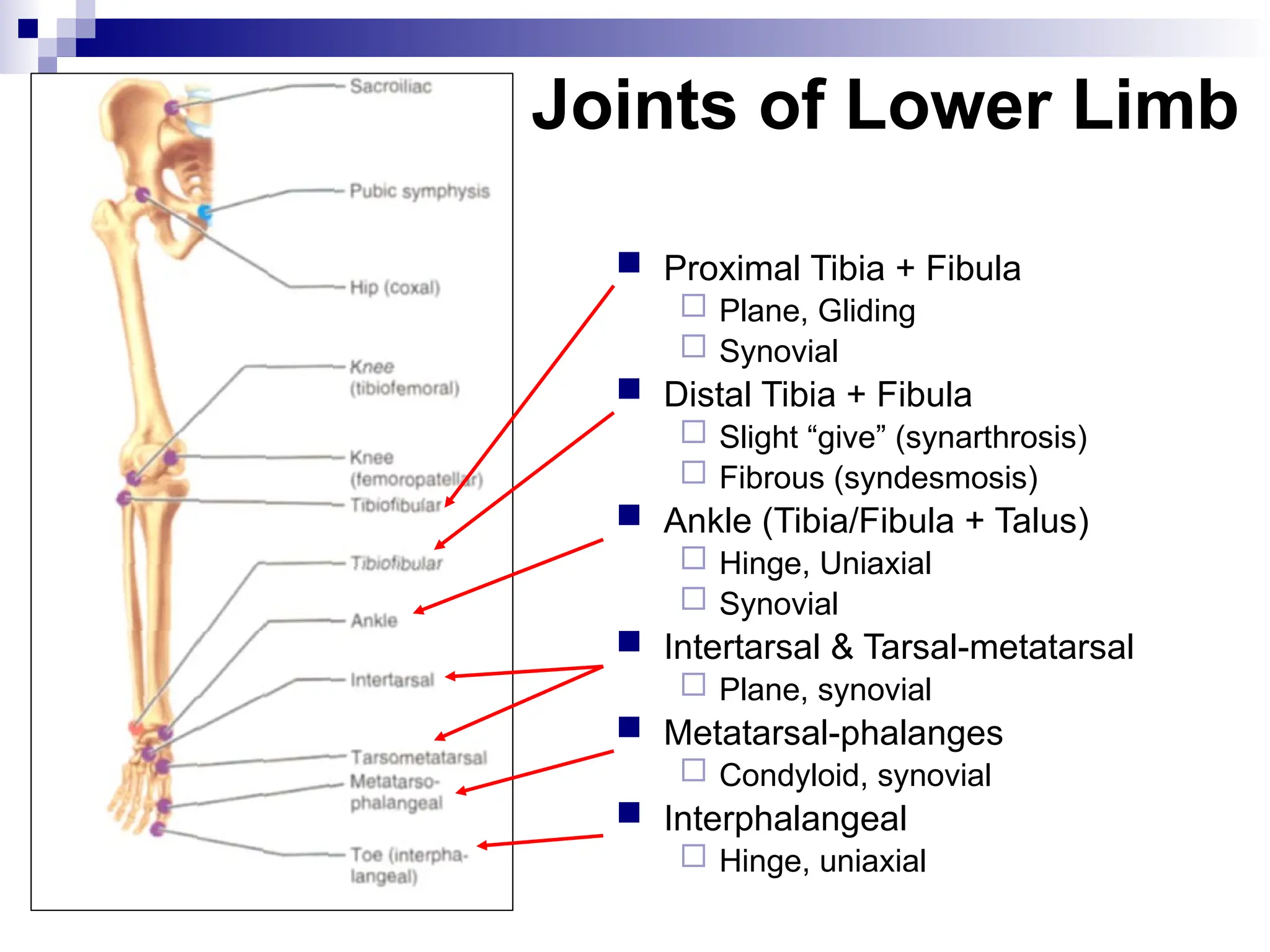
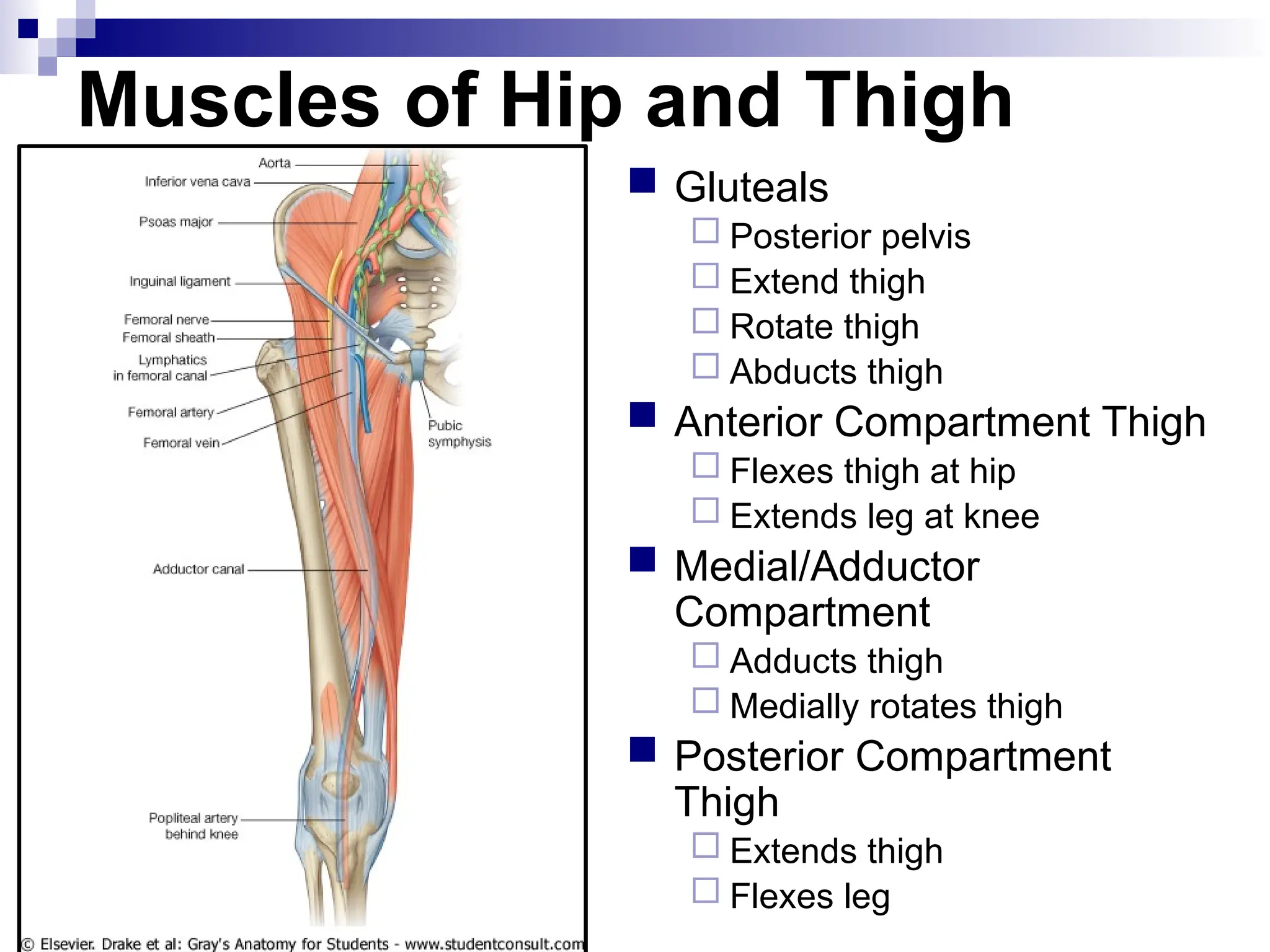
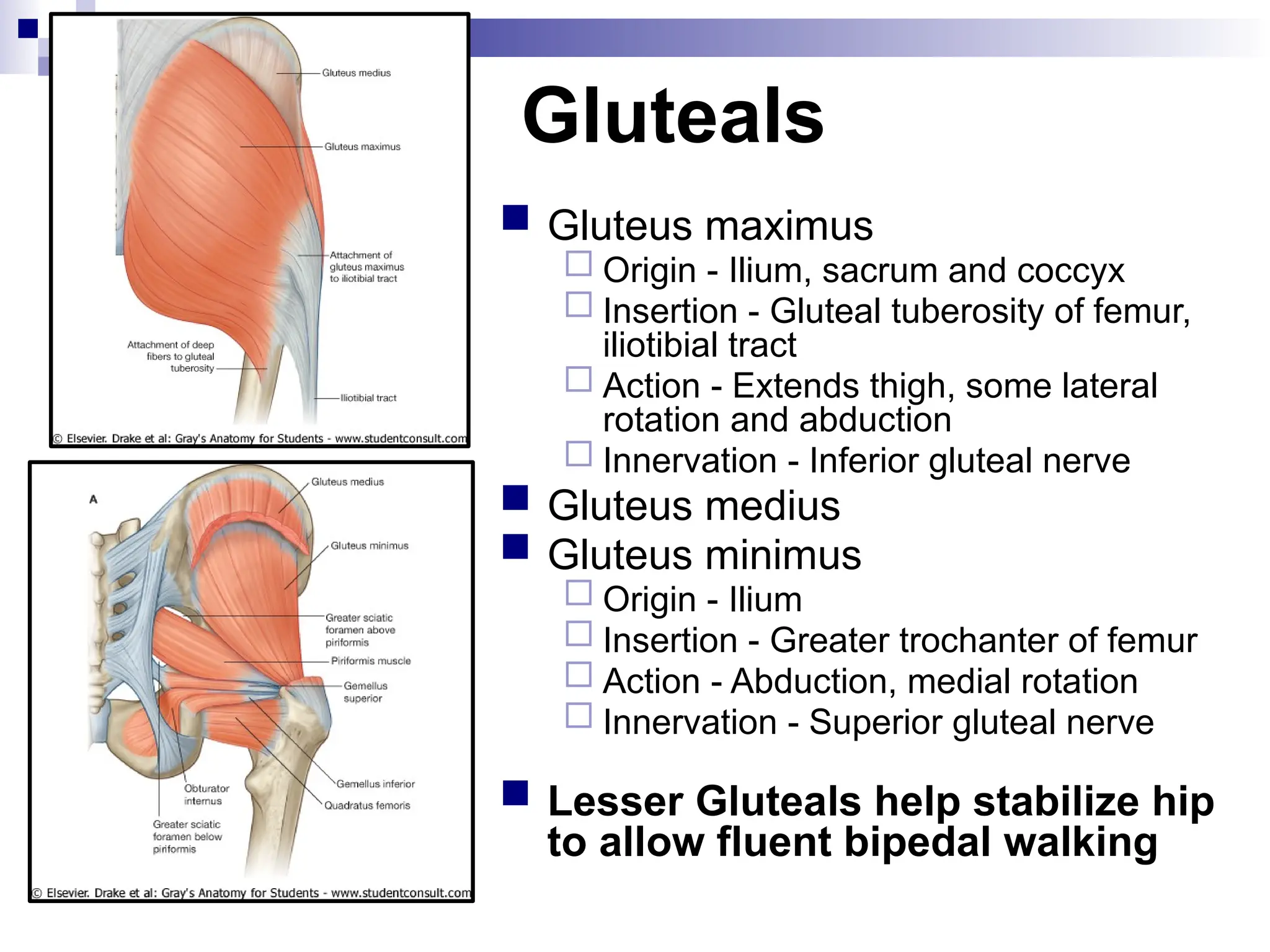
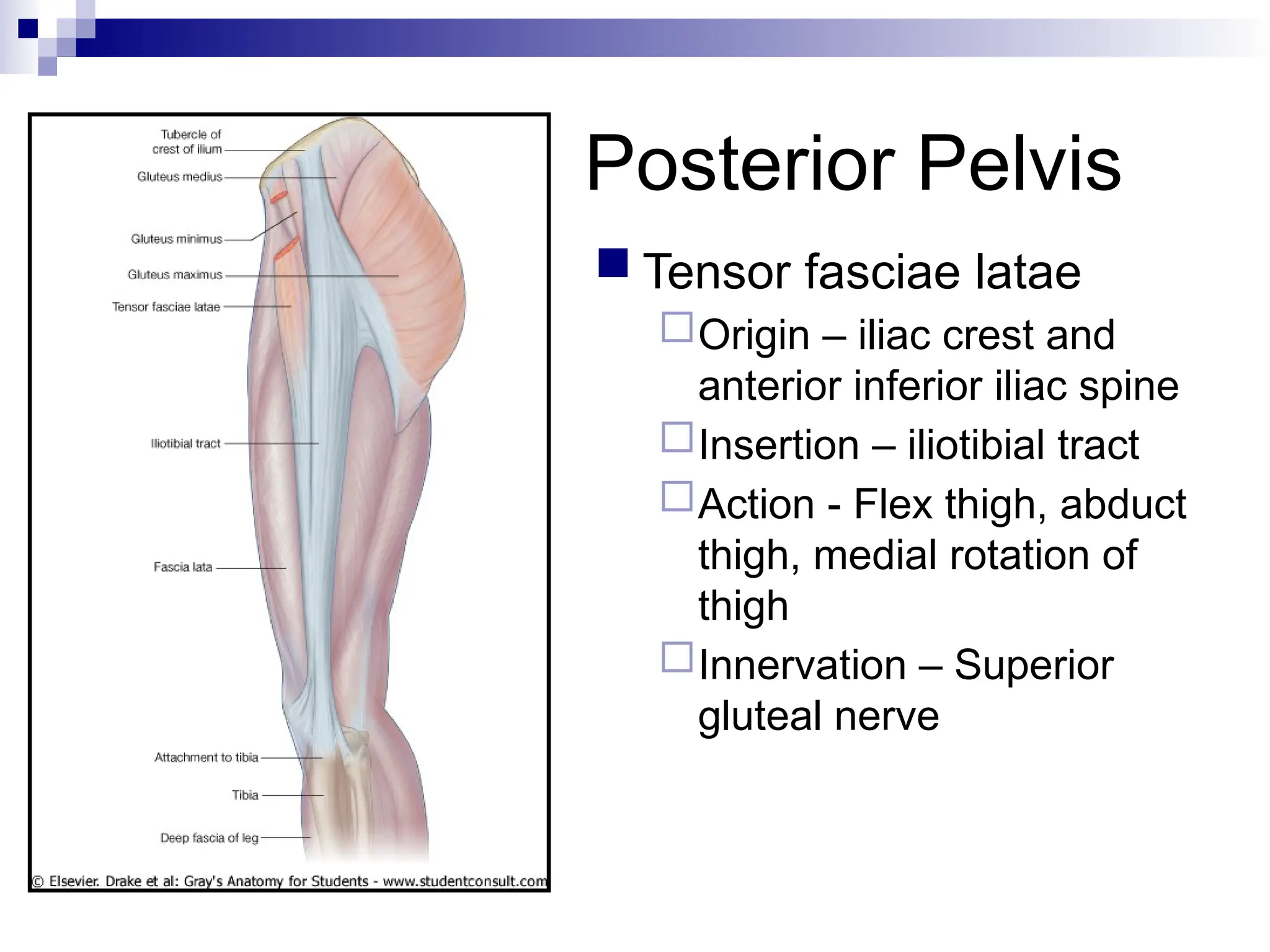
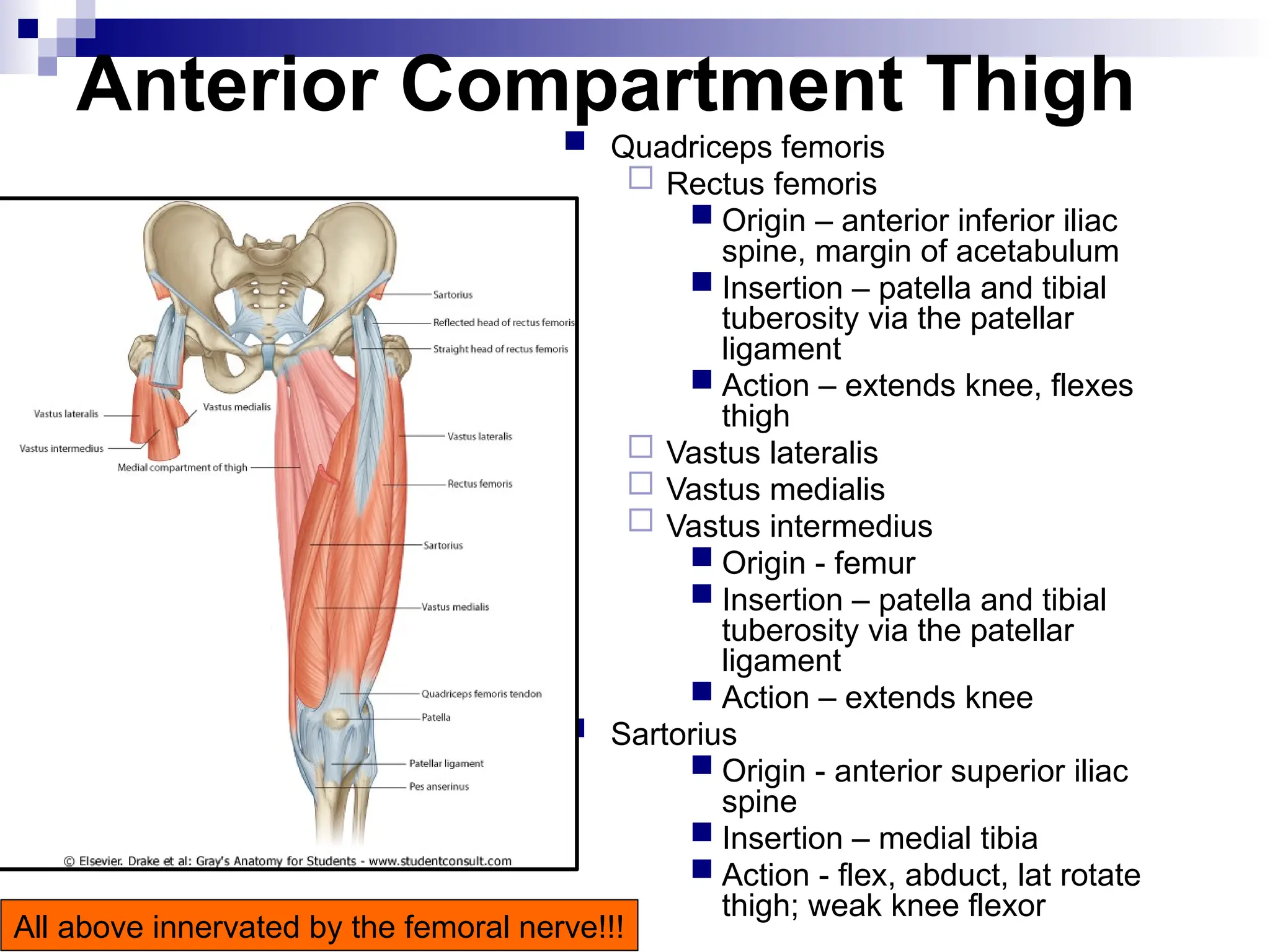
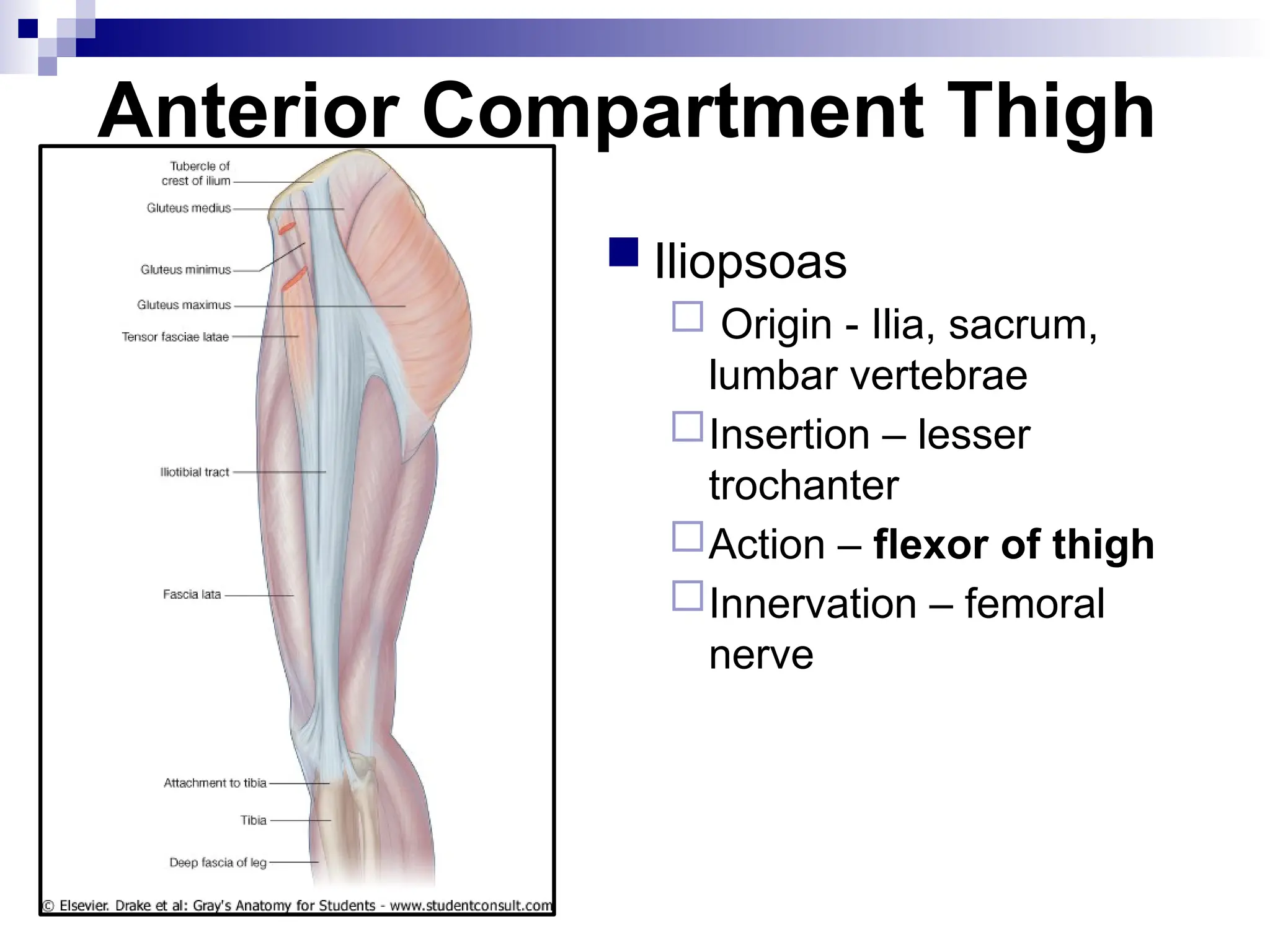
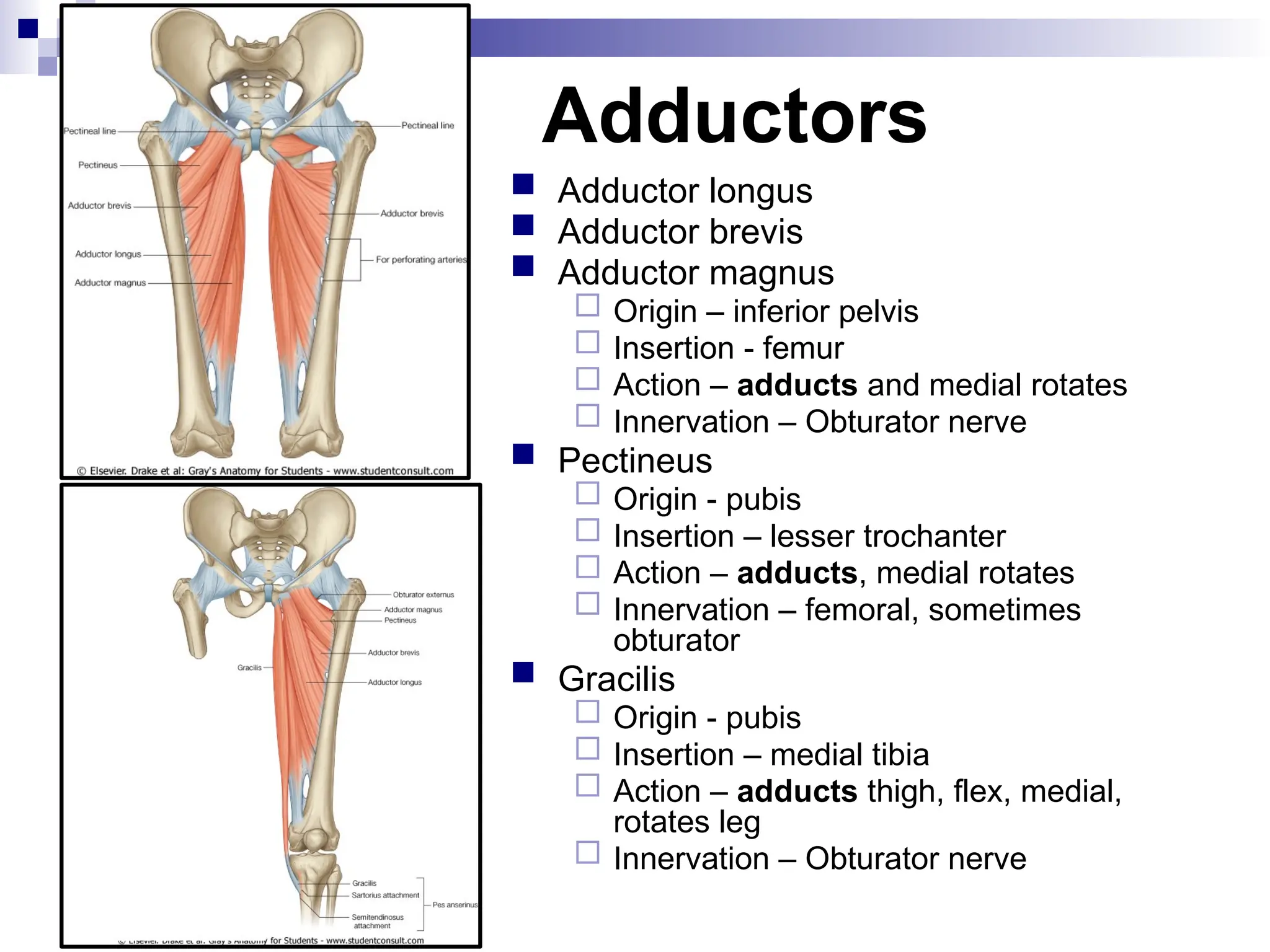
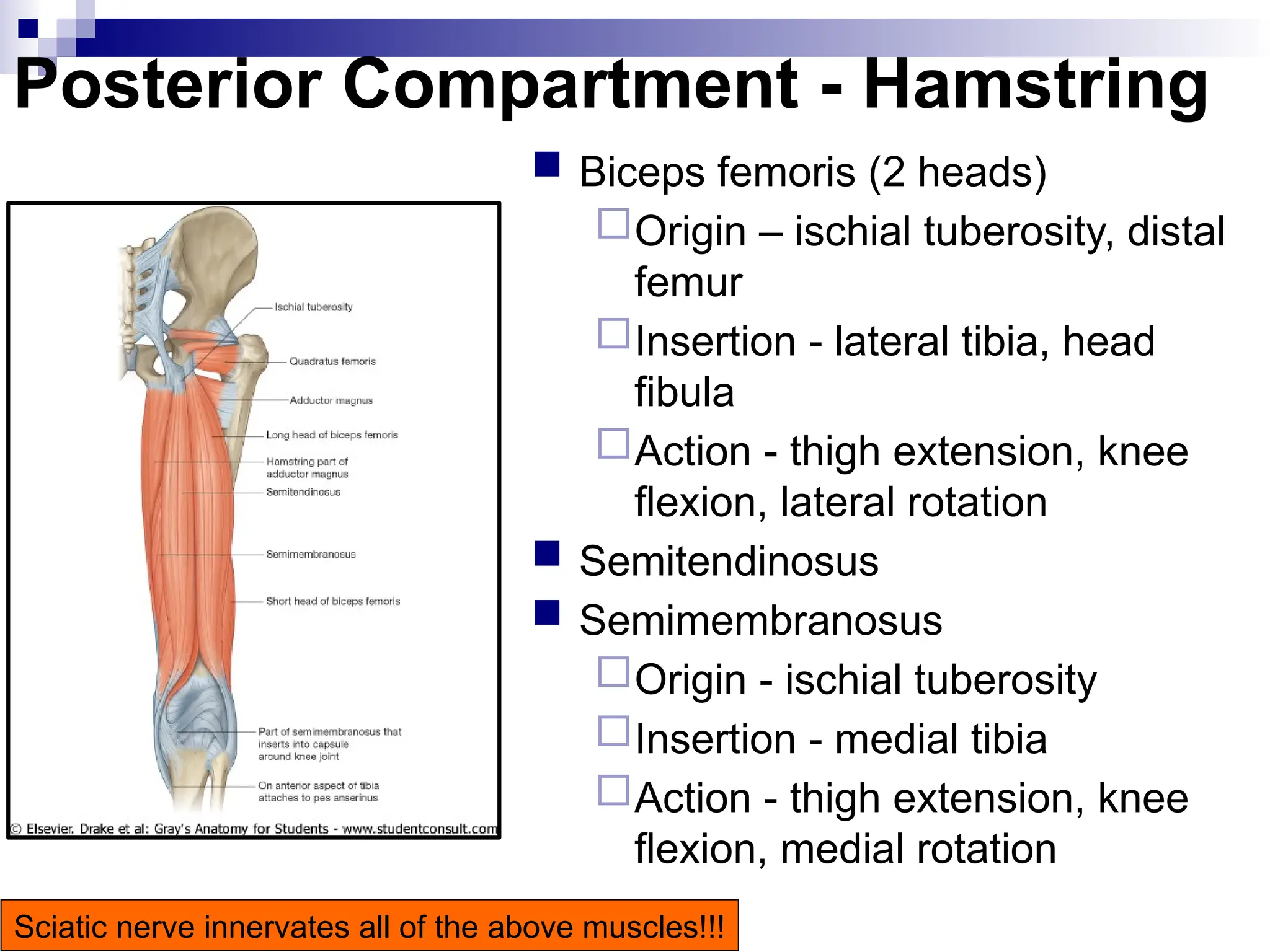
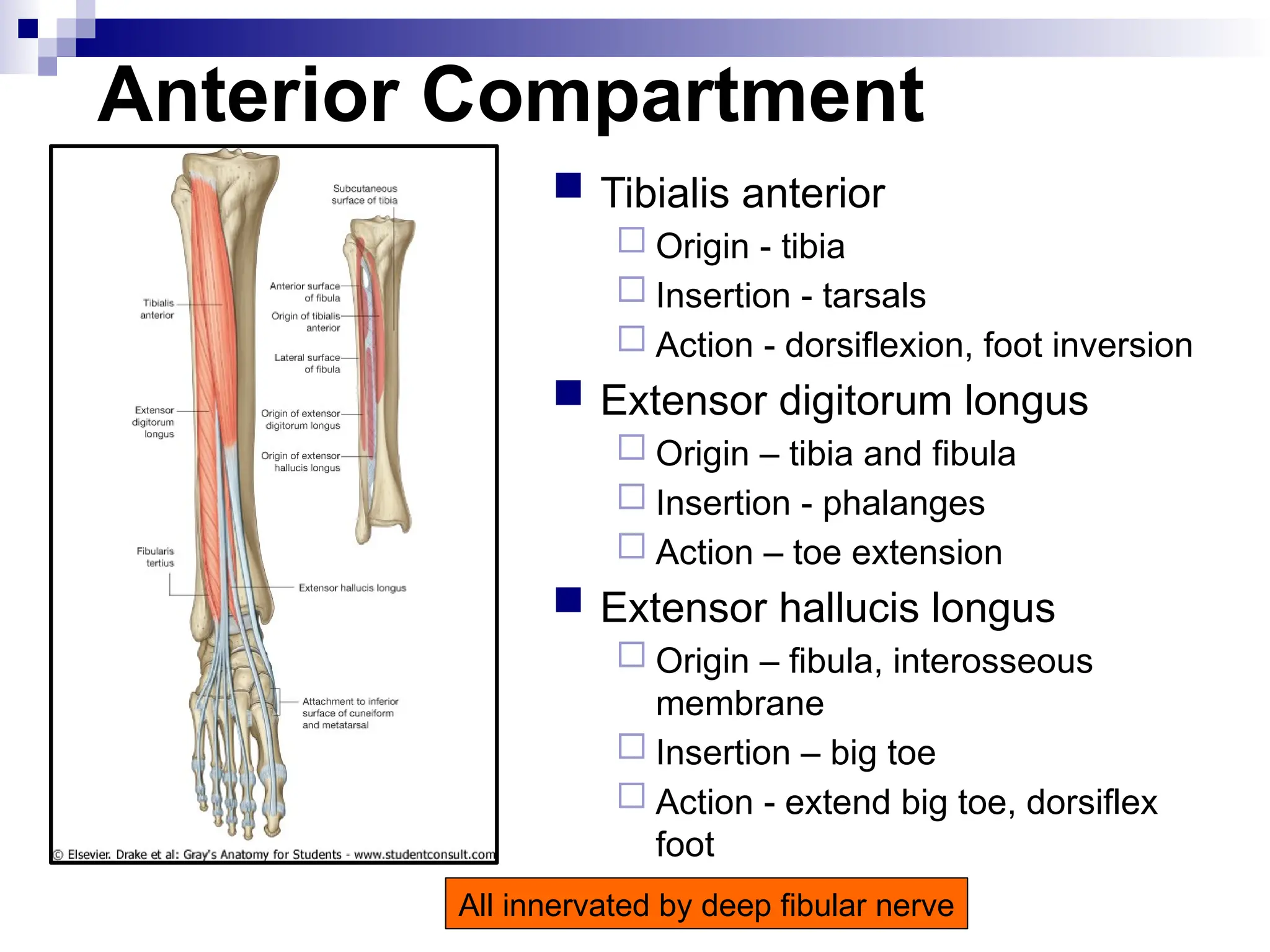
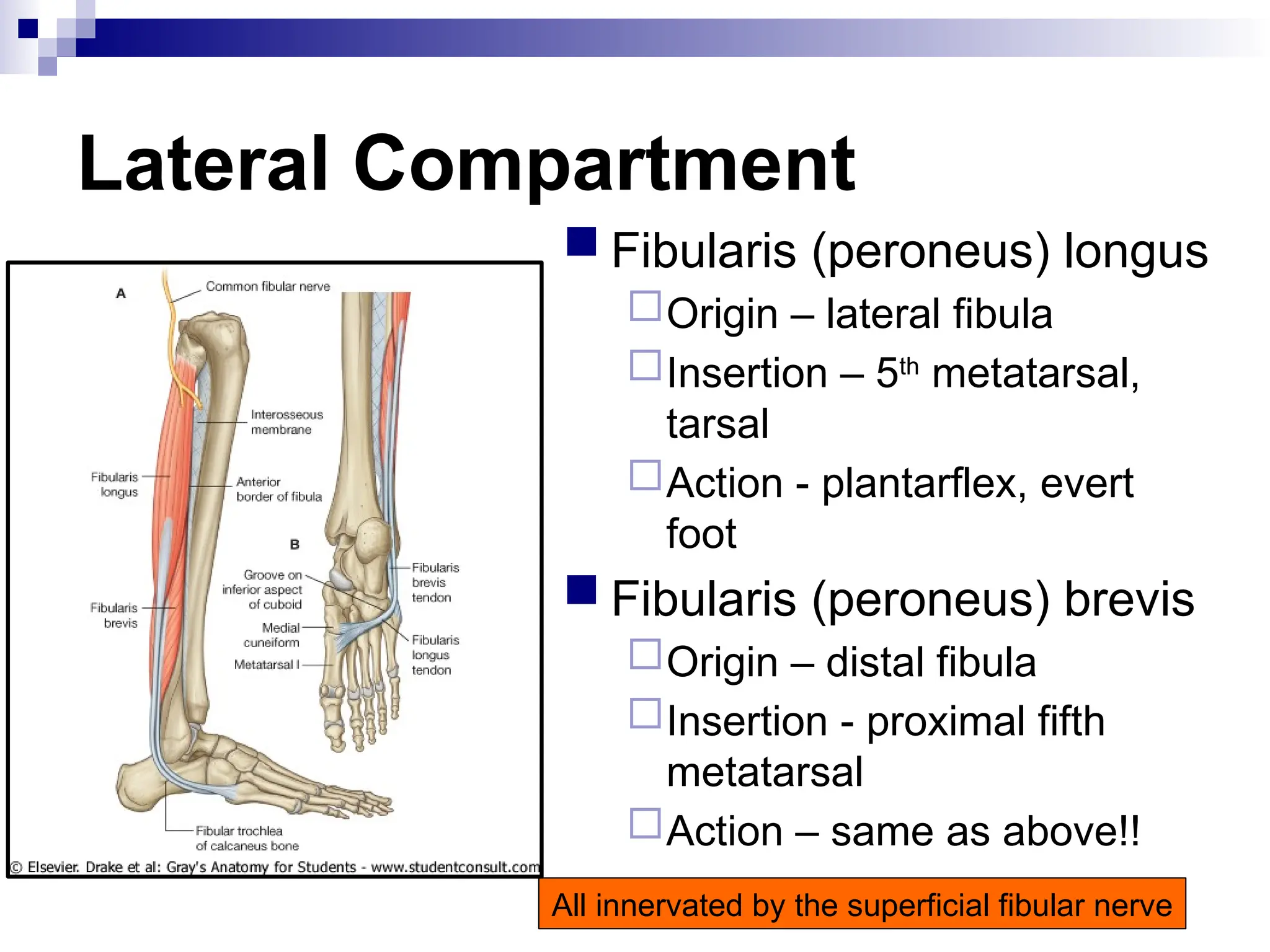
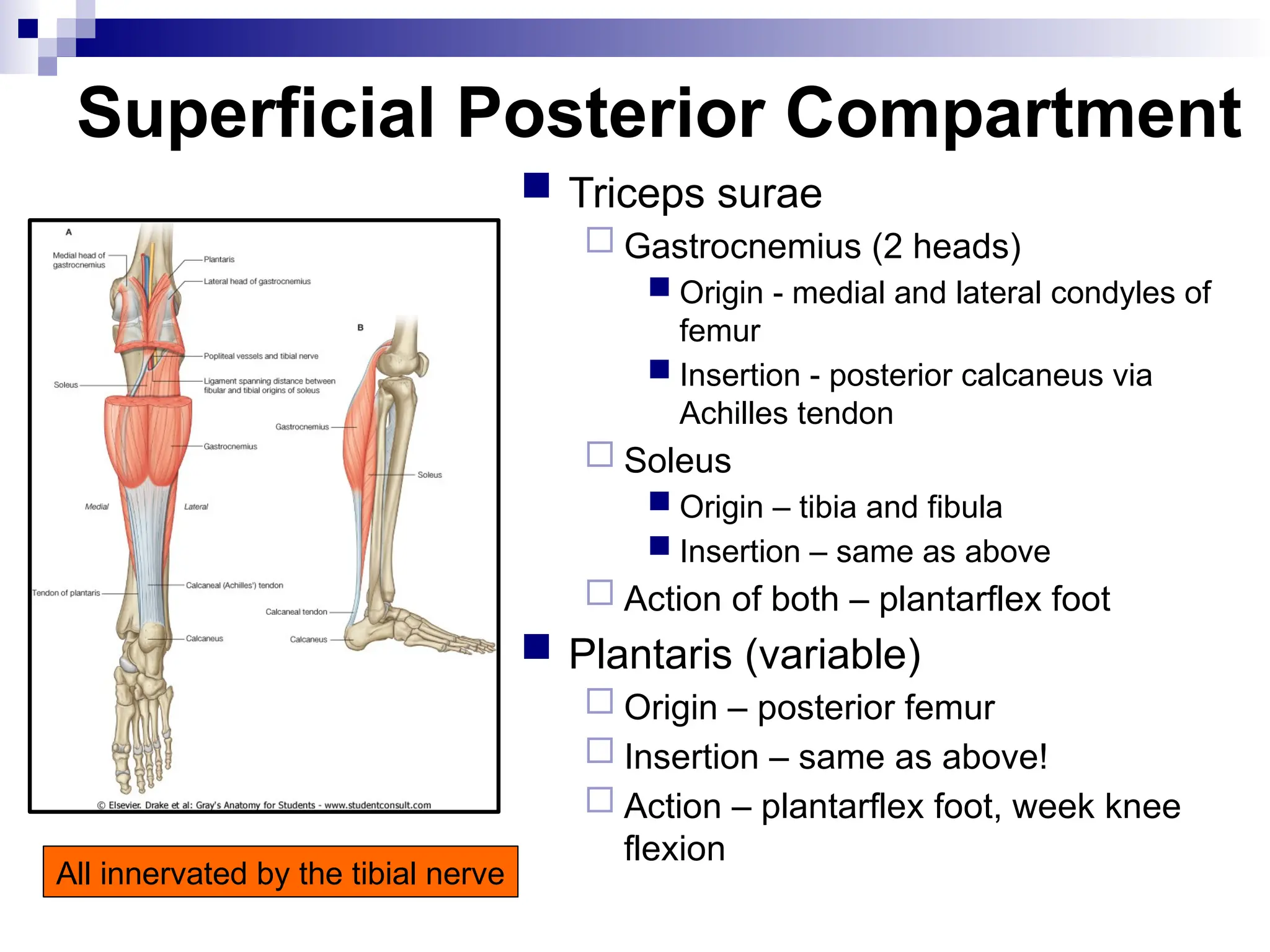
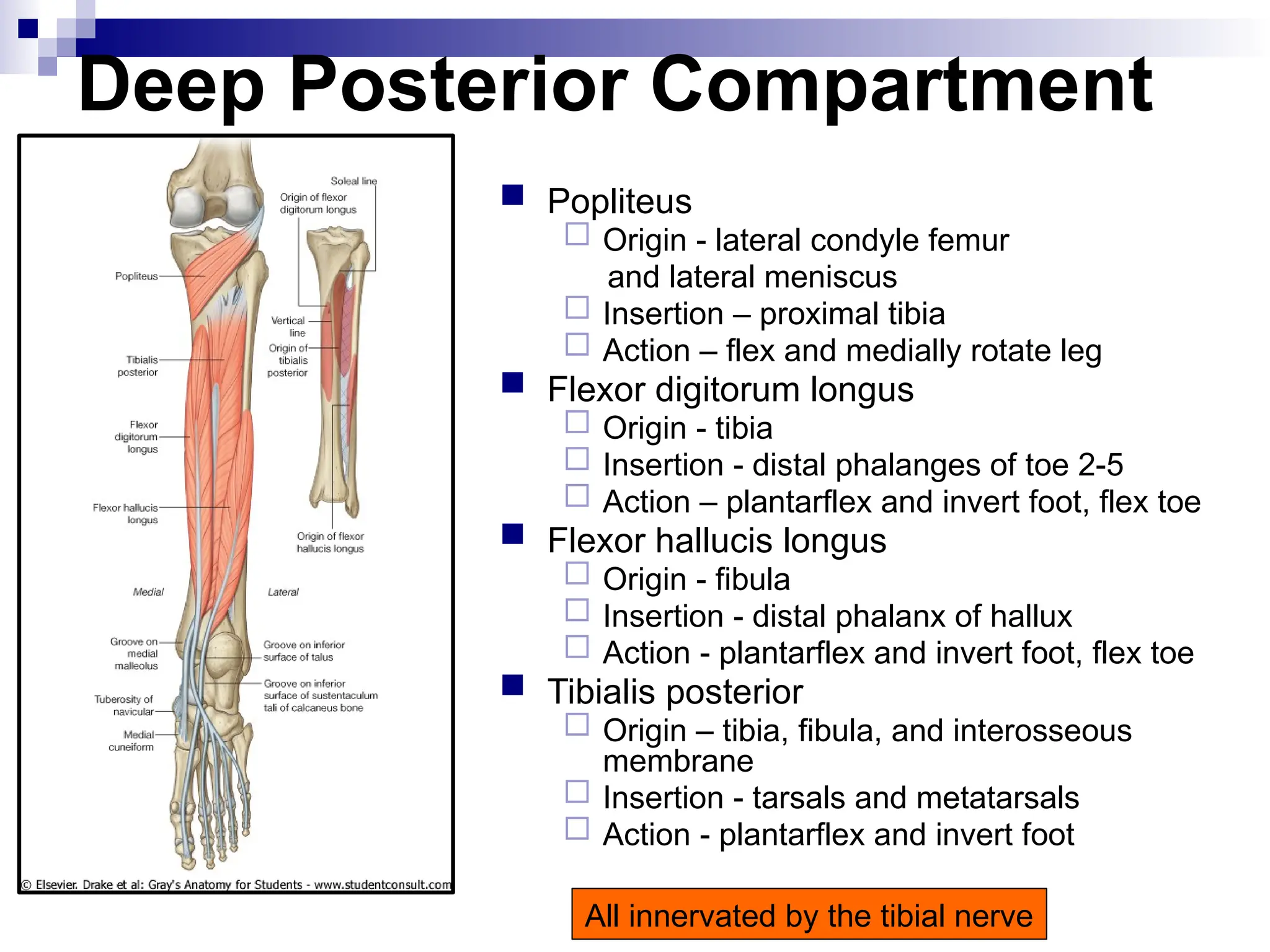
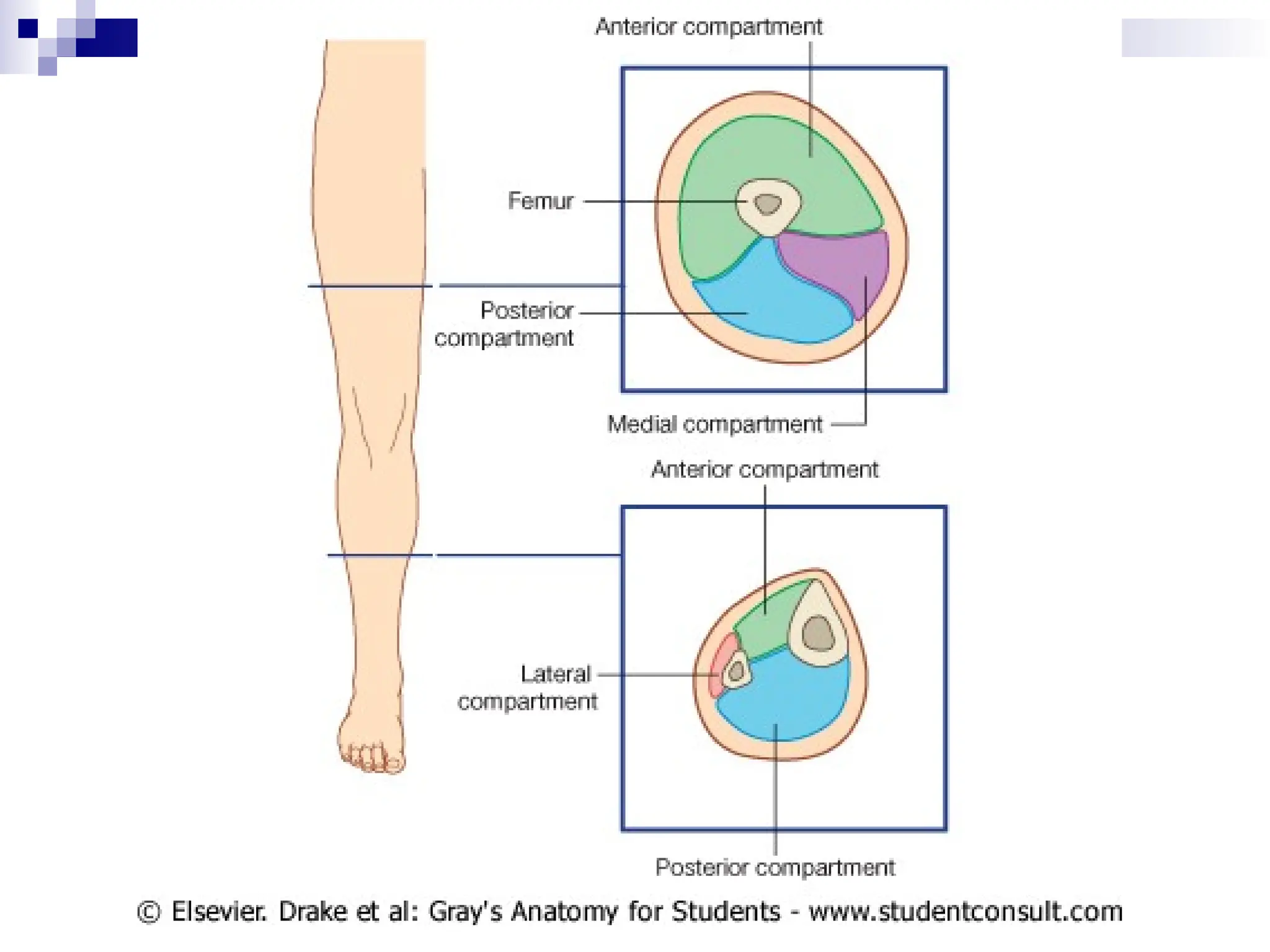
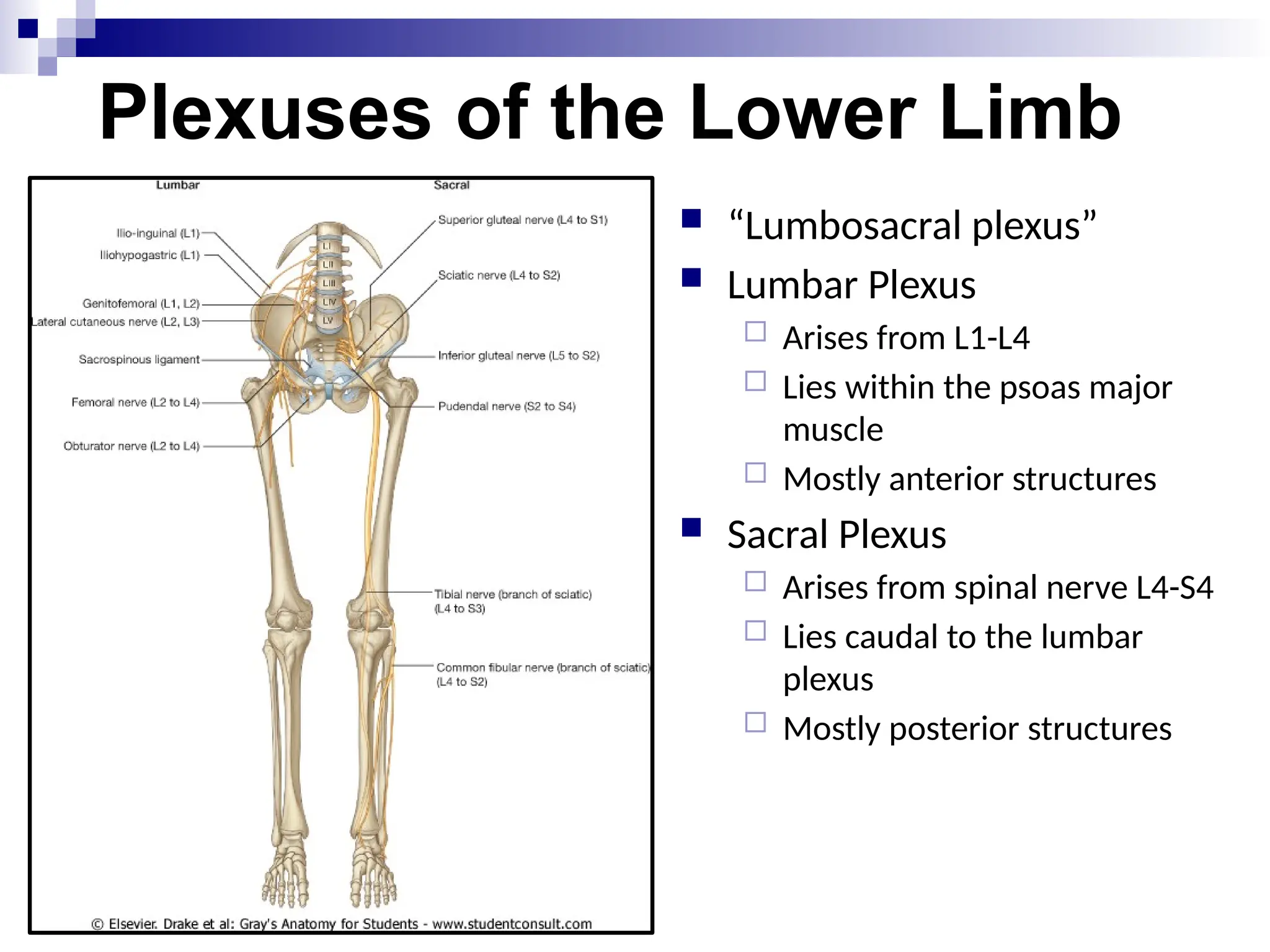
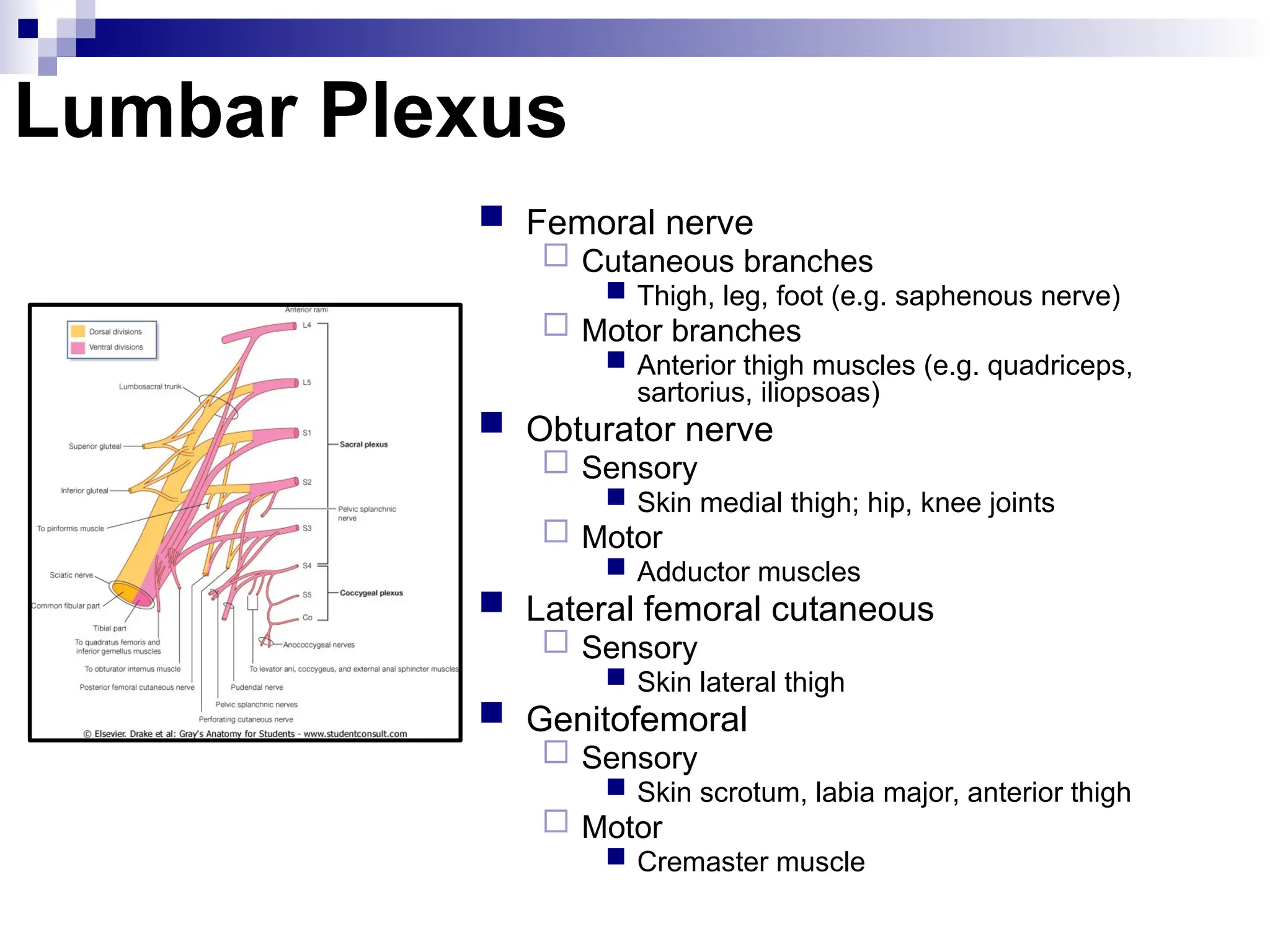
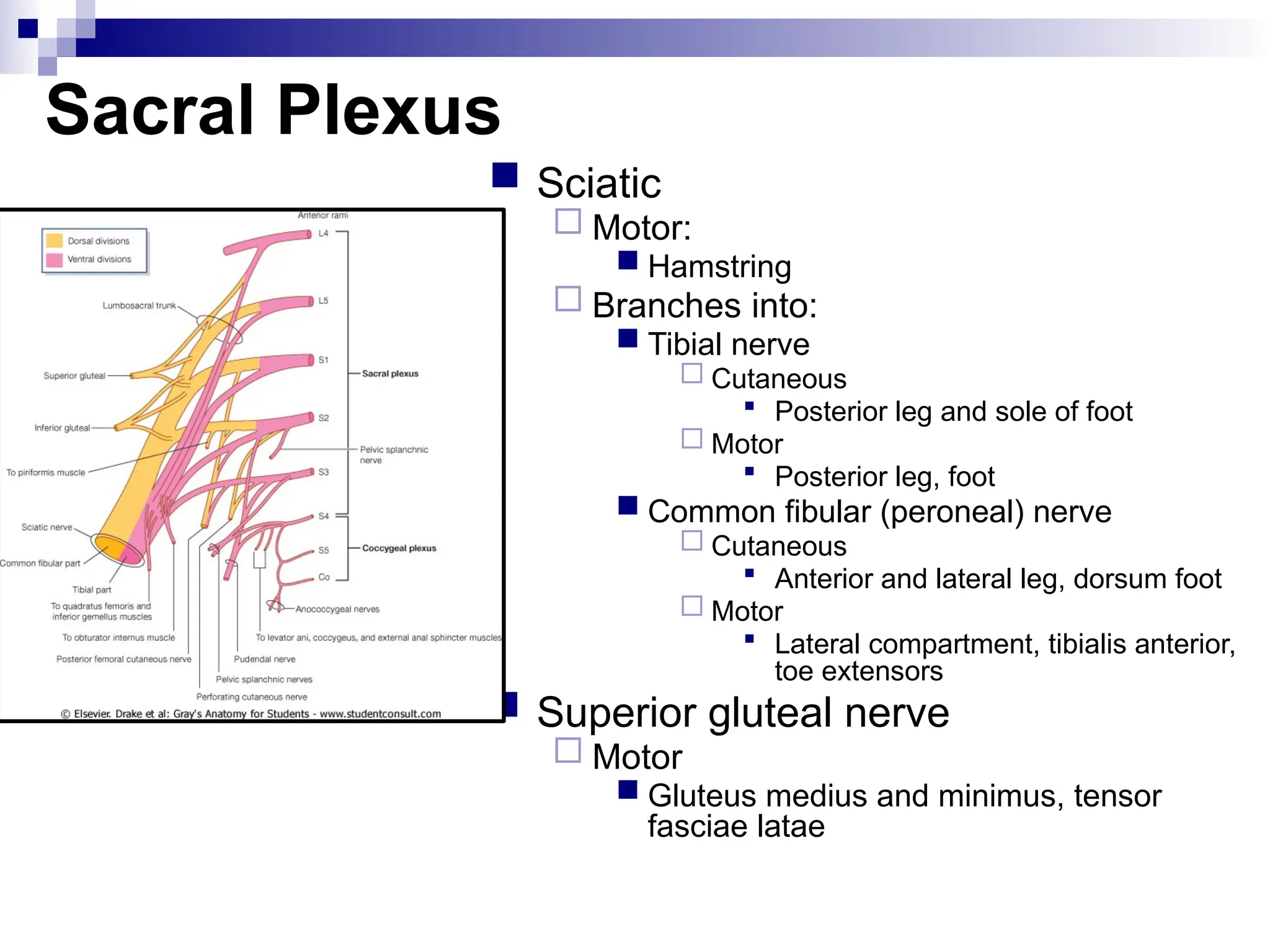
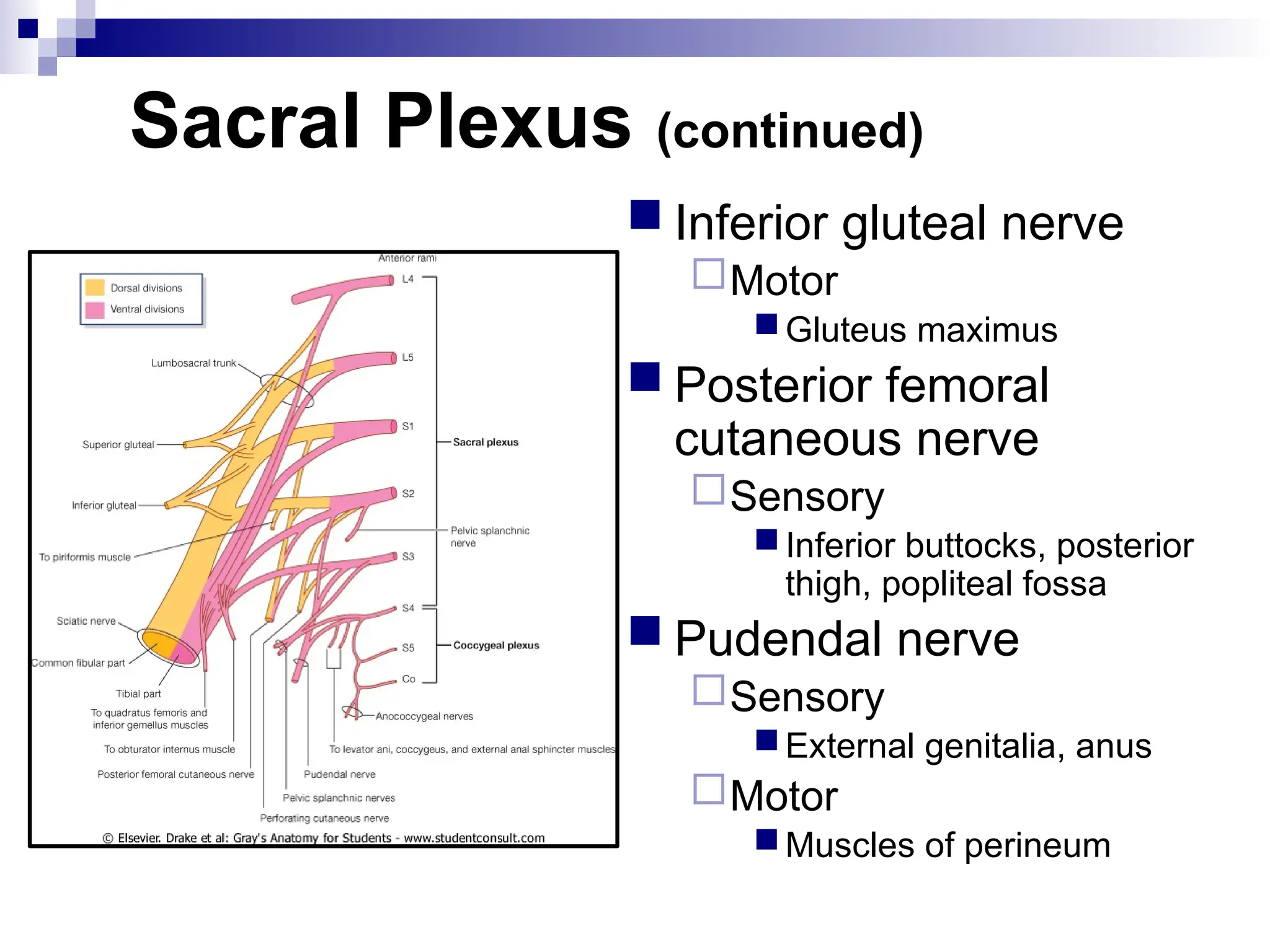
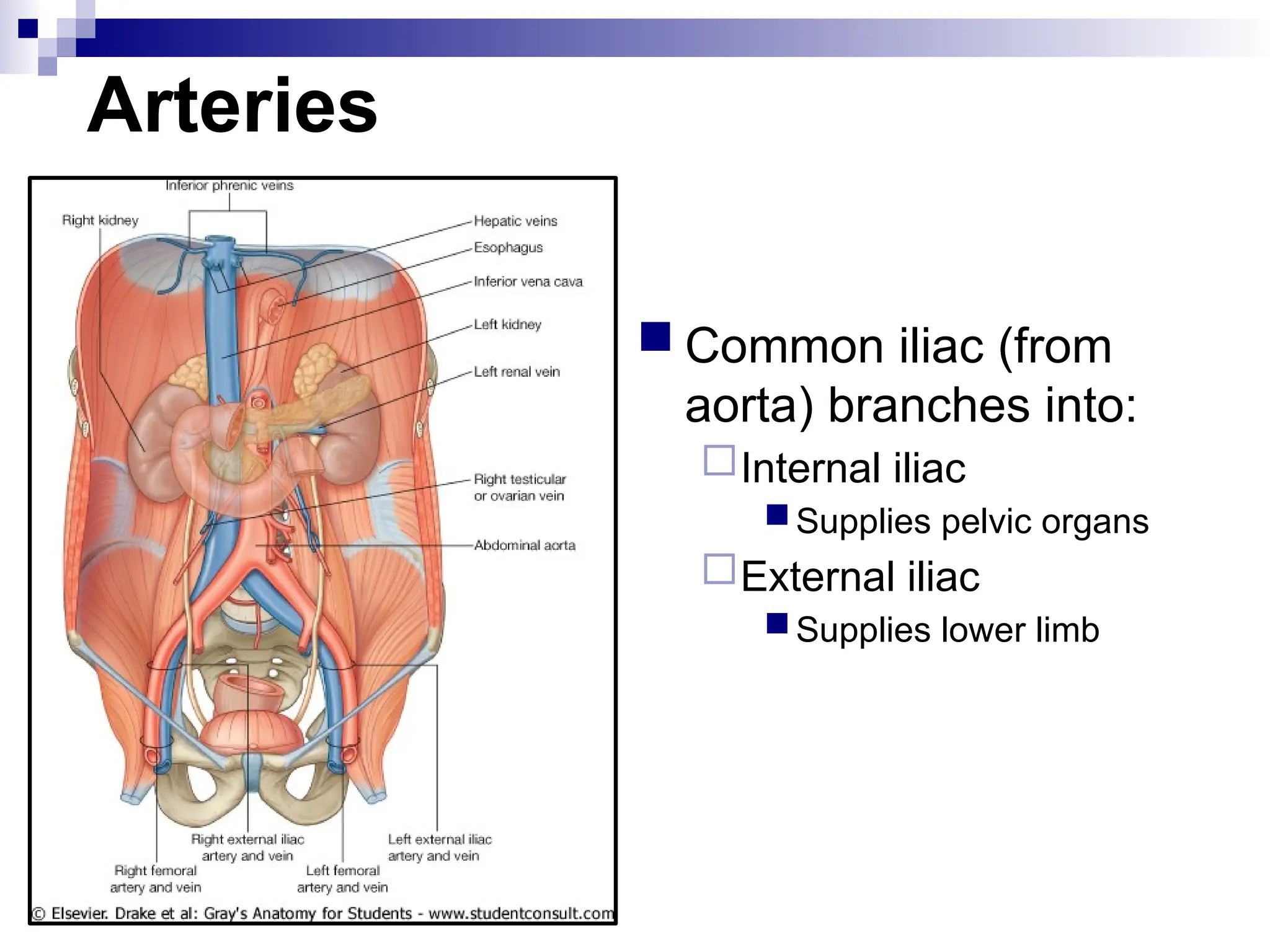
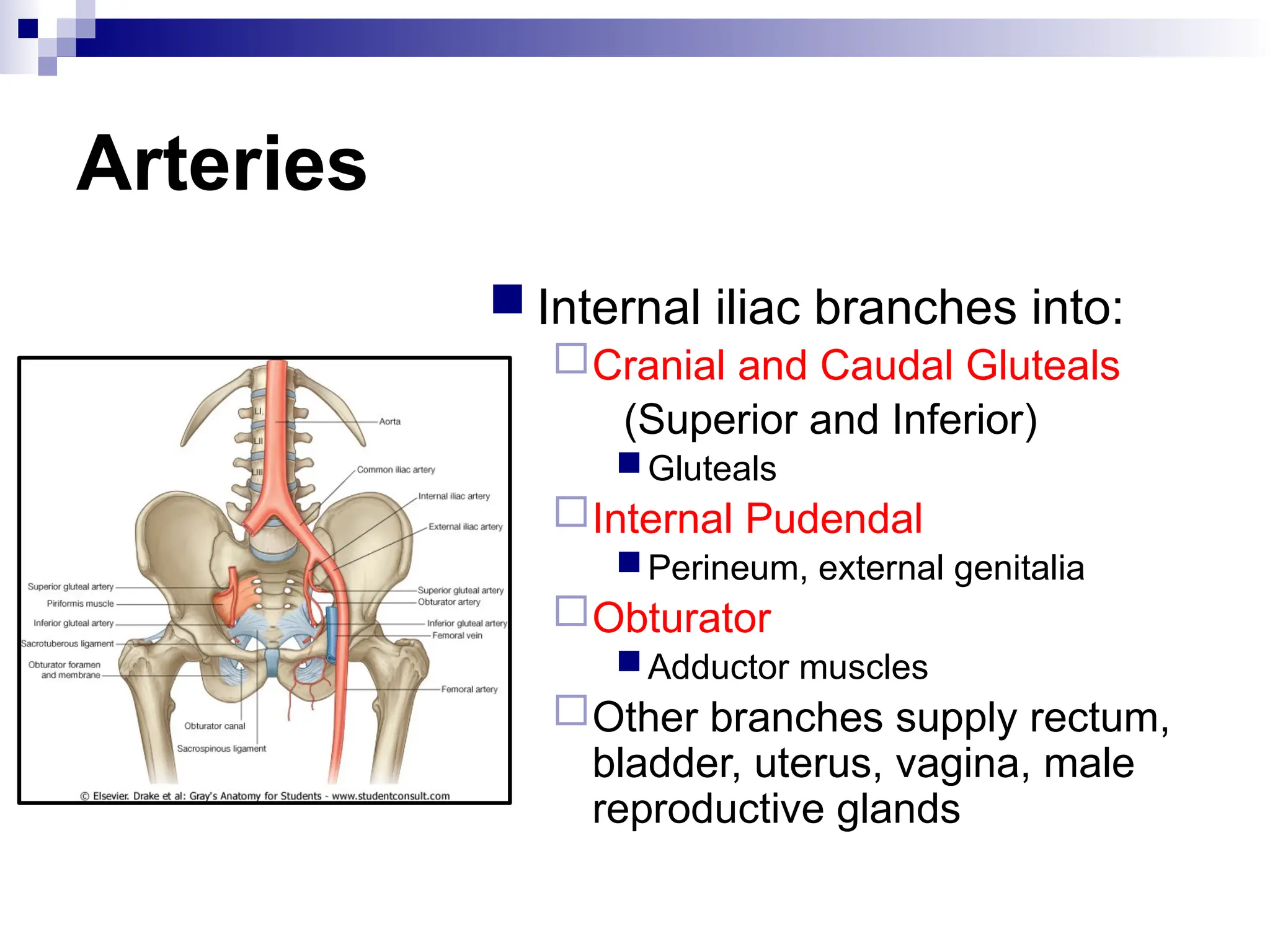
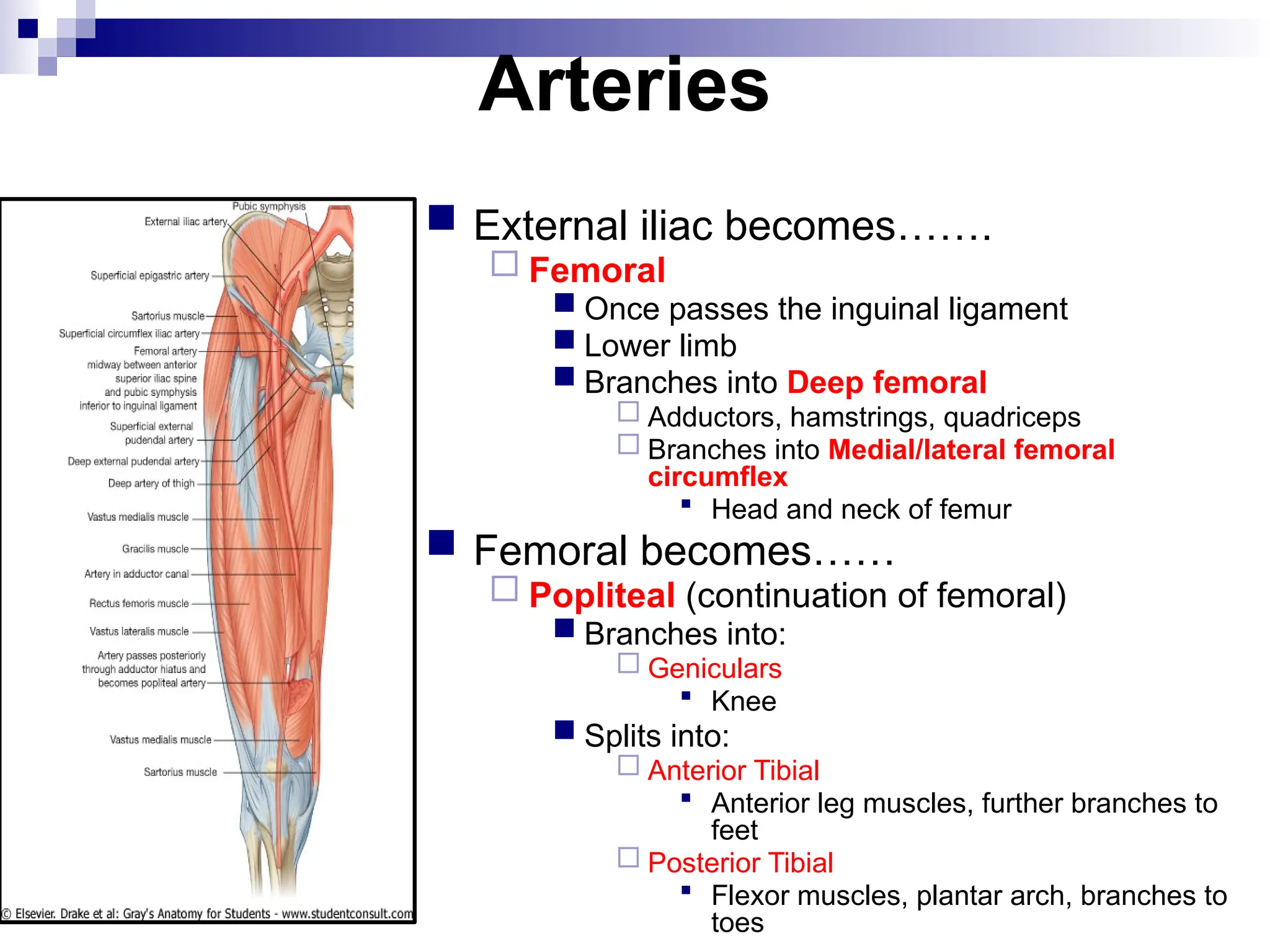
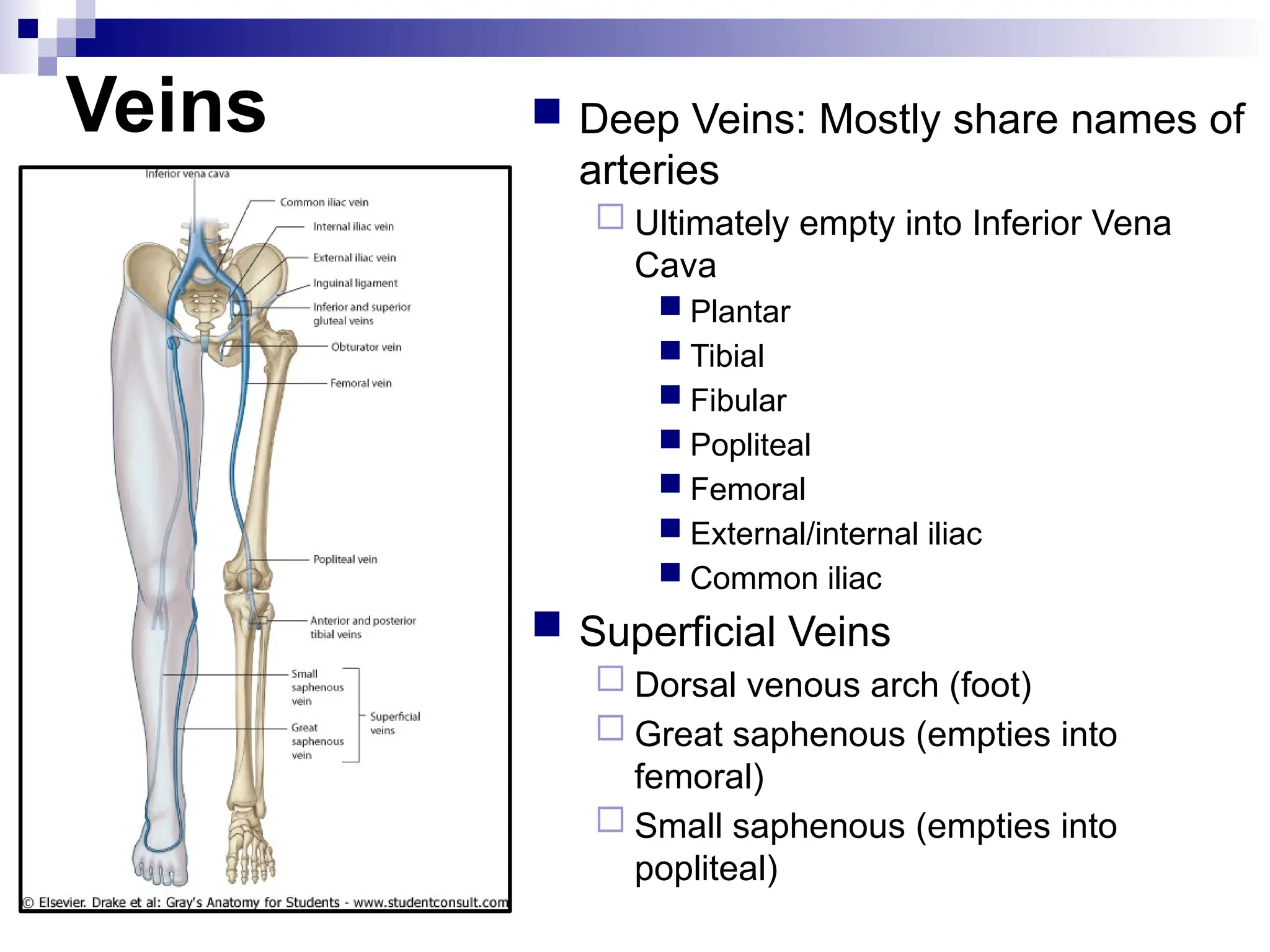
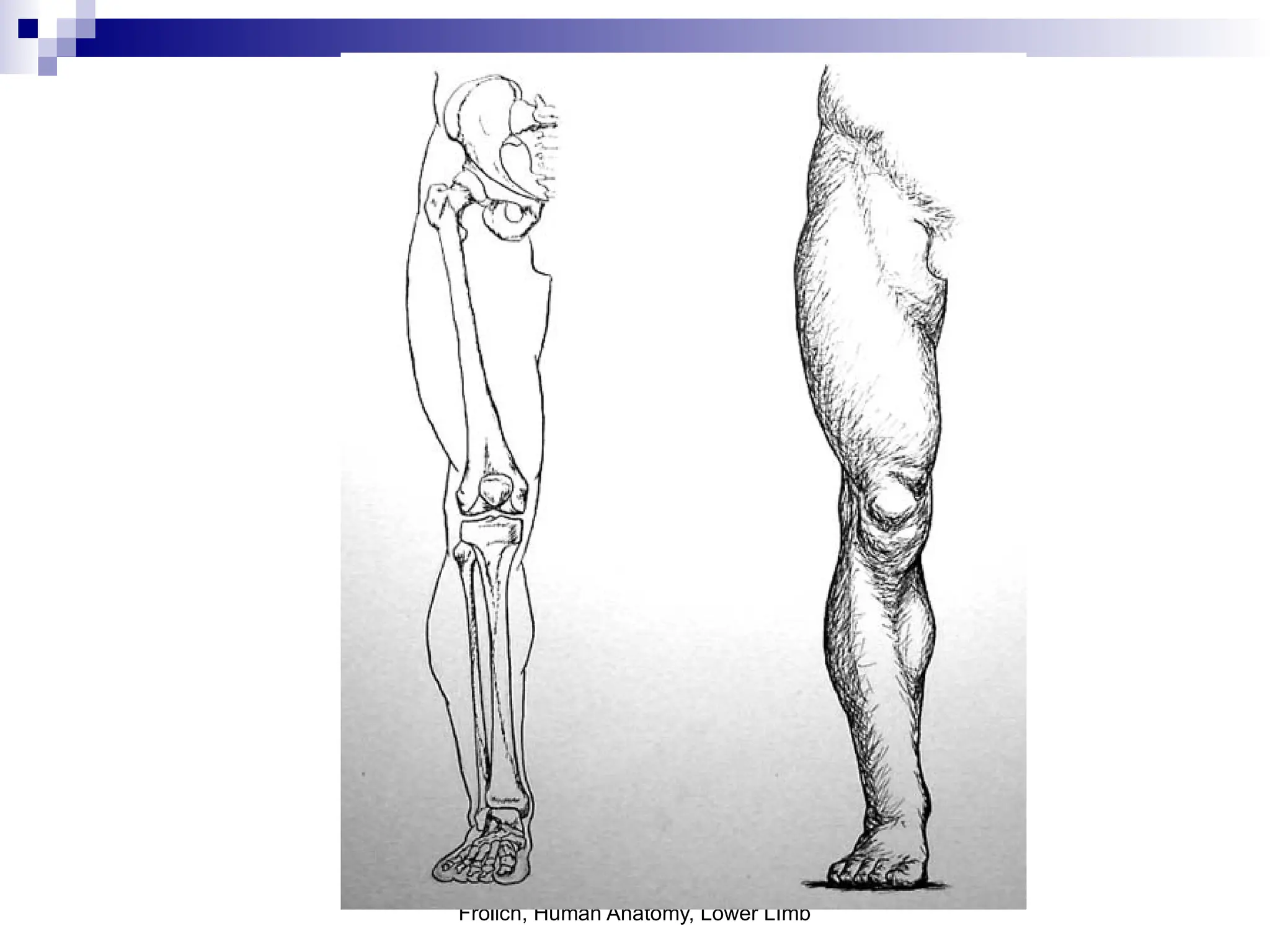
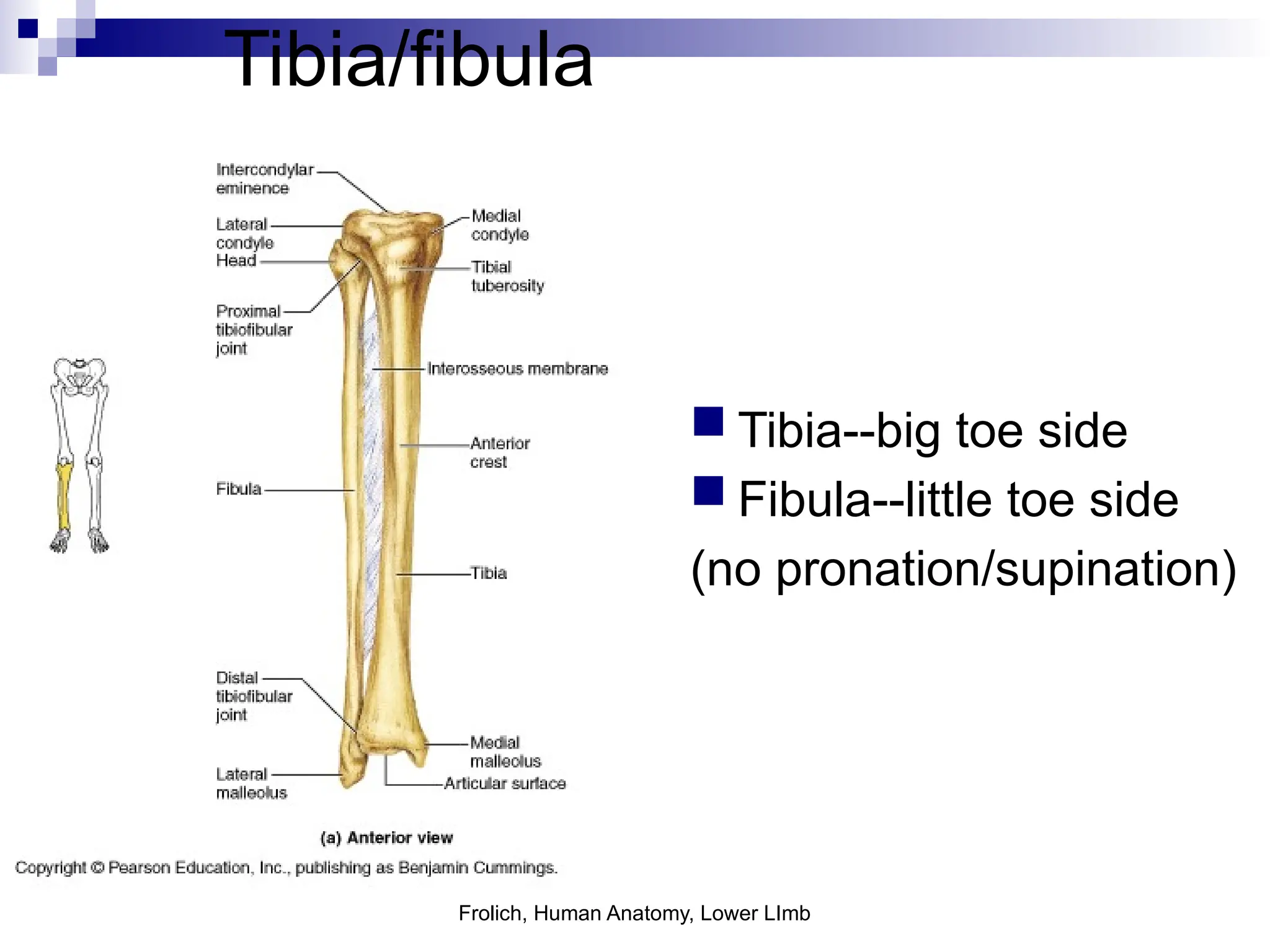
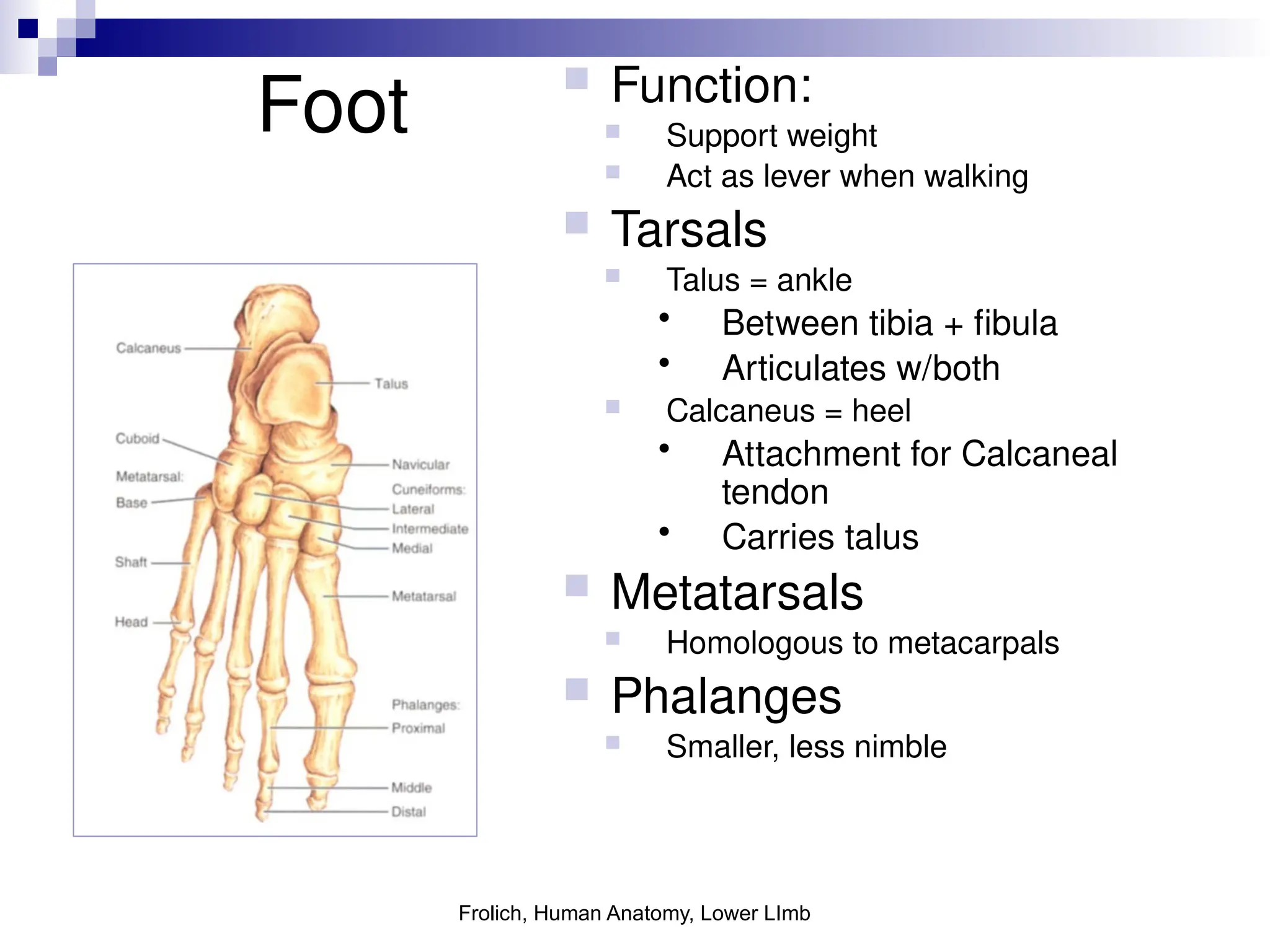
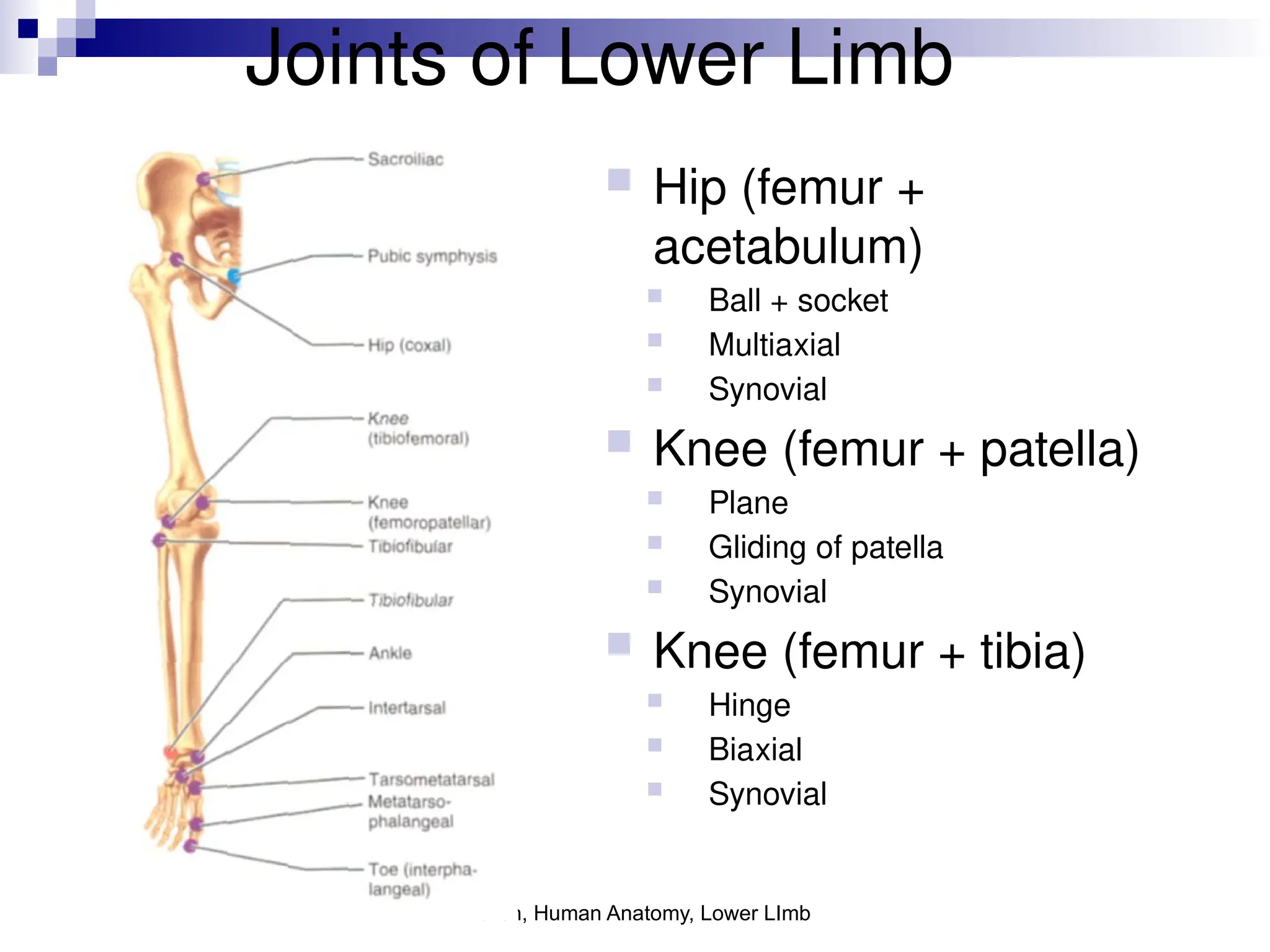
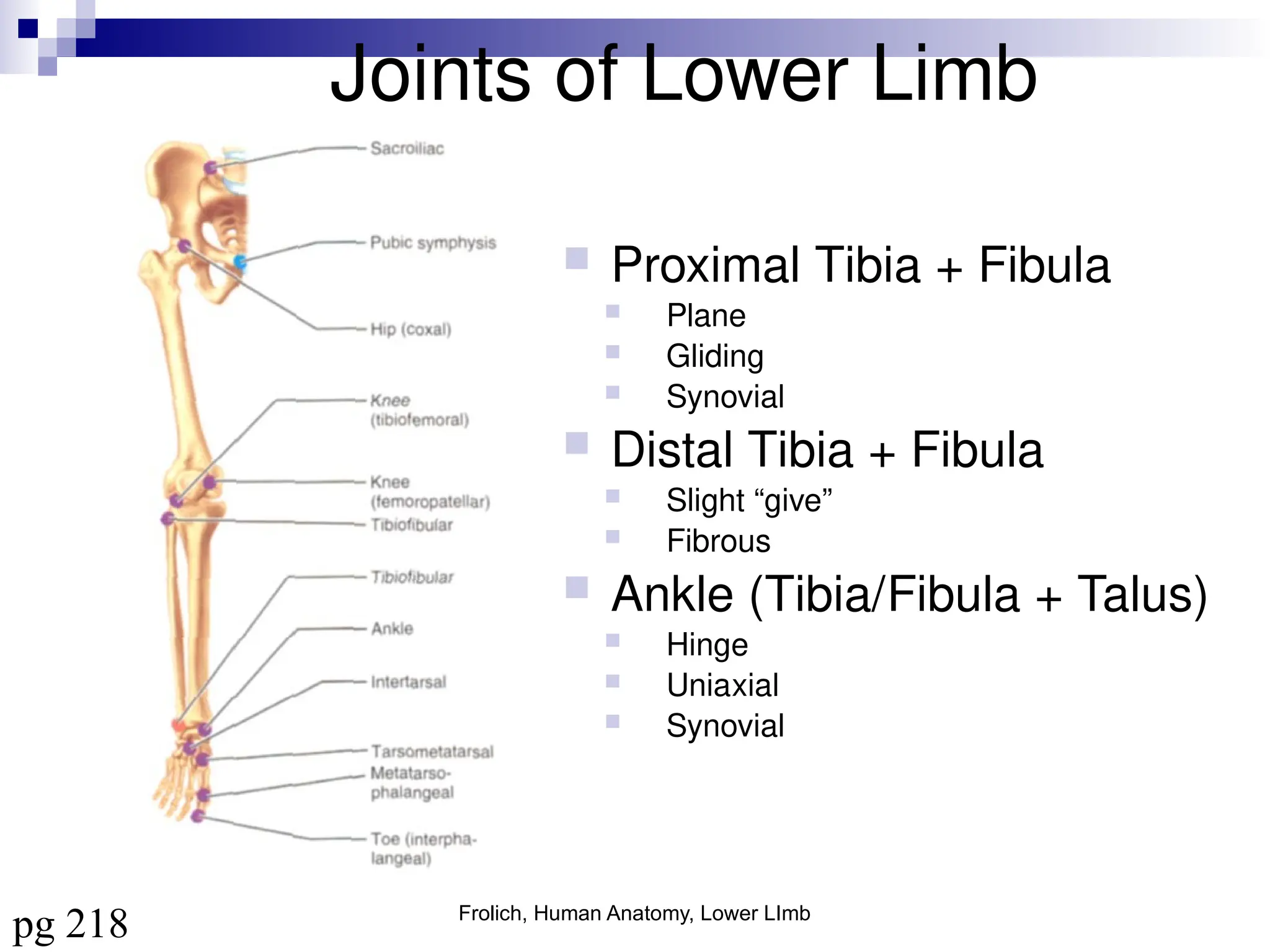
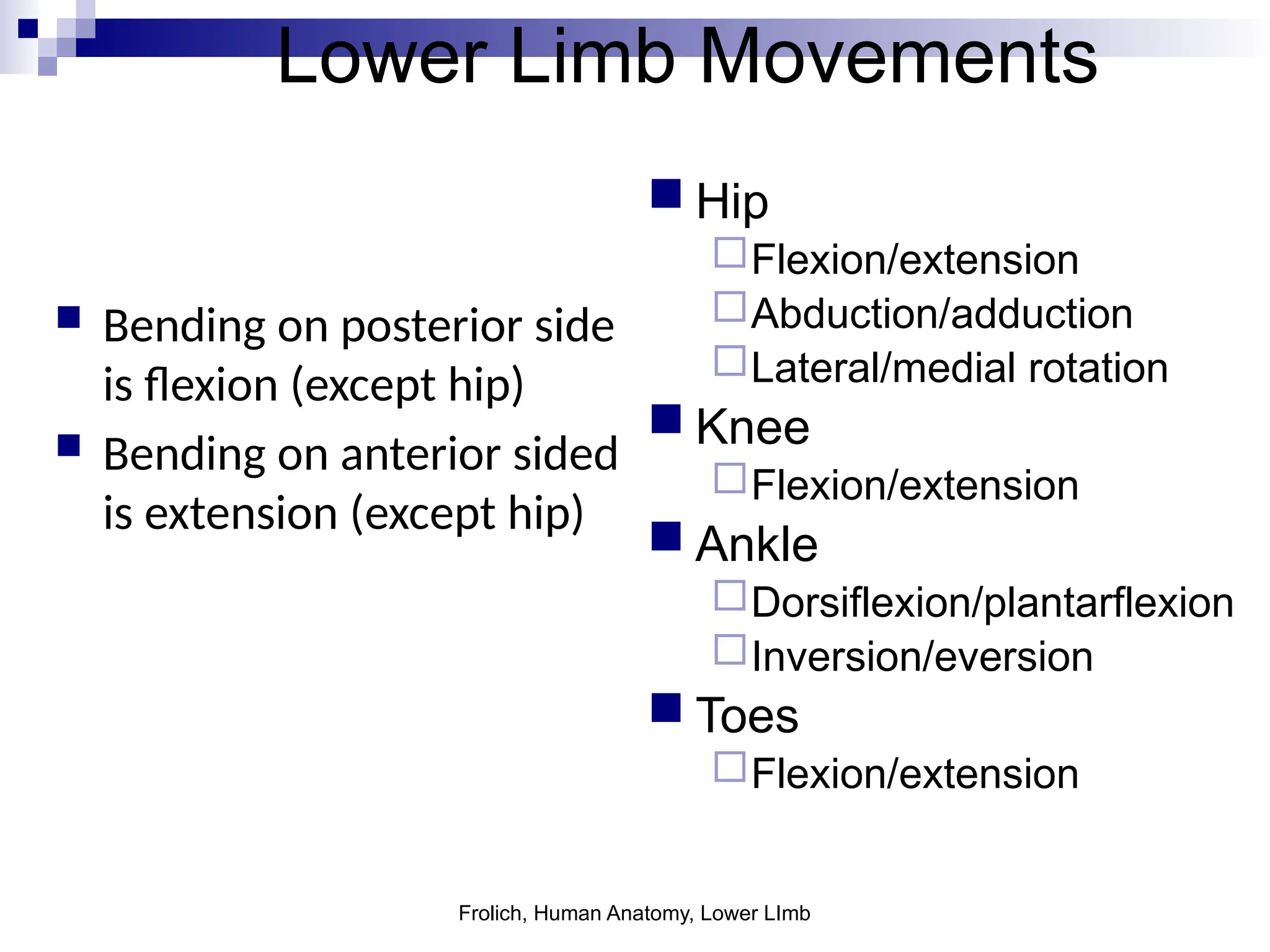
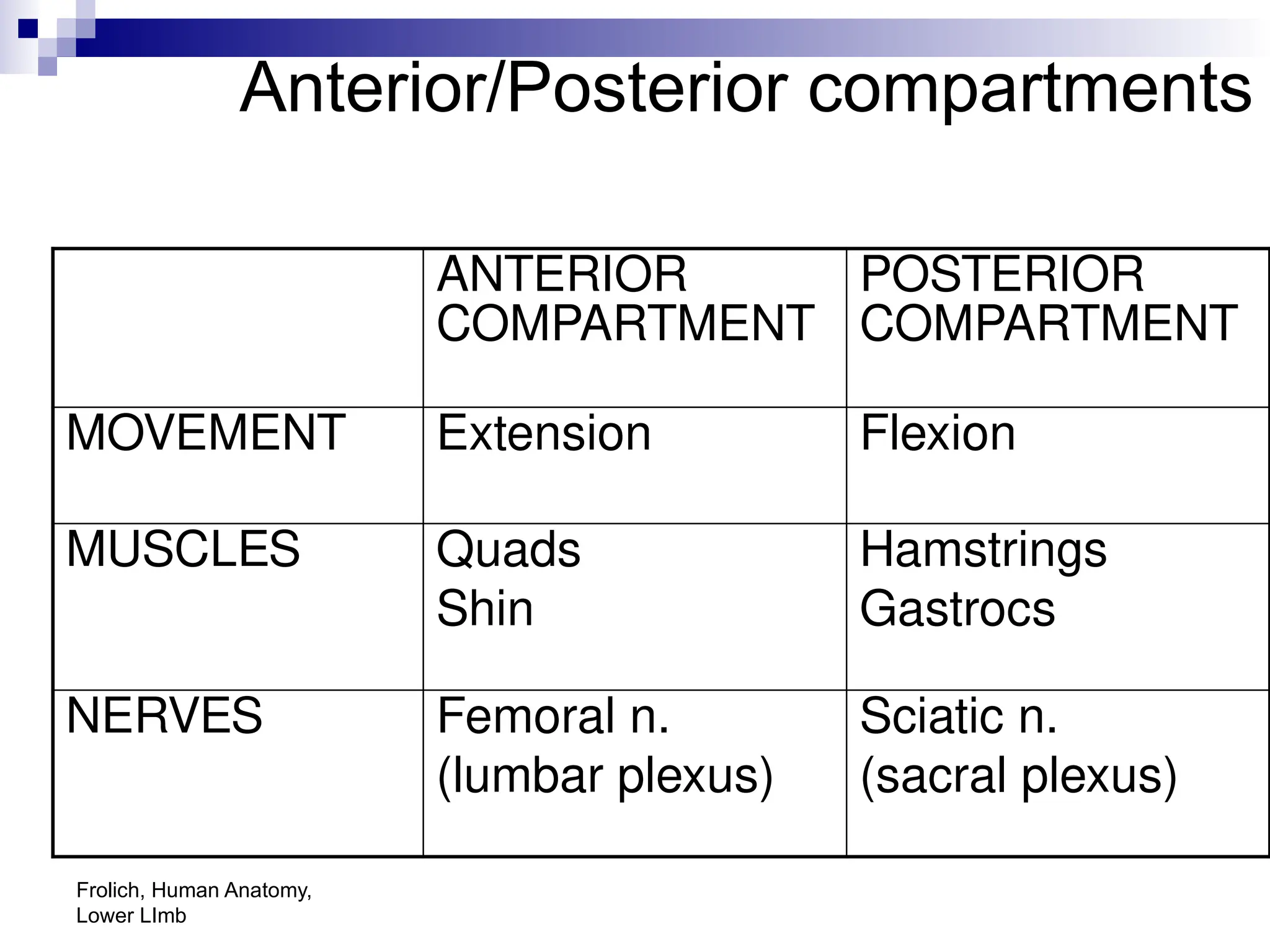
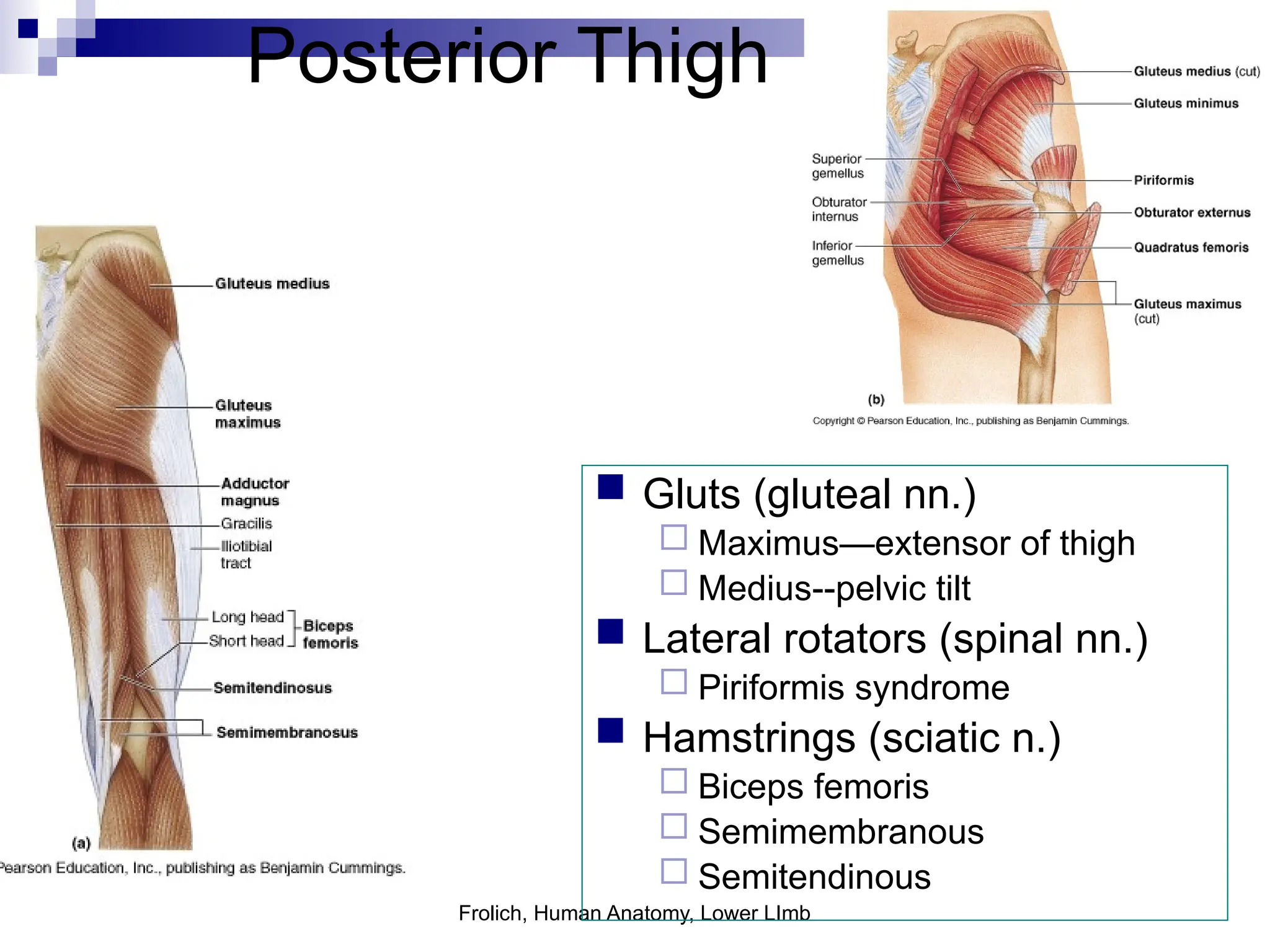
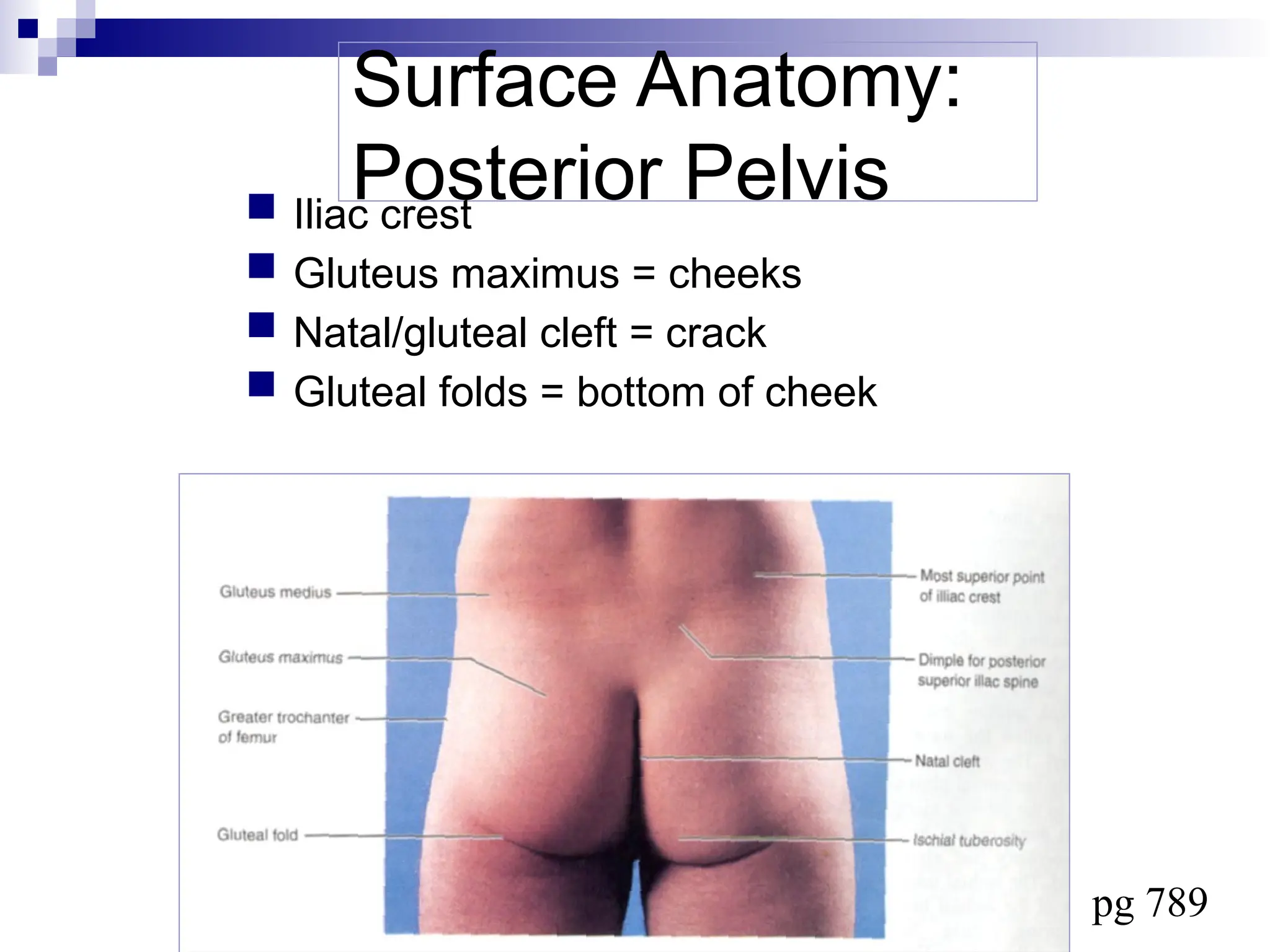
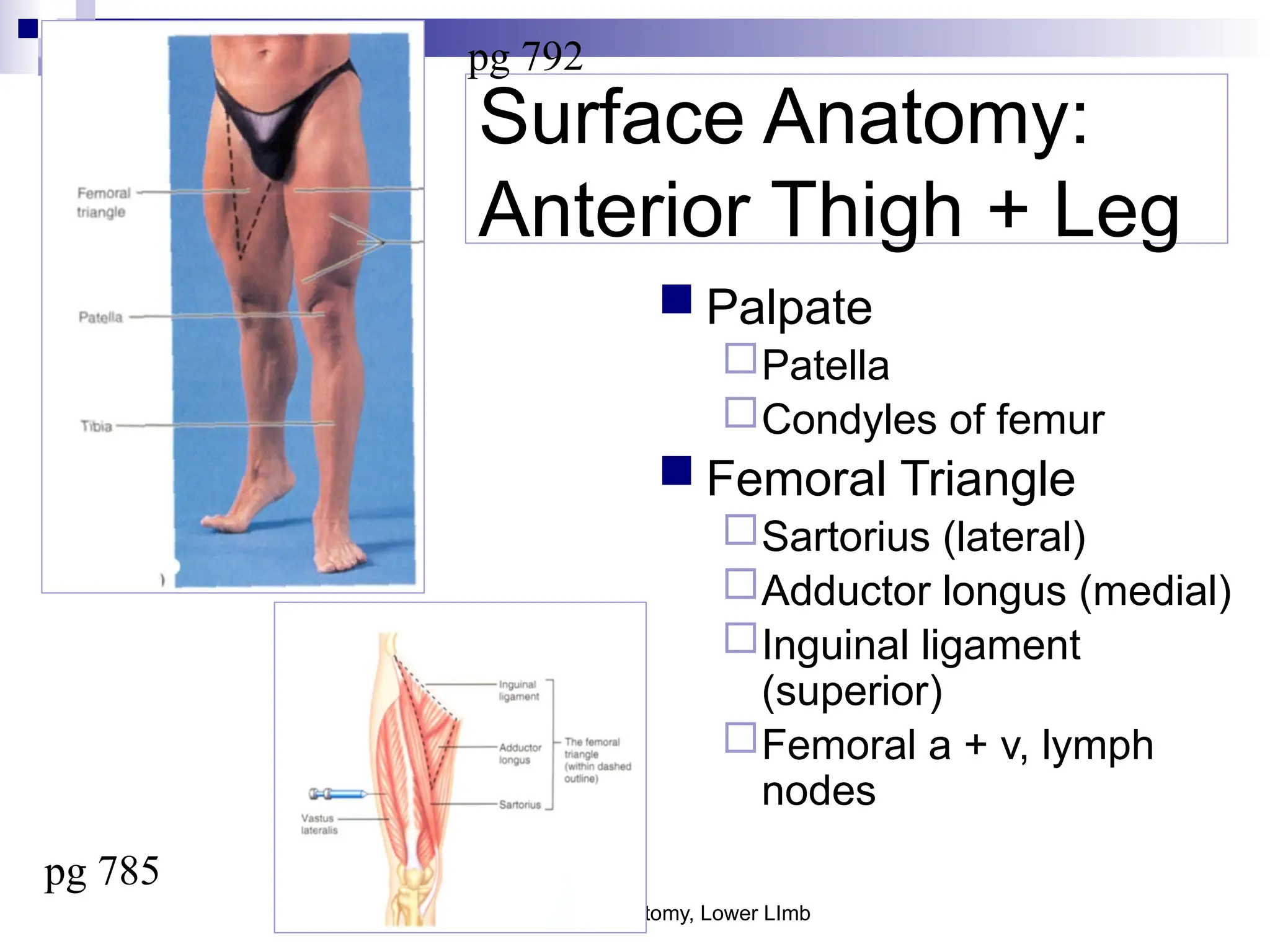
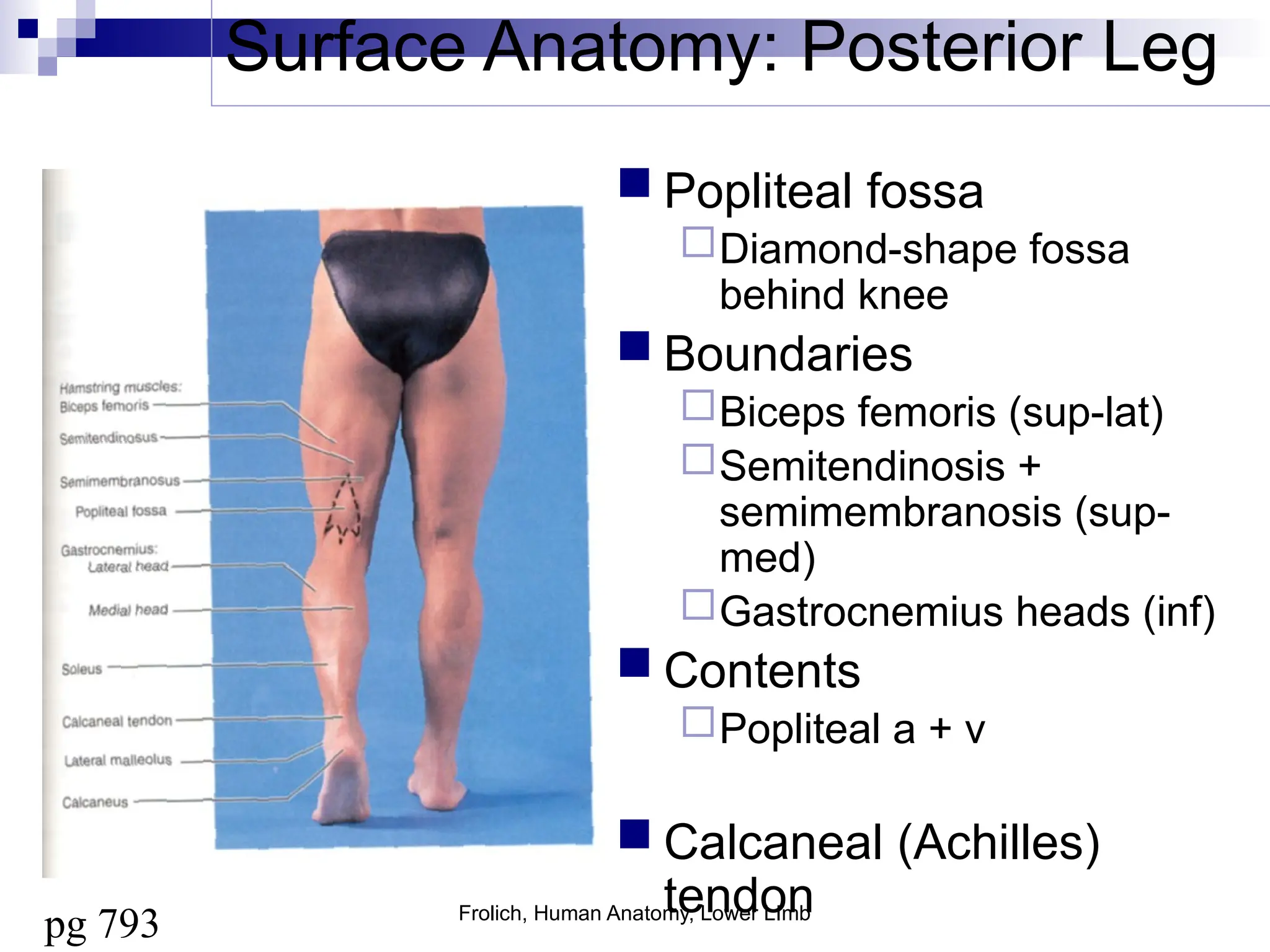
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the anatomy of the lower limb, detailing its surface anatomy, skeletal composition, joints, and muscle groups, along with their functions and innervations. It describes the major bones, such as the femur, tibia, and fibula, and explains the roles of various muscles in movement and locomotion. Additionally, it covers the neurovascular structures associated with the lower limb and their anatomical relationships.