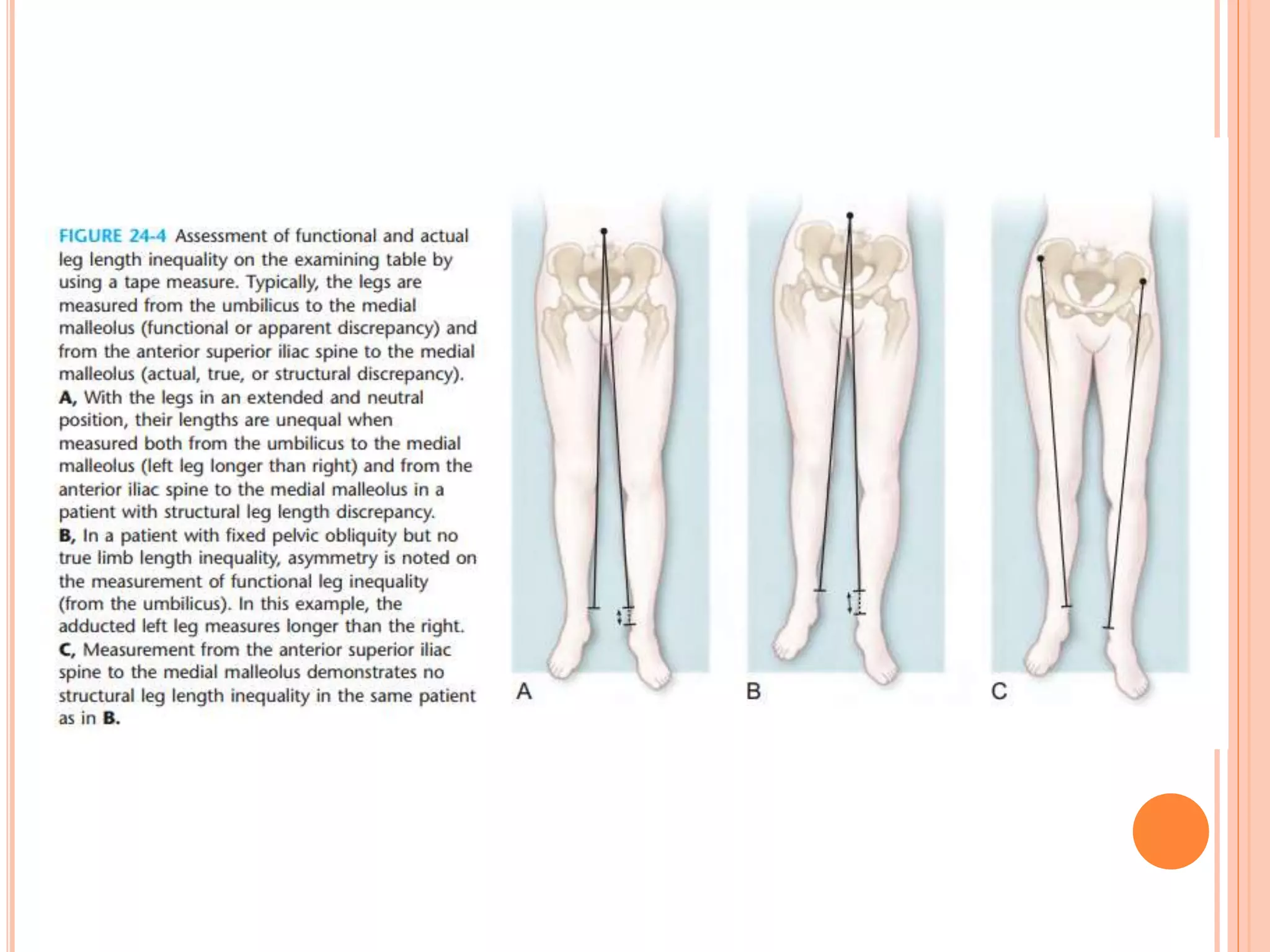
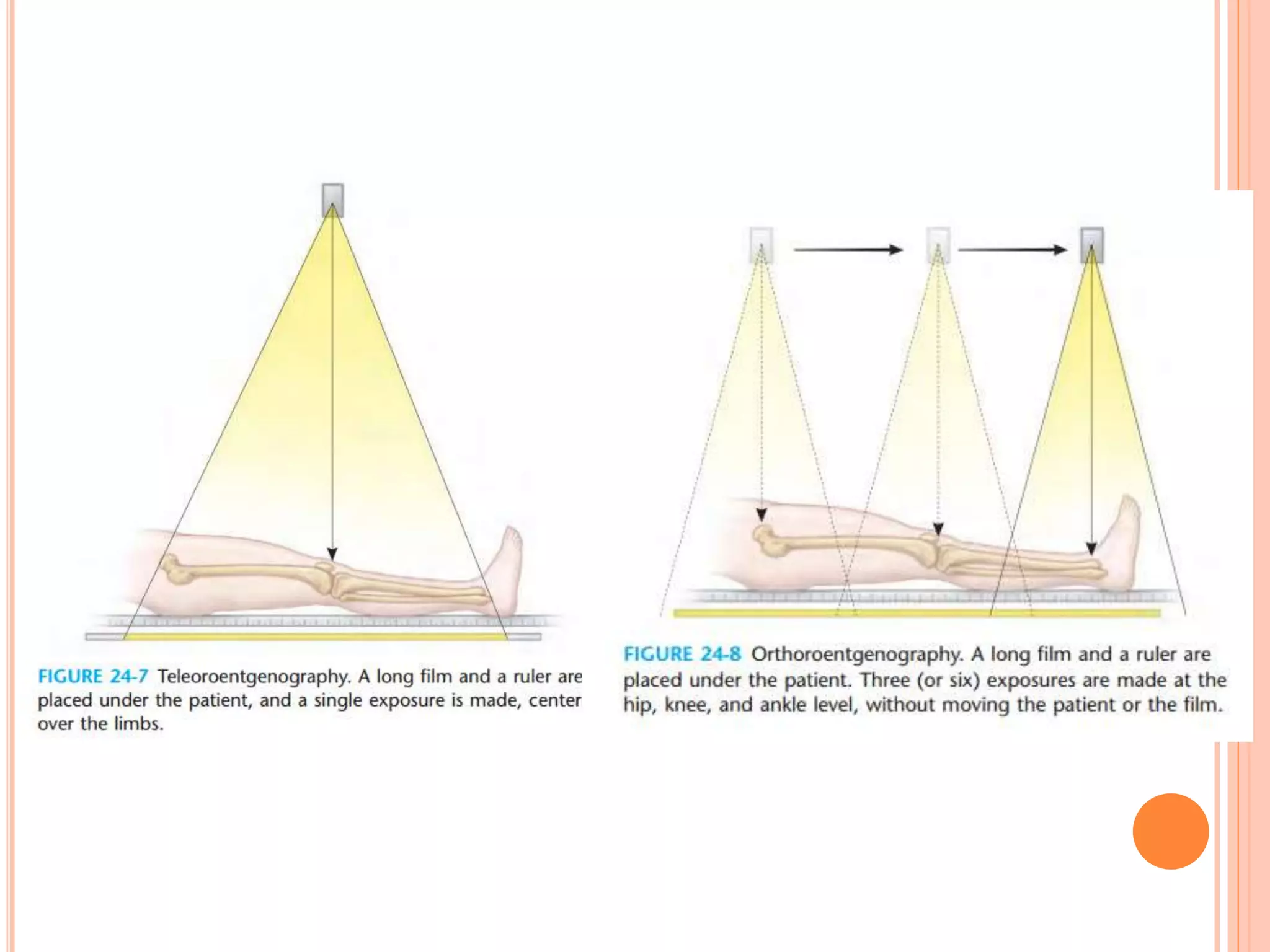
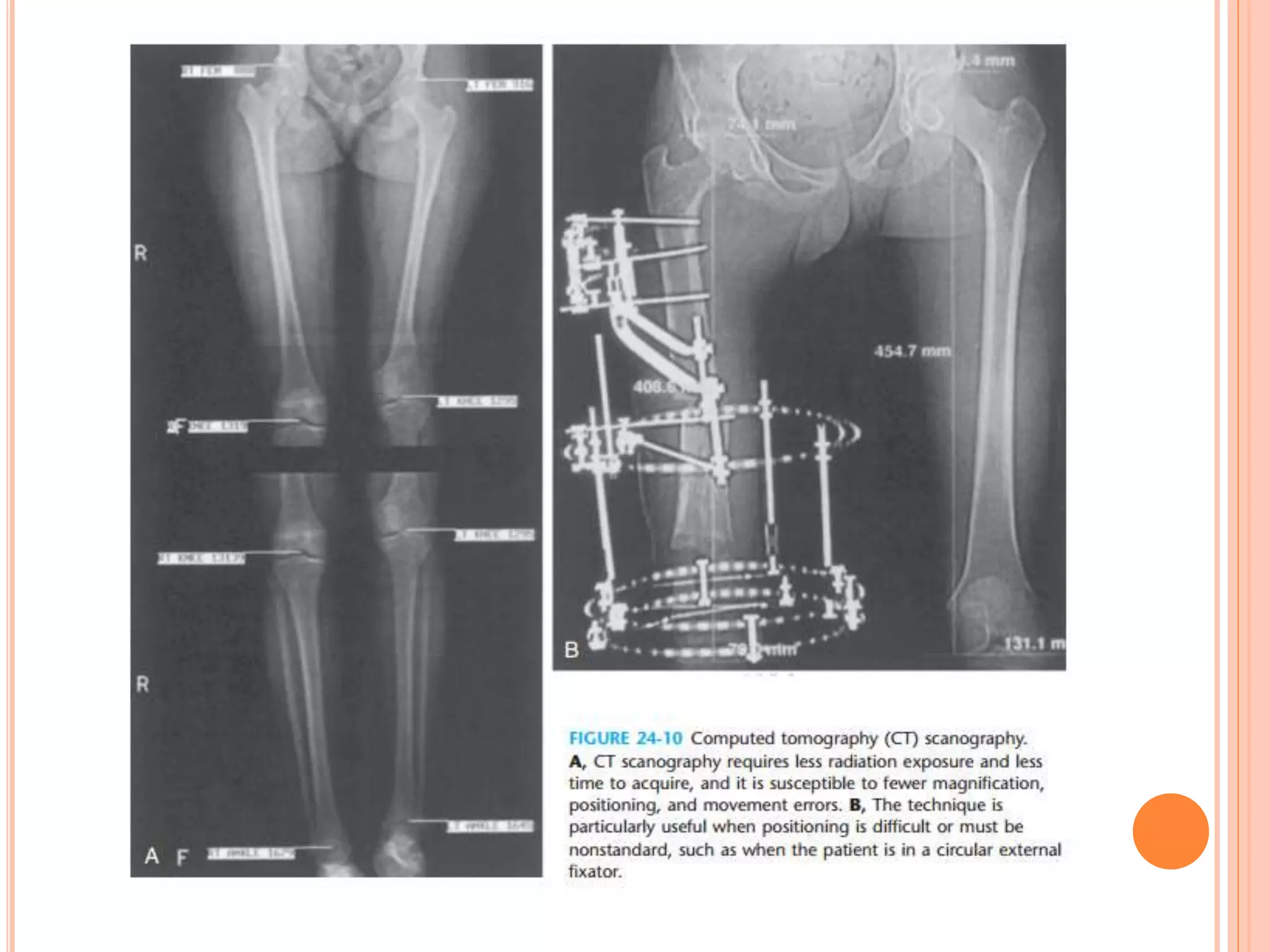
This document provides an overview of limb length discrepancy, including leg length inequality and angular deformities. It discusses the causes, impact, assessment, and prediction of leg length inequality in children. Key points include:
- Leg length discrepancies of 0.5-2cm are common, while over 2.5cm can cause back/joint pain due to abnormal gait.
- Causes include congenital factors, trauma, infection, or irradiation damaging growth plates.
- Assessment involves history, exam including blocks under the short leg, and imaging like radiography or CT to measure discrepancy.
- Several methods can predict remaining growth, like the Anderson-Green-Messner charts or Moseley straight-line graph