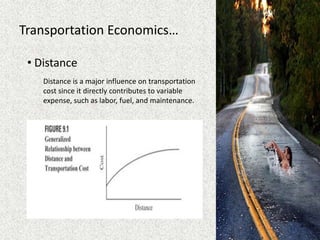
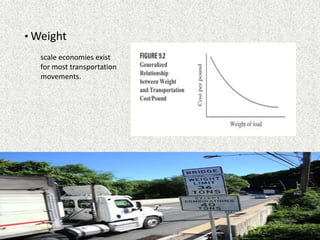
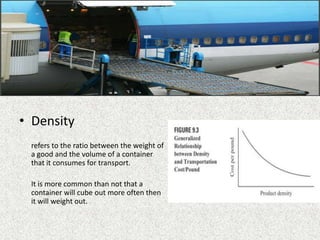
The document outlines key concepts in transportation management, focusing on factors affecting transportation costs, such as distance, weight, and stowability. It discusses carrier pricing strategies including cost-of-service and value-of-service approaches, as well as various rate determination methods such as class rates and commodity rates. Additionally, the impact of handling, liability, and market considerations on transportation economics is emphasized.