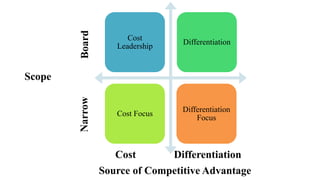
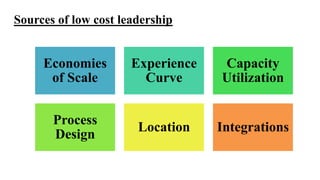
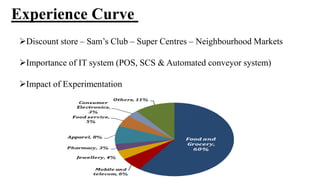
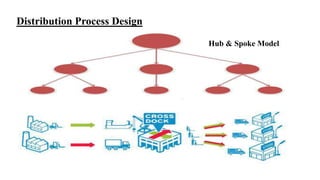
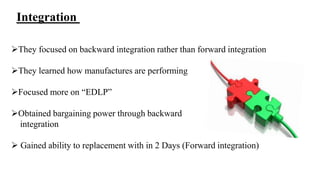
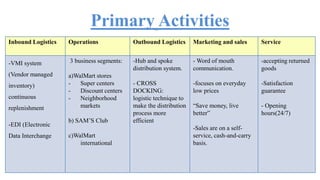
Wal-Mart has pursued a strategy of cost leadership since it was founded in 1962. It focuses on offering low prices through various cost-cutting measures such as economies of scale, experience curve effects, efficient distribution processes, and strategic sourcing. Wal-Mart grew rapidly by opening many discount stores, Sam's Club warehouses, and large Supercenters, becoming the largest company in the world by revenue. It aims to save people money so they can live better lives.