Embed presentation
Download to read offline
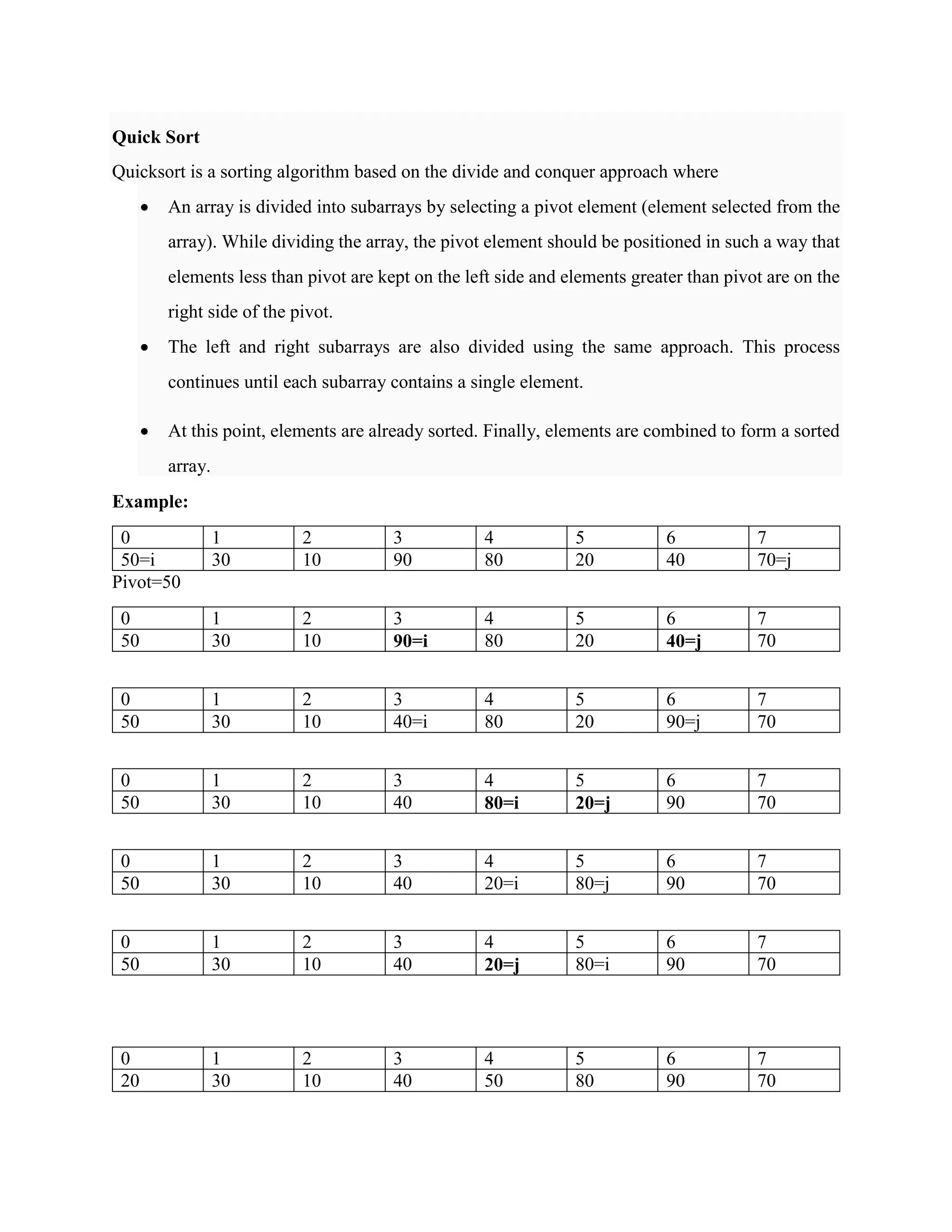

![5 6 7
80 70=j 90=i
5 6 7
70 80 90
Finally
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 20 30 40 50 70 80 90
Algorithm QuickSort(l,h)
{
if(l<h)
{
j=Partition(l,h);
QuickSort(l,j);
QuickSort(j+1,h);
}
}
Algorithm Partition(l,h)
{
Pivot=A[l];
i=l,j=h;
while(i<j)
{
do
{
i++;
}while(A[i]<=pivot);
do
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-210706145445/85/Quick-sort-3-320.jpg)
![j--;
}while(A[j]>pivot);
if(i<j)
swap(A[i],A[j]);
}
Swap(A[l],A[j]);
return j;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-210706145445/85/Quick-sort-4-320.jpg)

Quicksort is a sorting algorithm that uses a divide and conquer approach. It works by selecting a pivot element and partitioning the array around the pivot so that elements less than the pivot are to its left and greater elements are to its right. It then recursively applies this process to the subarrays until each contains a single element, at which point the array is fully sorted. The example demonstrates quicksort sorting an array from 0 to 7.


![5 6 7
80 70=j 90=i
5 6 7
70 80 90
Finally
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 20 30 40 50 70 80 90
Algorithm QuickSort(l,h)
{
if(l<h)
{
j=Partition(l,h);
QuickSort(l,j);
QuickSort(j+1,h);
}
}
Algorithm Partition(l,h)
{
Pivot=A[l];
i=l,j=h;
while(i<j)
{
do
{
i++;
}while(A[i]<=pivot);
do
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-210706145445/85/Quick-sort-3-320.jpg)
![j--;
}while(A[j]>pivot);
if(i<j)
swap(A[i],A[j]);
}
Swap(A[l],A[j]);
return j;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicksort-210706145445/85/Quick-sort-4-320.jpg)