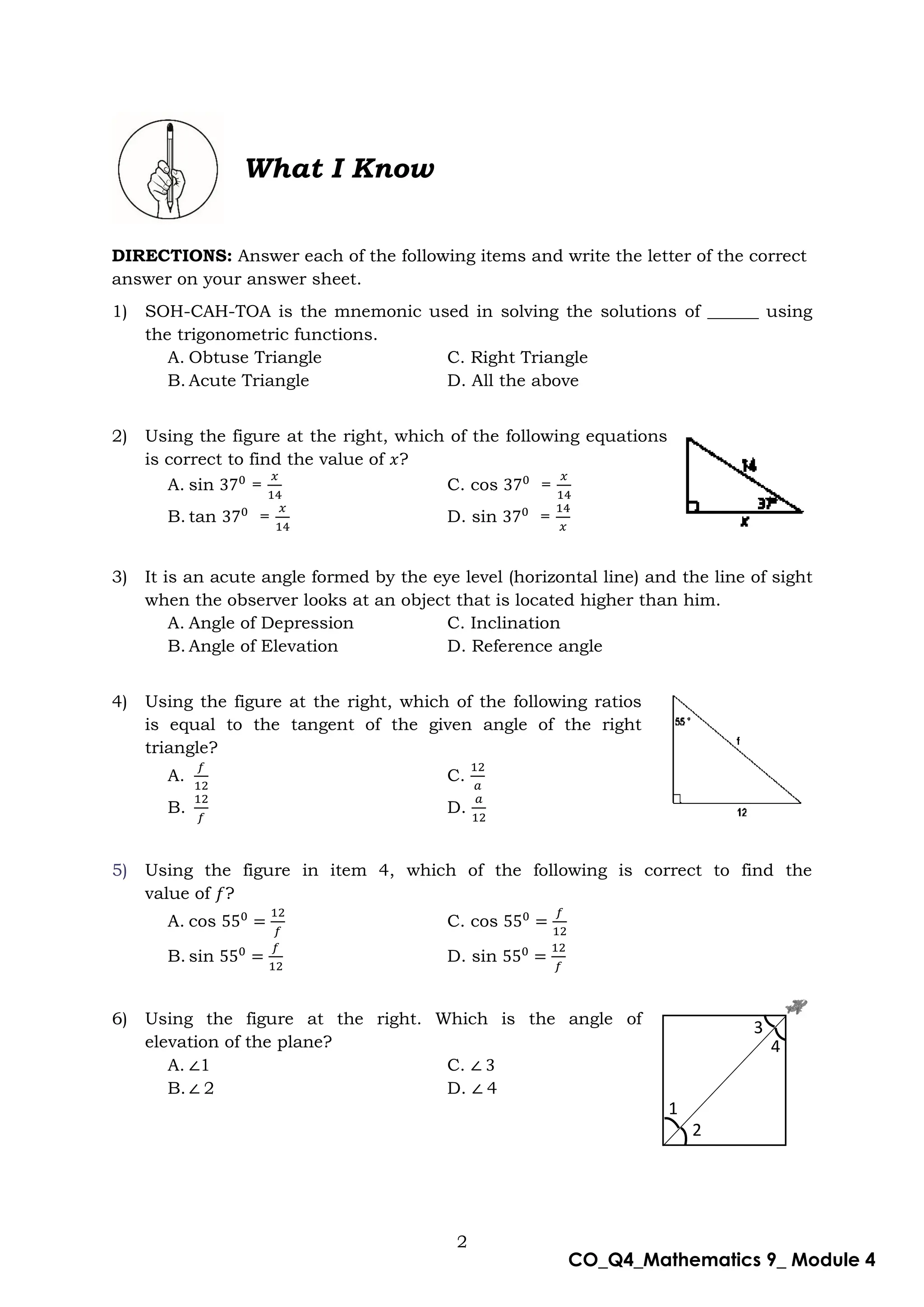
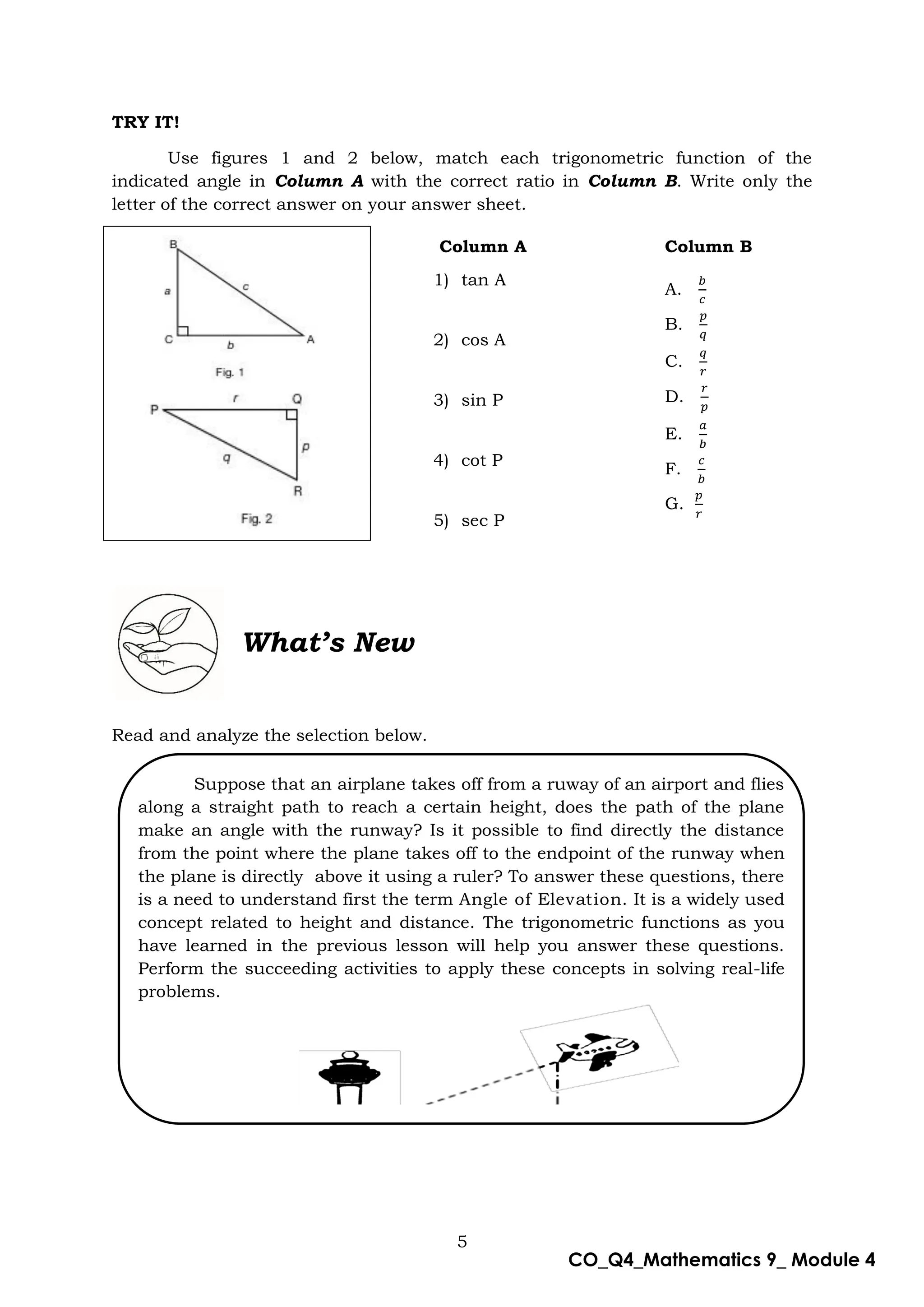
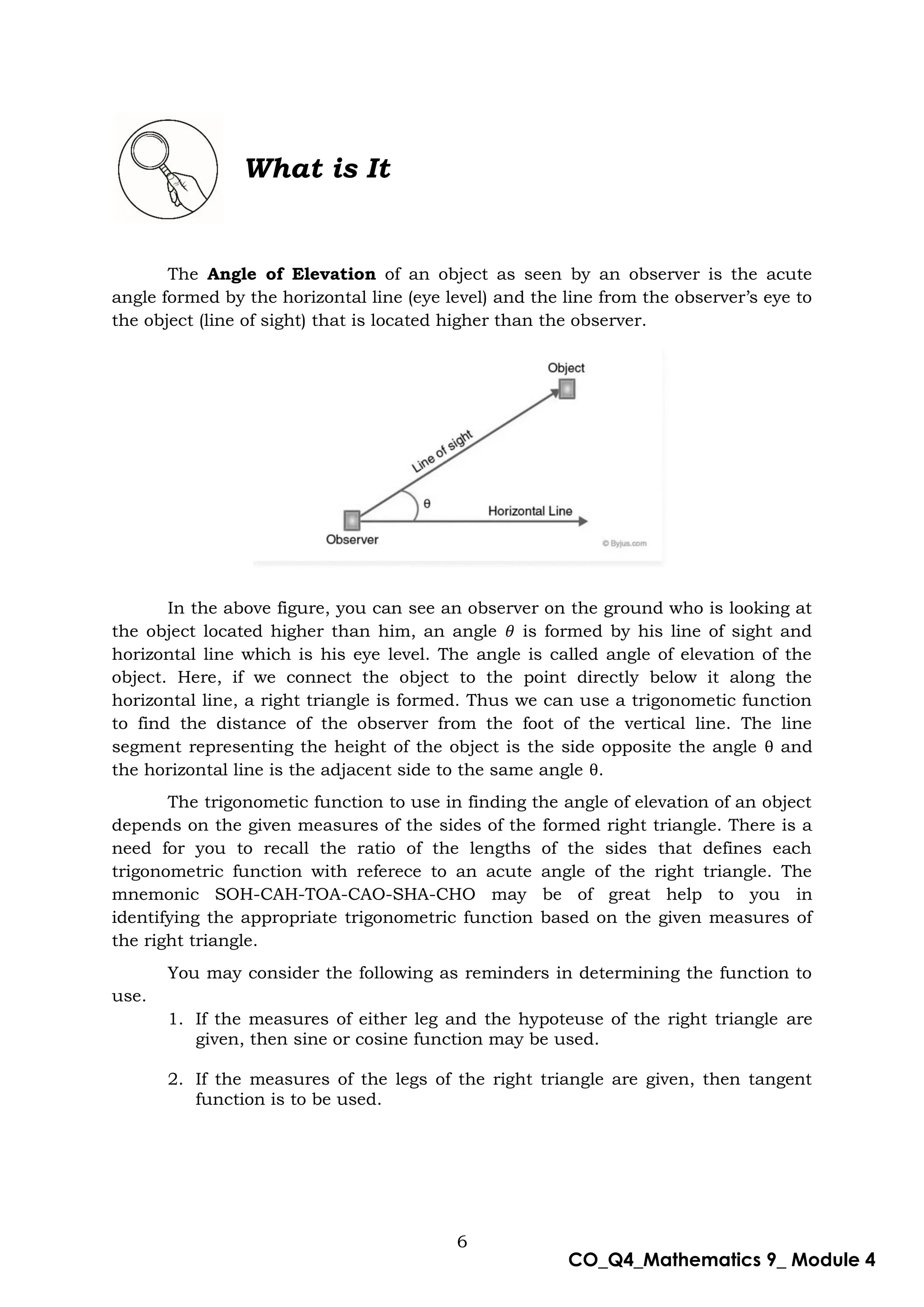
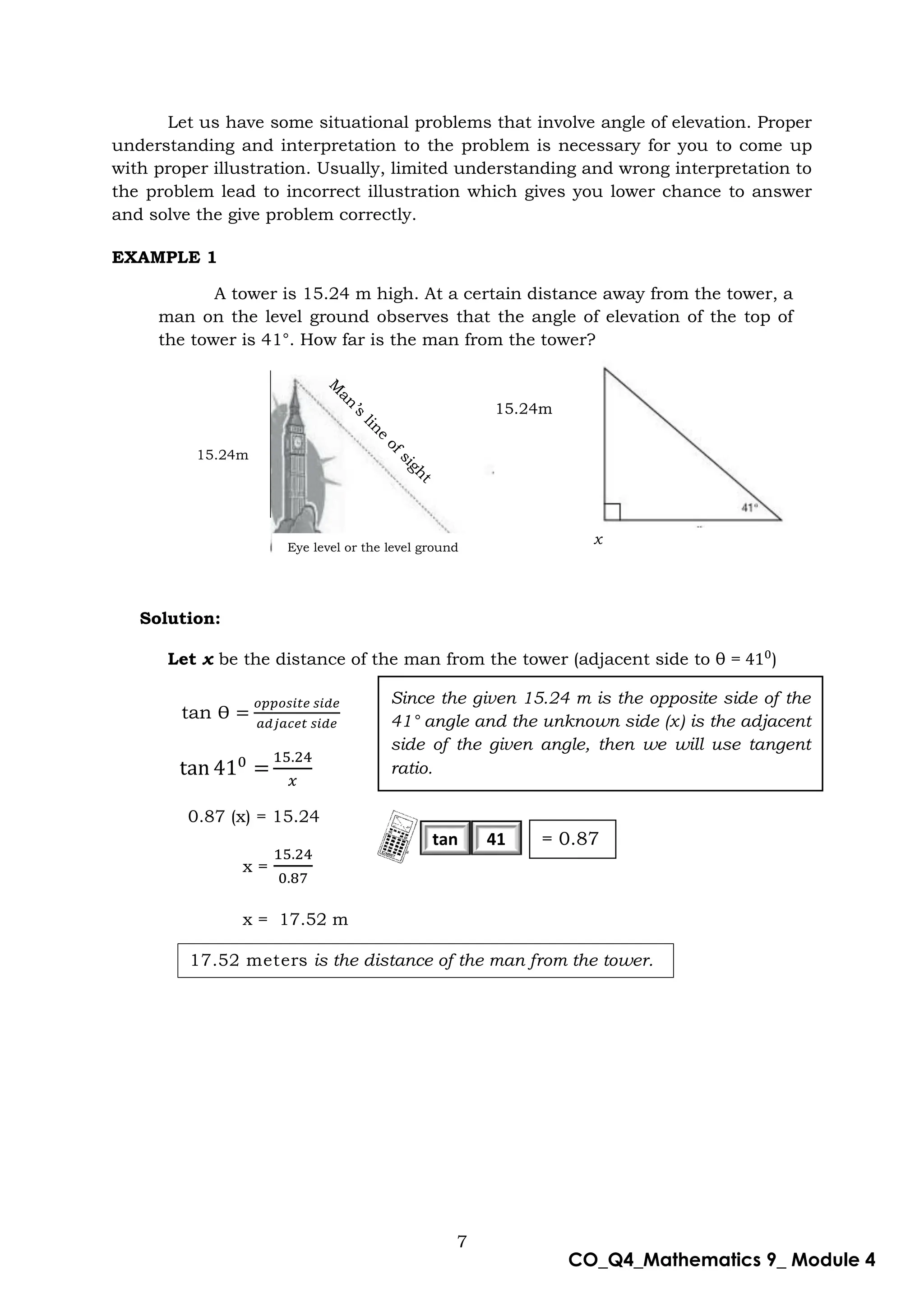
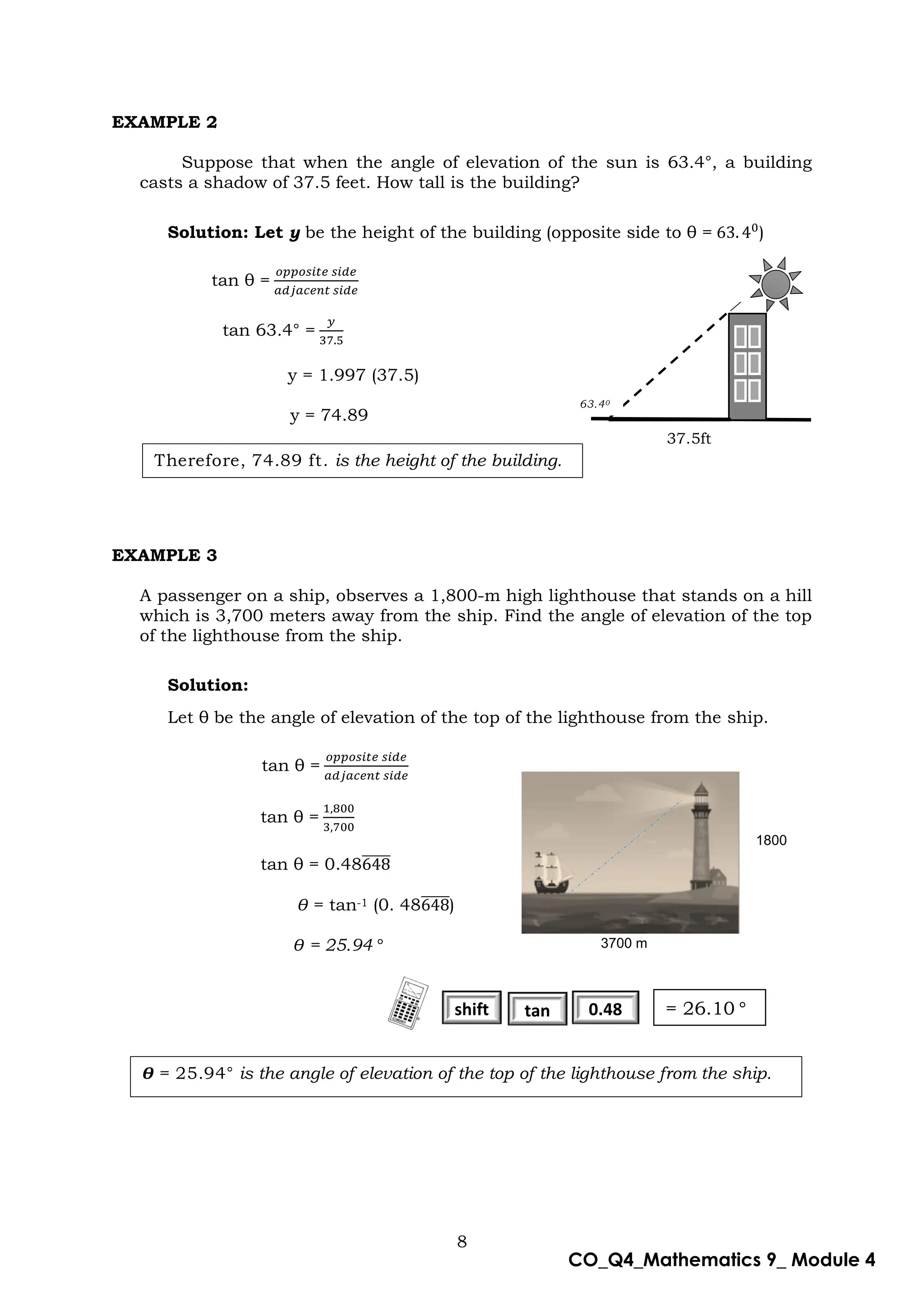
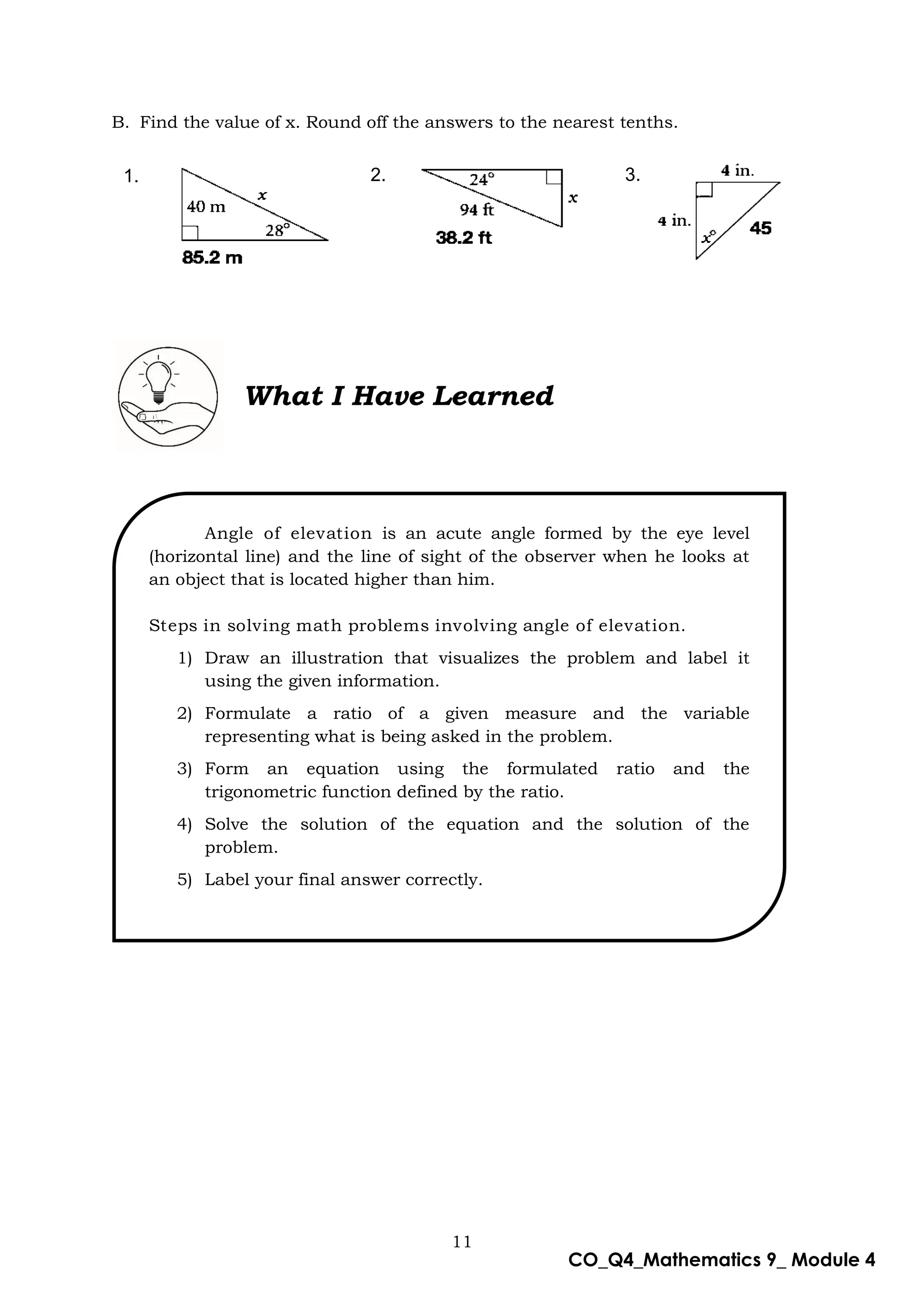
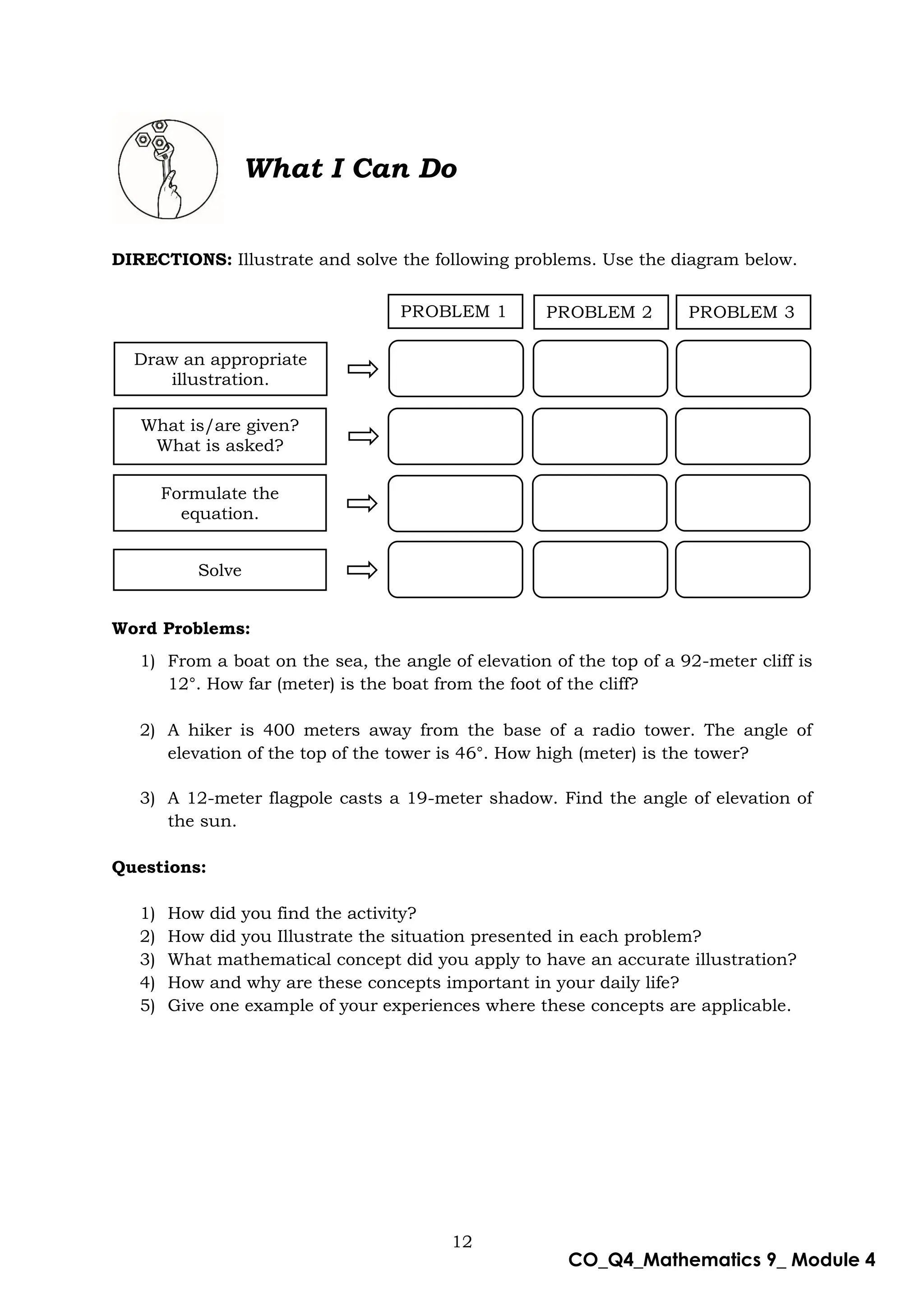
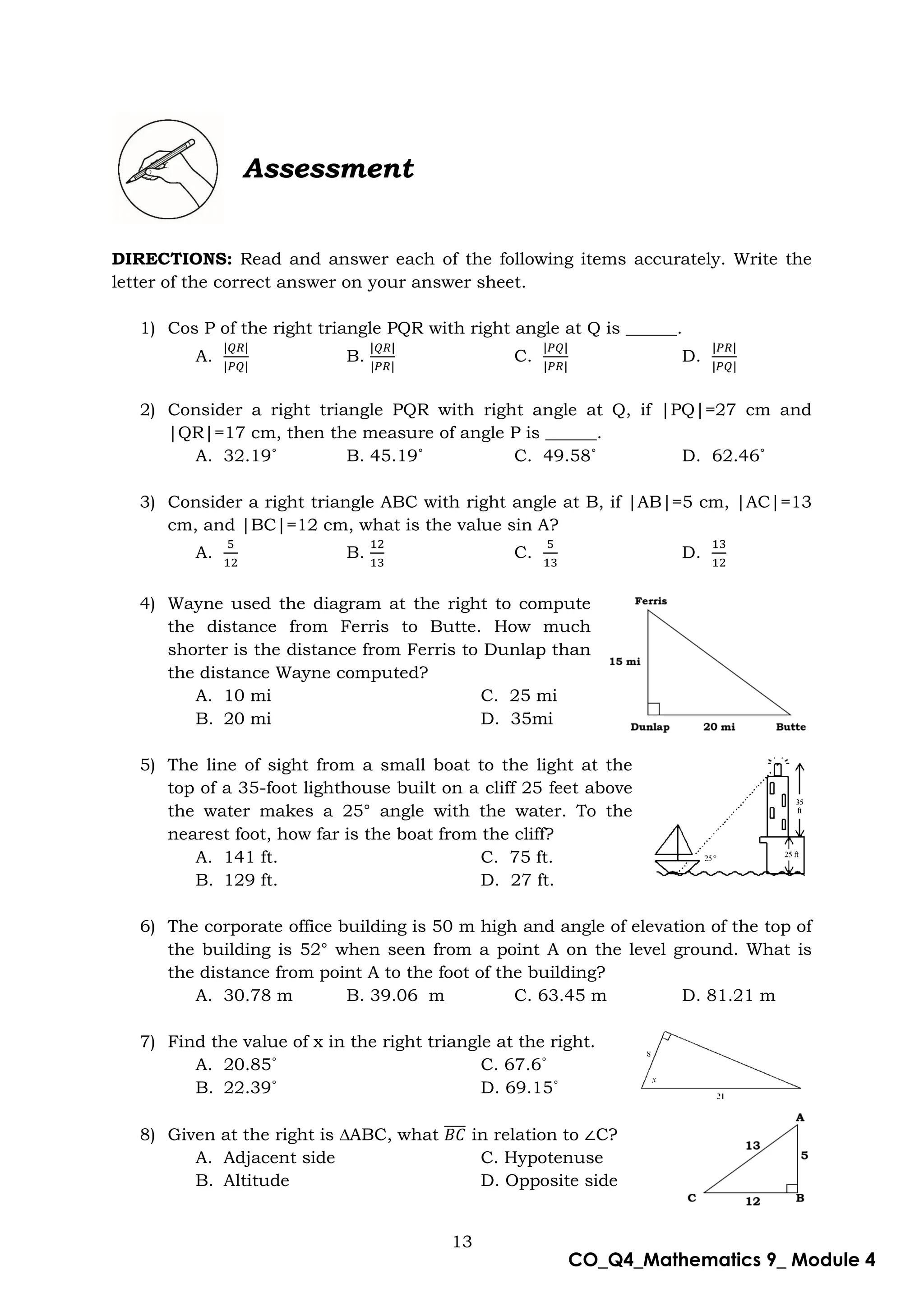
This document is a mathematics module for Grade 9 focused on the concept of angle of elevation, designed for self-learning. It includes various activities, example problems, and lessons structured to help students grasp trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent. The module emphasizes practical application and understanding of the topic while providing guidance for both learners and facilitators.