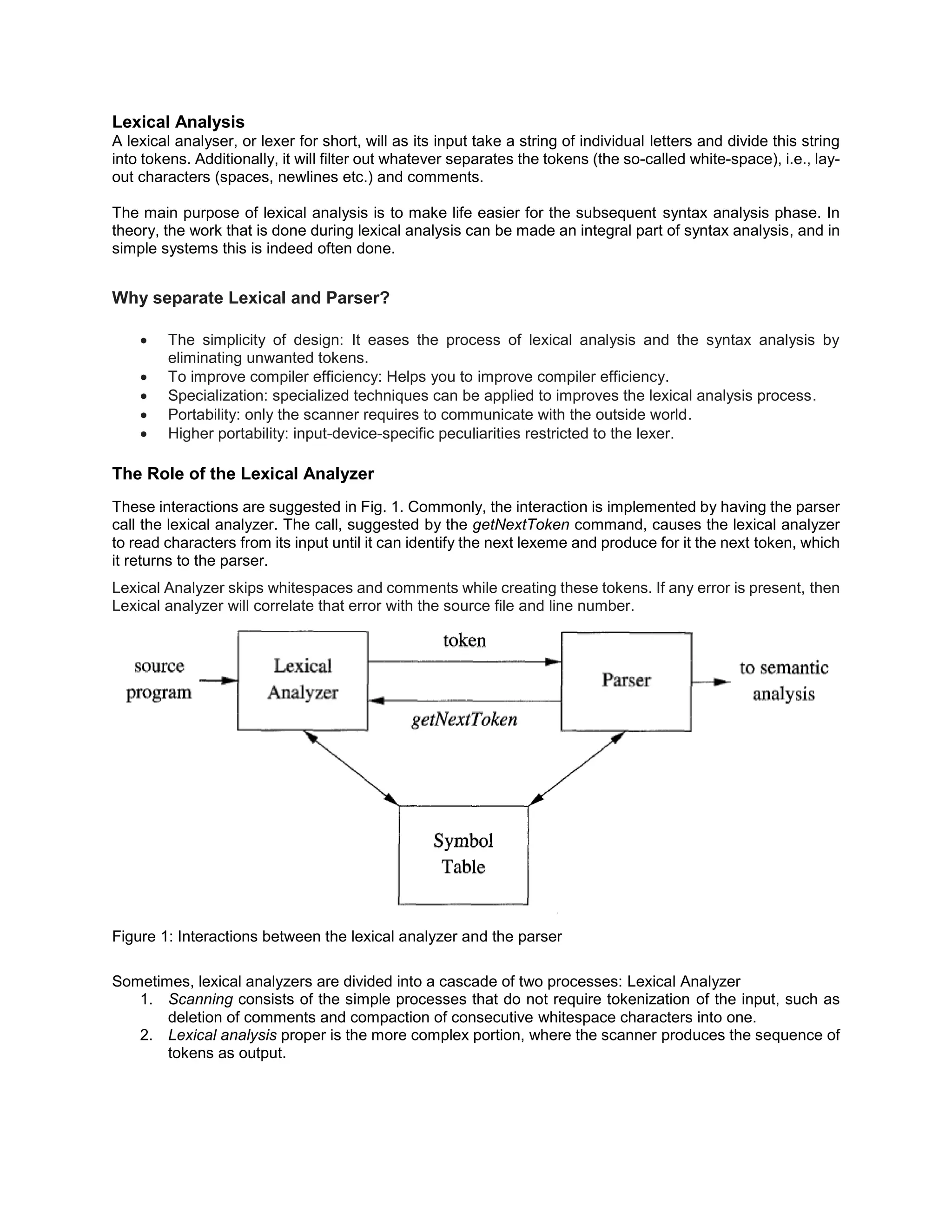
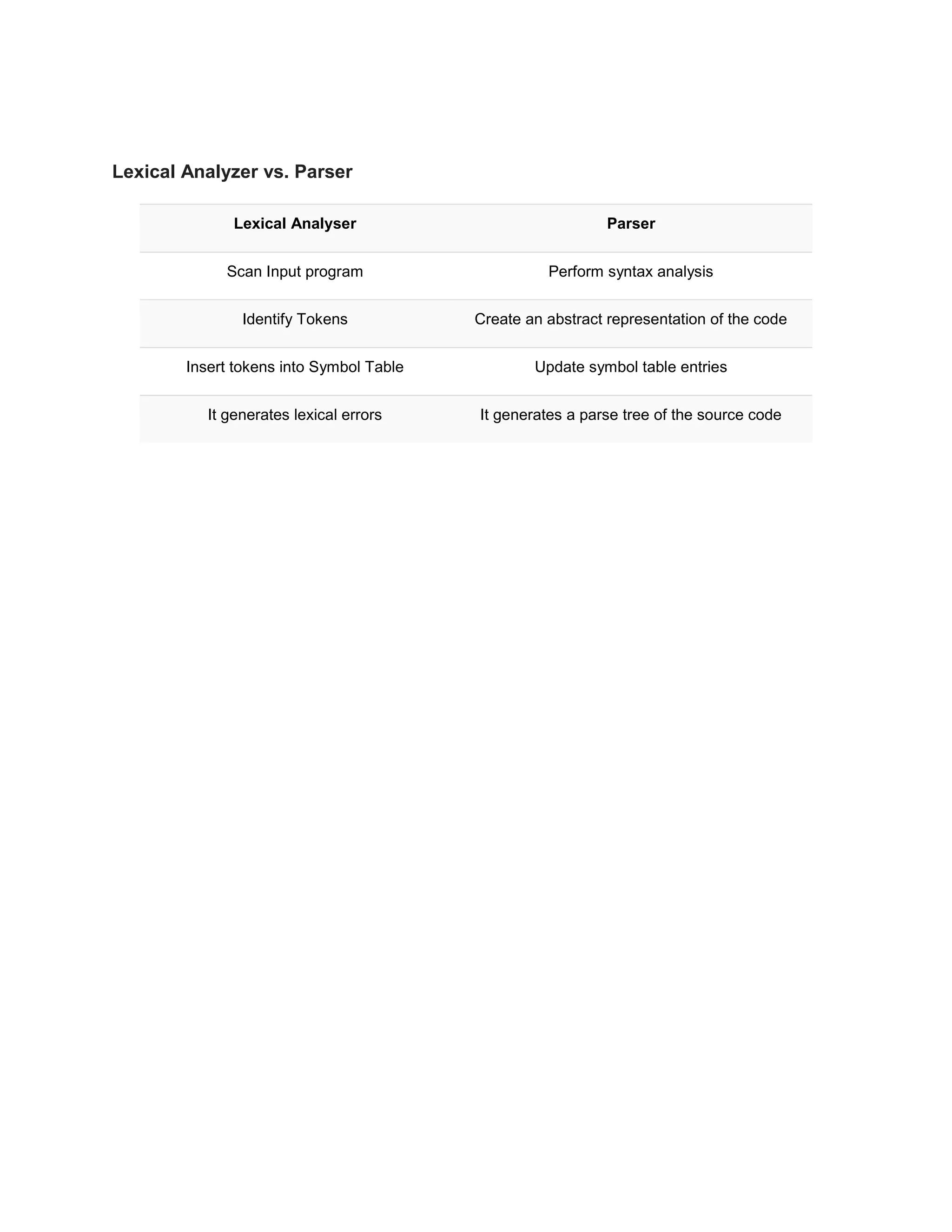
The lexical analyzer takes a string of characters as input and divides it into tokens, filtering out whitespace and comments. It interacts with the parser by returning tokens one by one when called. The lexical analyzer simplifies the work of the parser by eliminating unwanted tokens and errors are correlated with line numbers. It is sometimes divided into a scanning and analysis process. In comparison, the parser performs syntax analysis by creating an abstract representation and symbol table entries while the lexical analyzer identifies tokens and inserts them into the symbol table.