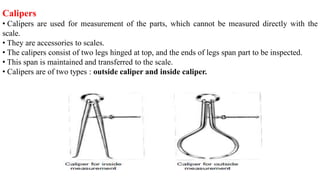
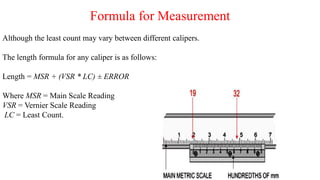
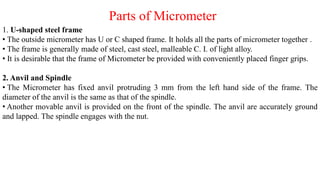
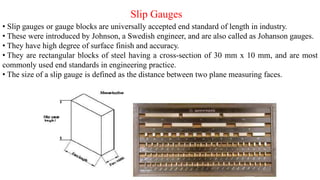
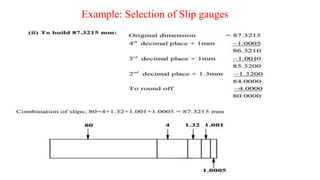
This document discusses various linear measurement instruments categorized as either non-precision or precision tools. Non-precision tools like steel rules and calipers provide measurements to the nearest line on the tool. Precision tools like vernier calipers, micrometers, and slip gauges provide highly accurate measurements. The document describes the parts and operating principles of vernier calipers, micrometers, height gauges, and slip gauges. It also provides formulas for calculating measurements and measurement errors using these precision tools.