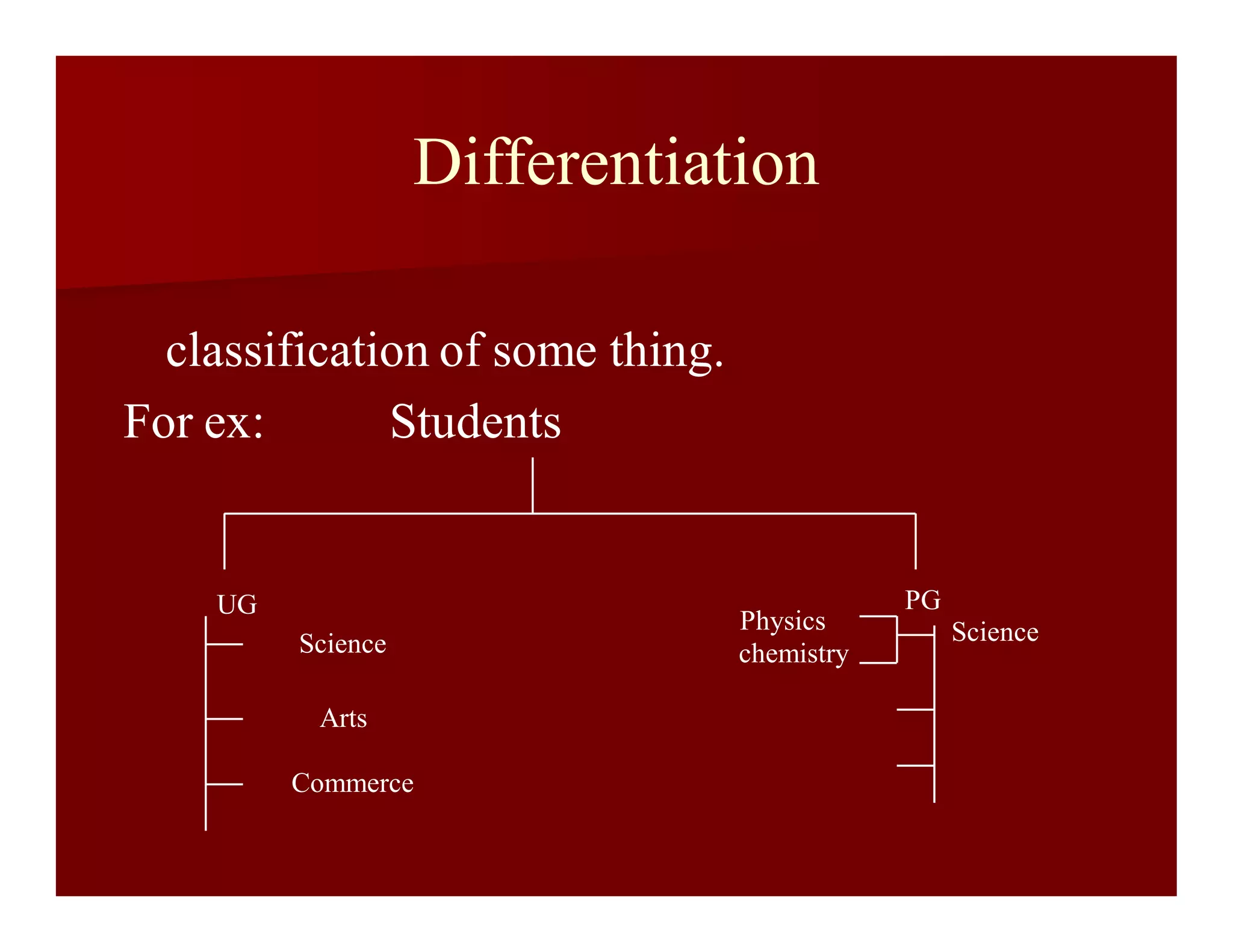
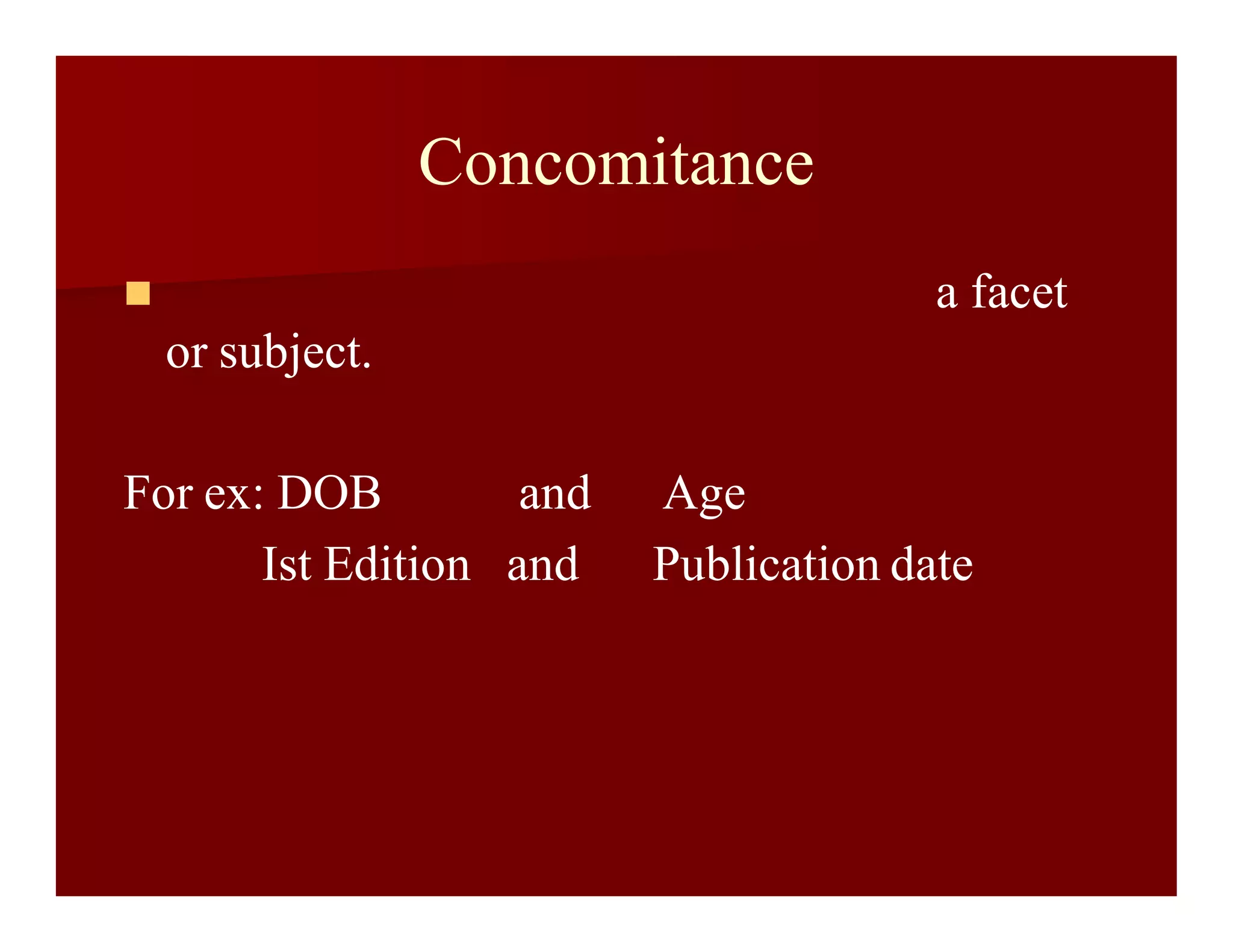
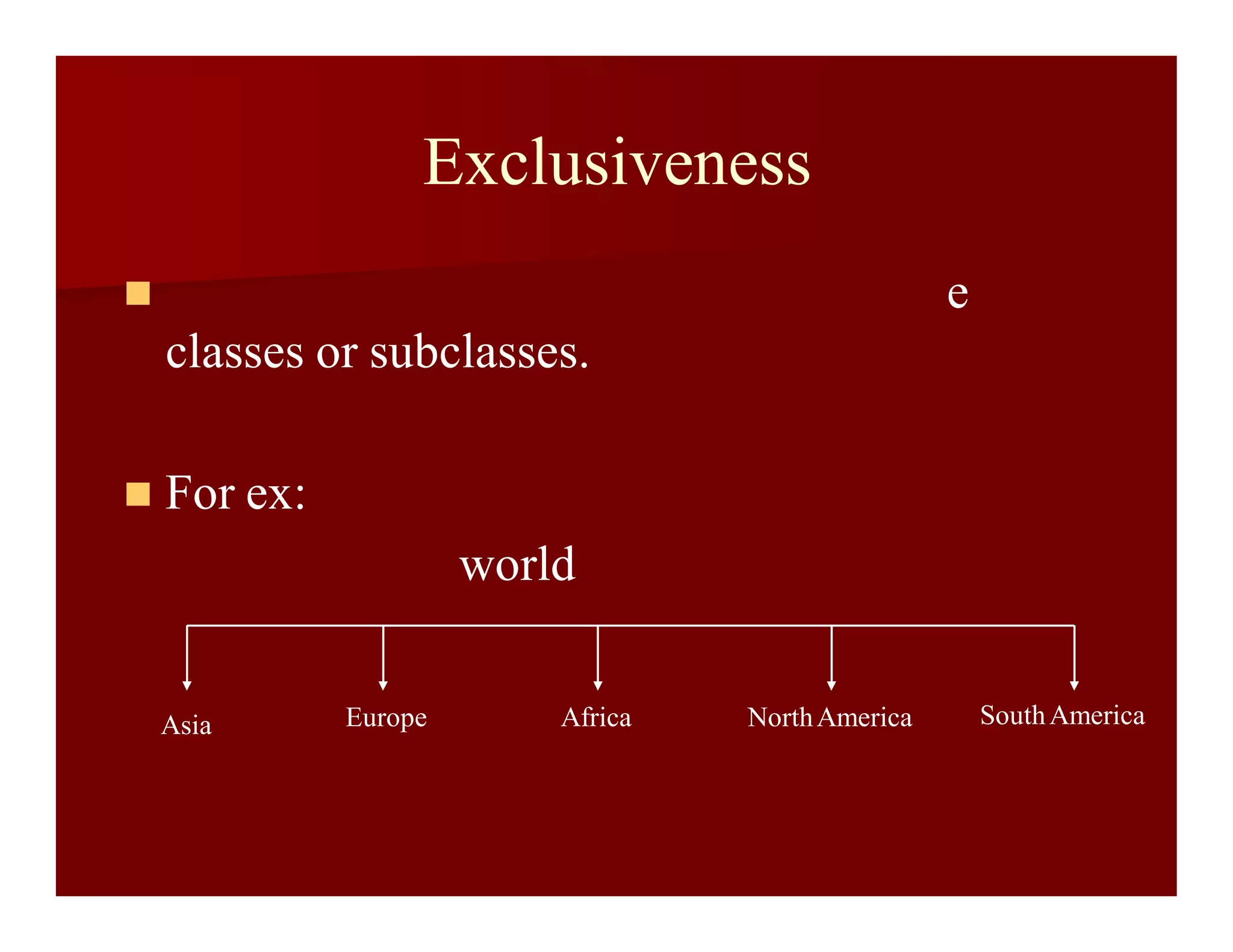
This document discusses the canons of library classification, which are principles for developing effective classification systems. It describes several groups of canons, including canons of array of classes, chain of classes, filiatory sequence, terminology, and notation. Some key canons mentioned are differentiation, concomitance, relevance, exhaustiveness, exclusiveness, and relativity. The document provides examples to illustrate how each canon applies to organizing a classification system.







![Consistency
permanent characteristics according to their
sequence.
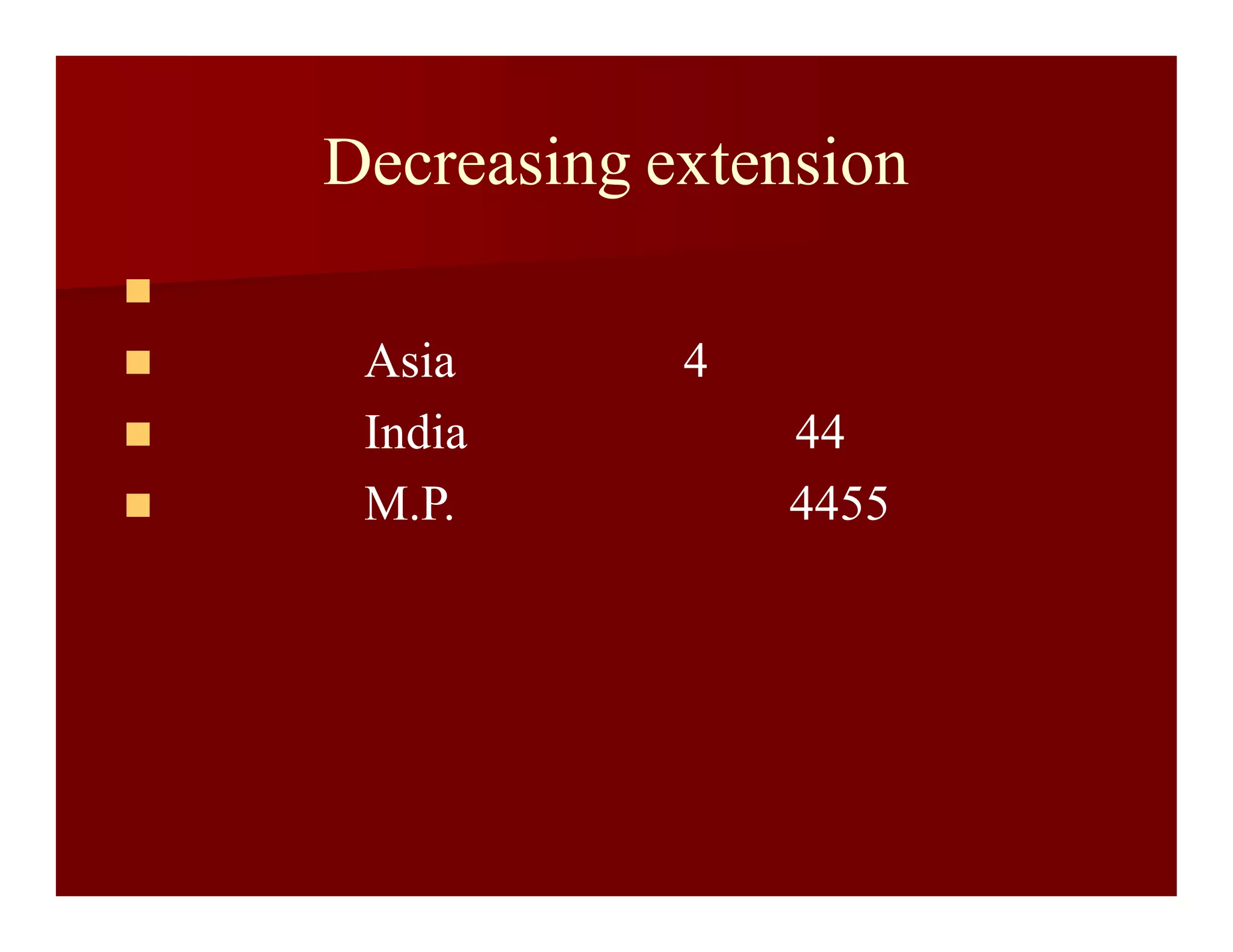
For ex:
O[P],[P2][P3],[P4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canonsoflibraryclassification-160108072428/75/Canons-of-library-classification-11-2048.jpg)











![Relativity
For ex: The particular symbols for five
fundamental categories in Colon Classification
such as
[P] , [E] :
[M] ; [S] .
[T] ‘](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canonsoflibraryclassification-160108072428/75/Canons-of-library-classification-29-2048.jpg)

