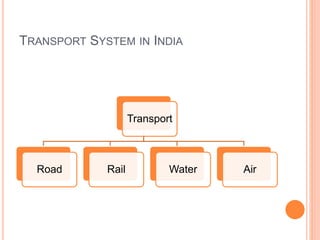
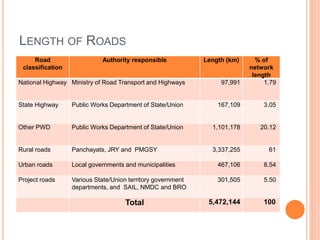
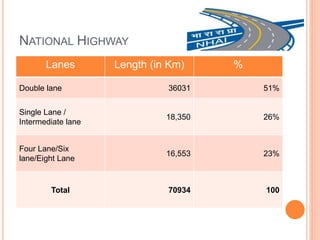
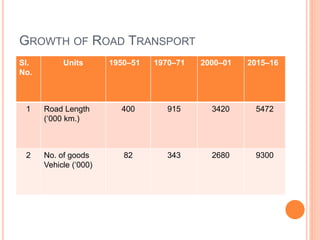
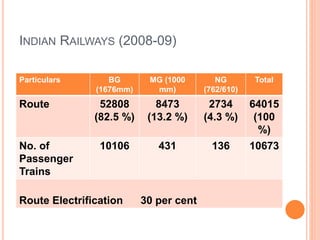
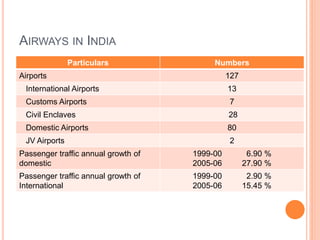
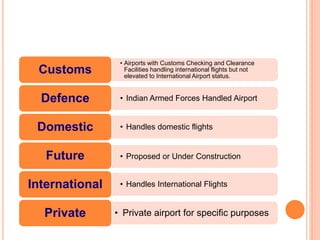
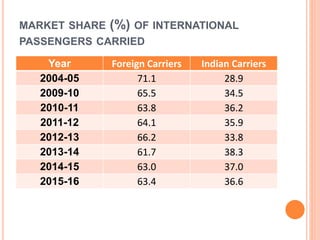
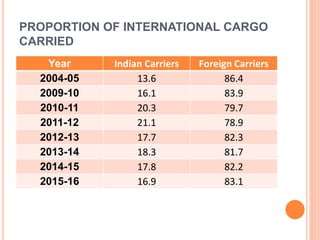
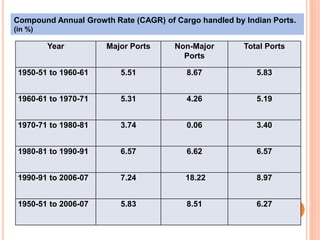
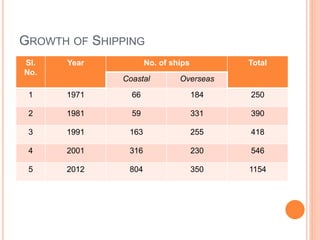
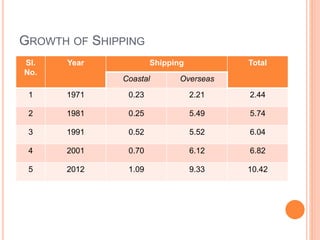
This document summarizes infrastructure in India, focusing on different modes of transportation. It discusses the road, rail, water, and air transportation networks in India. For roads, it provides statistics on total length and key expressways and national highways. For rail, it outlines the size of the rail network and growth statistics. It then summarizes ports and inland waterways, noting some challenges for each mode of transportation in India.