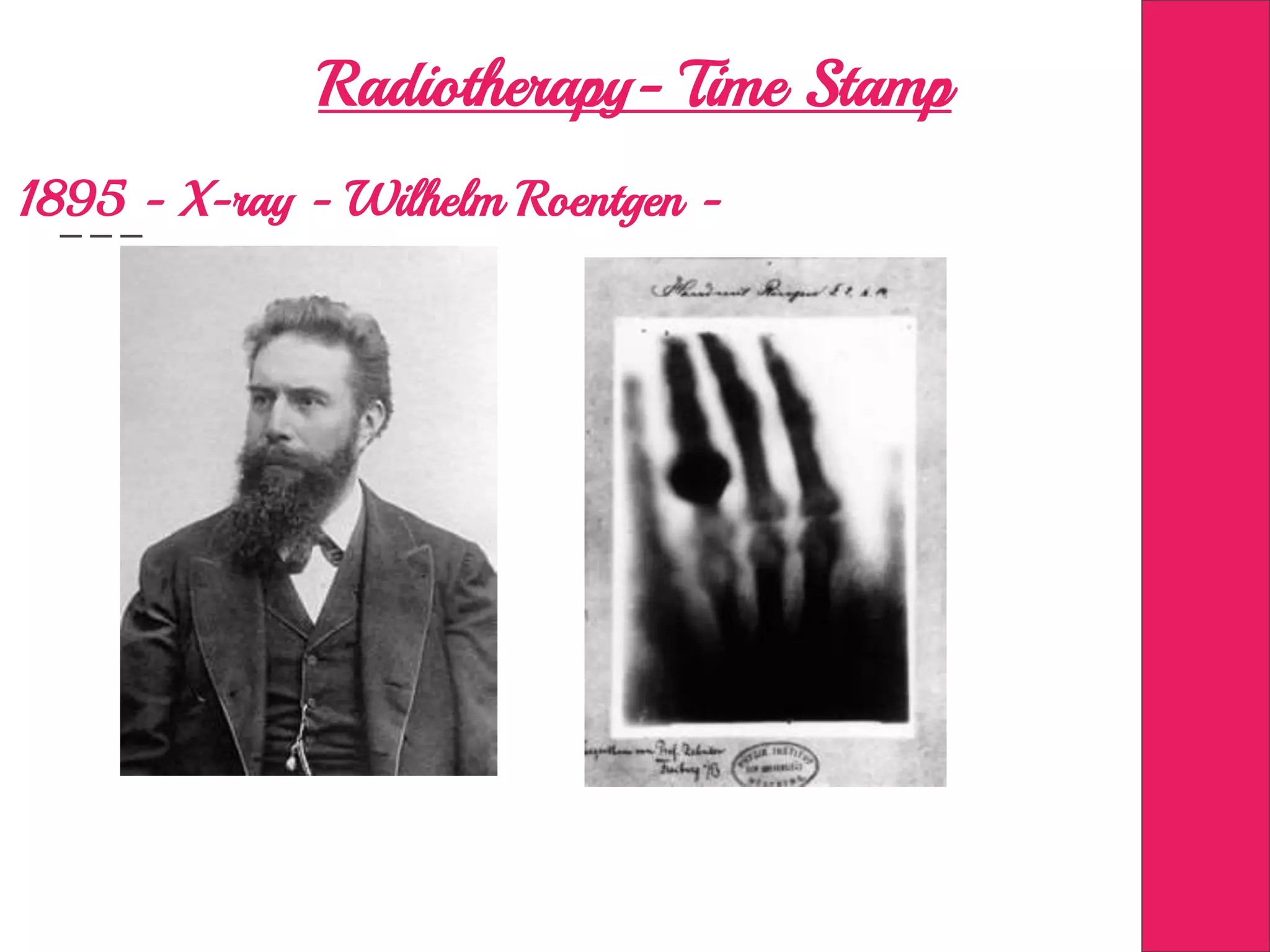
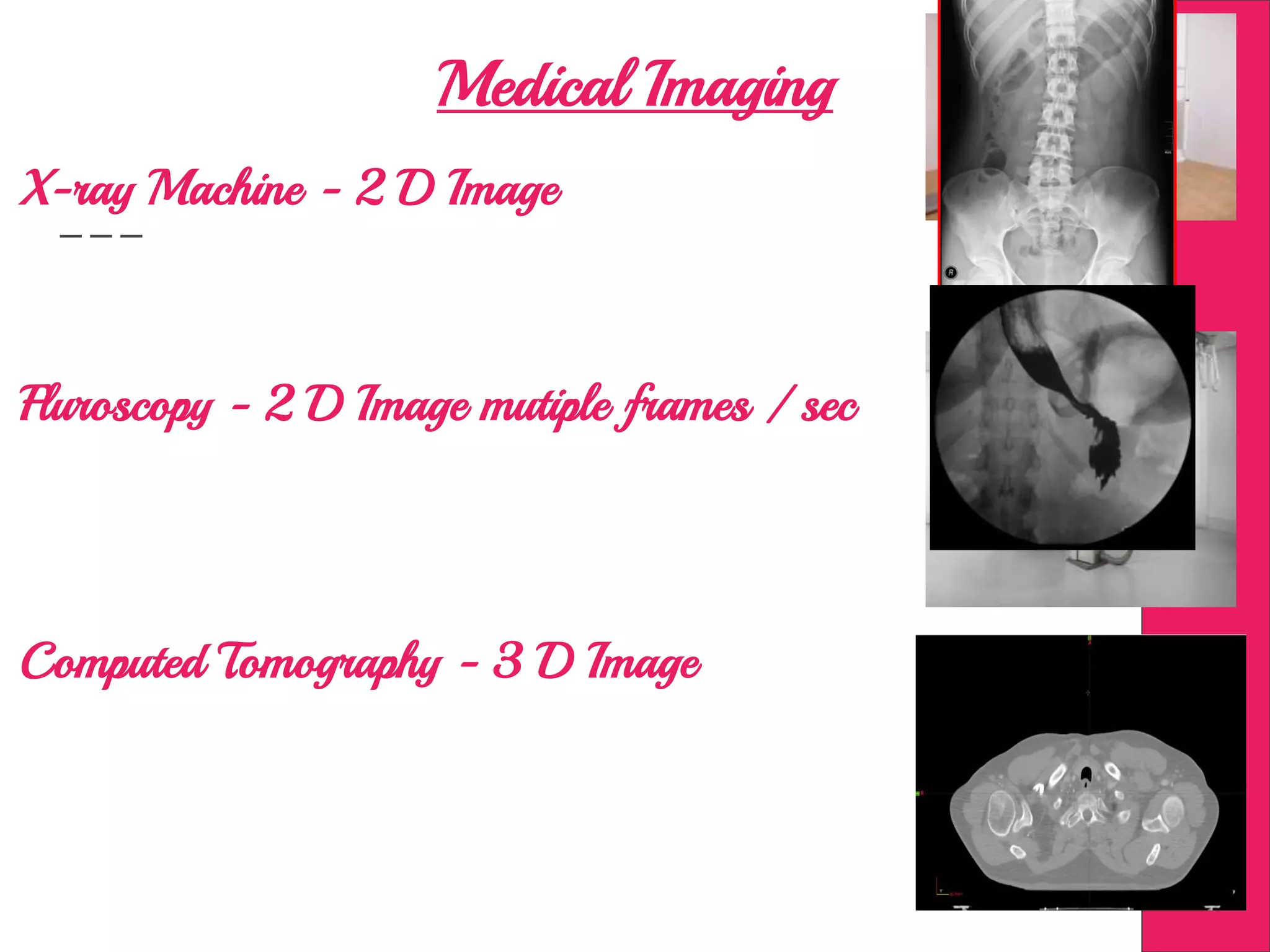
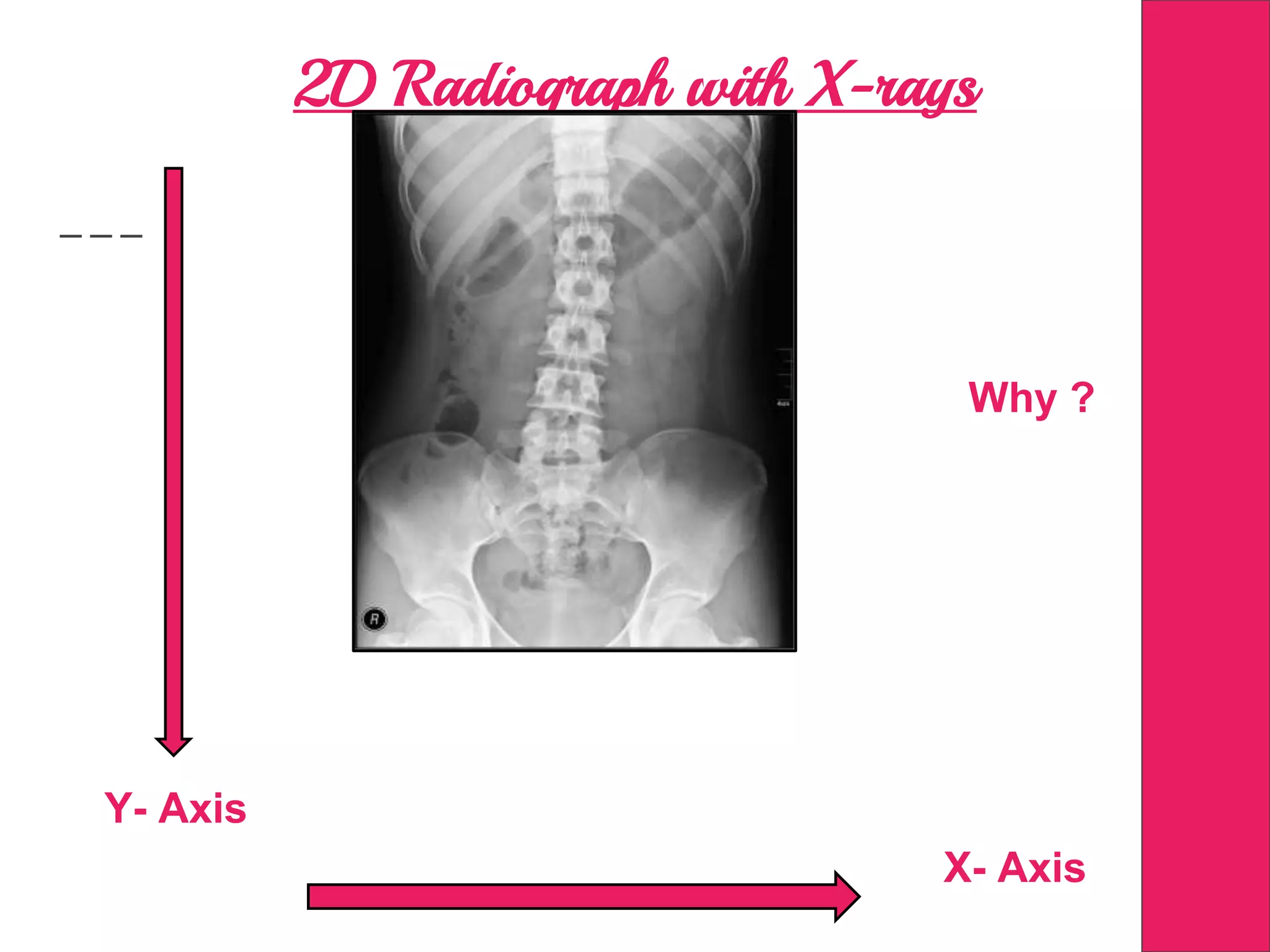
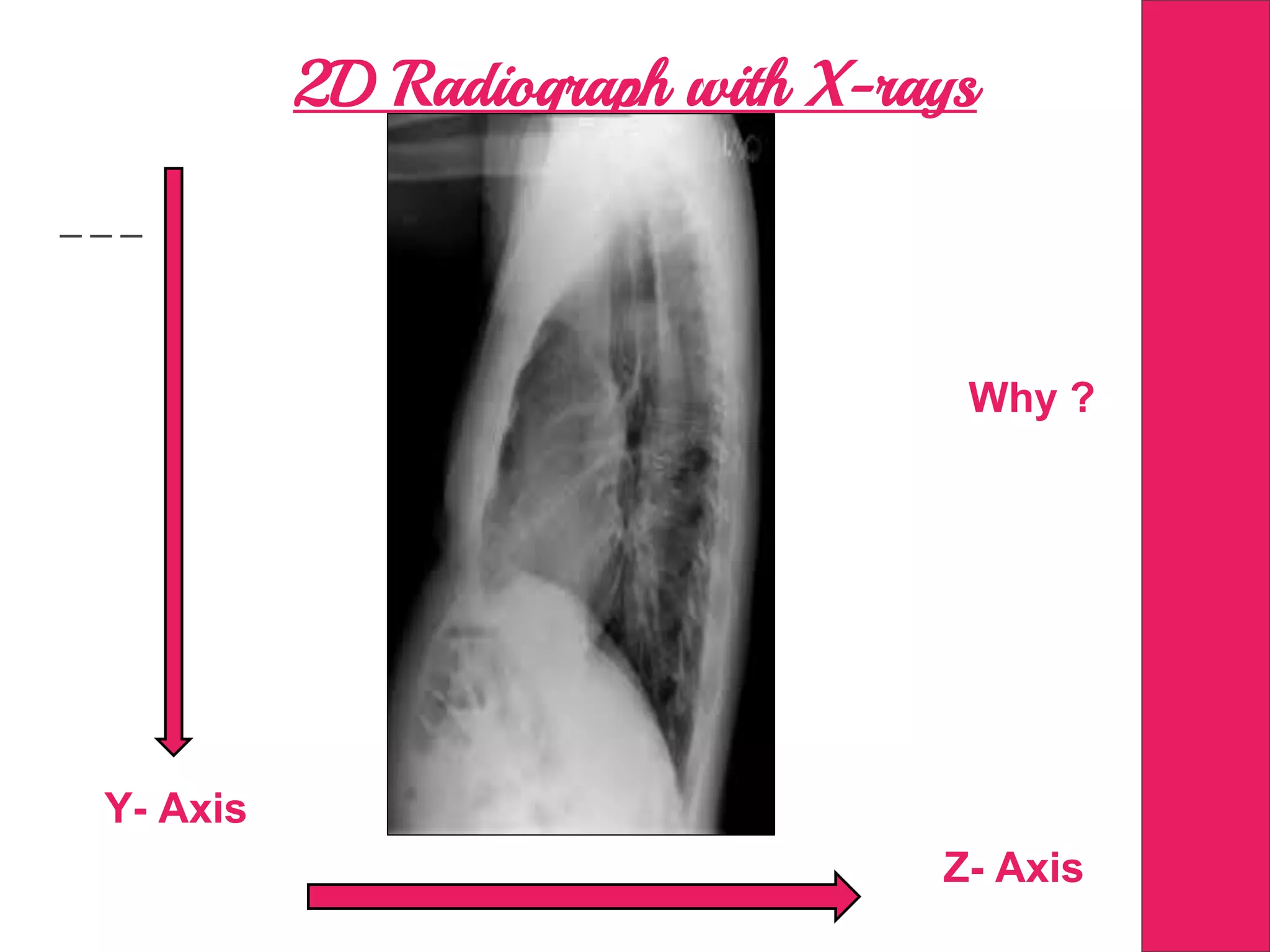
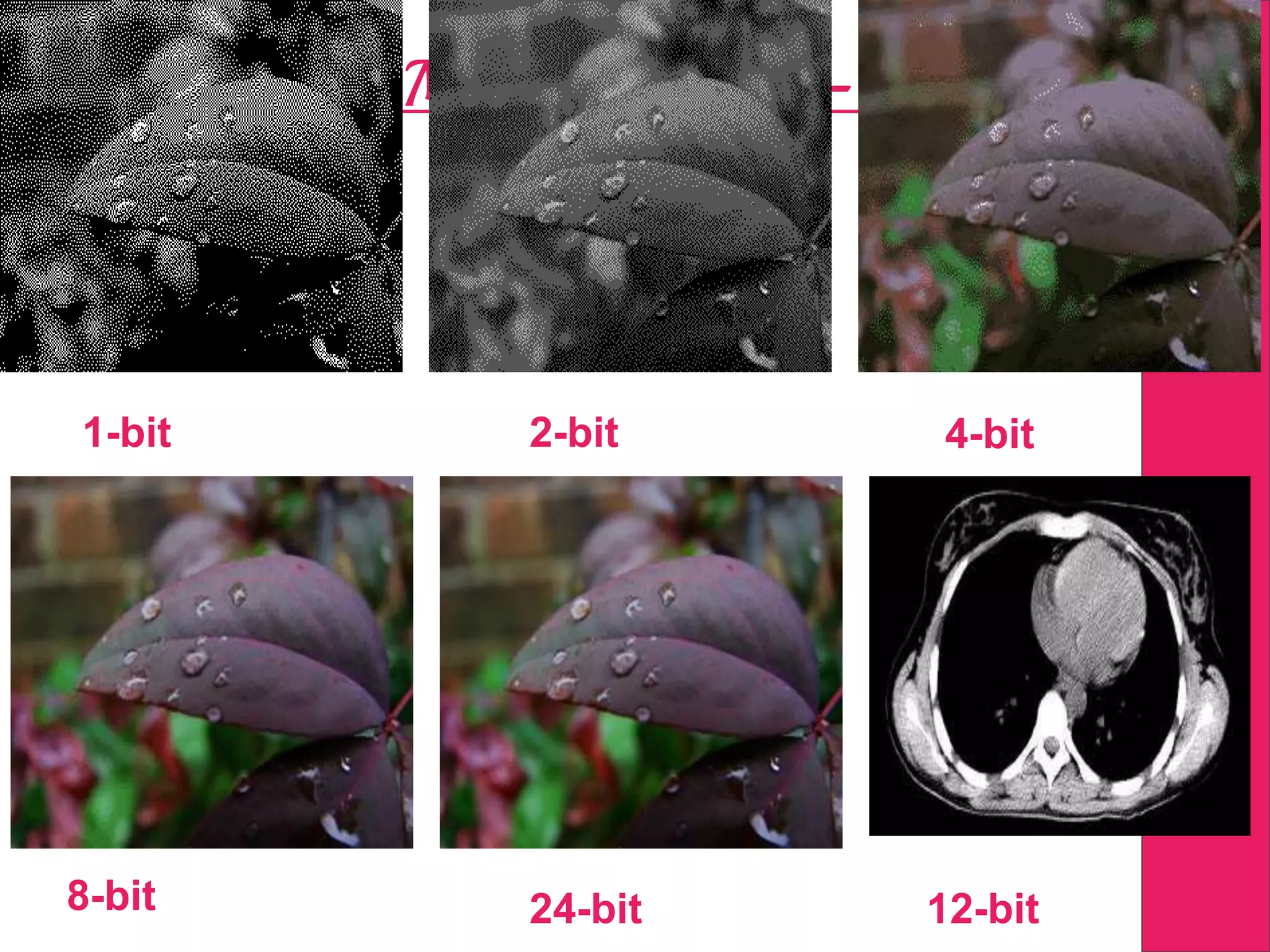
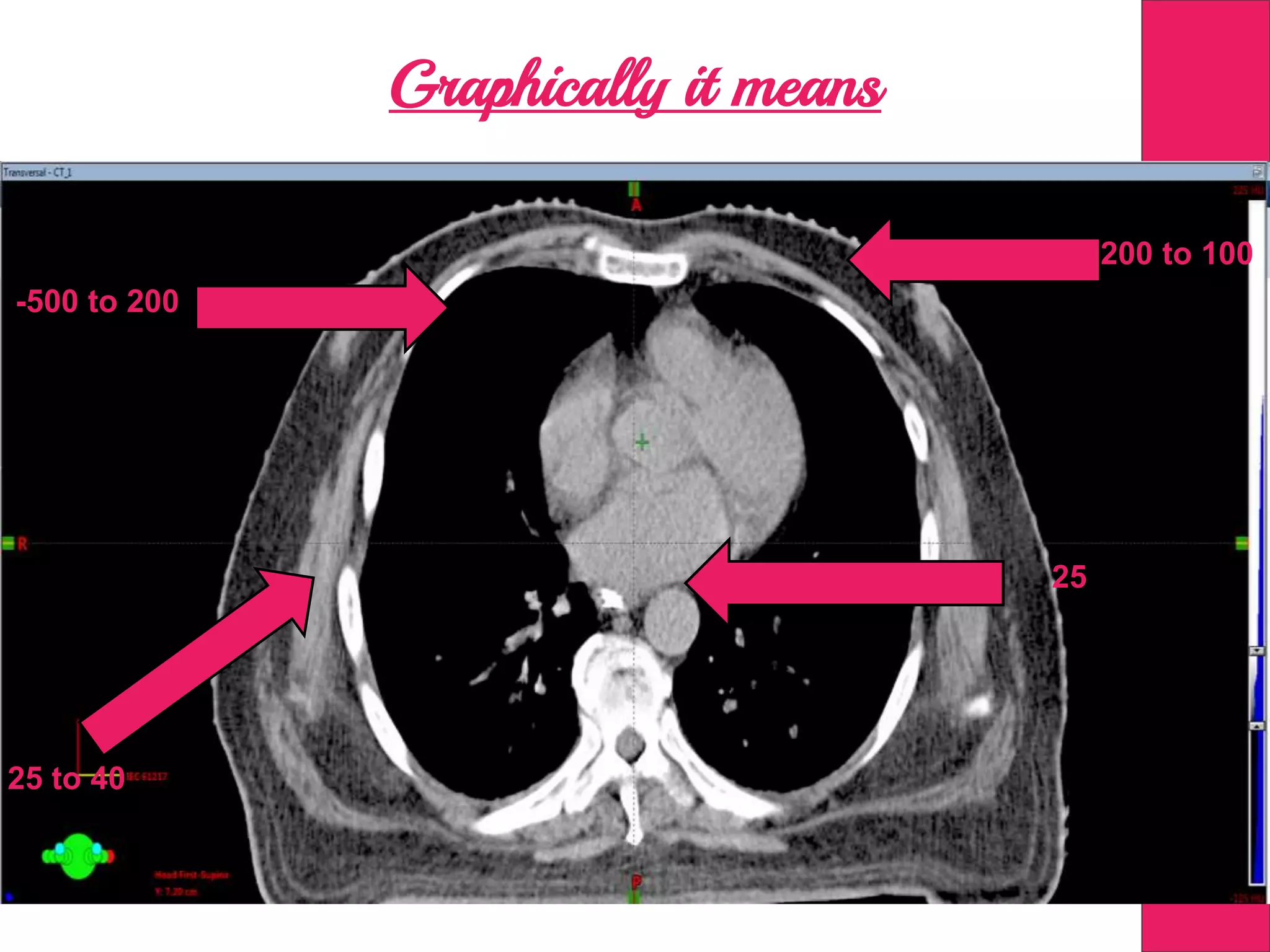
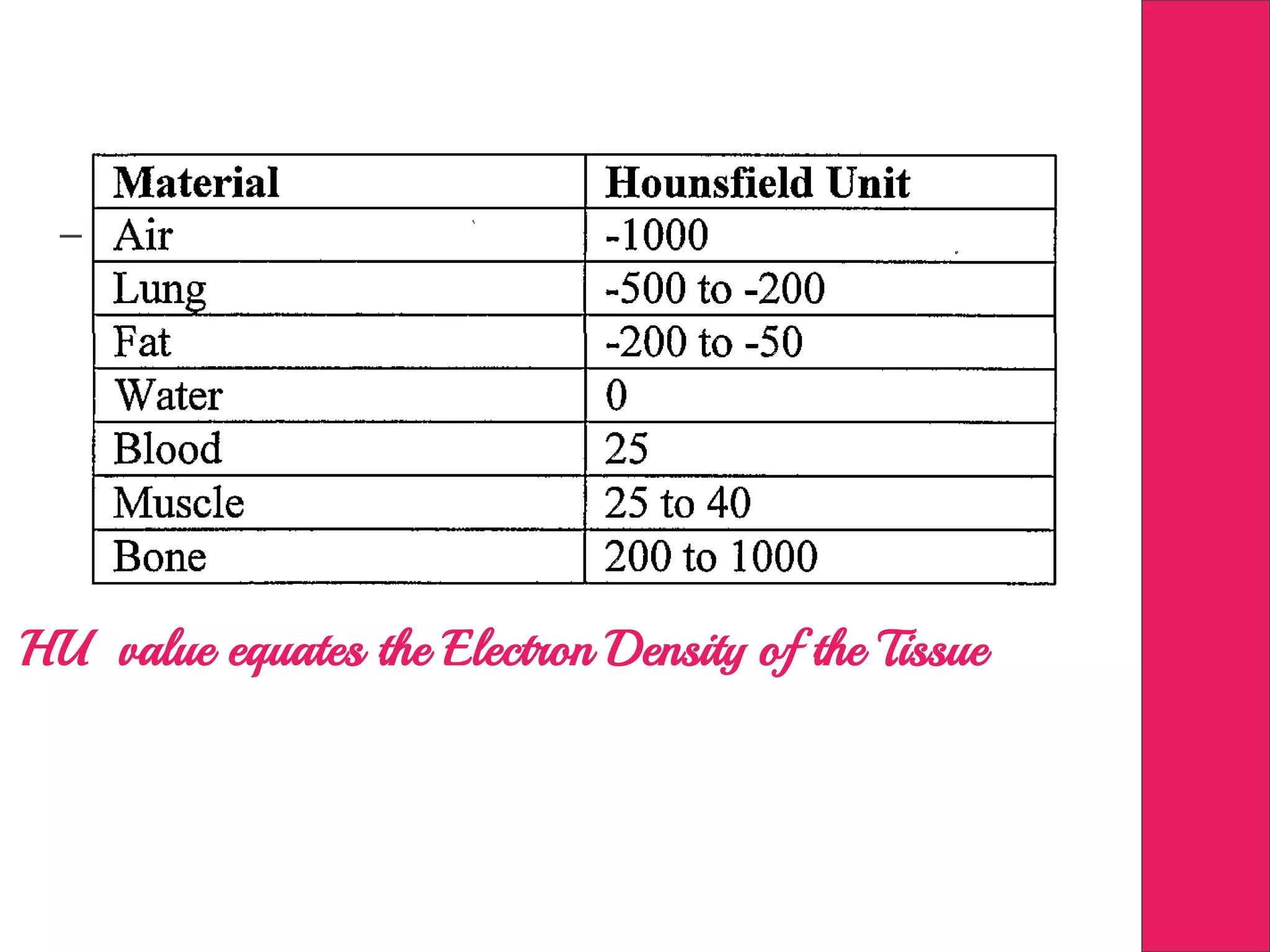
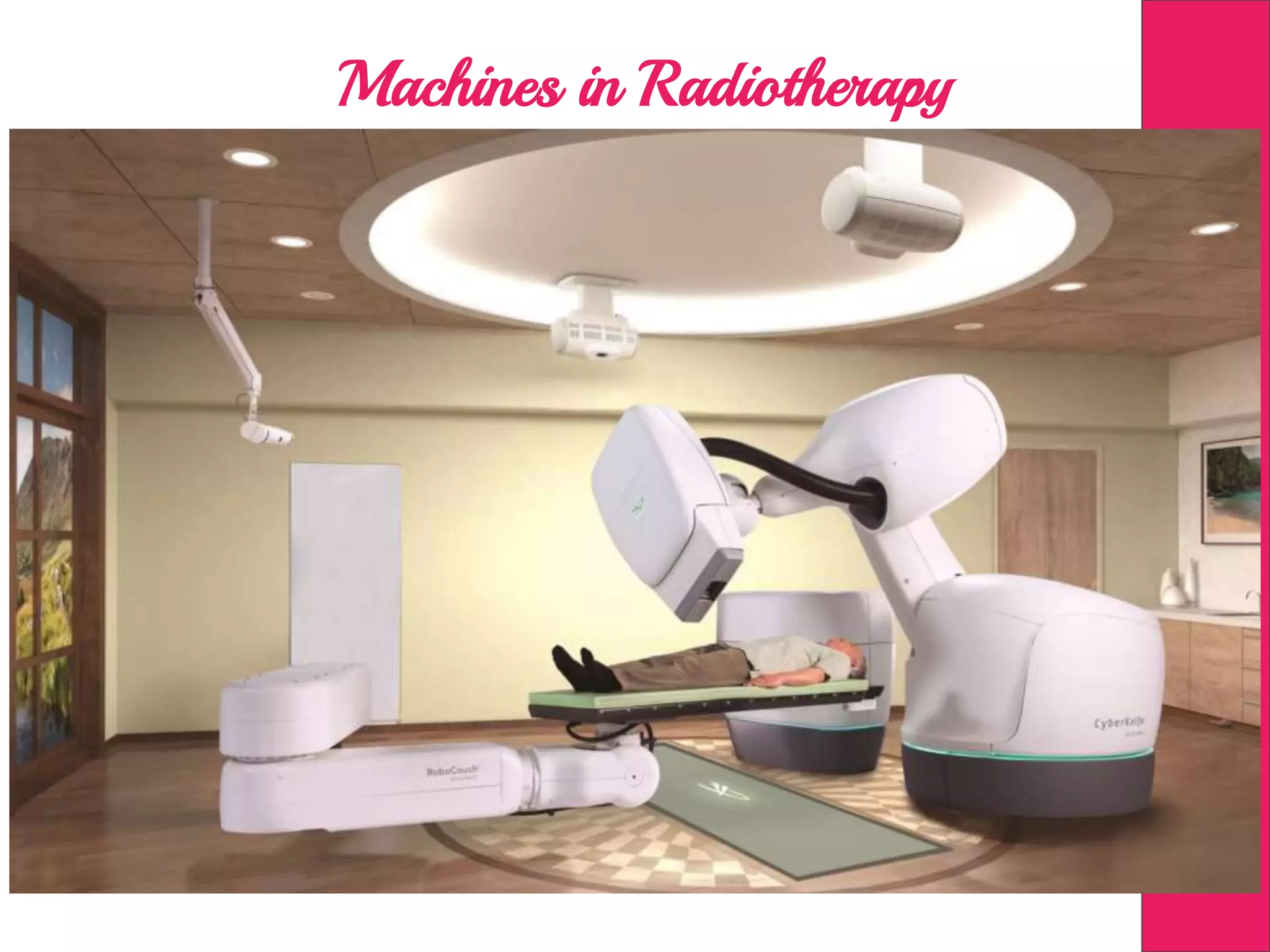
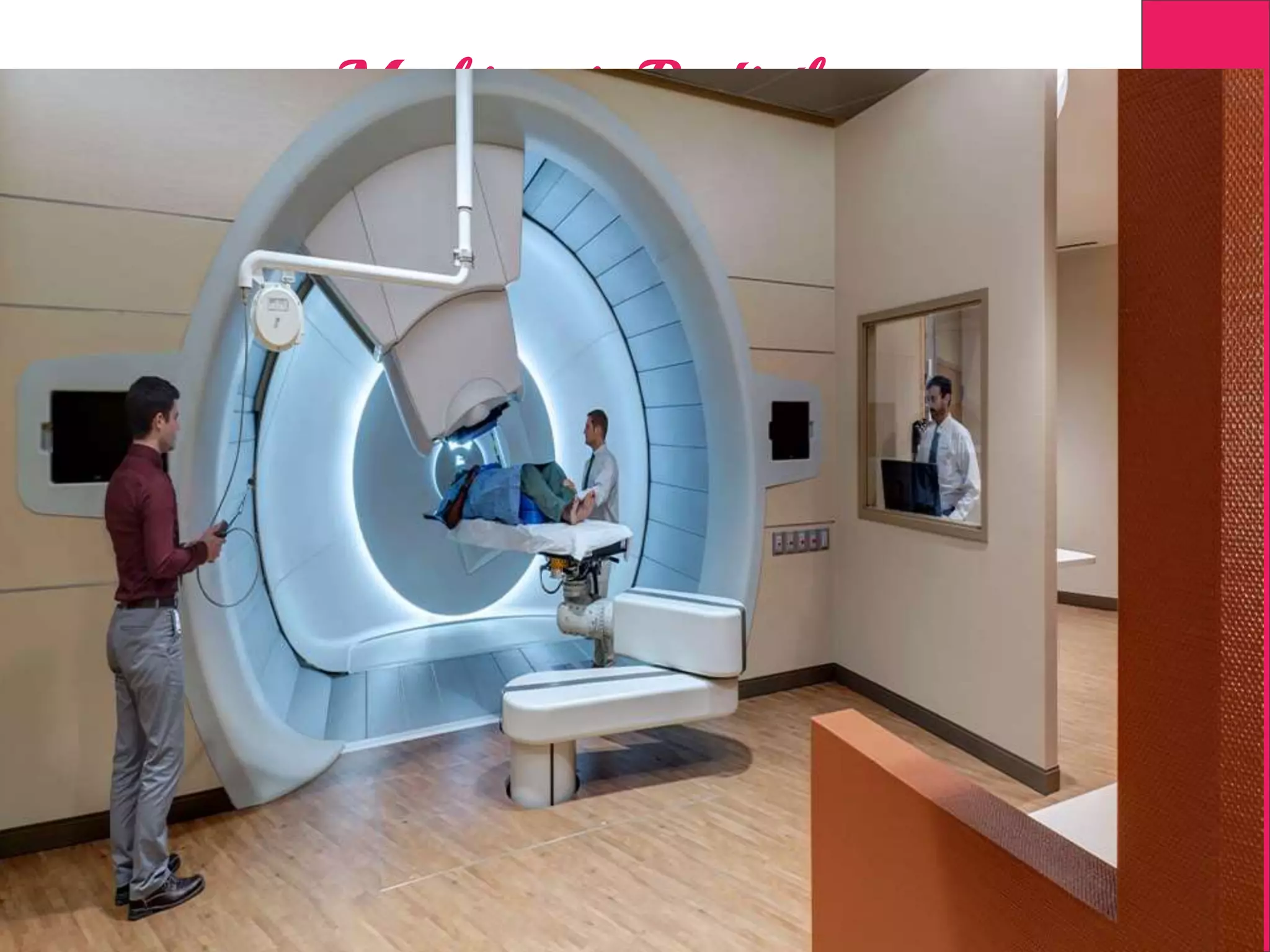
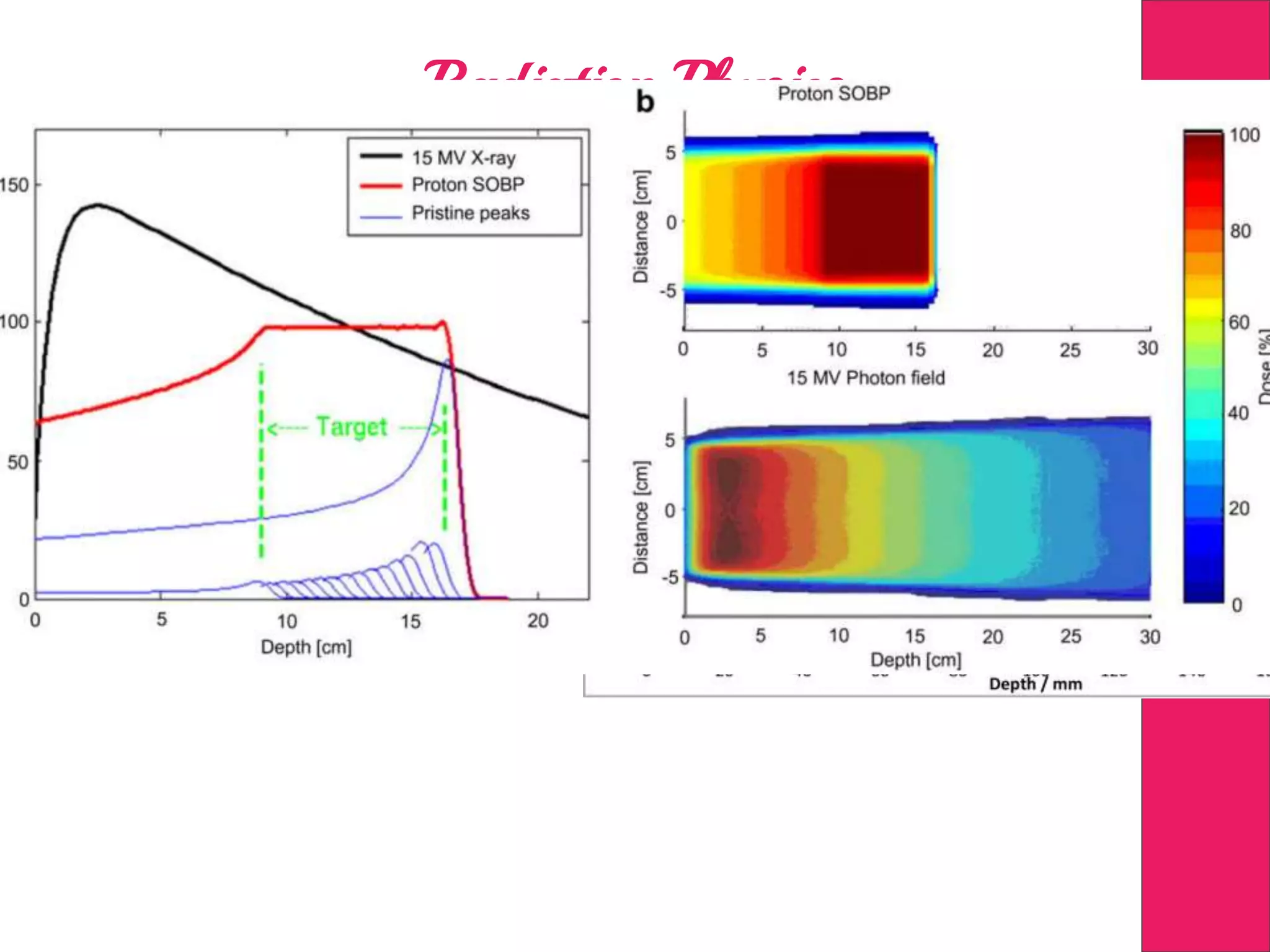
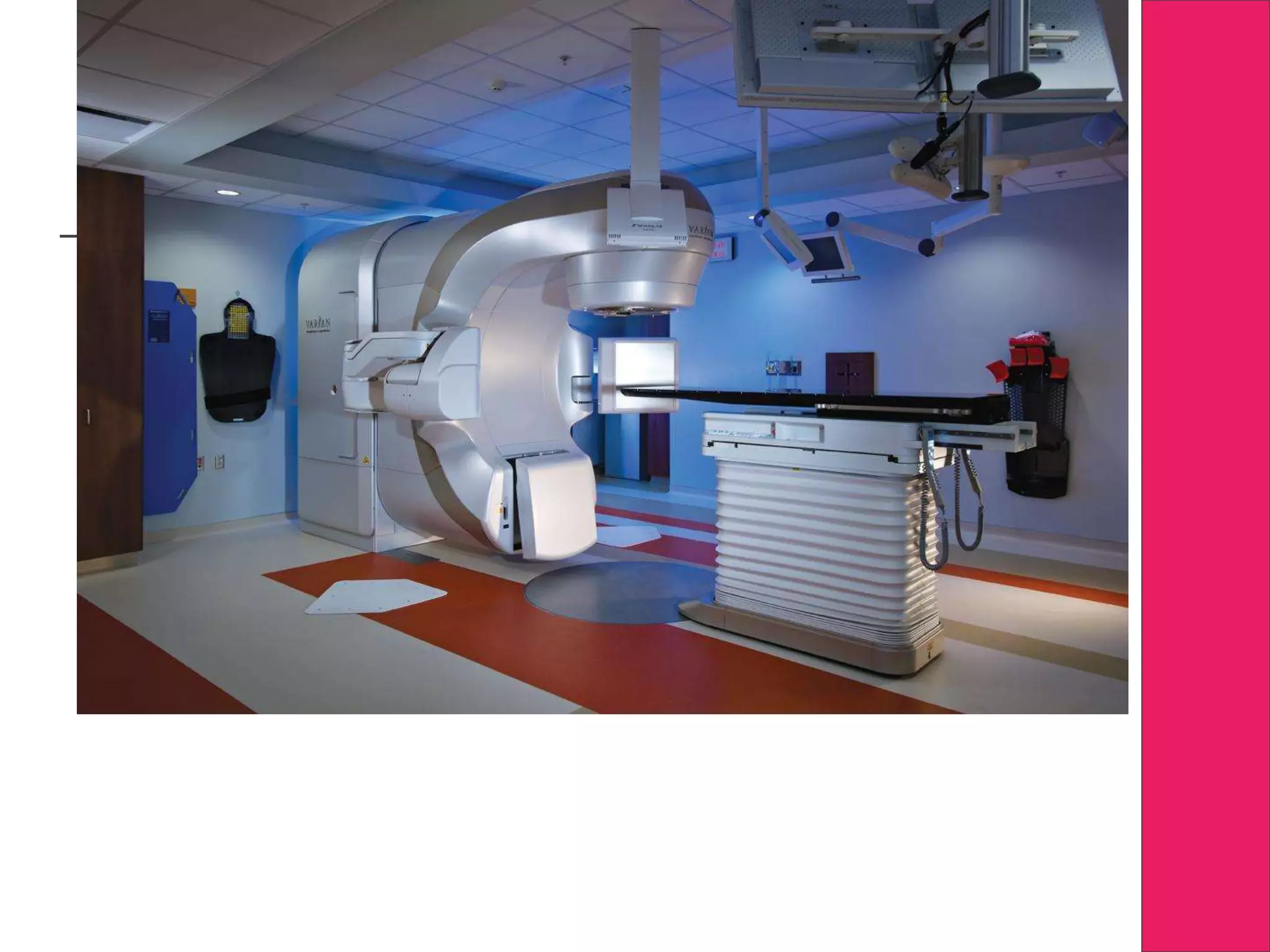
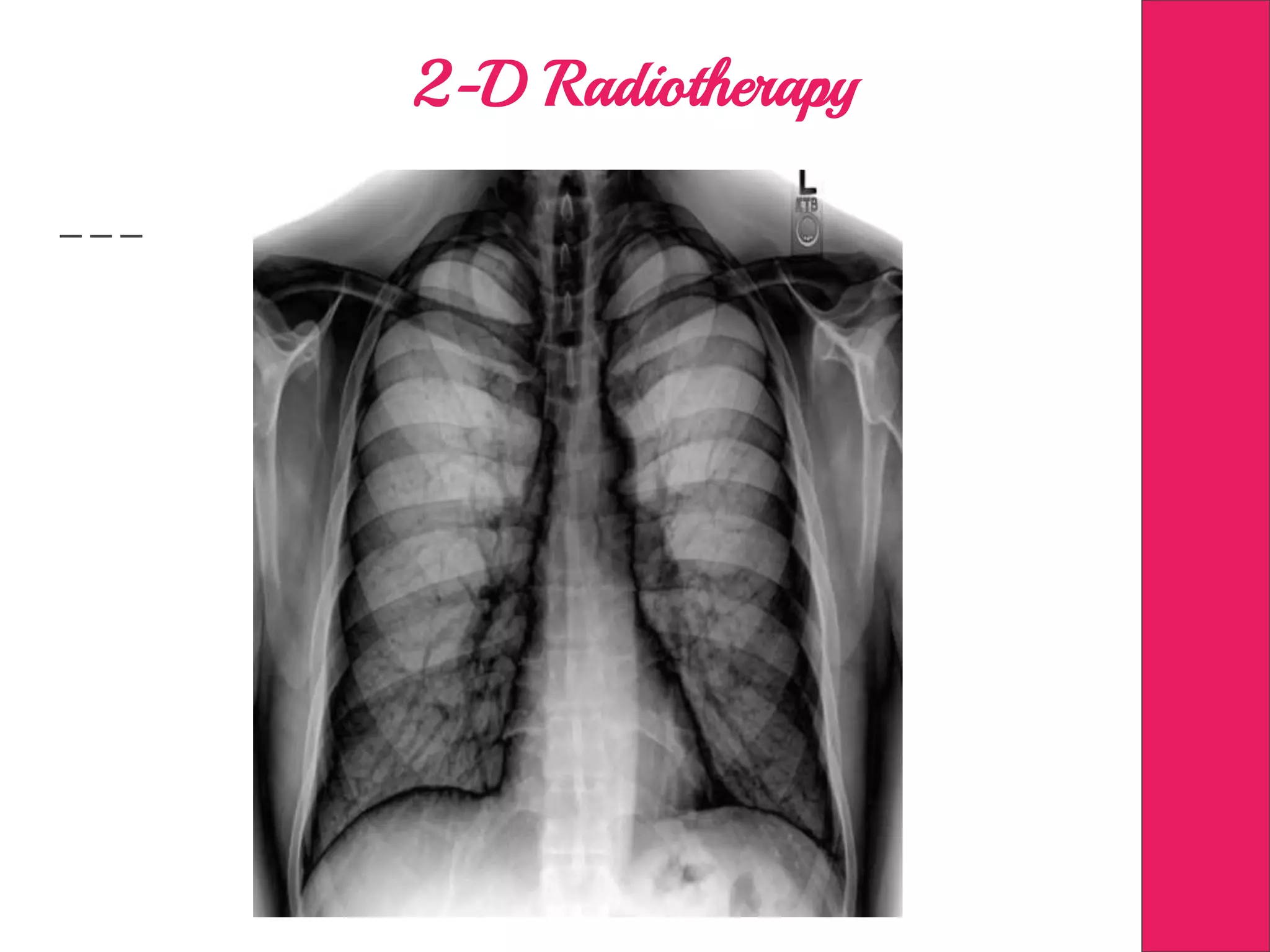
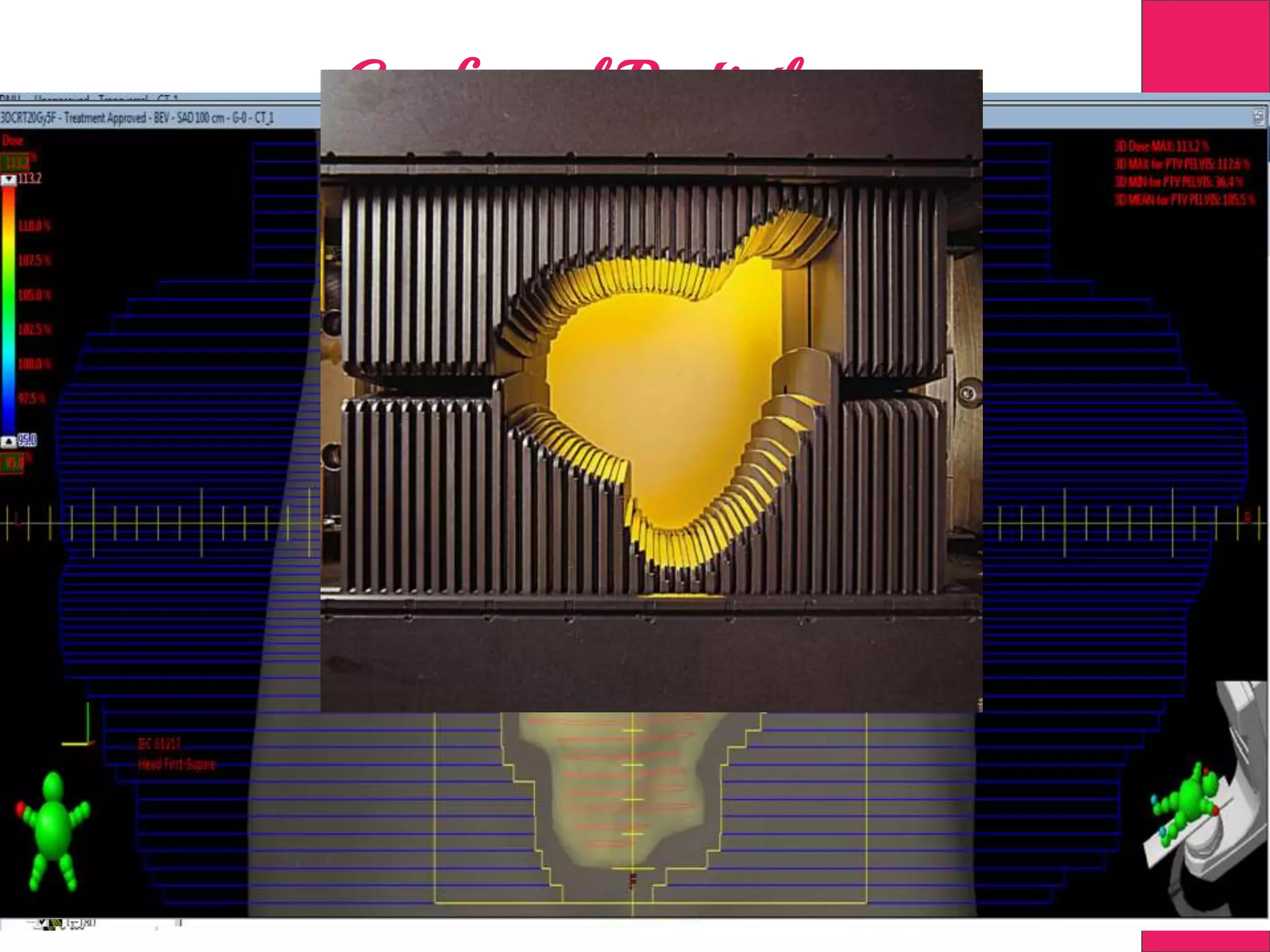
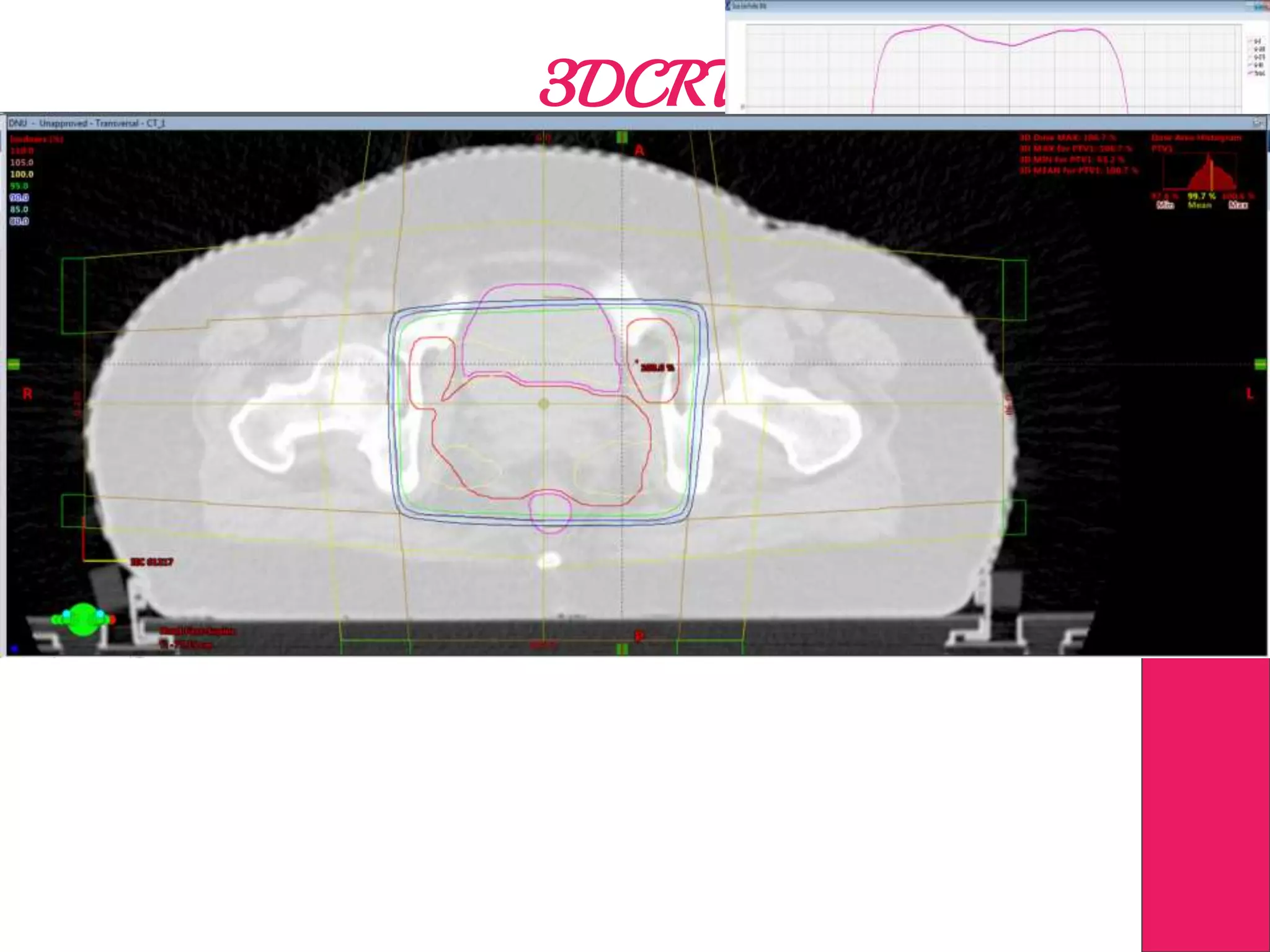
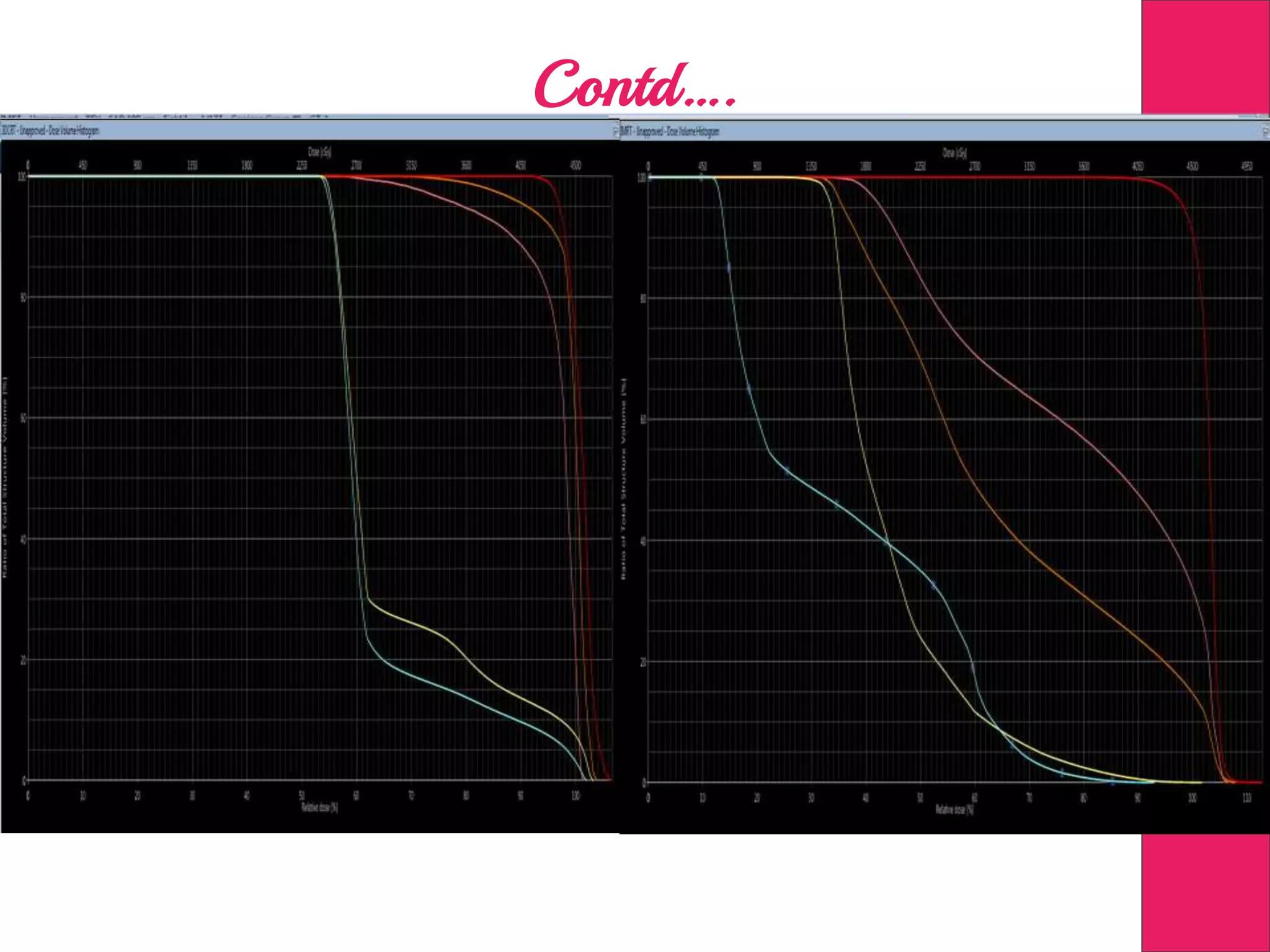
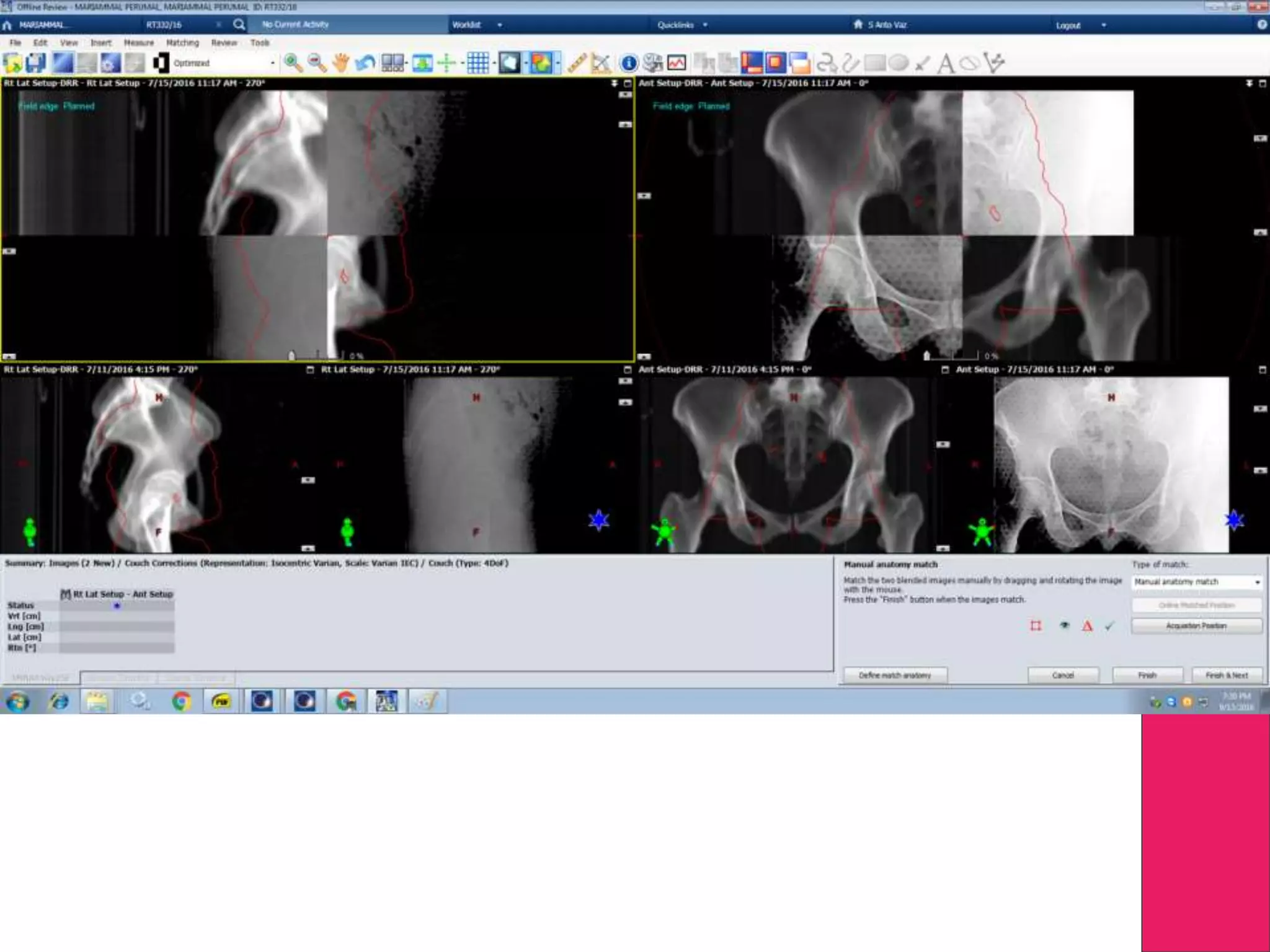
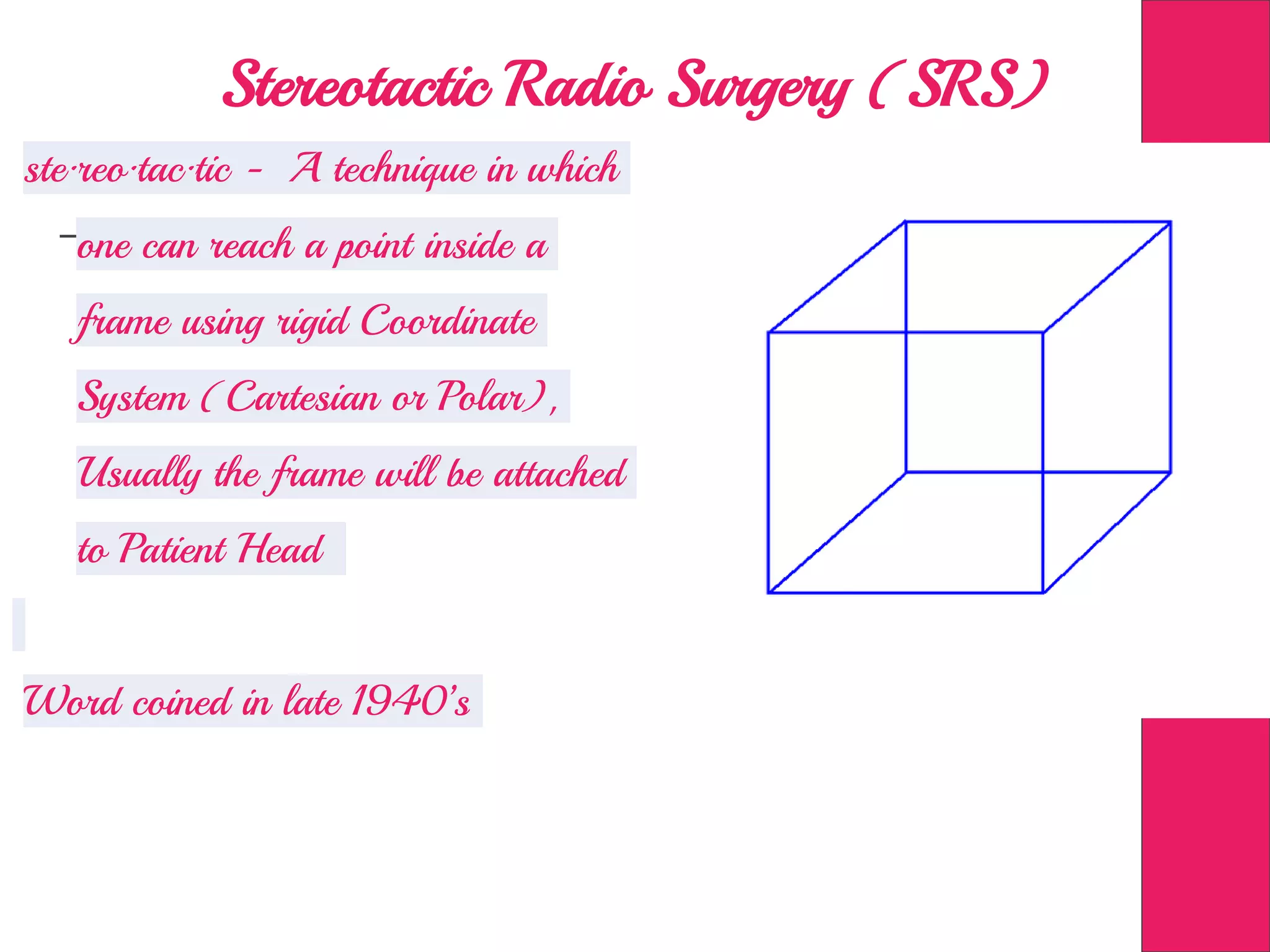
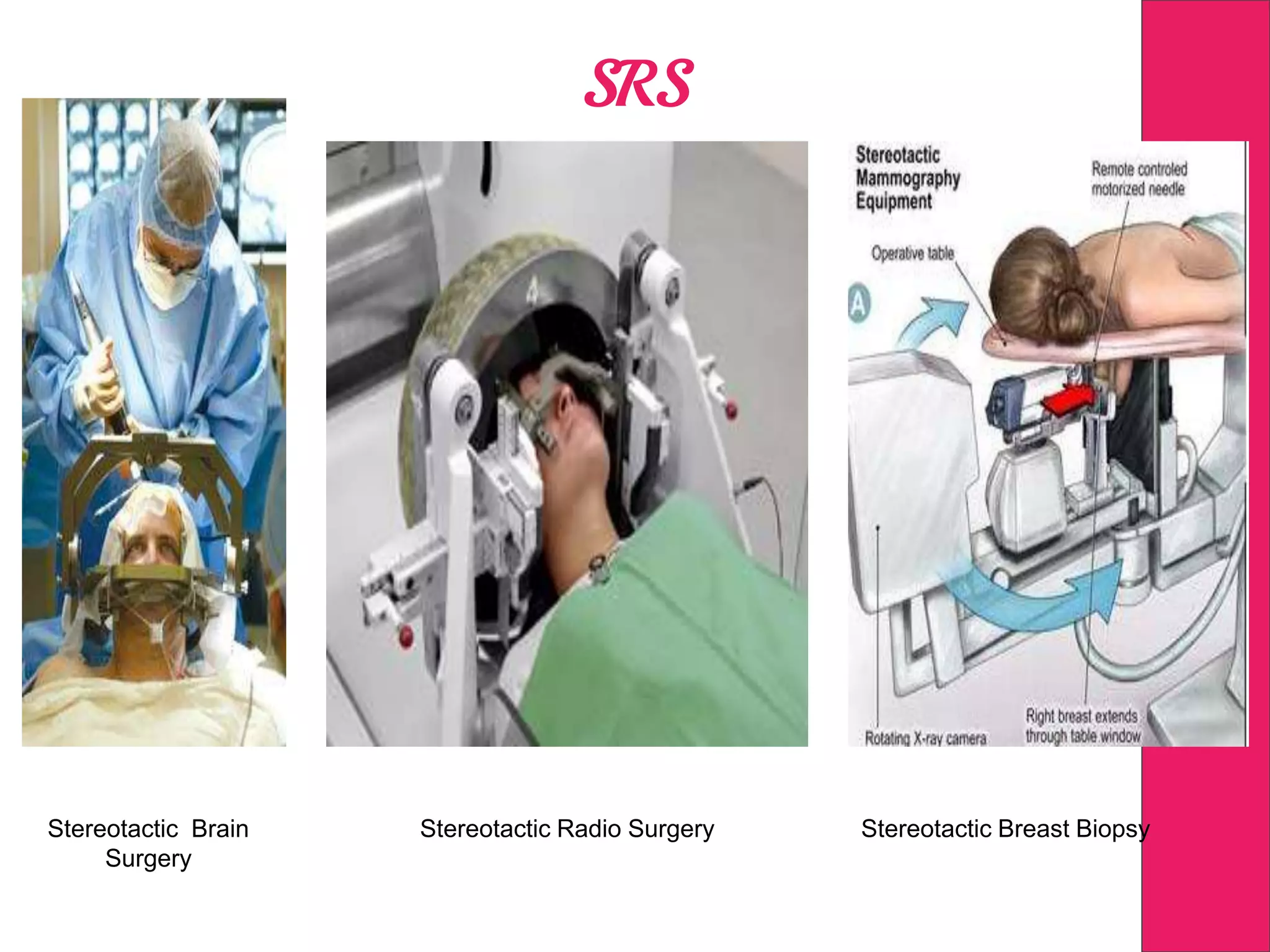
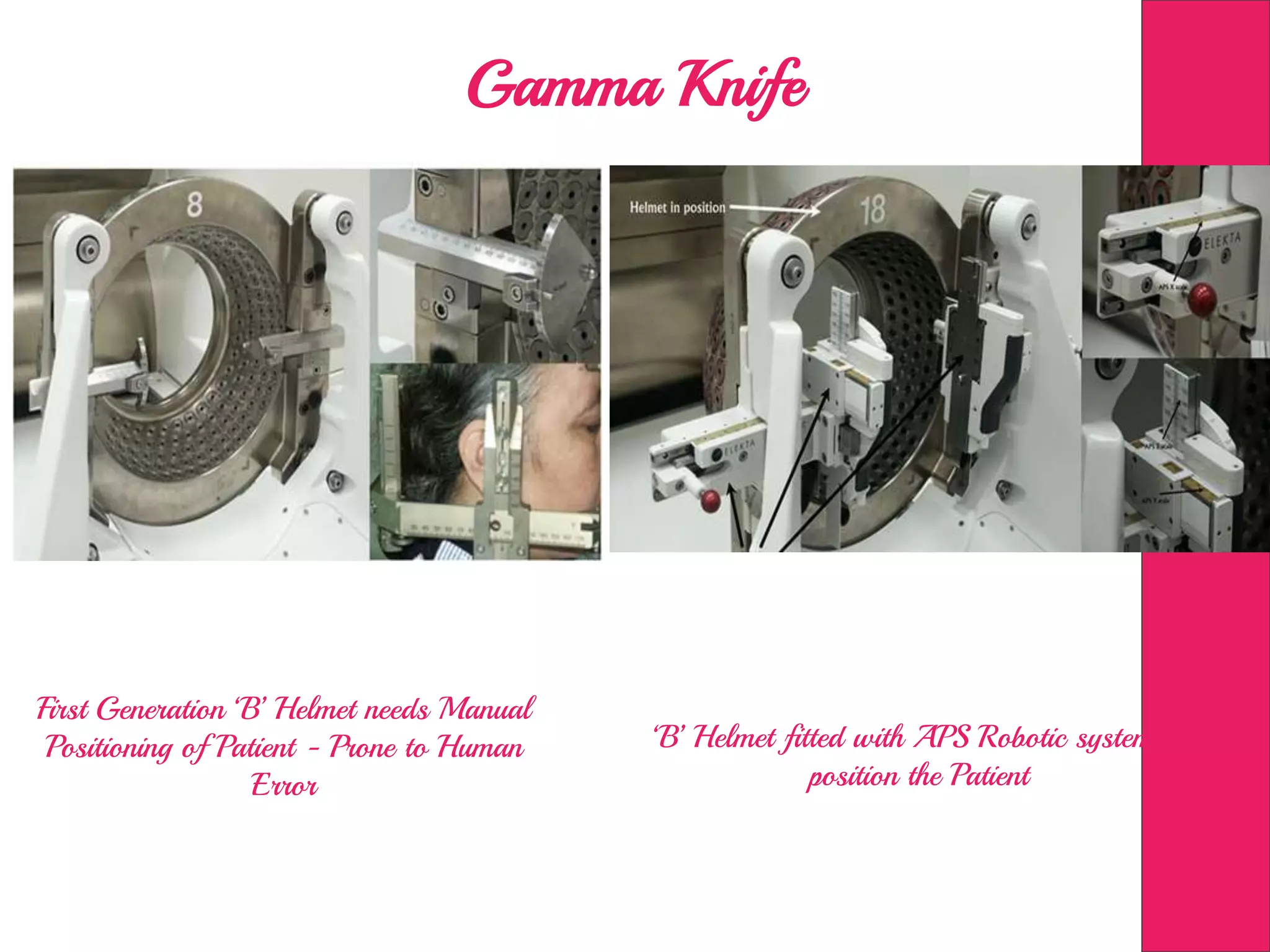
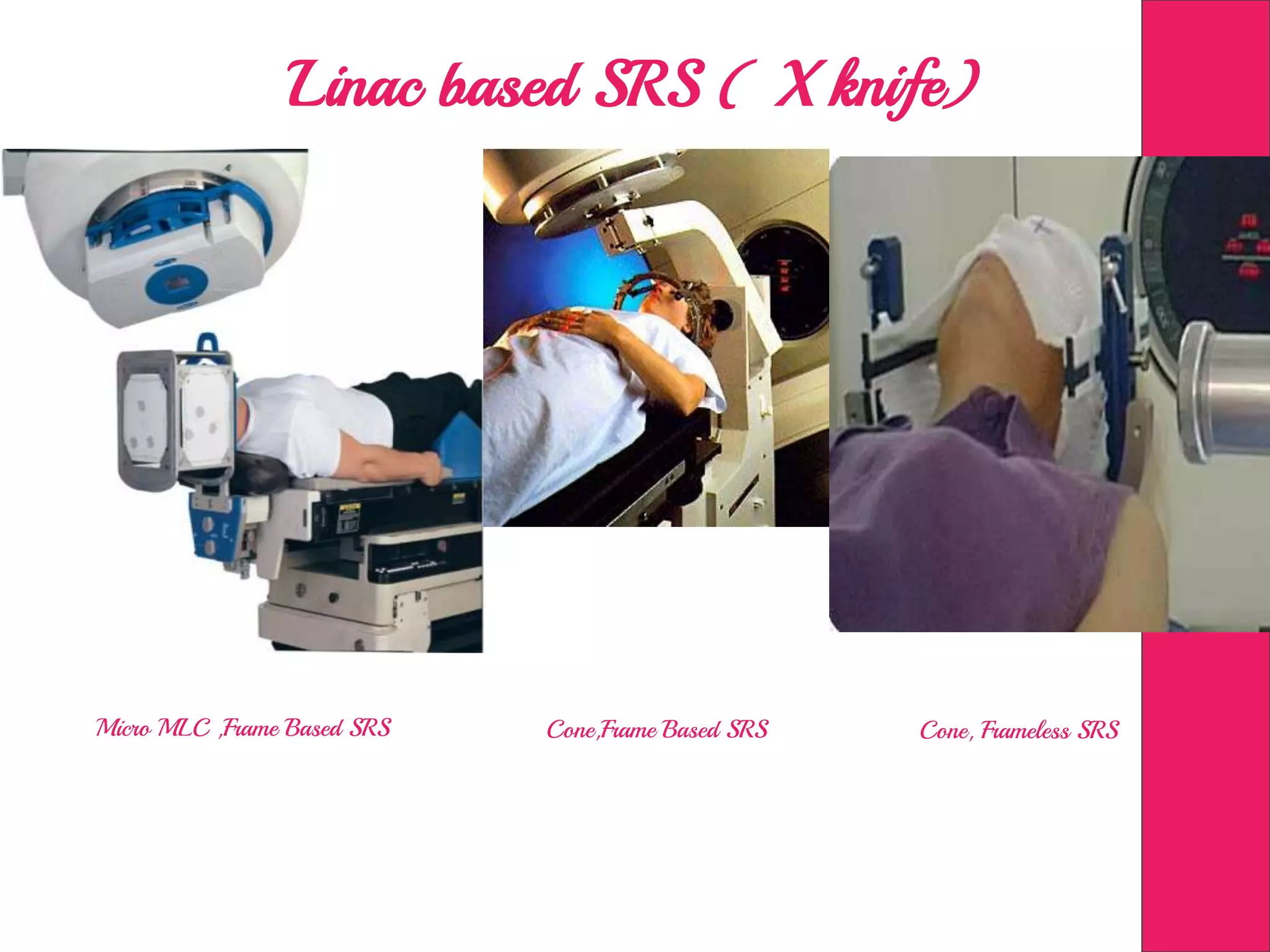
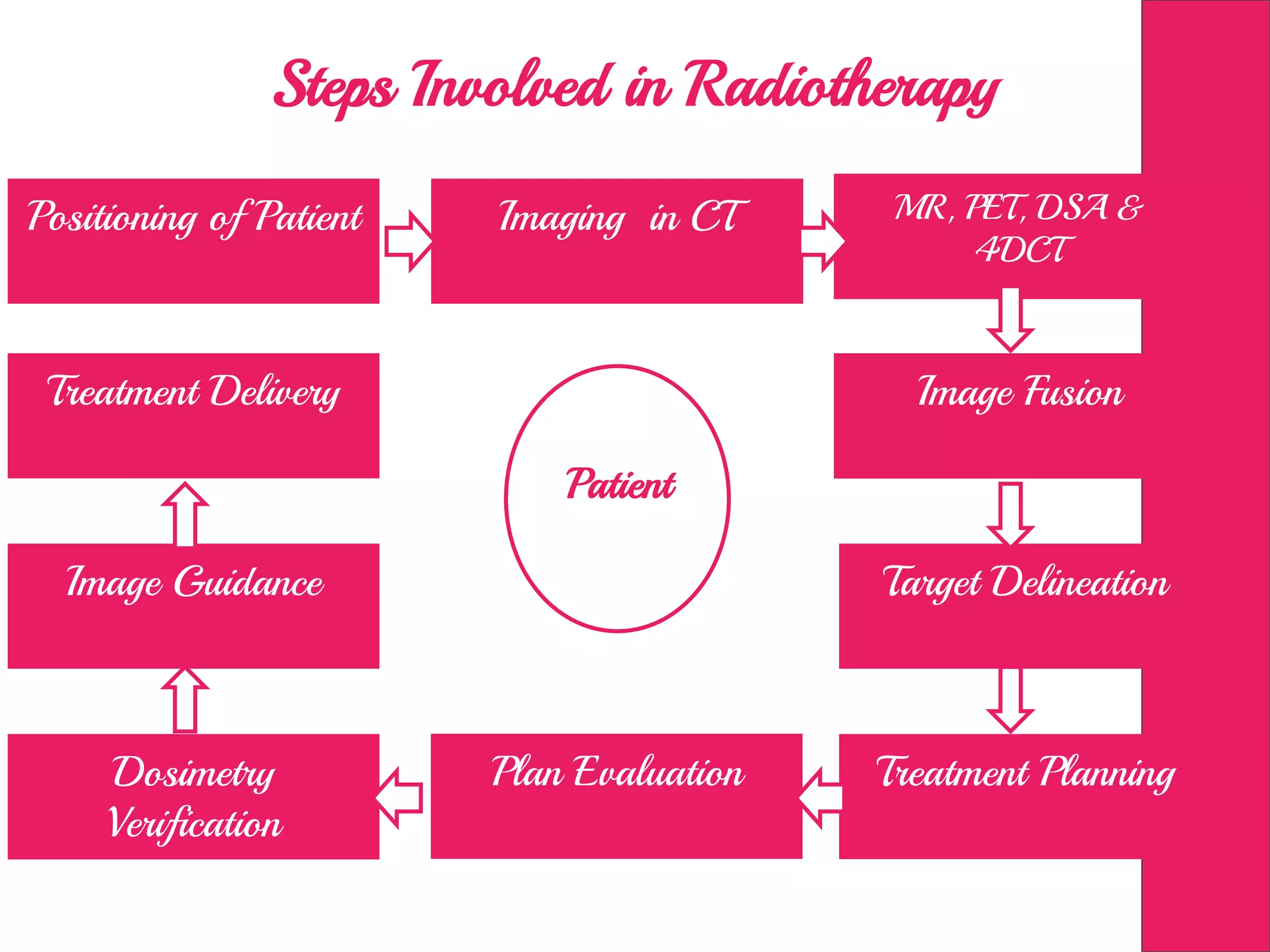
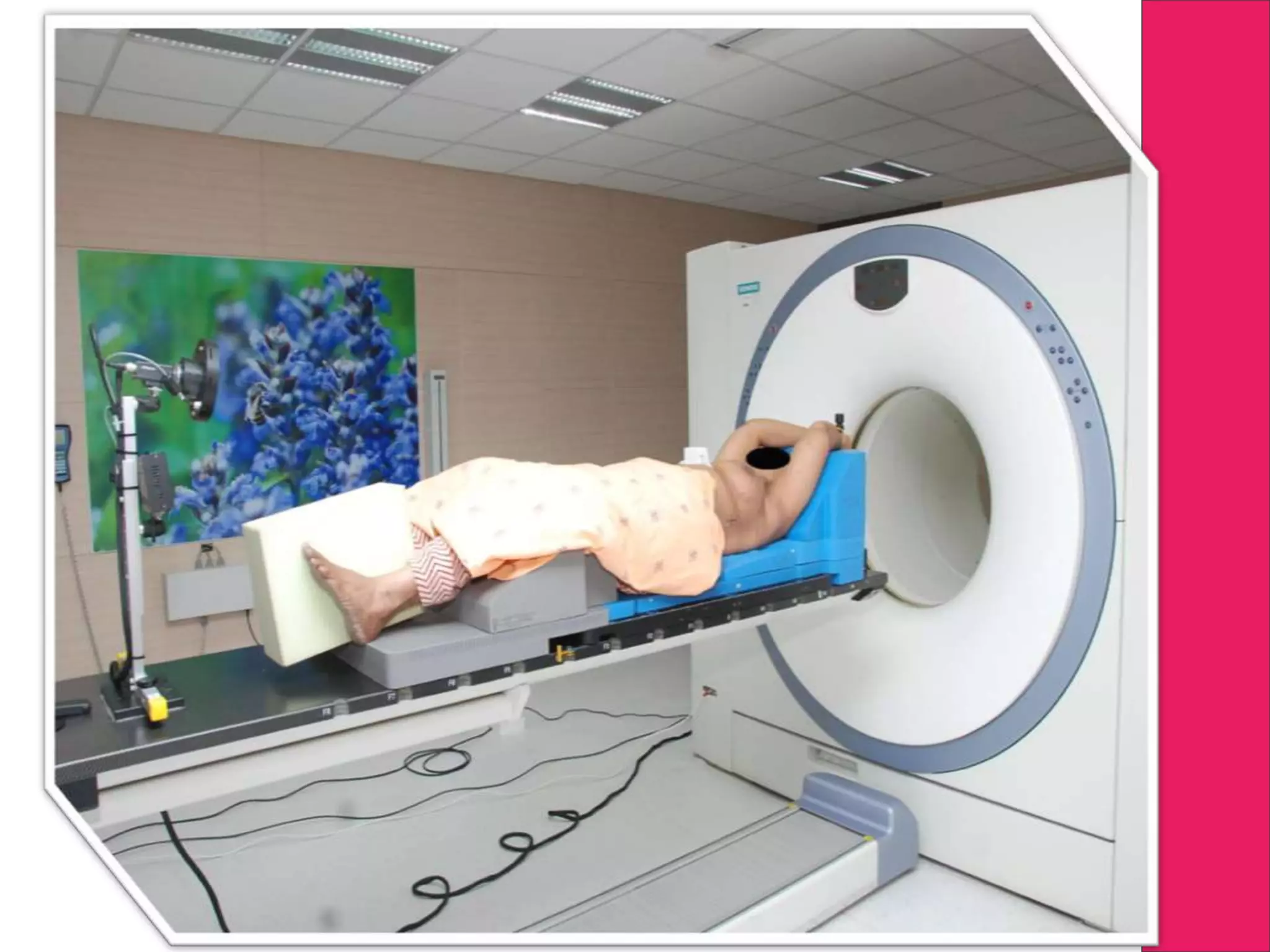
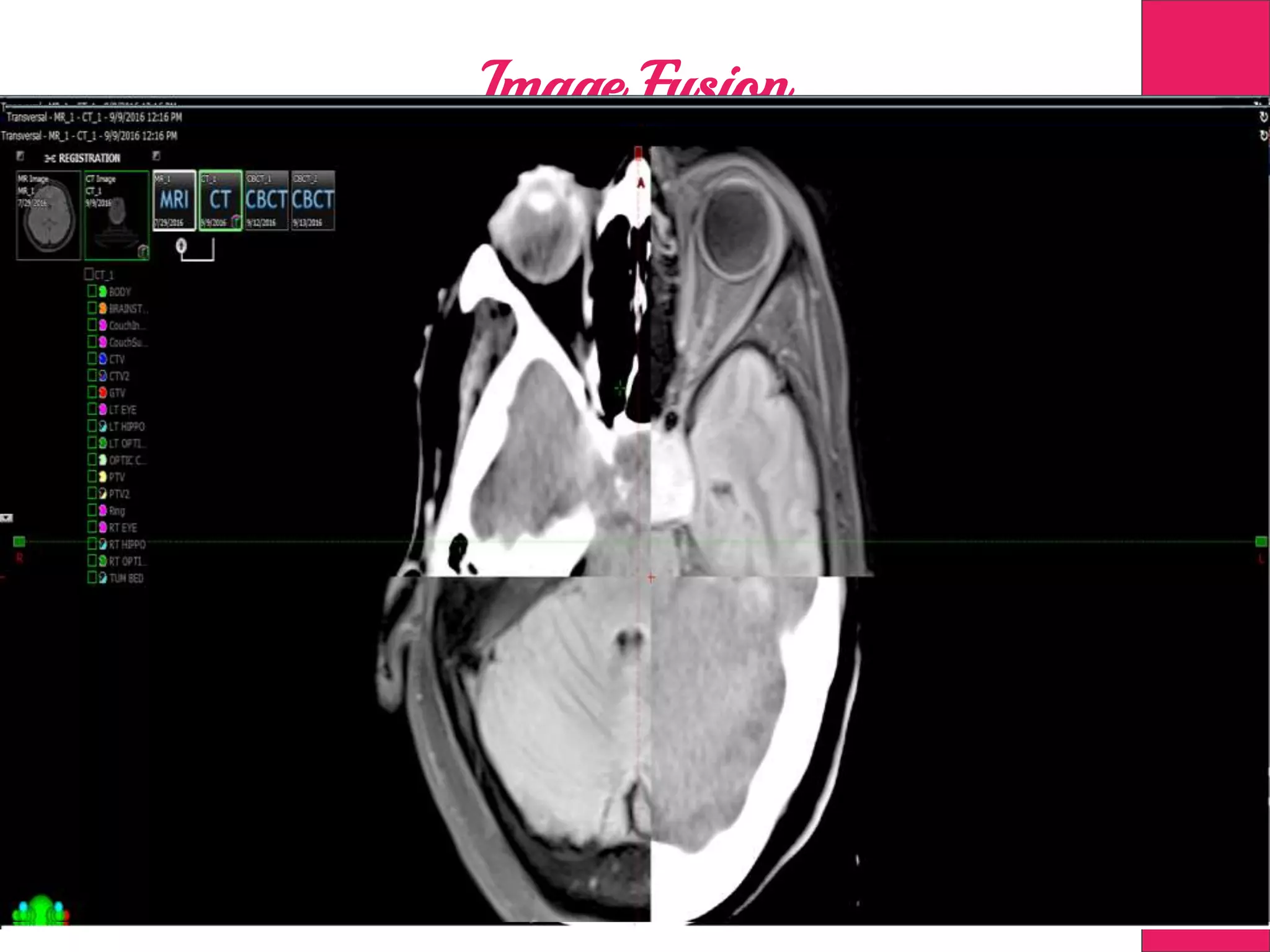
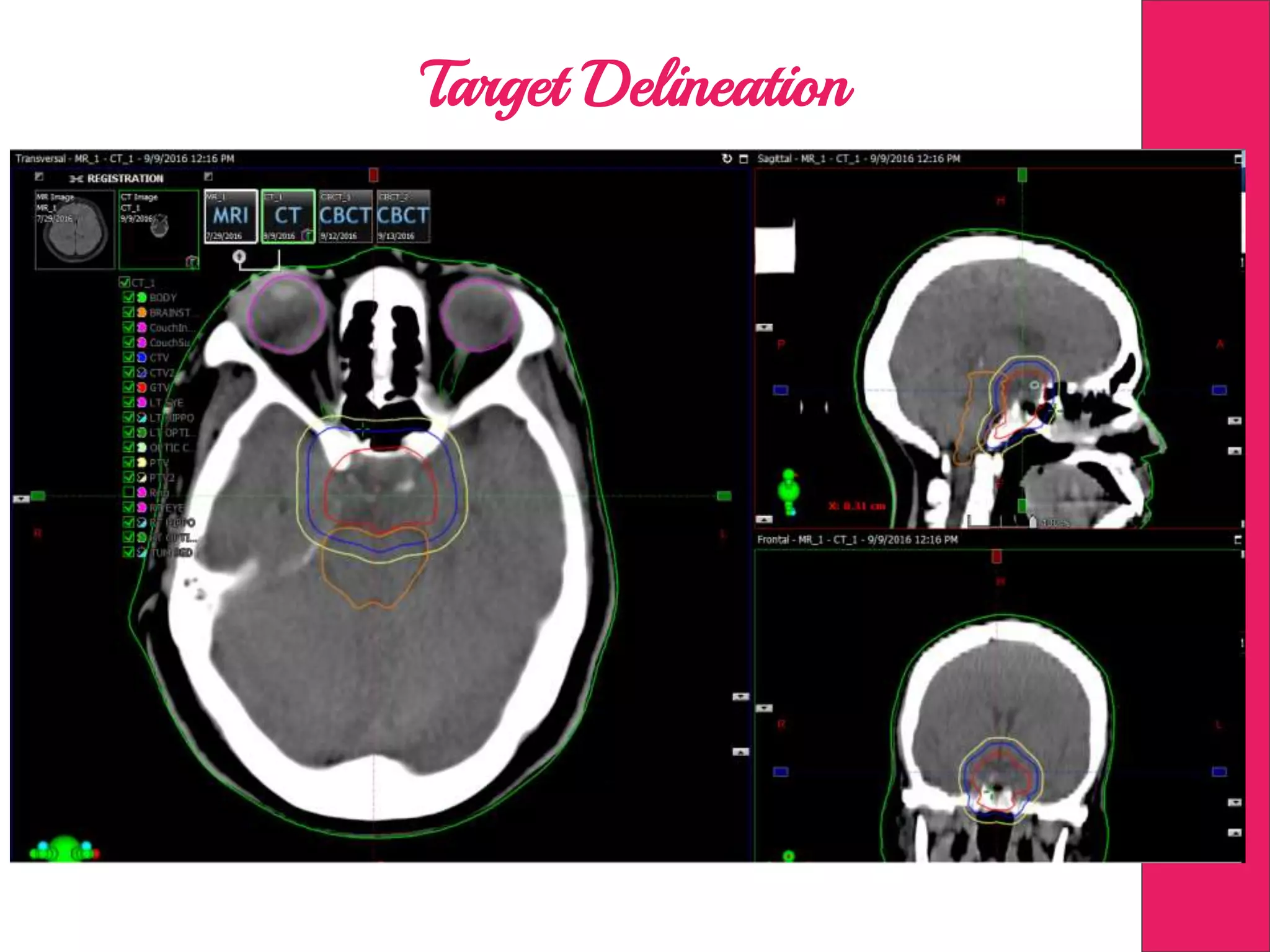
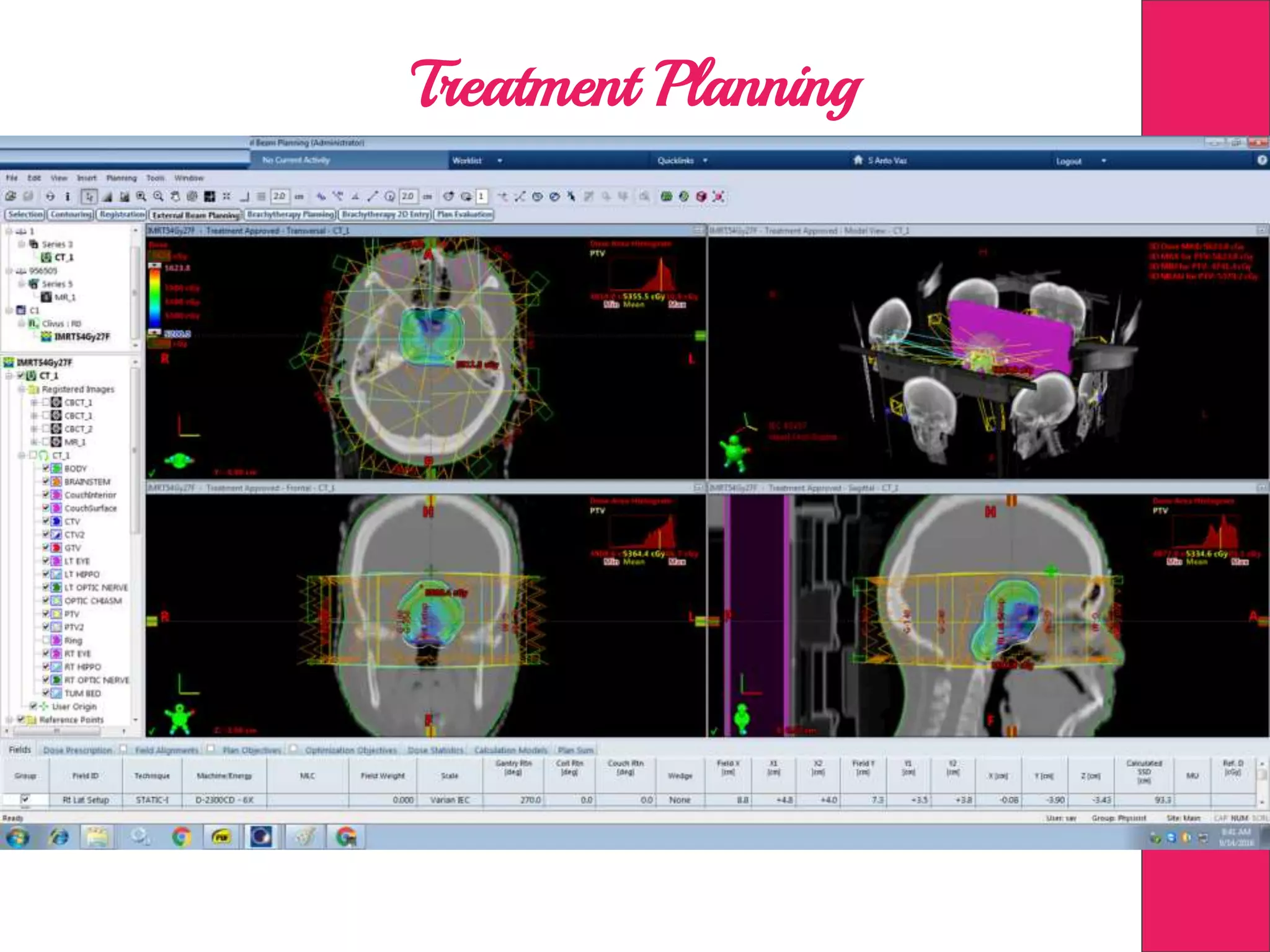
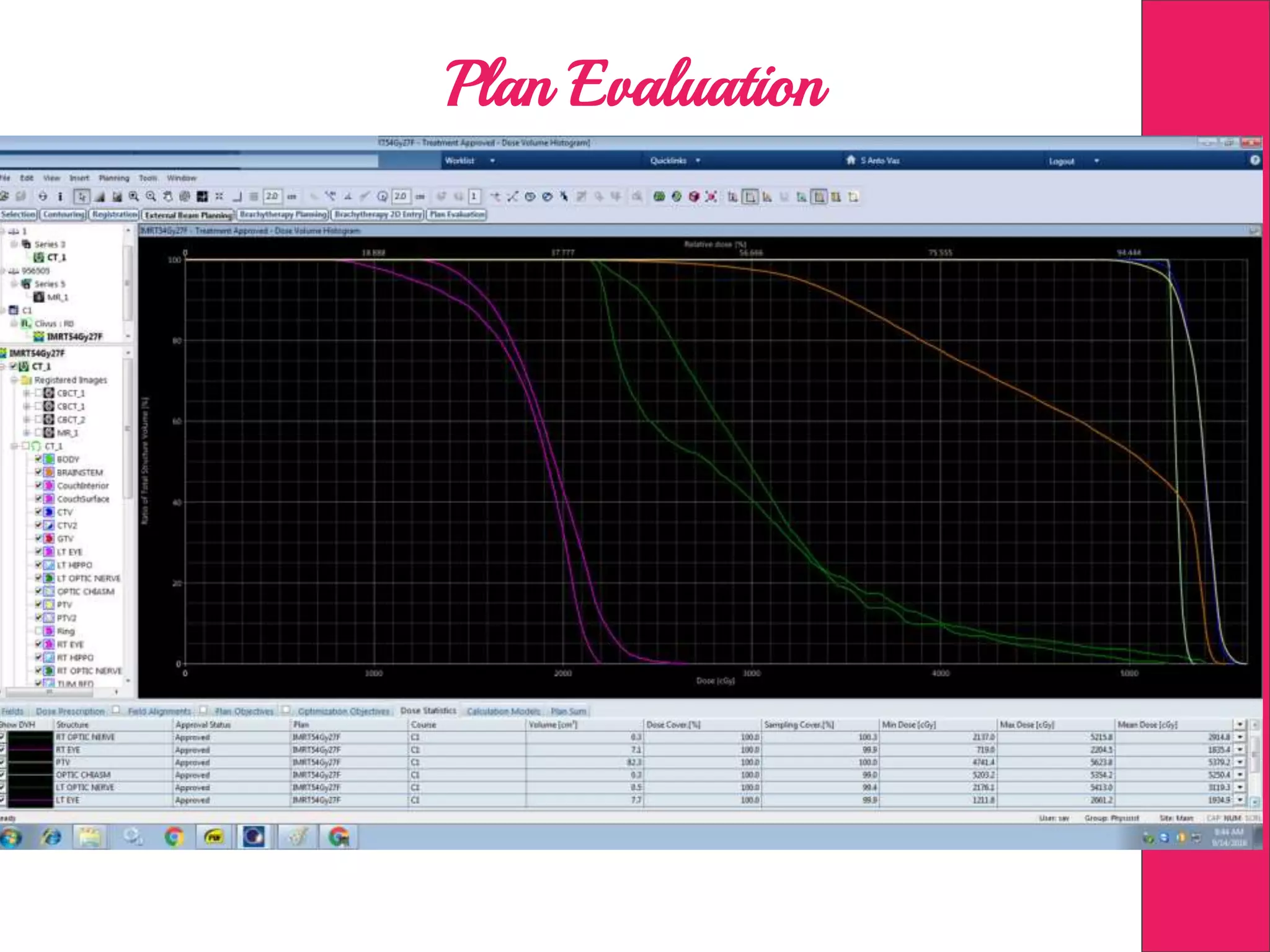
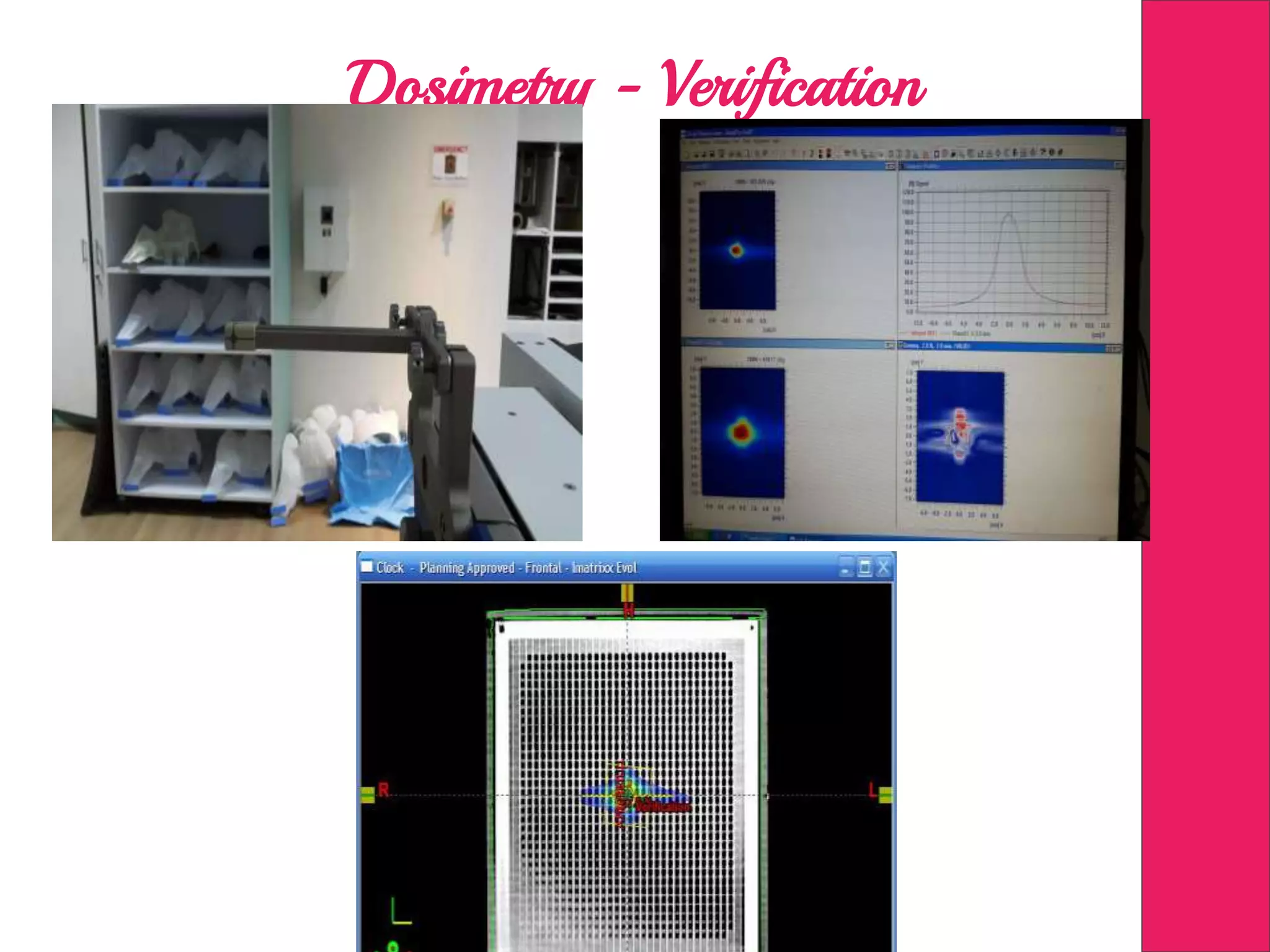
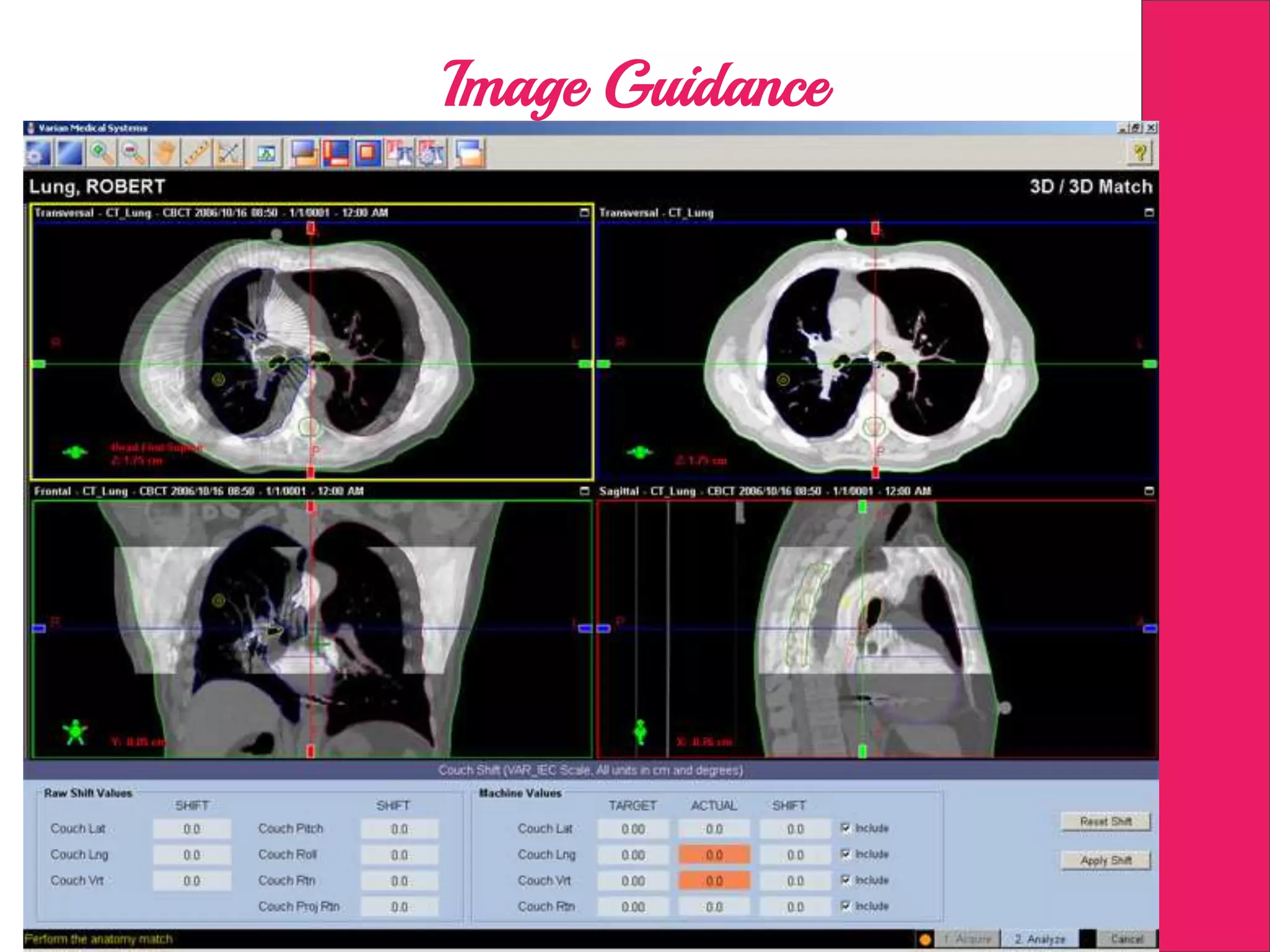
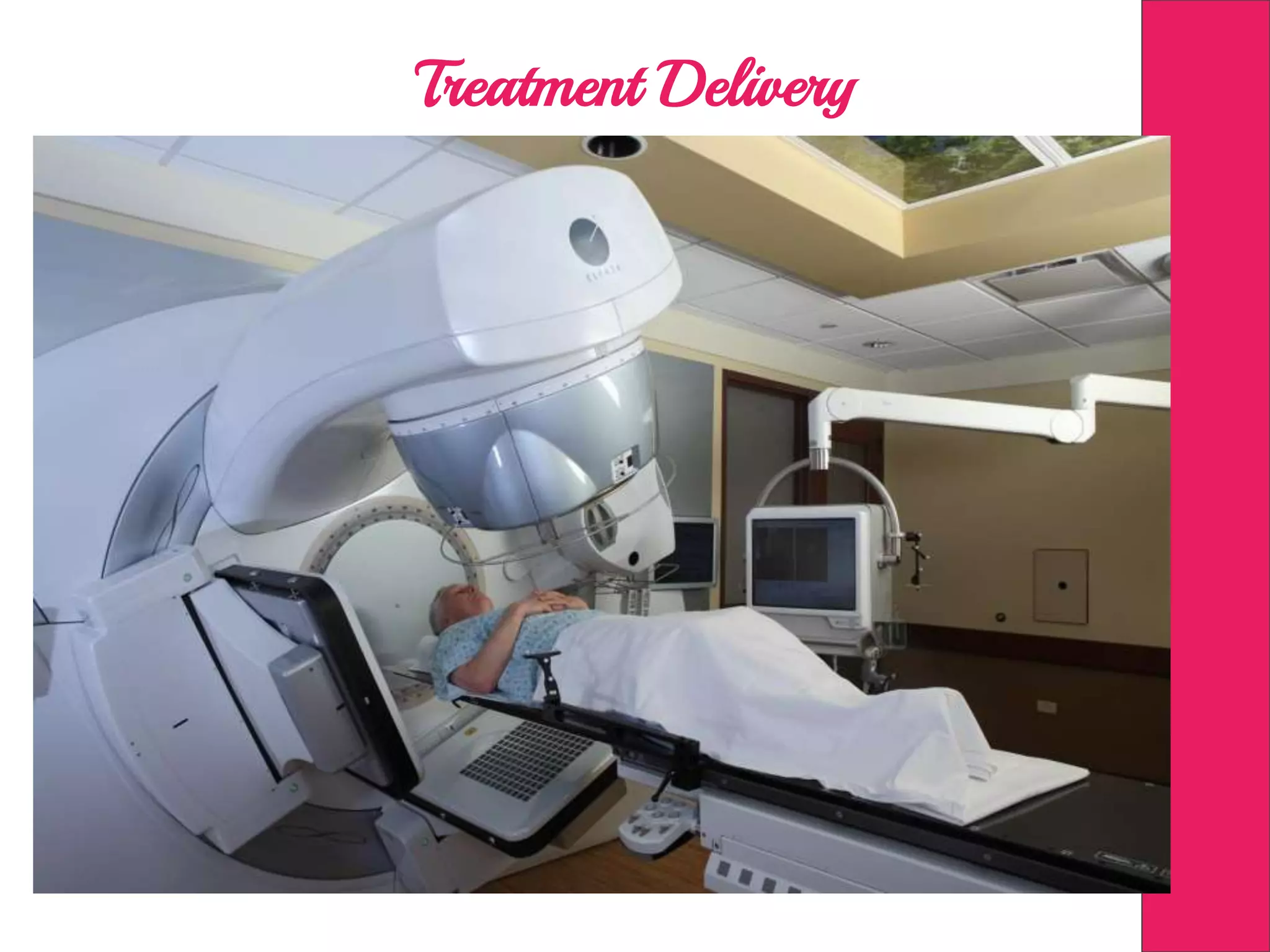
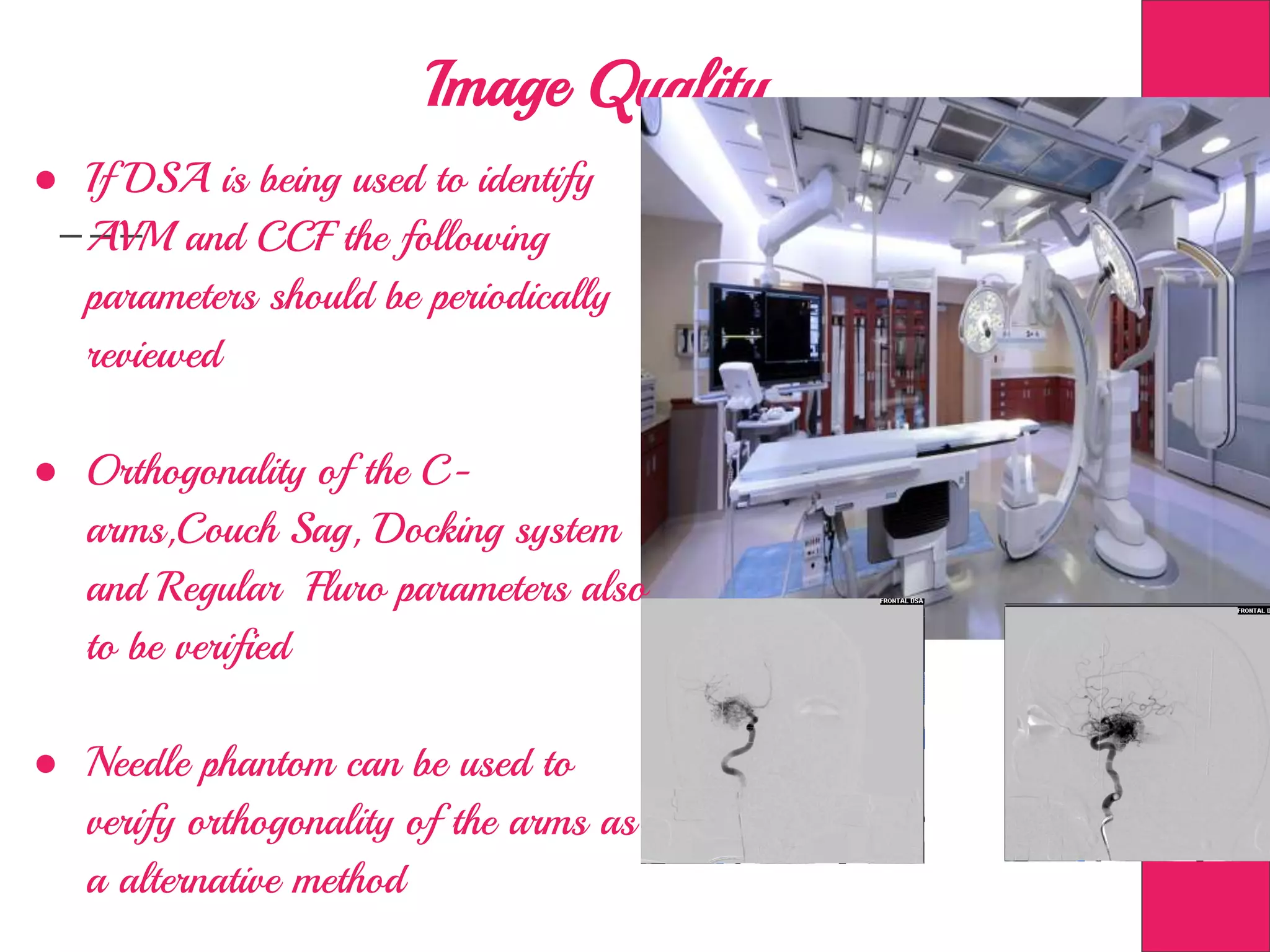
This document discusses image processing in measurement guided radiotherapy and geometric accuracy. It provides an outline on the history of x-rays and medical imaging, types of radiotherapy including 2D, 3DCRT, IMRT, IGRT and SRS. It describes the key steps involved in radiotherapy including patient positioning, imaging, treatment planning, dosimetry and treatment delivery. It emphasizes the importance of quality assurance for imaging and treatment machines to ensure geometric accuracy and highlights periodic training as important for all staff involved.