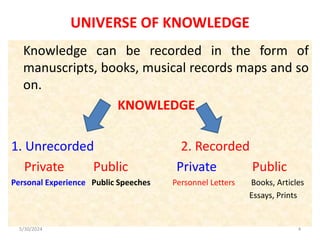
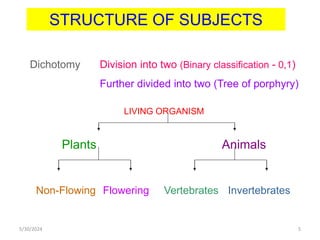
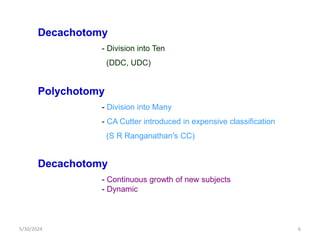
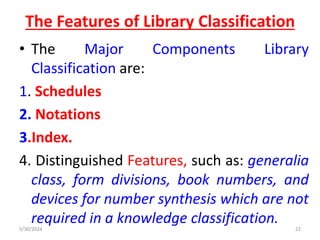
The document discusses the need and purpose of library classification, emphasizing its importance in organizing knowledge for efficient access to library resources. It explores various modes of subject formation and defines library classification as a systematic arrangement of information, crucial for helpful user access and management of collections. The document also highlights the essential functions of library classification, including aiding in the identification, retrieval, and organization of documents in a library setting.