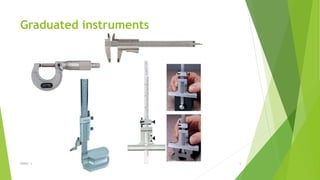
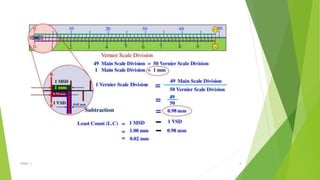
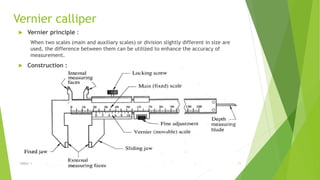
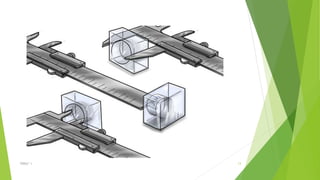
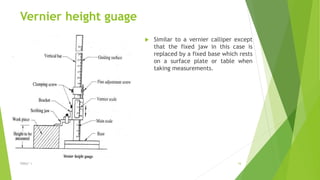
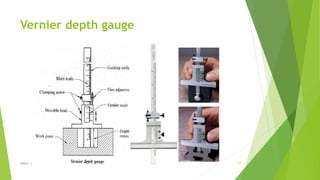
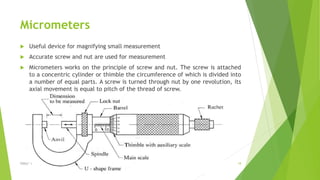
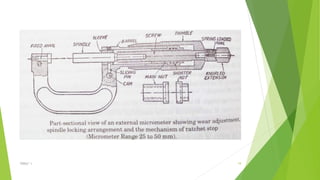
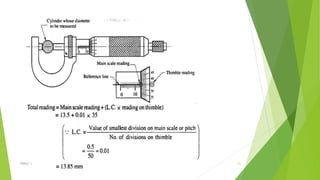
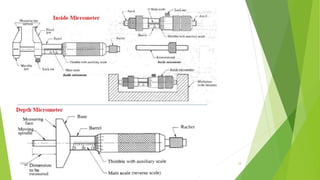
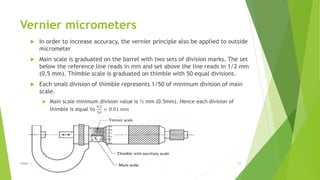
The document discusses linear measurement concepts, including the classification of measuring instruments into graduated and non-graduated types, along with precision and non-precision categories. It details specific instruments like vernier calipers, micrometers, and their principles, construction, types, errors, and usage precautions. Additionally, it covers the concept of least count and various types of micrometers, emphasizing their importance in achieving accurate measurements.