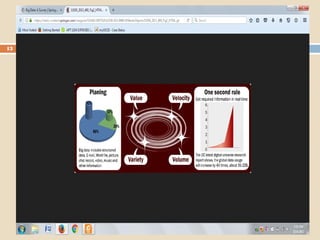
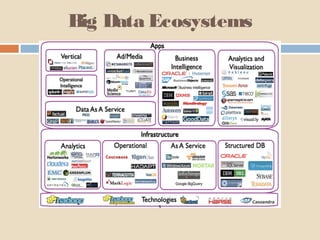
The document discusses the concept of big data and its significance in libraries and information centers, particularly focusing on WorldCat and the role of OCLC. It highlights how libraries utilize big data to improve services and accessibility, as well as the increasing importance of data management in various sectors, including academia. The conclusion emphasizes the need for libraries to adapt to the challenges of big data and suggests actions for enhancing library resources and digitalization.