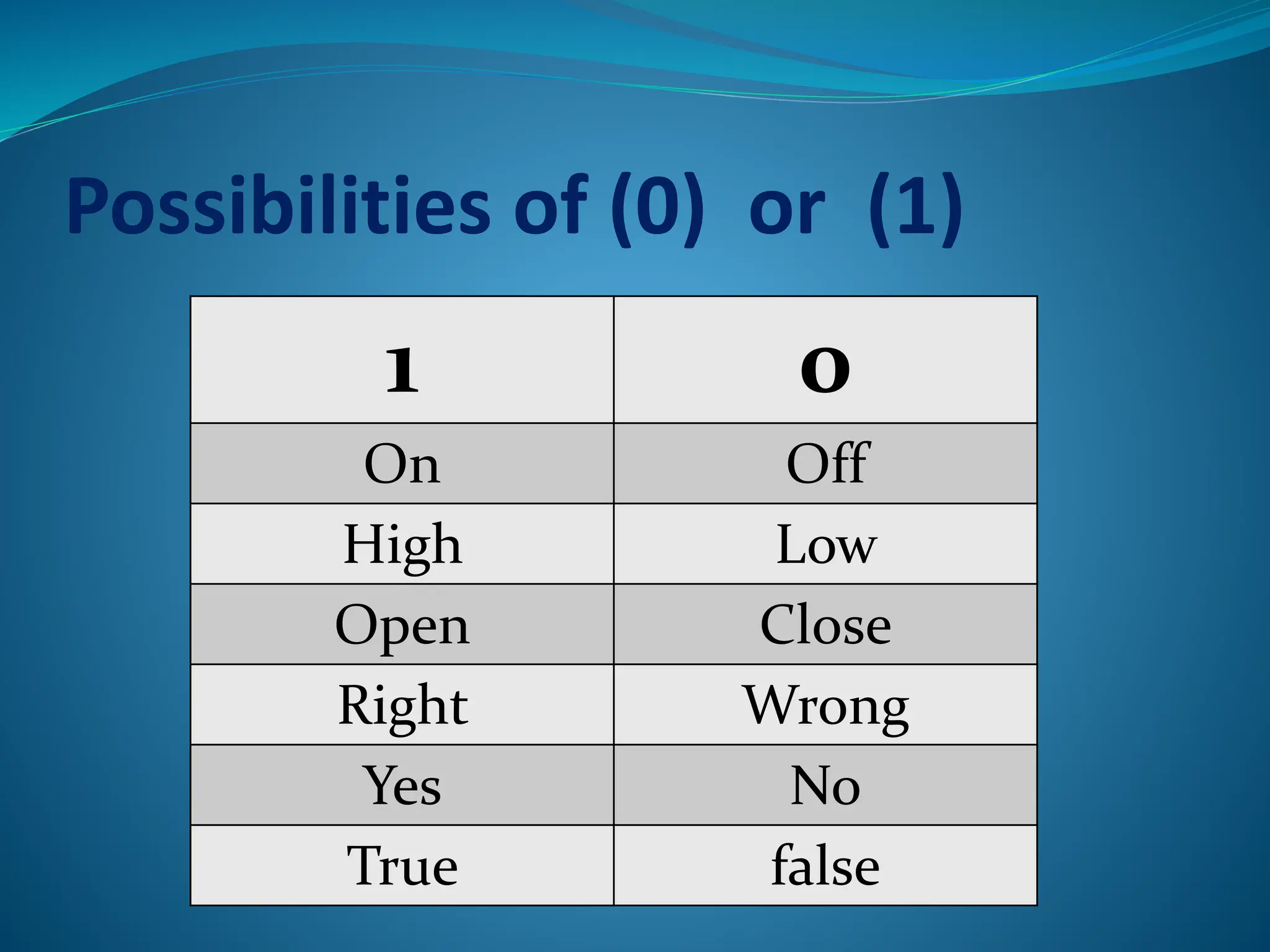
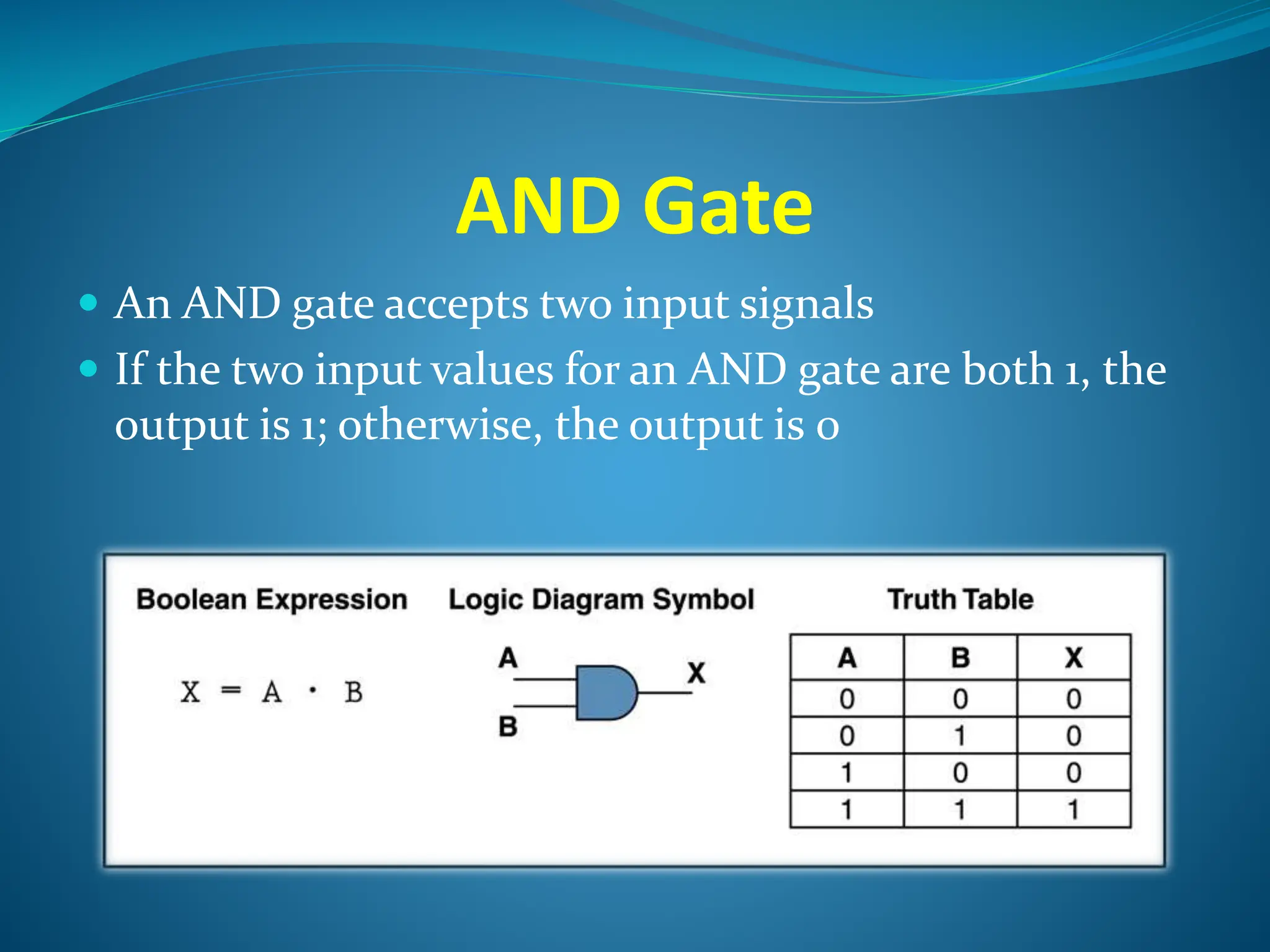
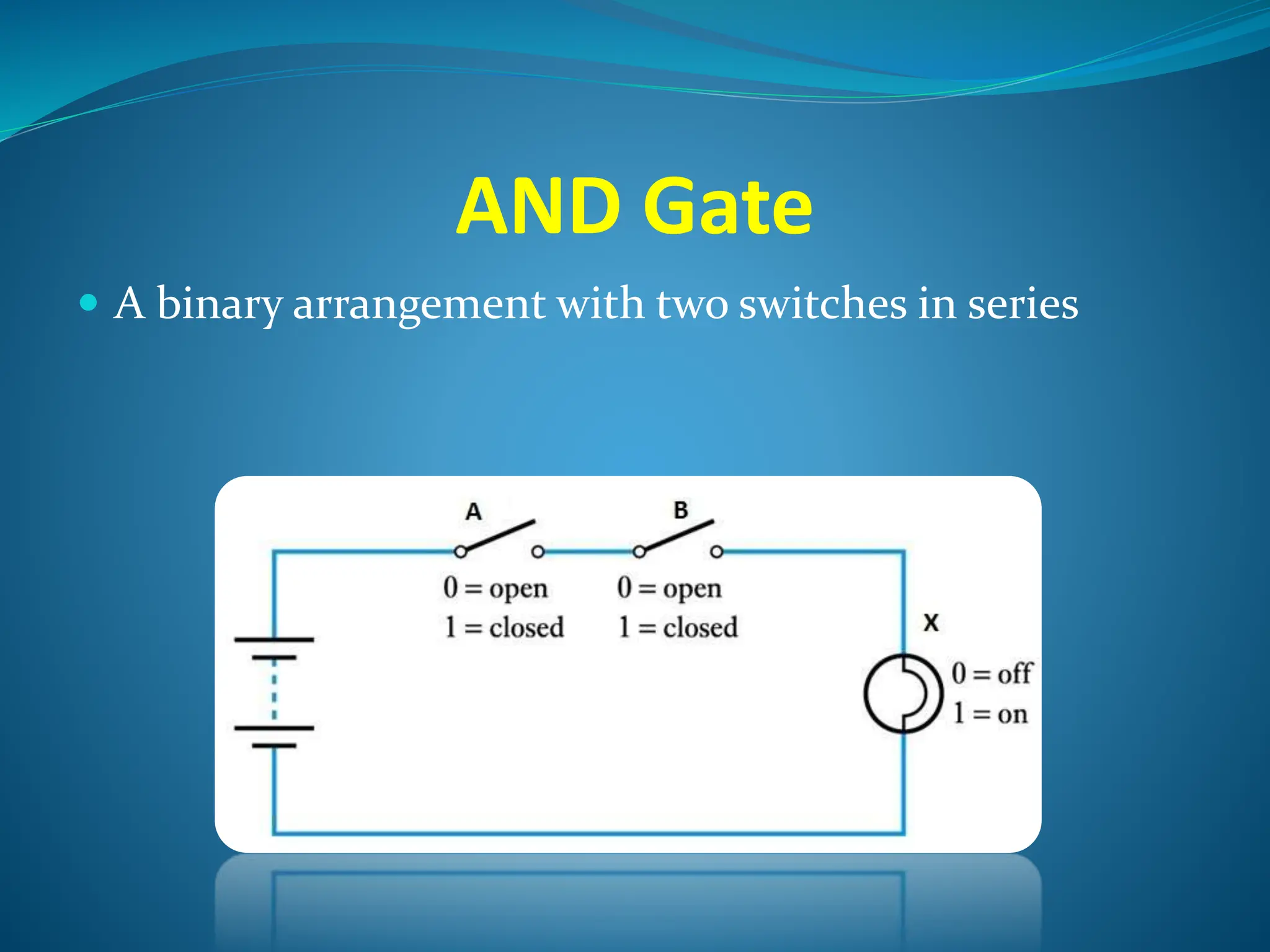
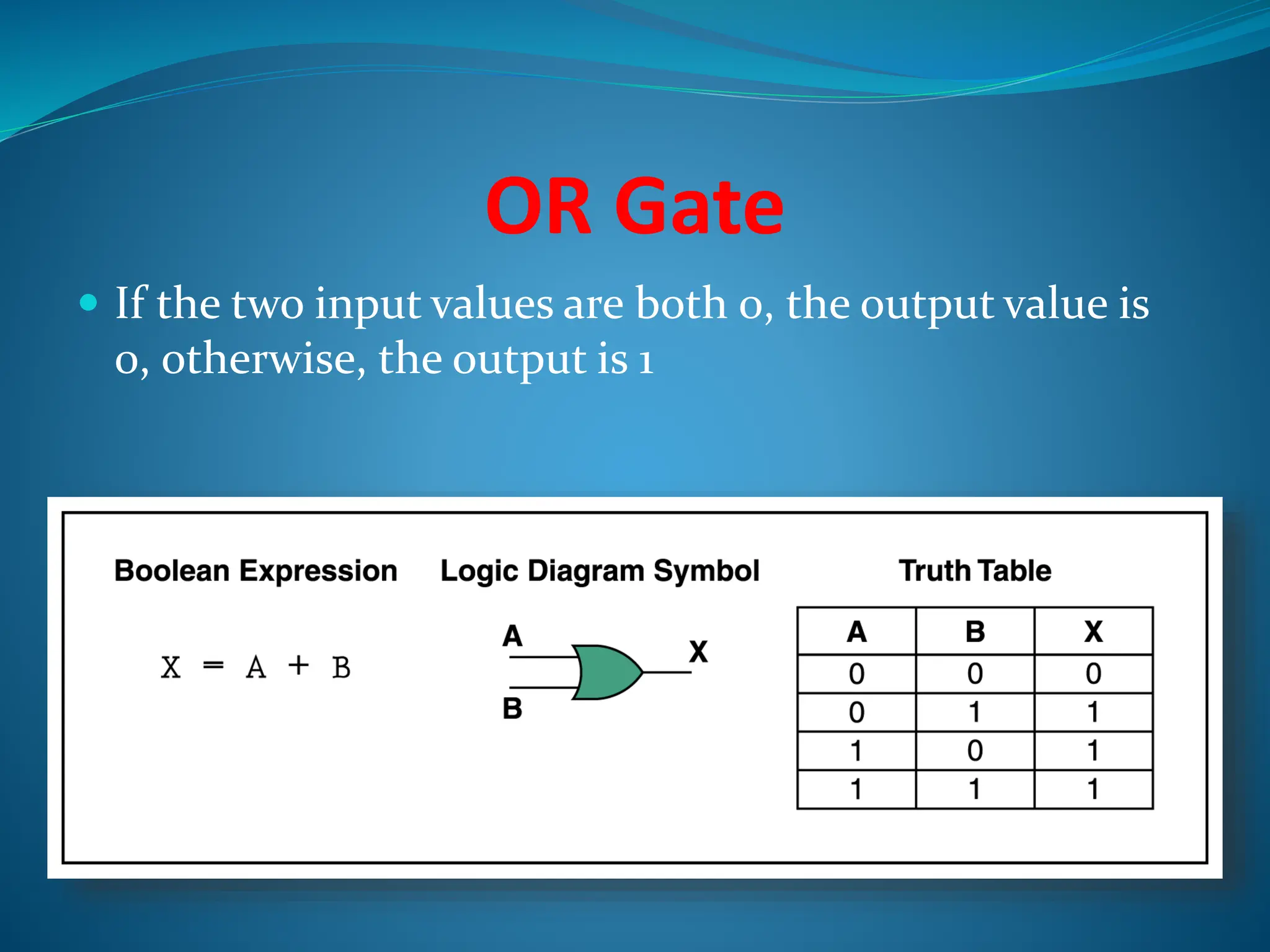
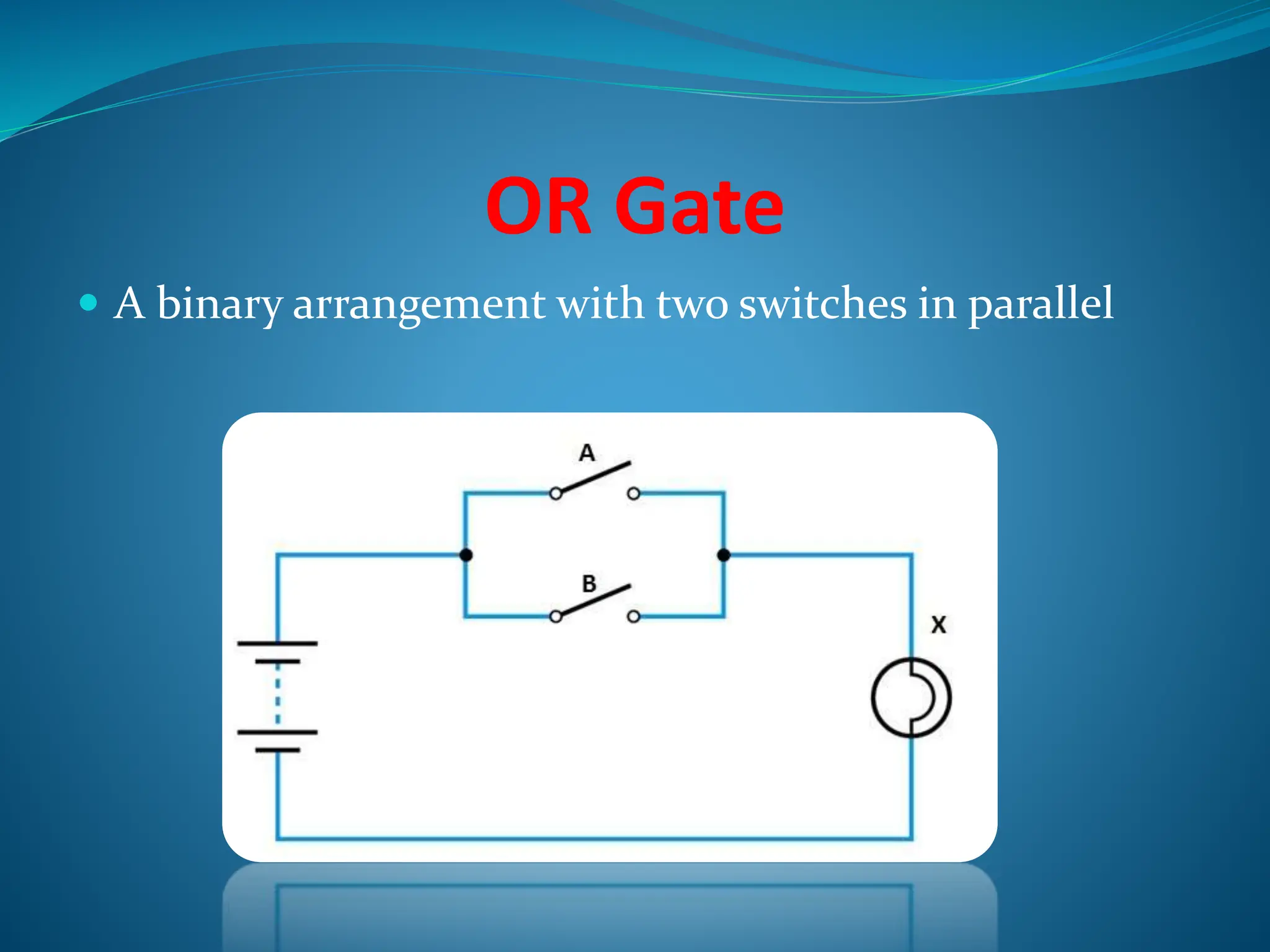
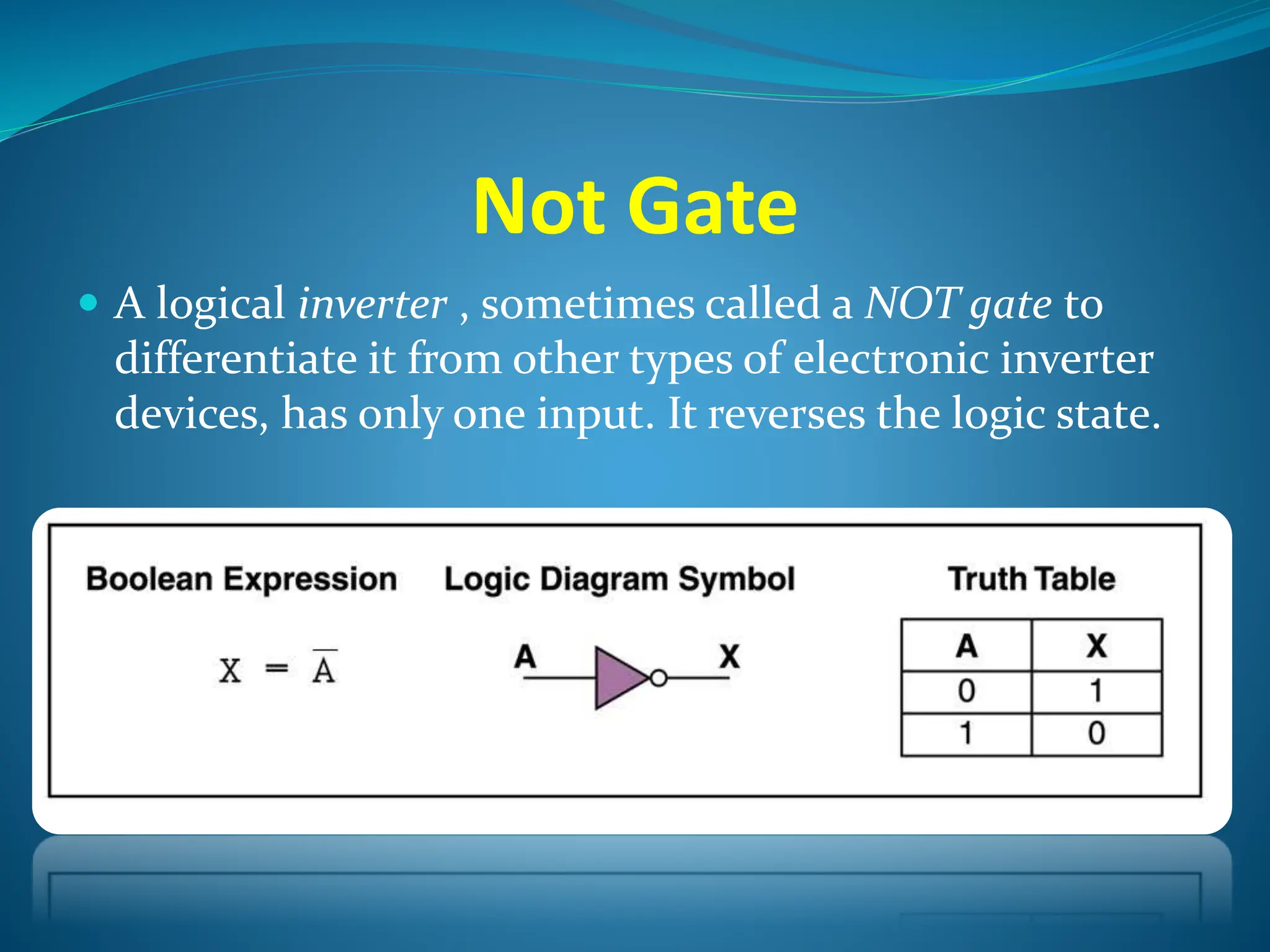
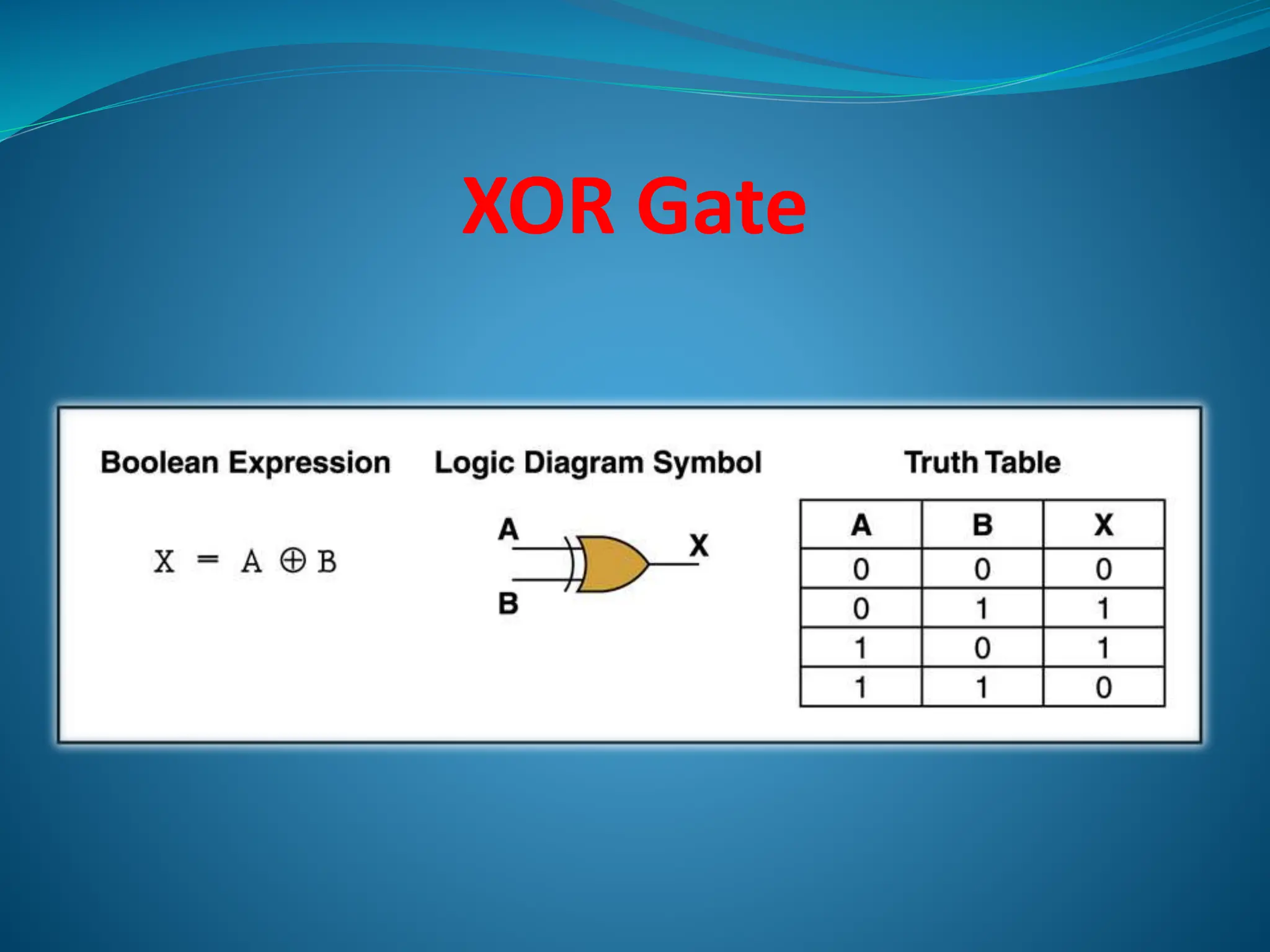
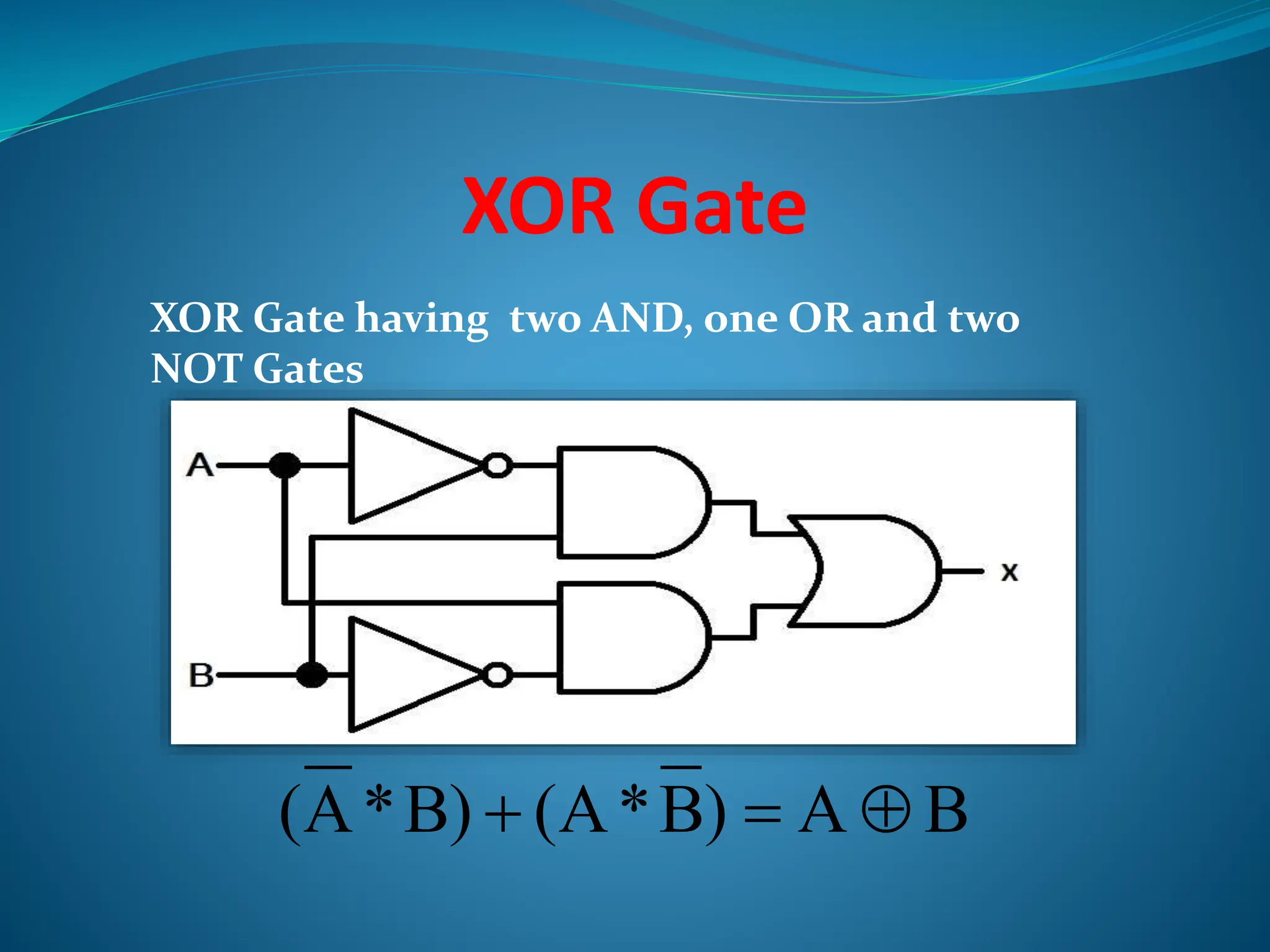
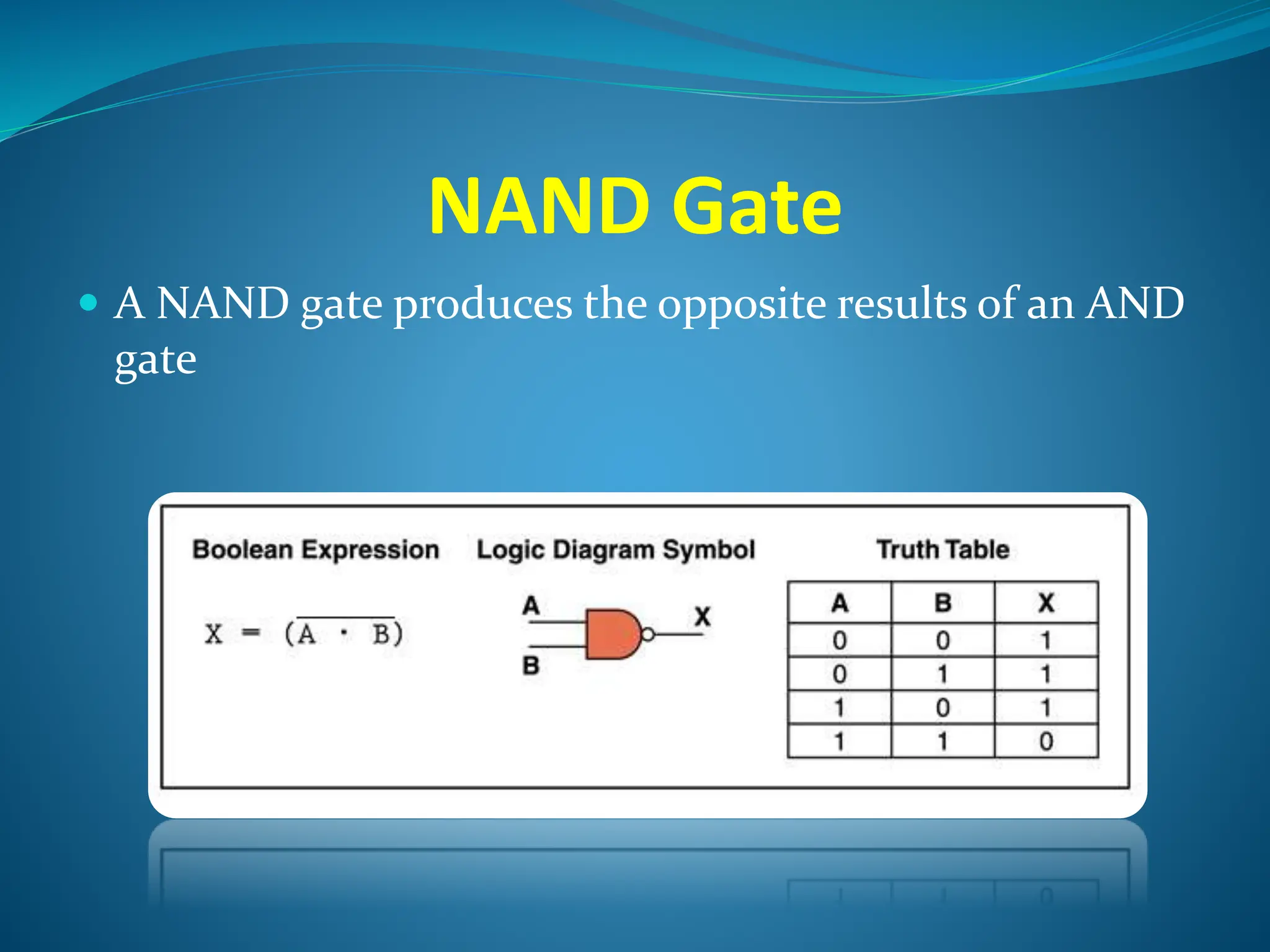
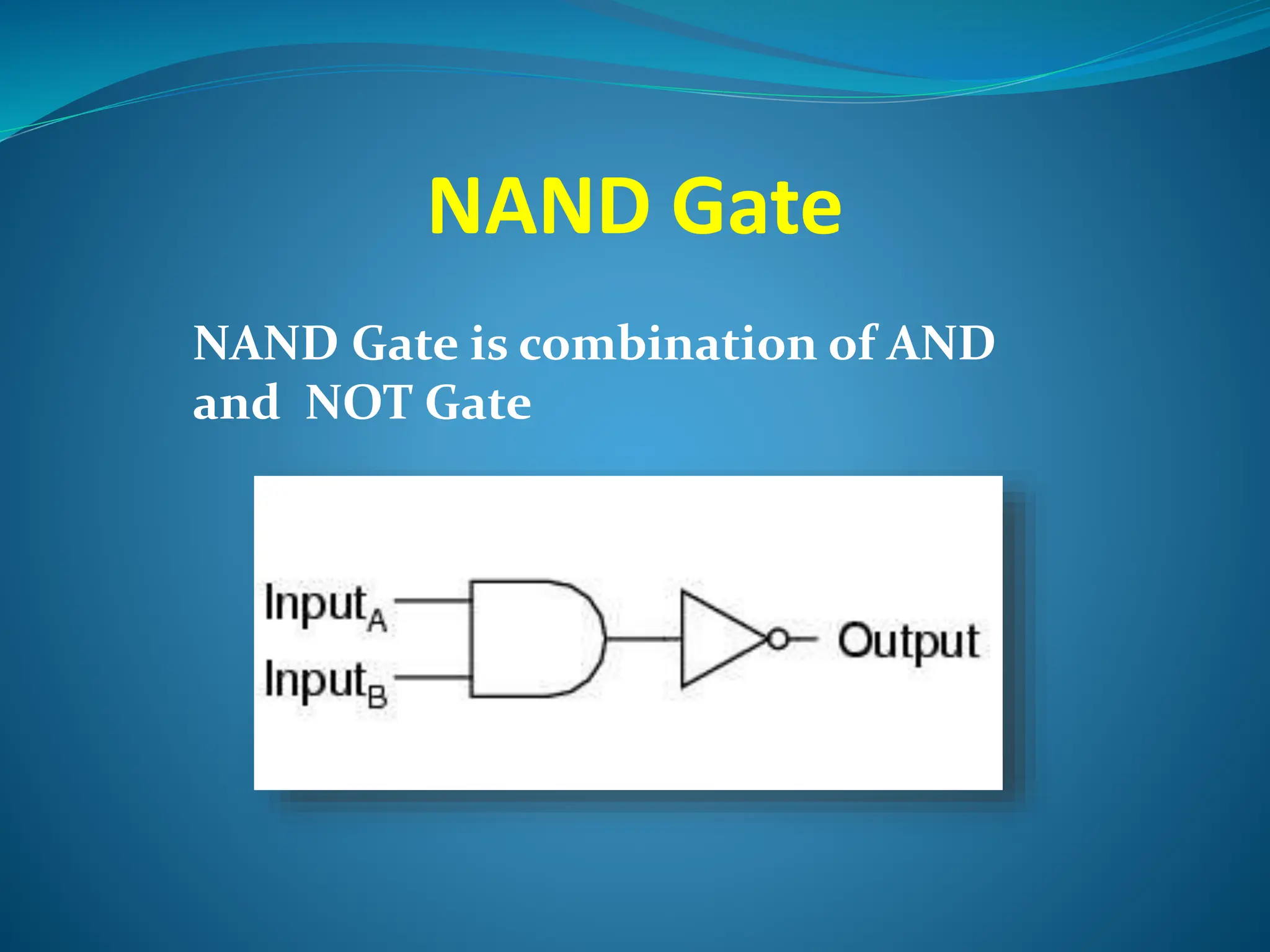
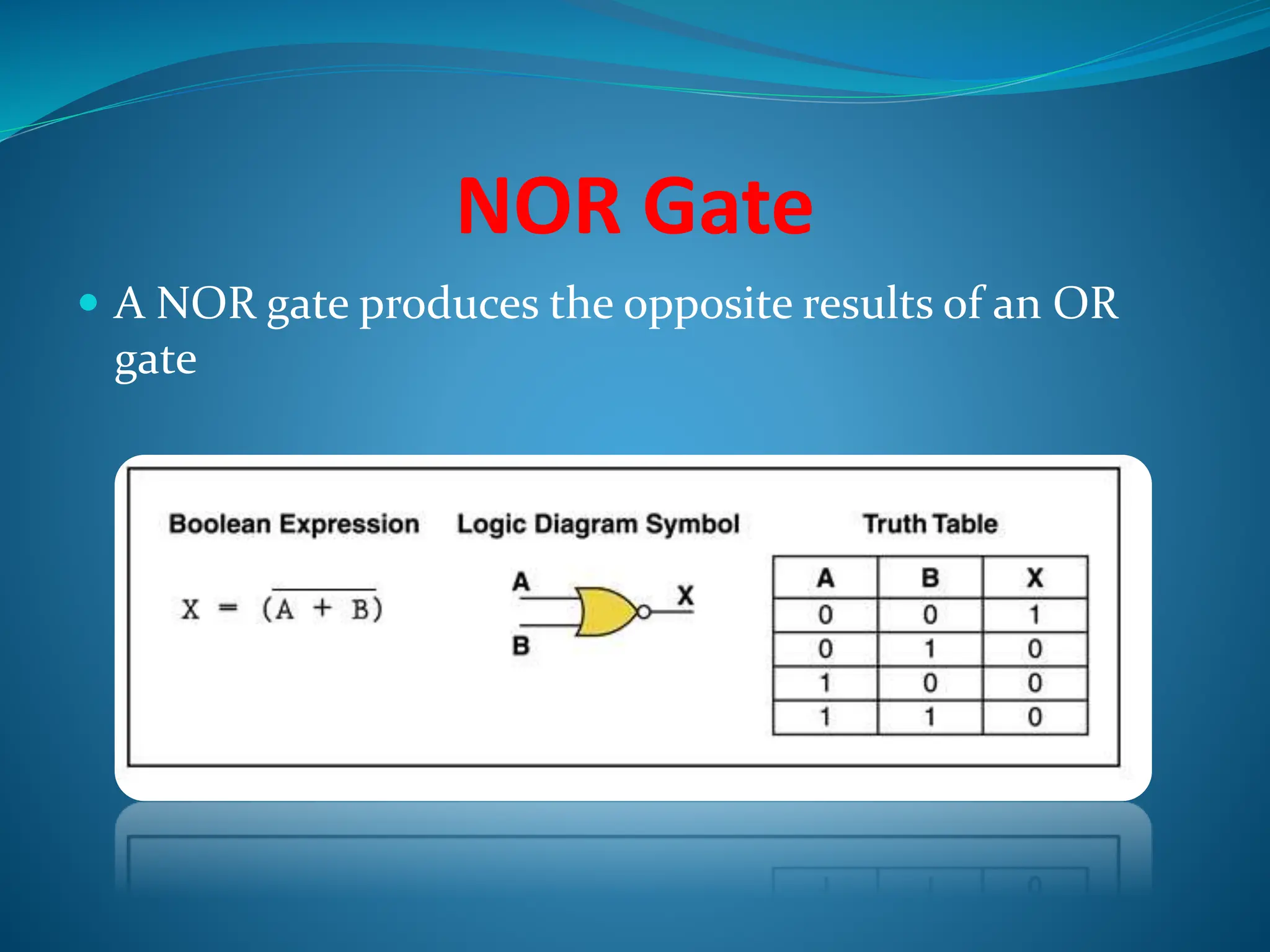
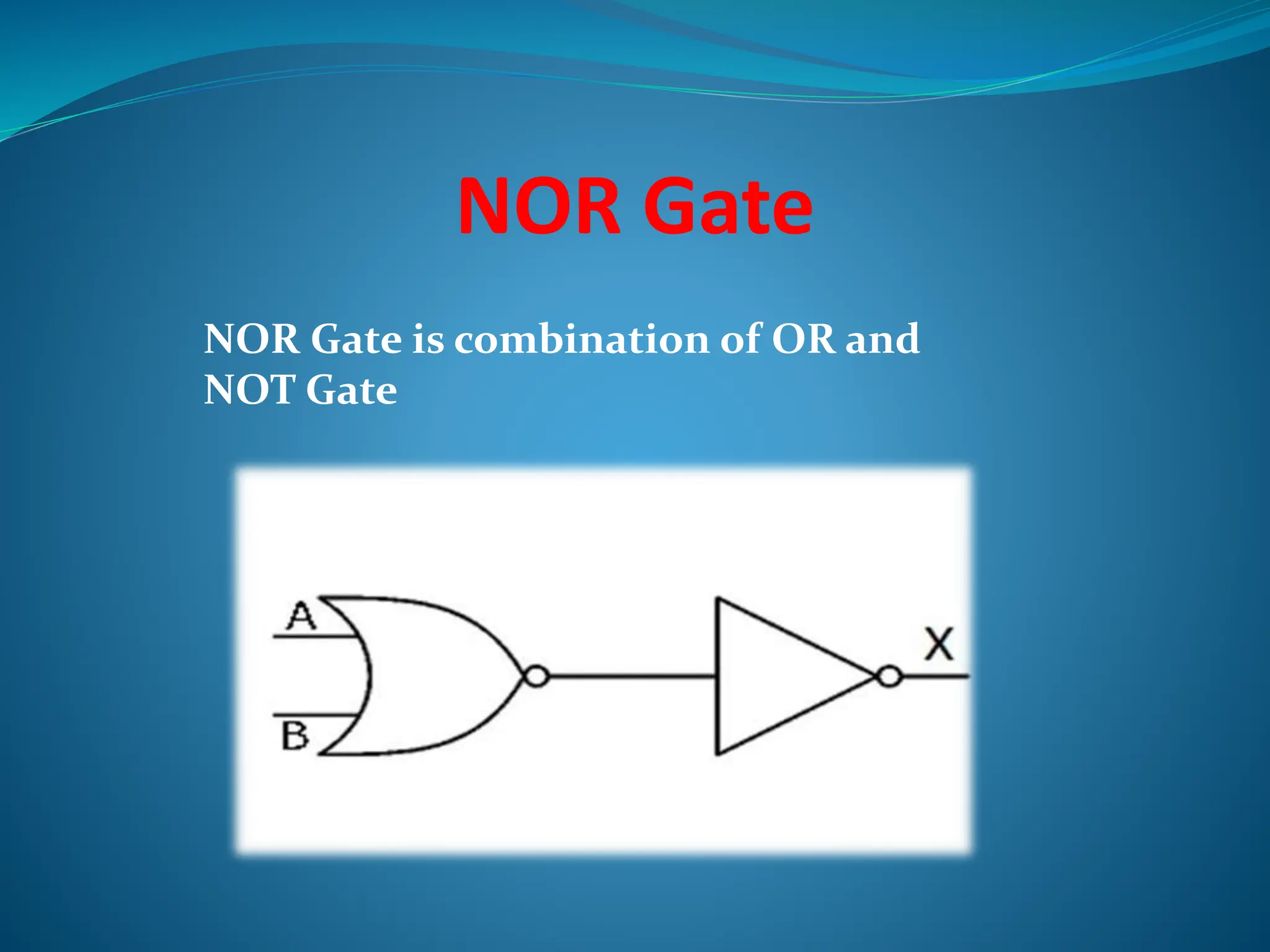
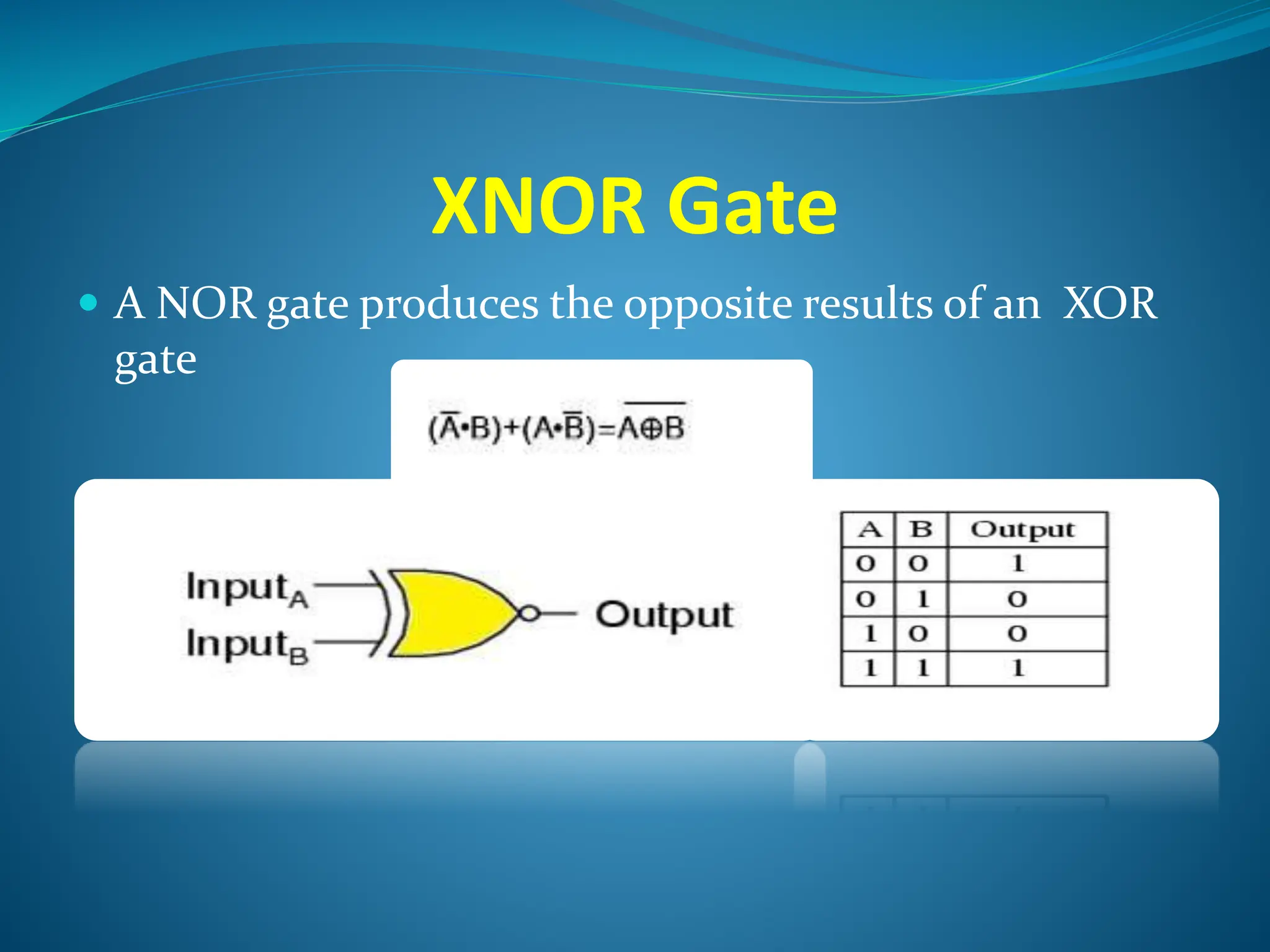
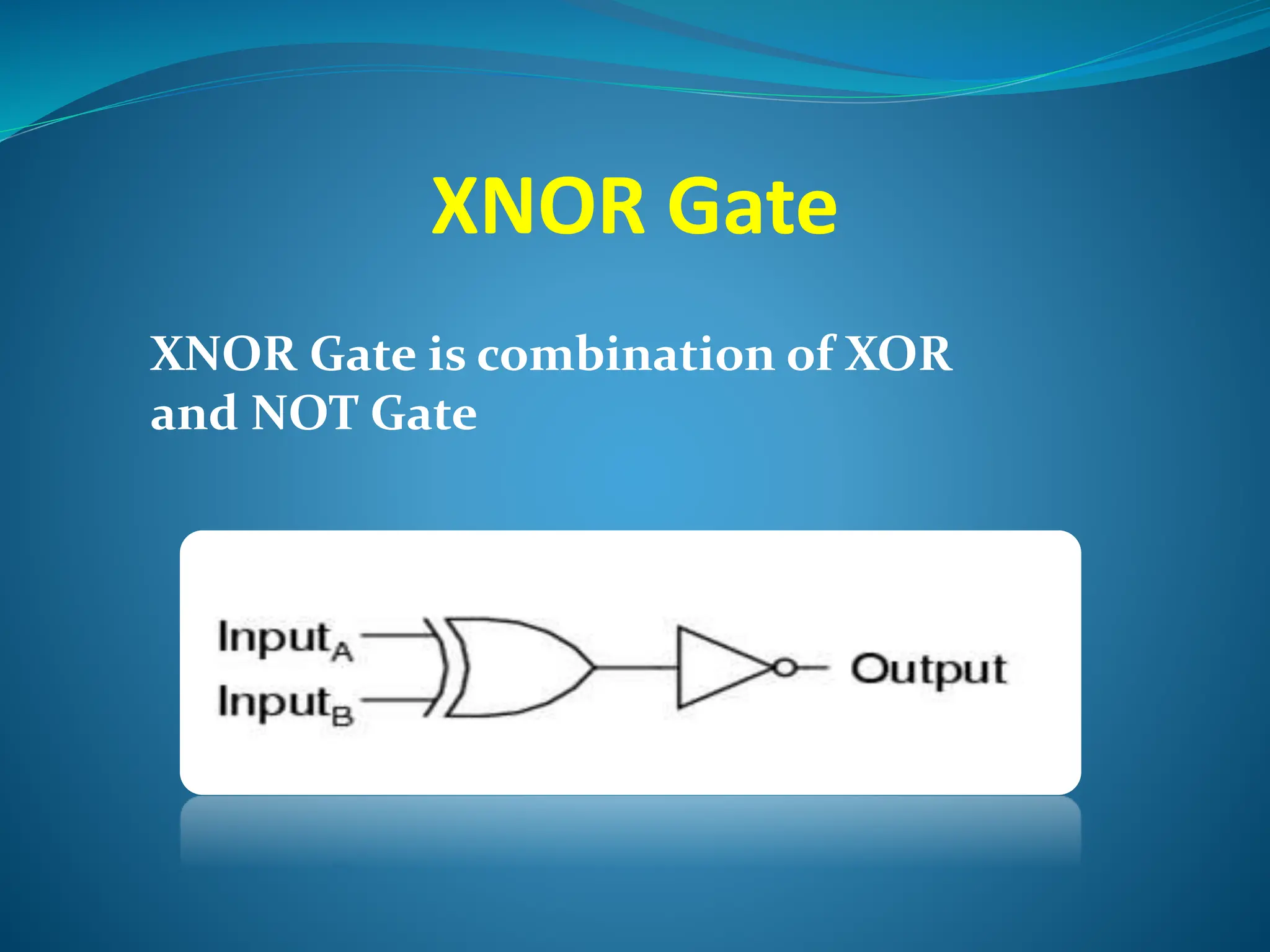
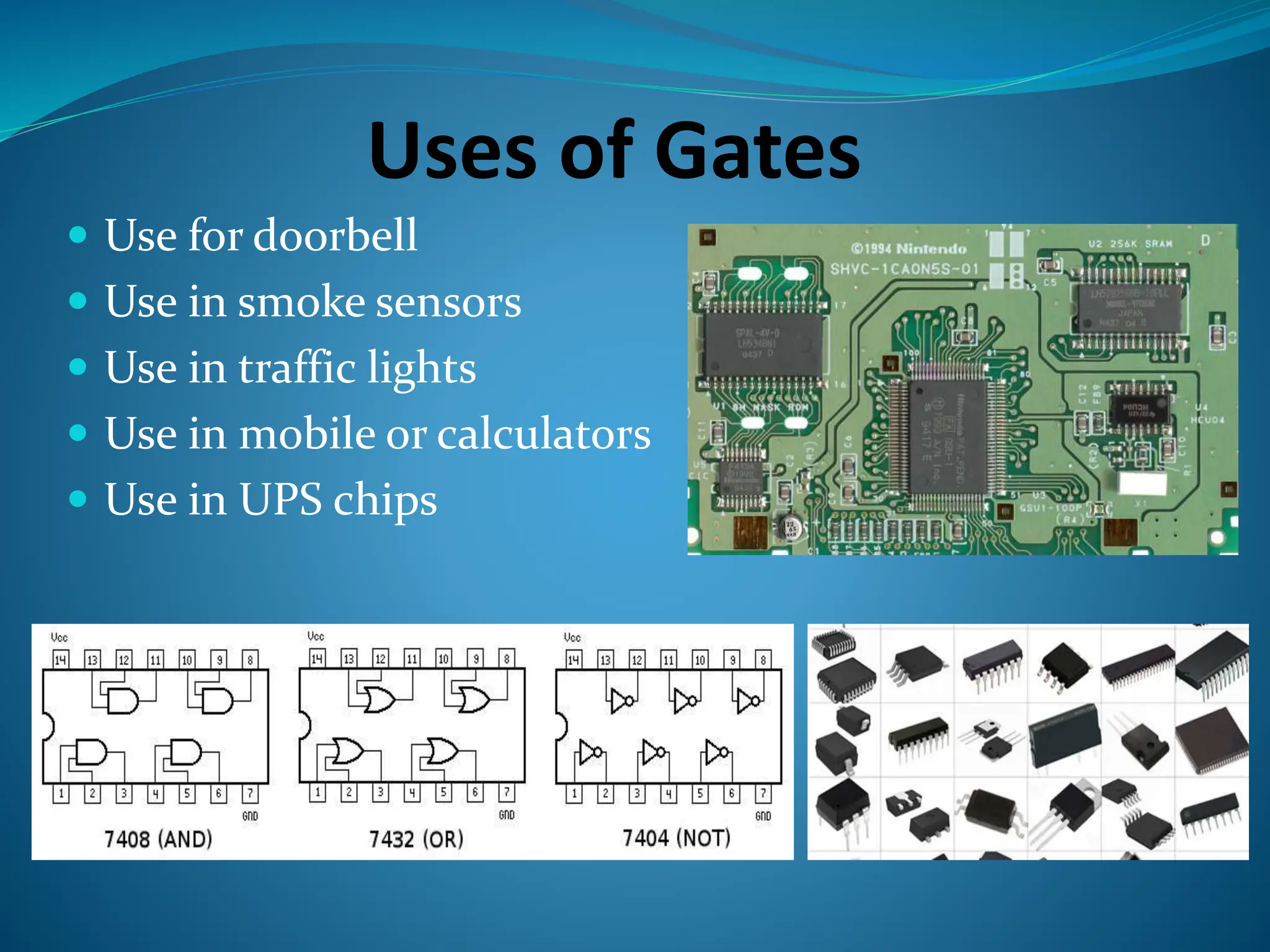
Logic gates are elementary building blocks of digital circuits that have inputs and outputs representing binary digits 0 and 1. There are several basic types of logic gates including AND, OR, NOT, XOR, NAND, NOR, and XNOR gates. Each gate functions according to specific rules - for example, an AND gate only outputs 1 if all its inputs are 1, while a NAND gate produces the opposite output of an AND gate. Logic gates are used in various electronic devices and circuits.