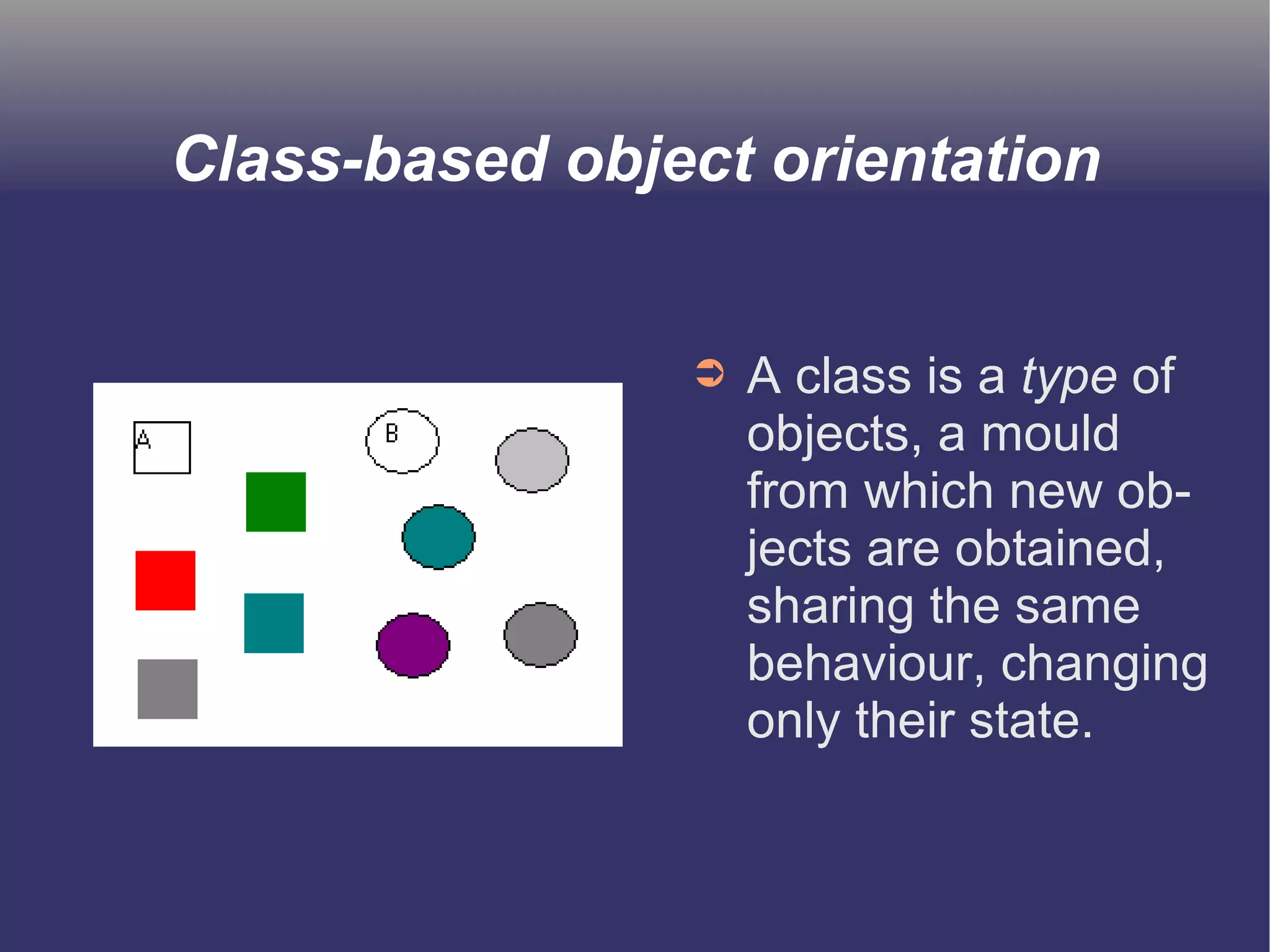
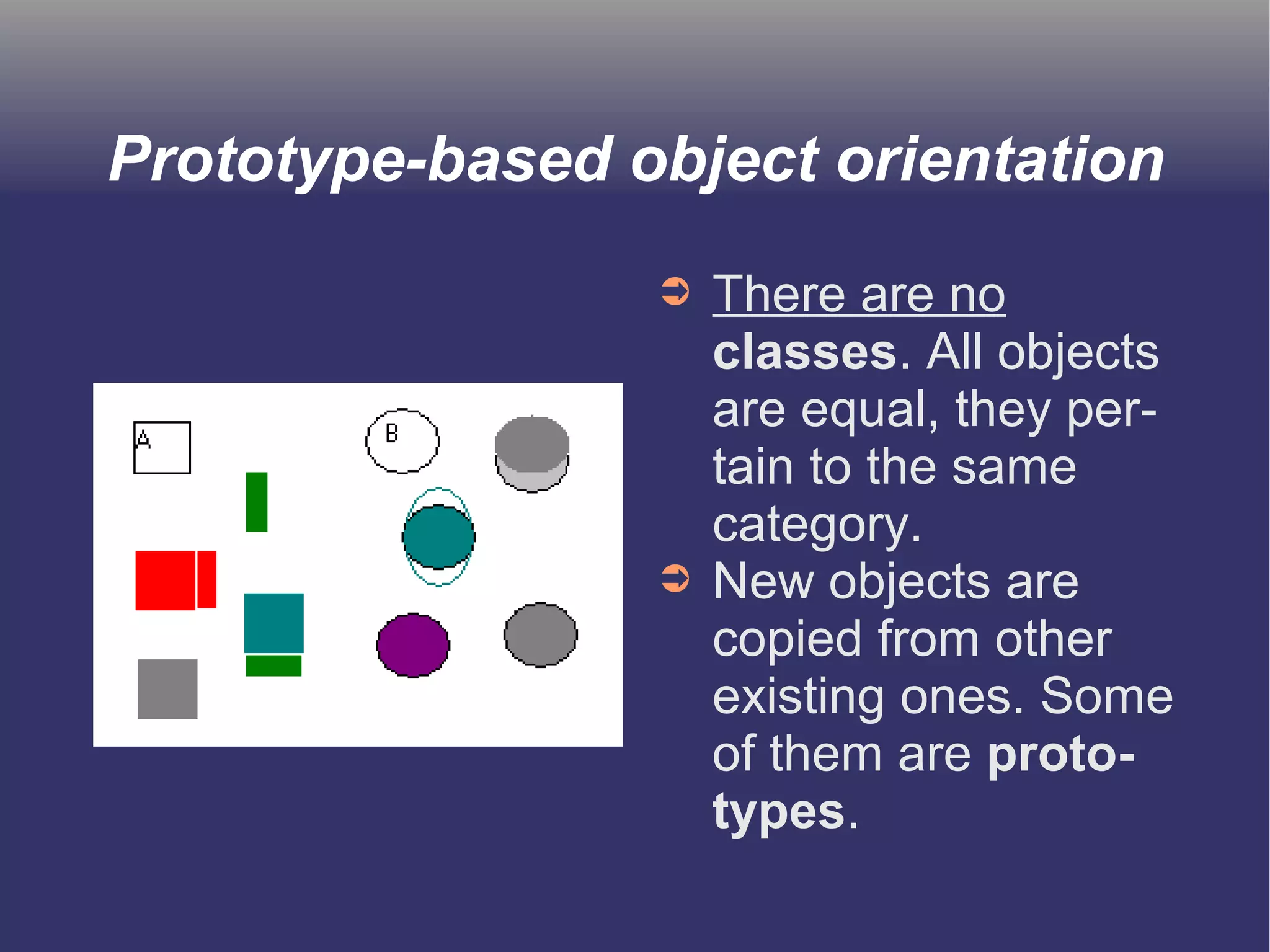
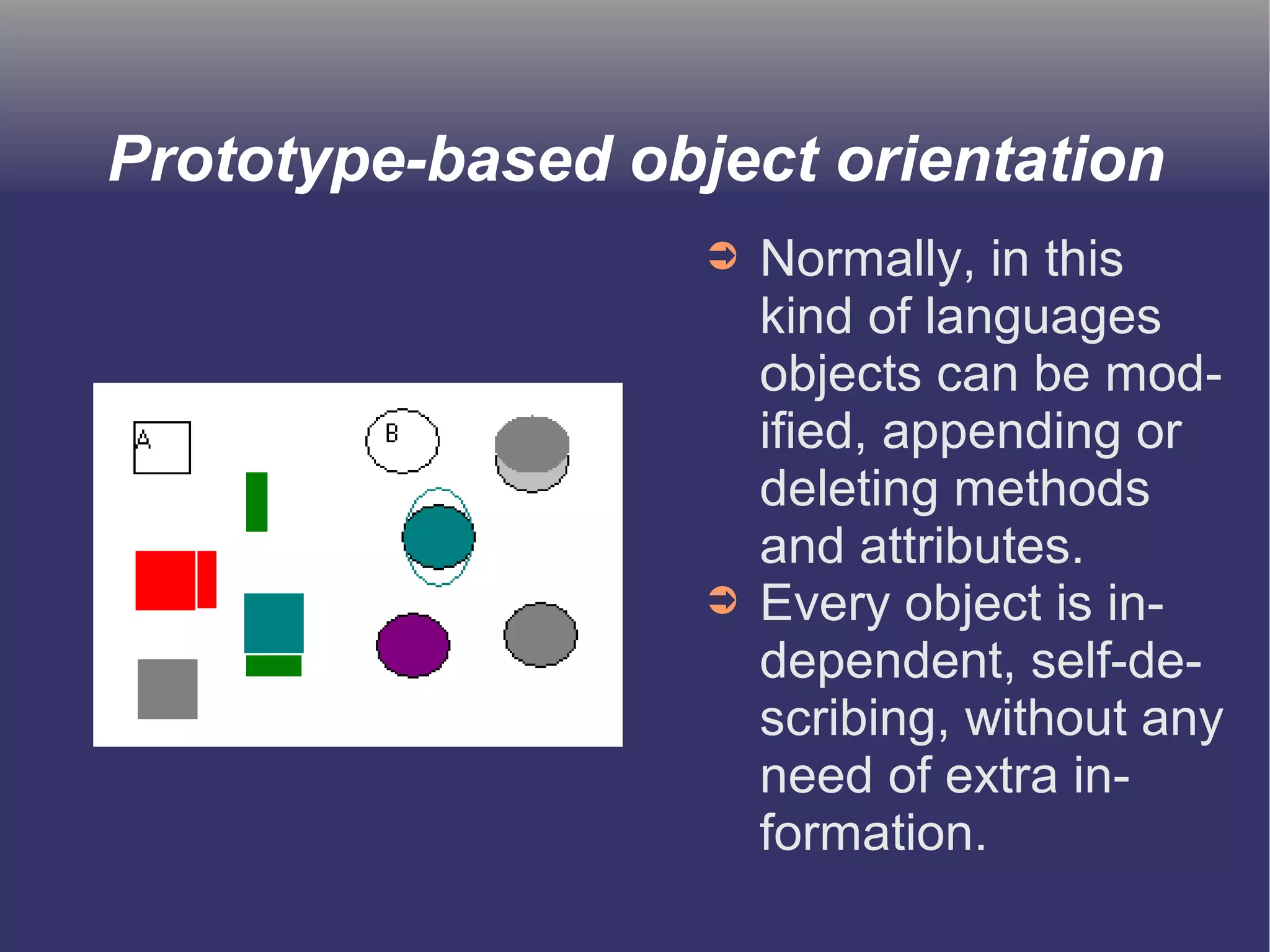
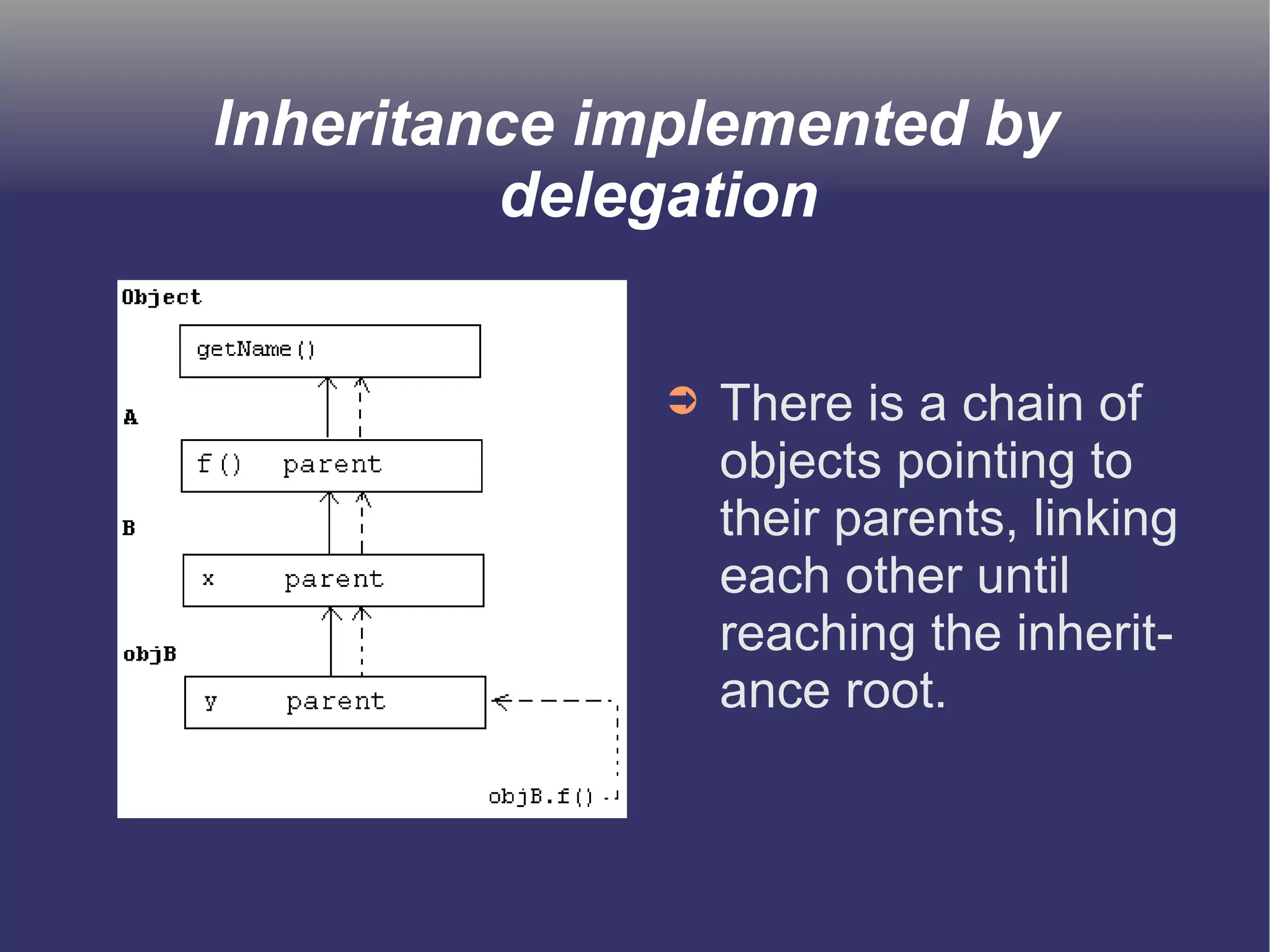
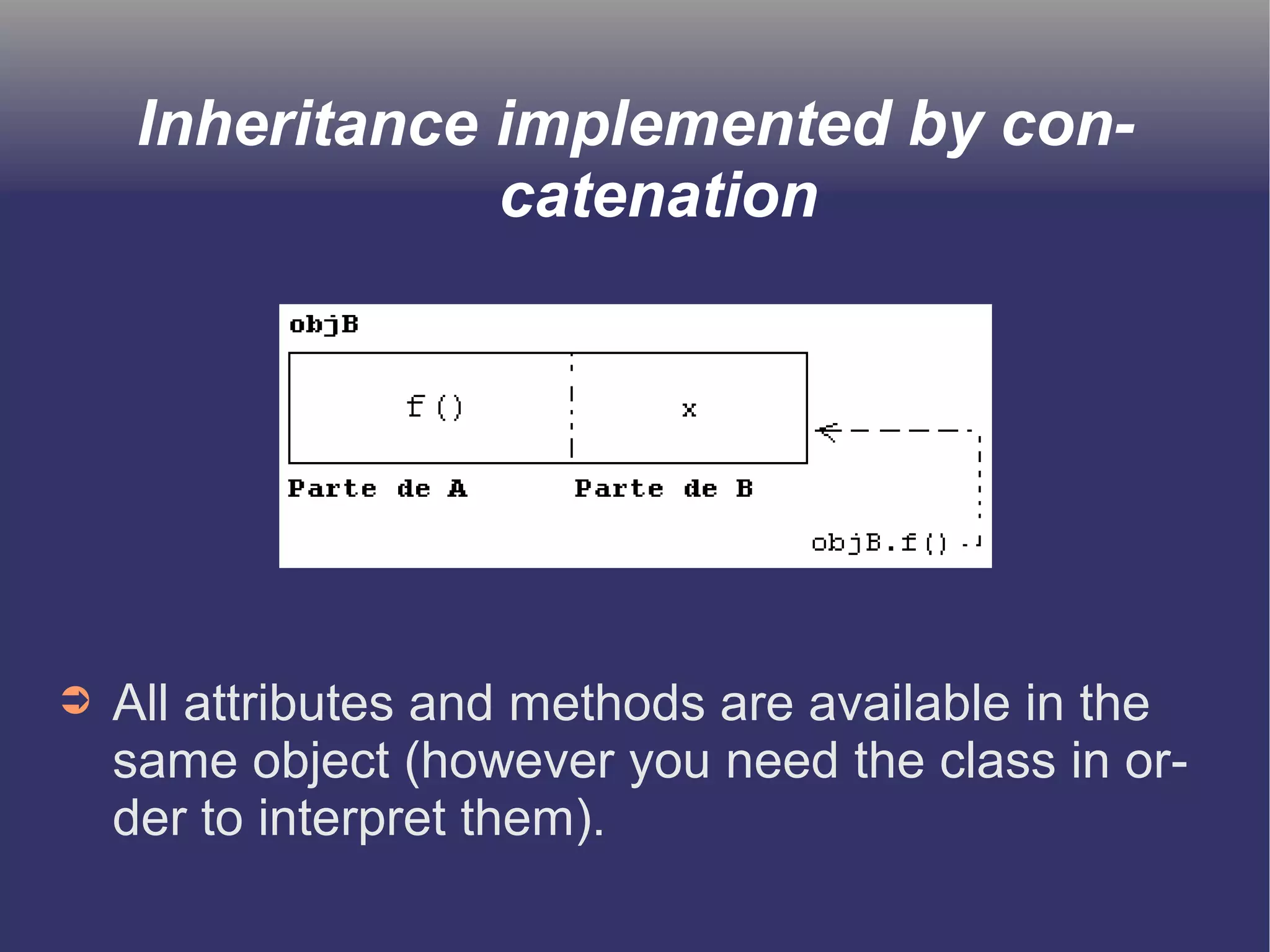
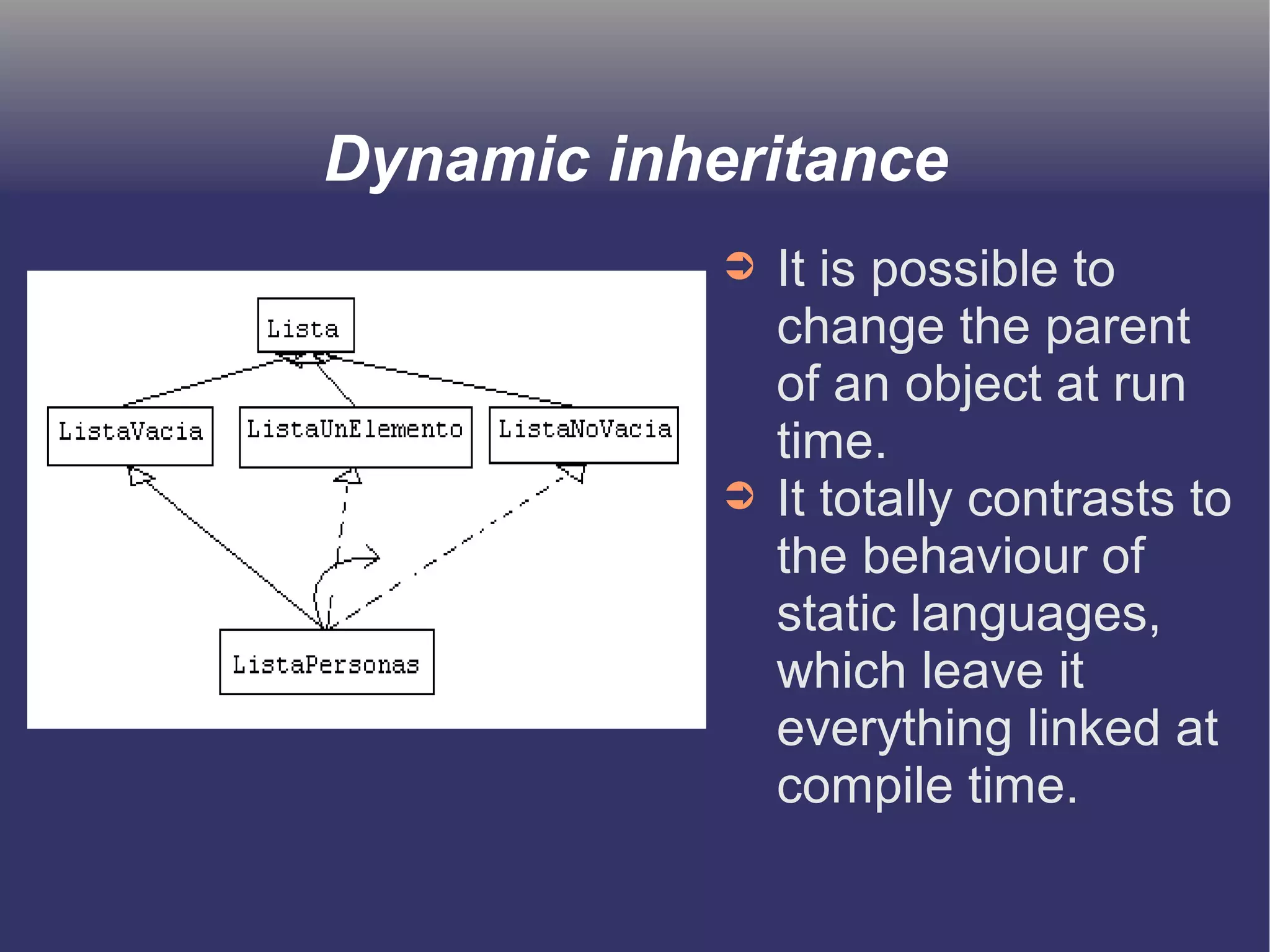
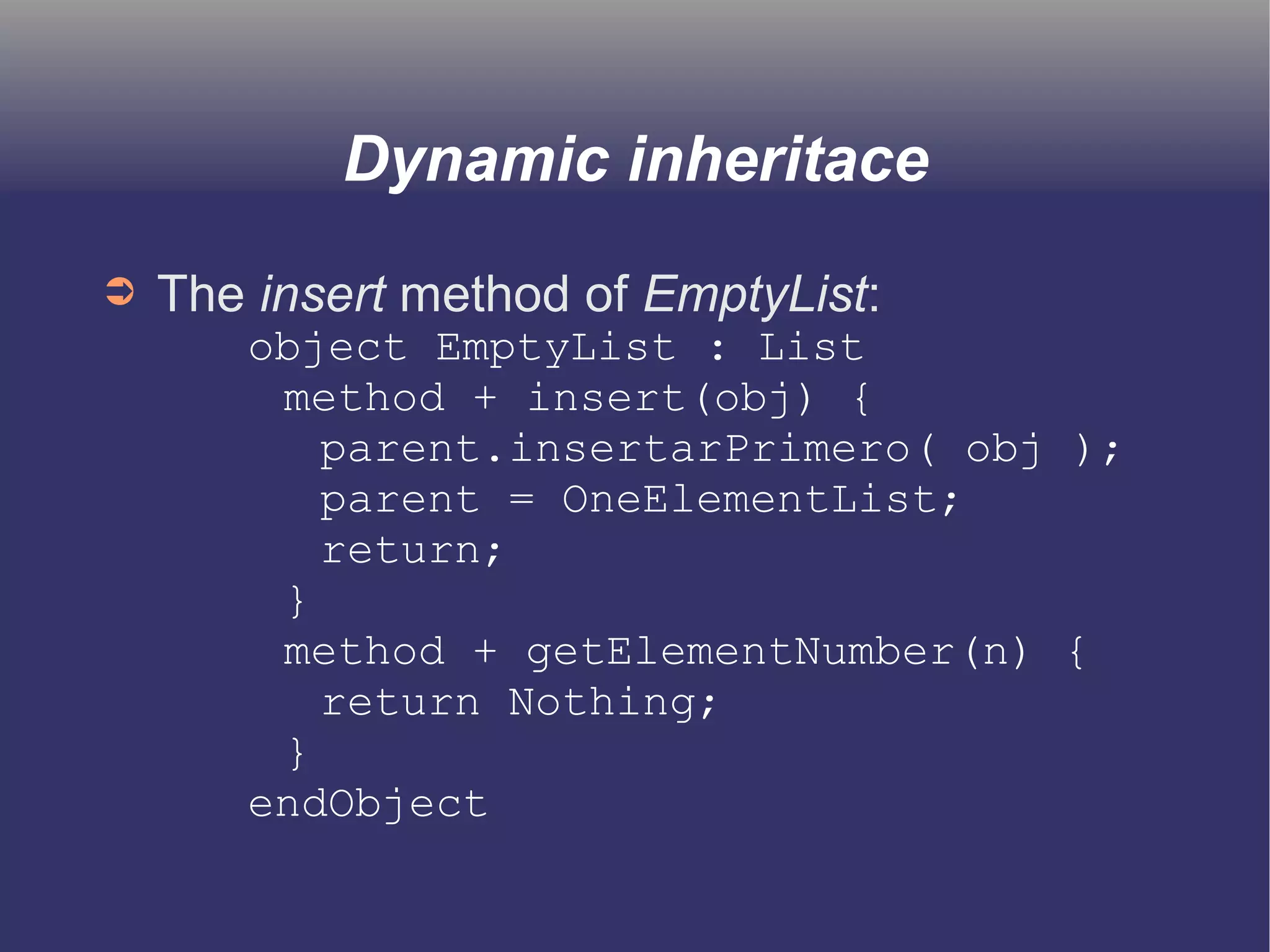
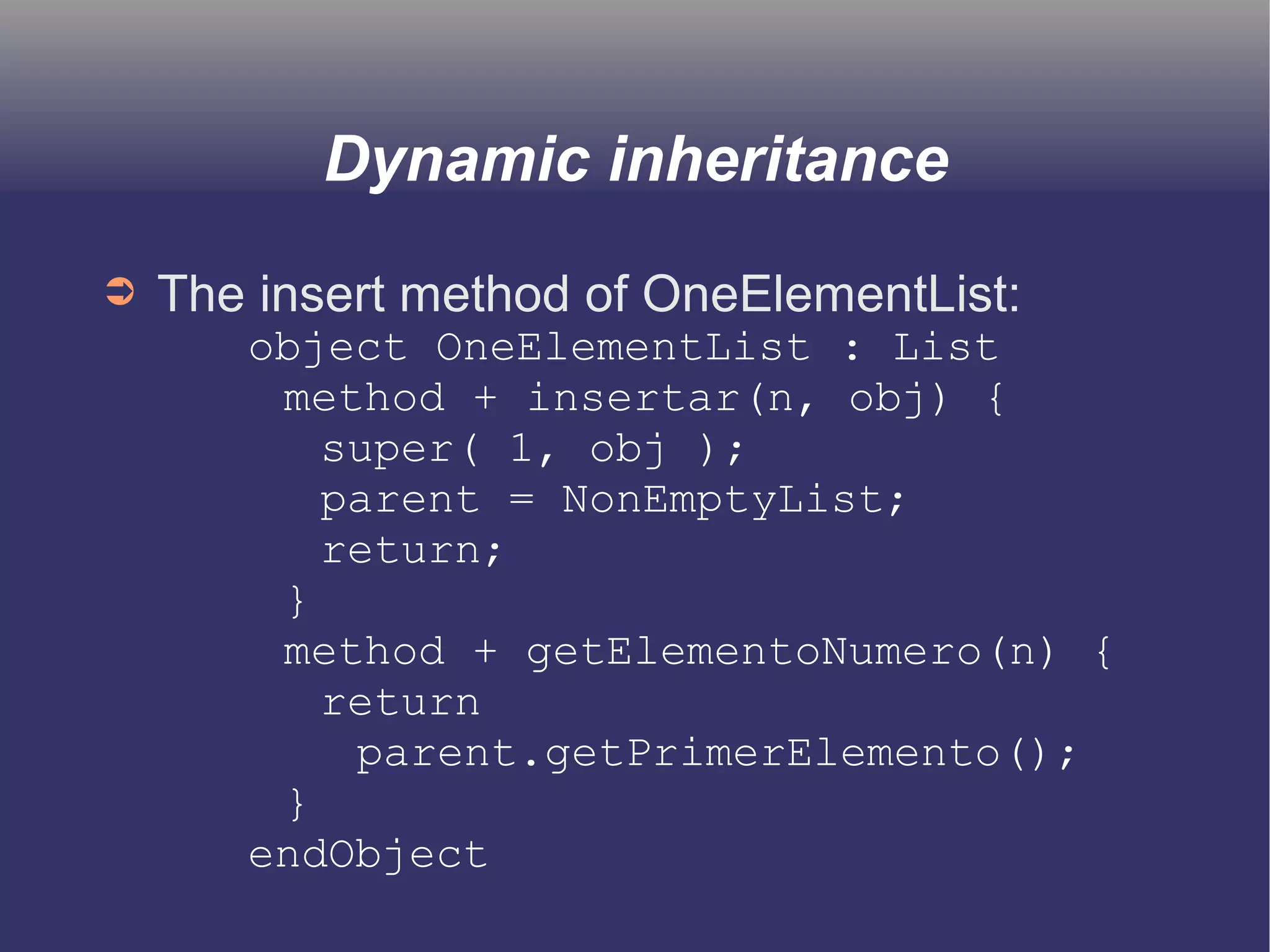
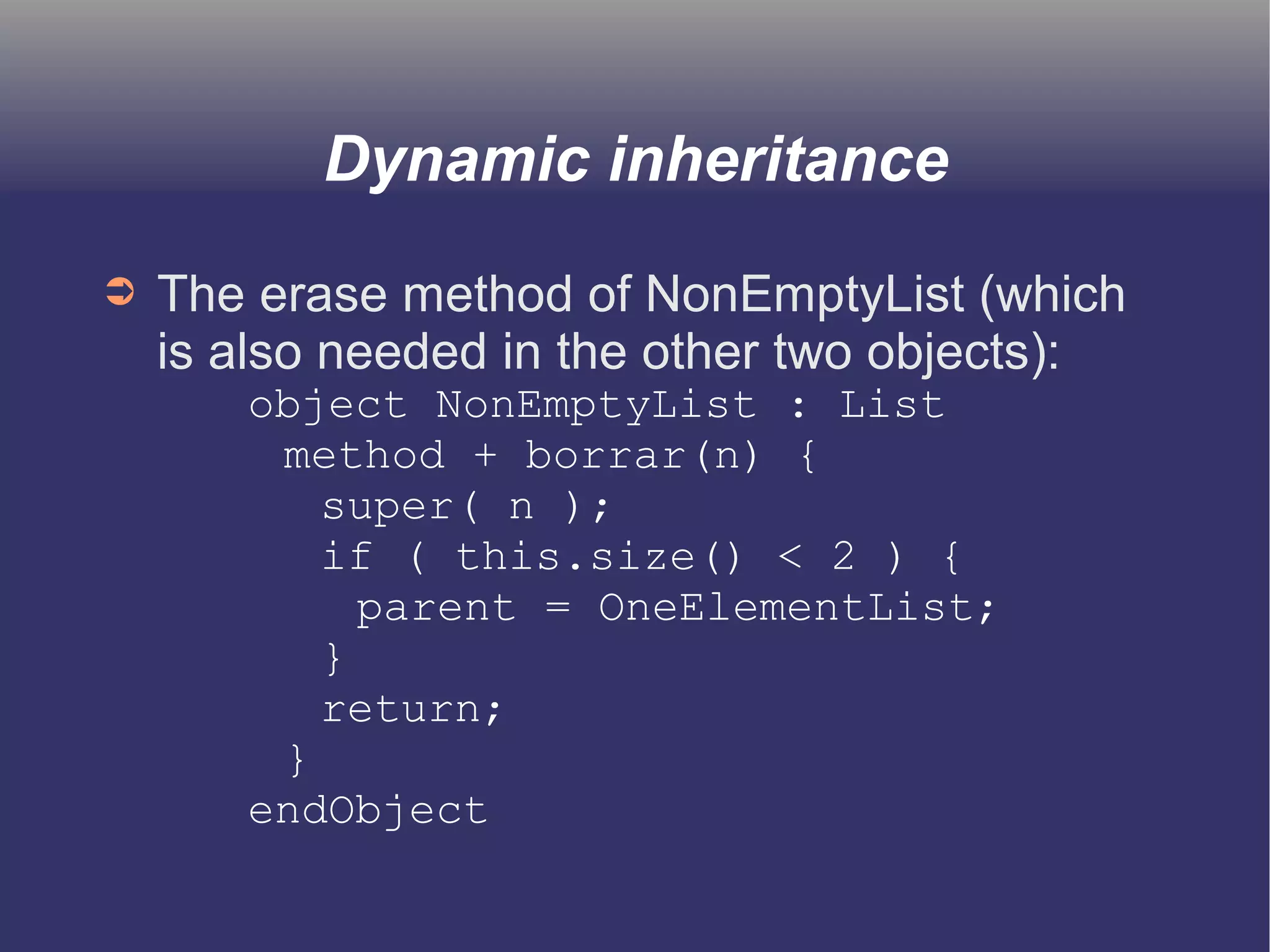
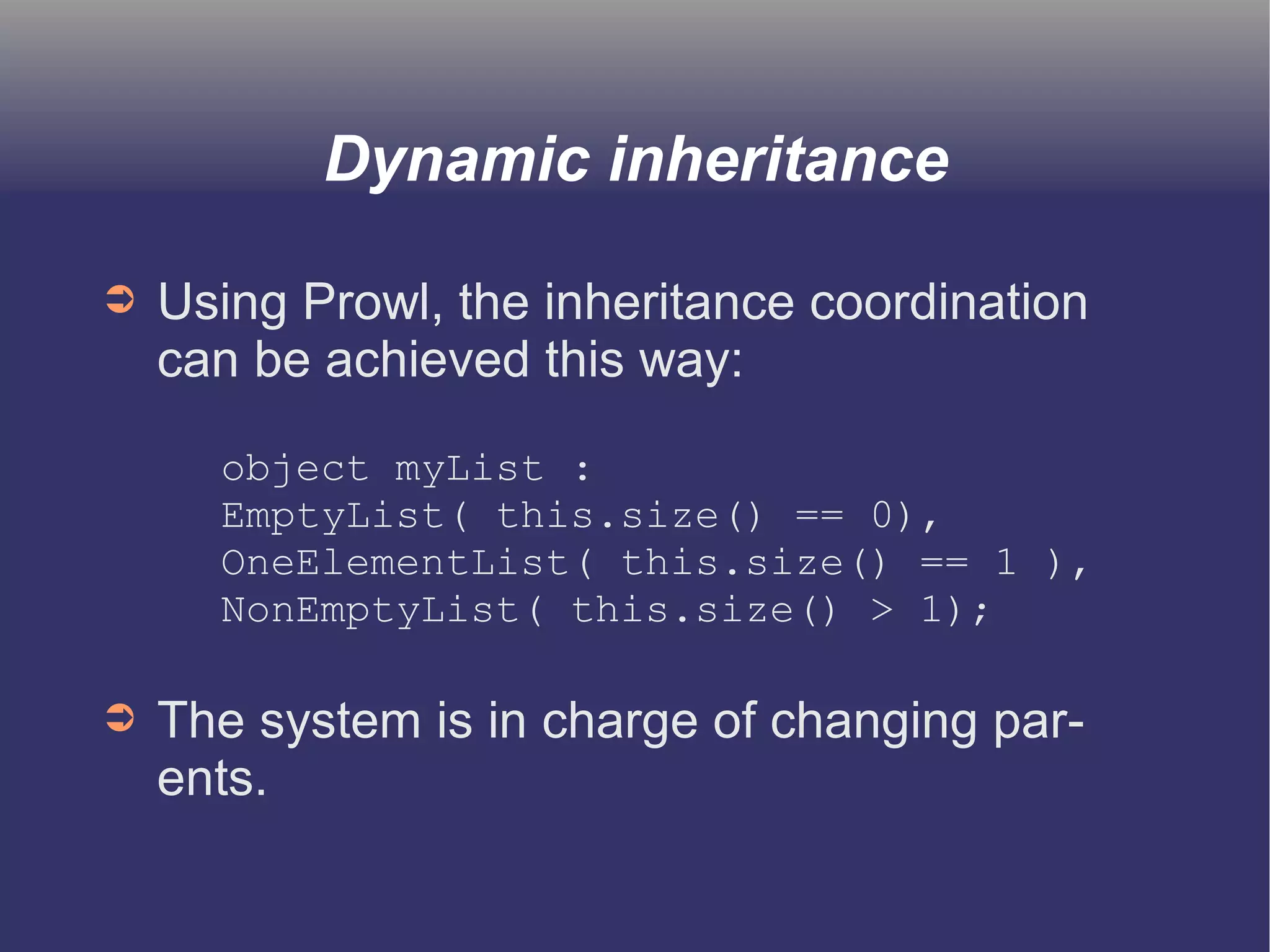
The document discusses prototype-based object-oriented programming, highlighting its differences from class-based programming languages, such as object creation, inheritance by delegation, and the flexibility of modifying objects. It explains key concepts including state, behavior, and message handling, while introducing prototype-based languages like Self, Io, Kevo, and Cecil. The document emphasizes that prototype-based model is more dynamic and flexible compared to class-based models, allowing for runtime changes and a unique method of inheritance.