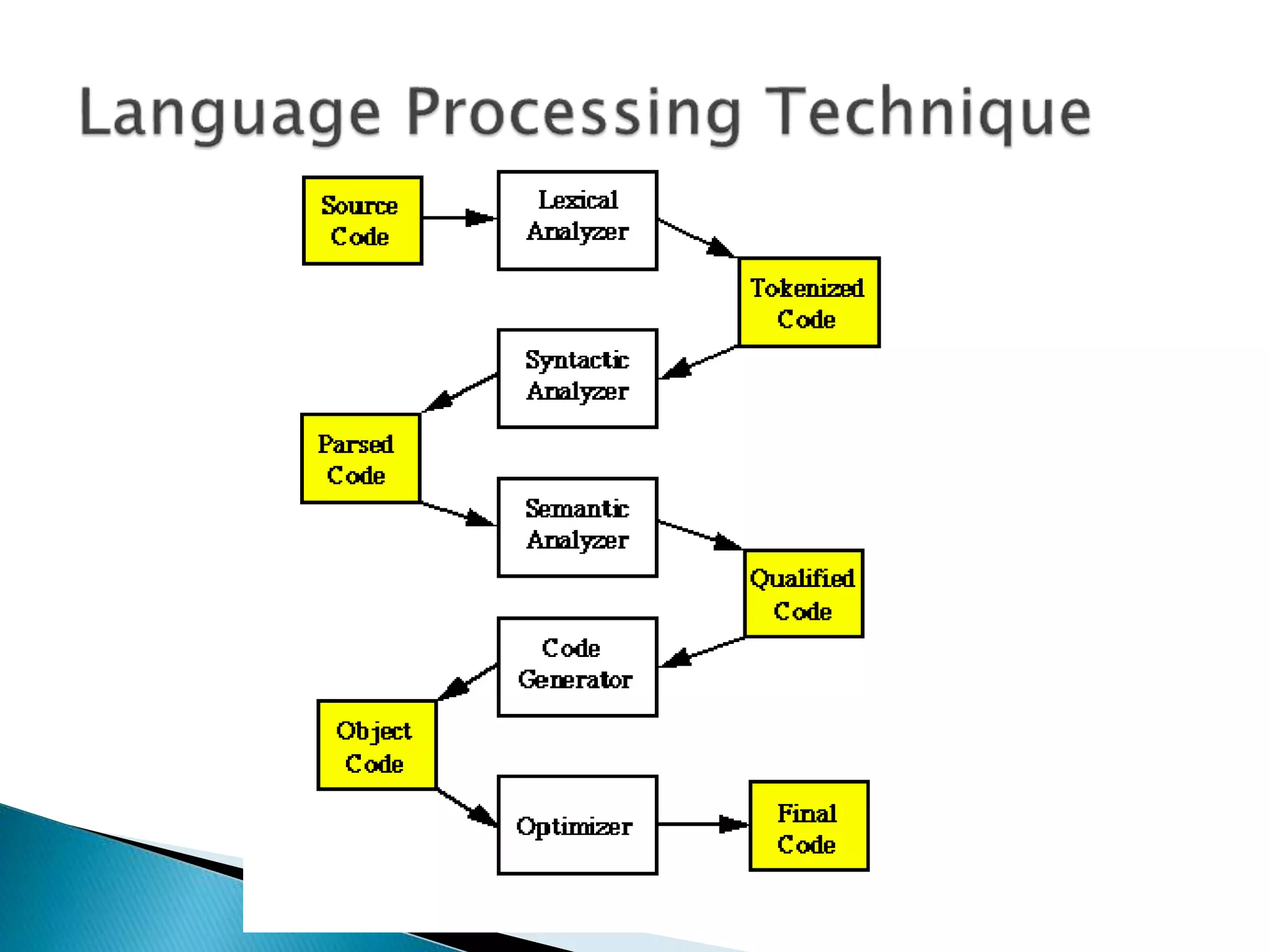
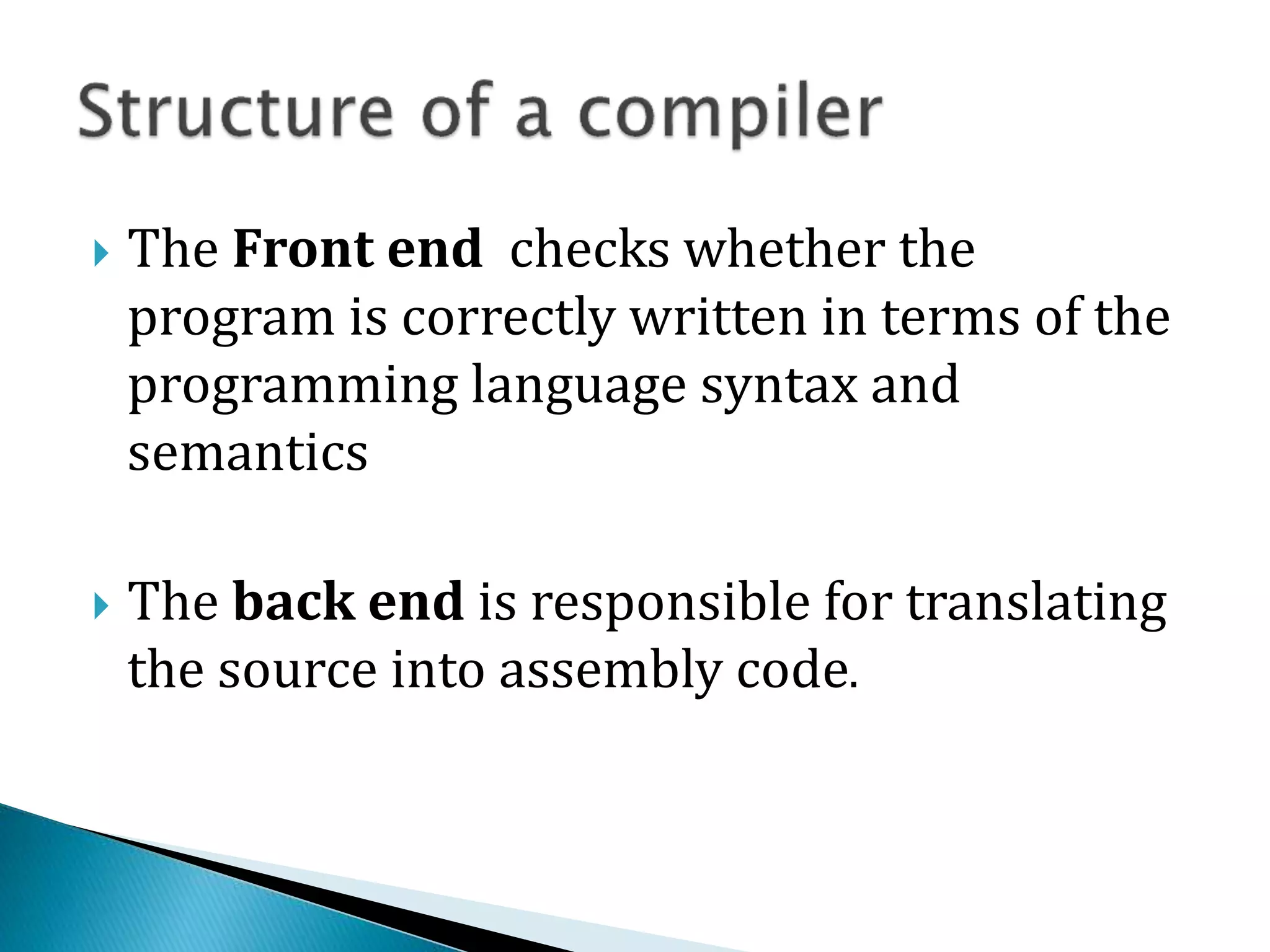
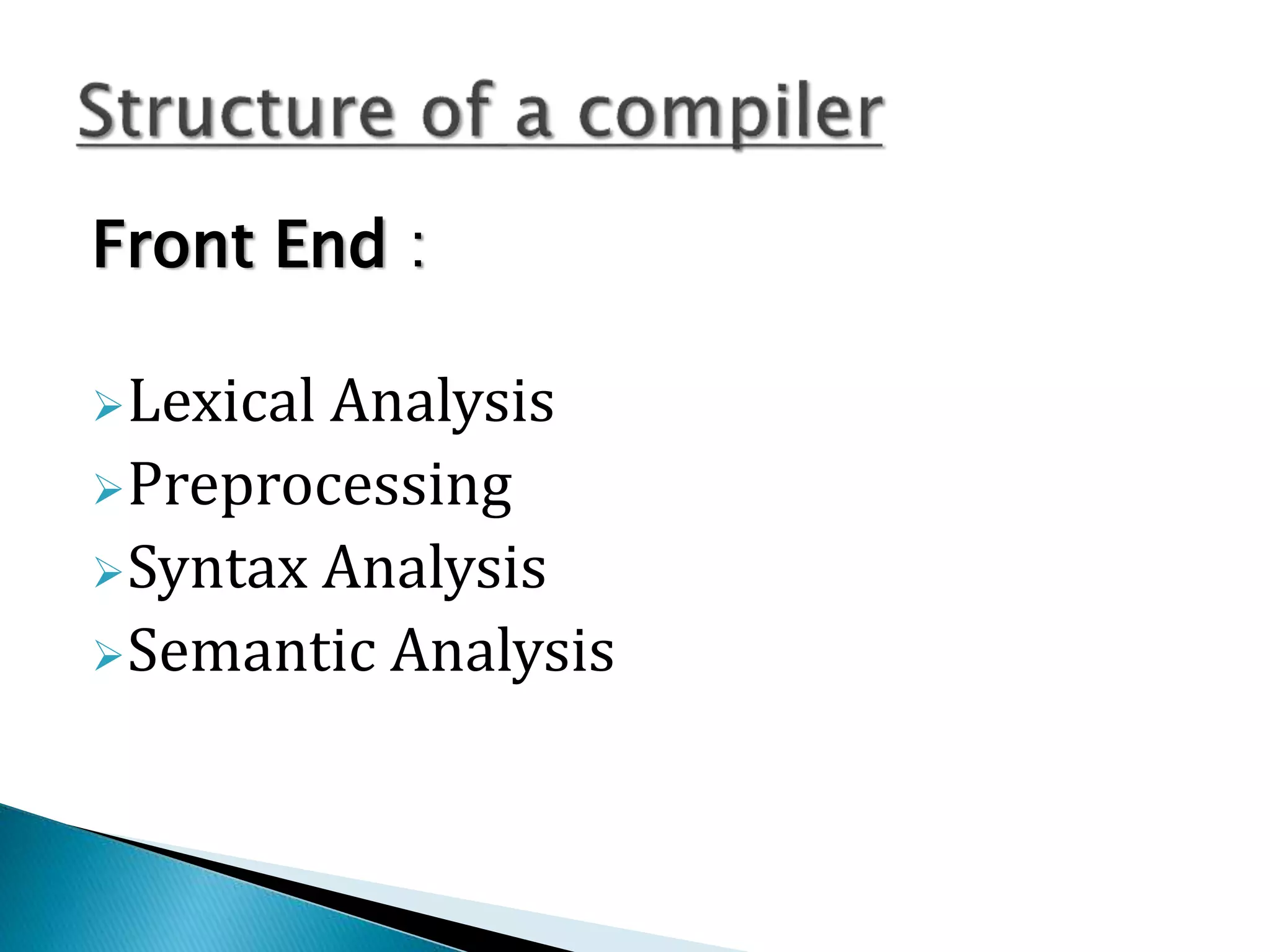
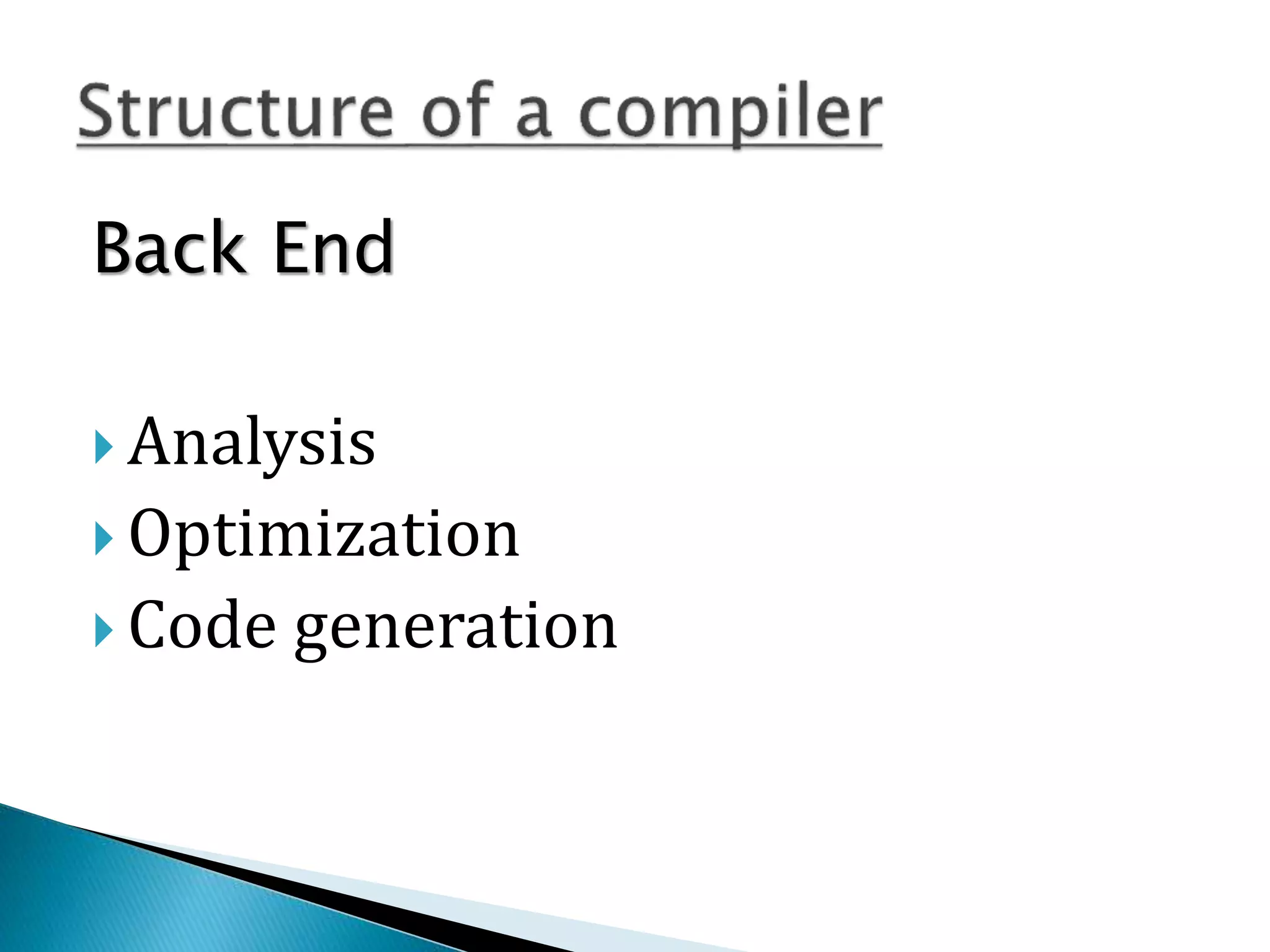
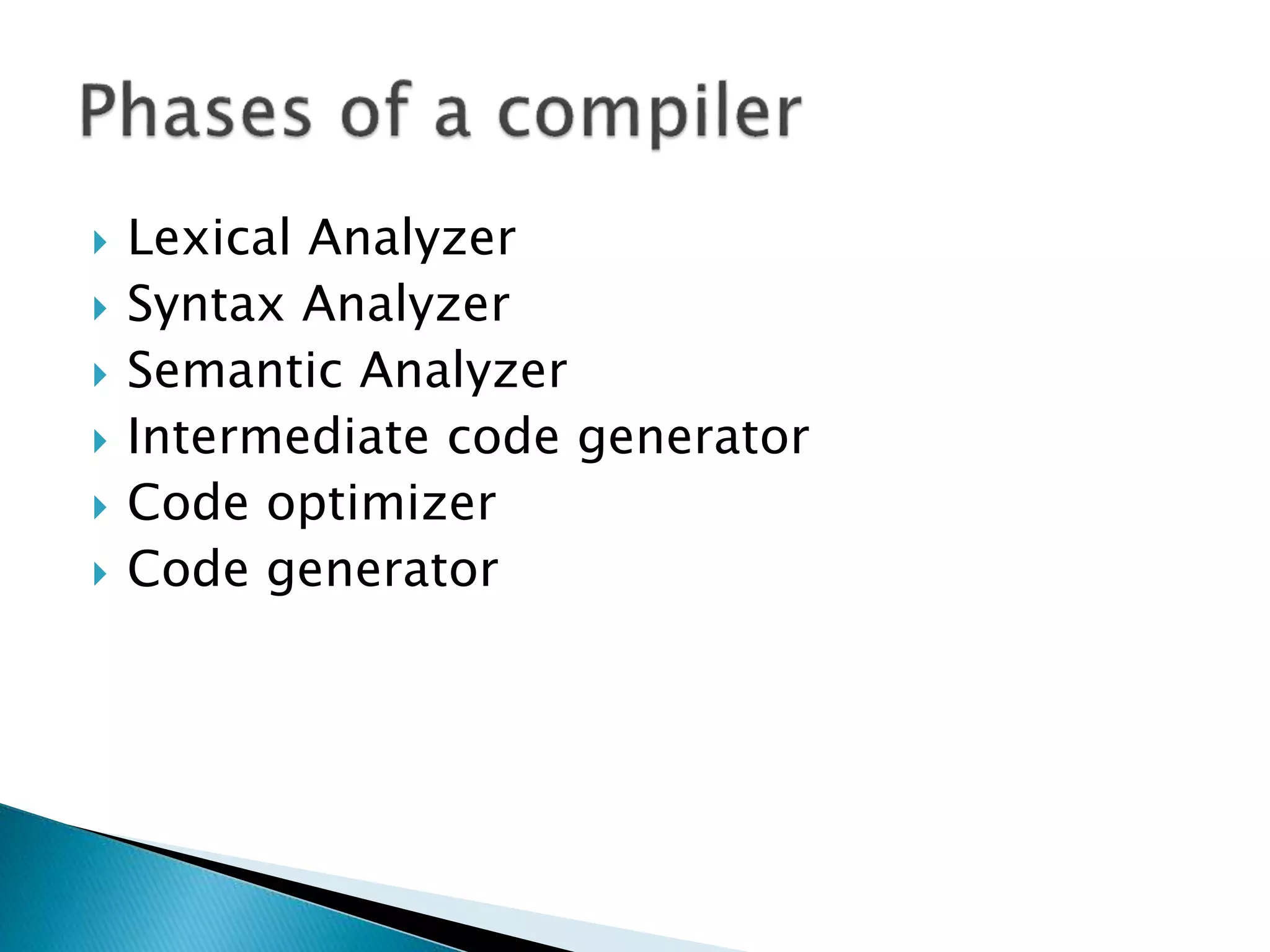
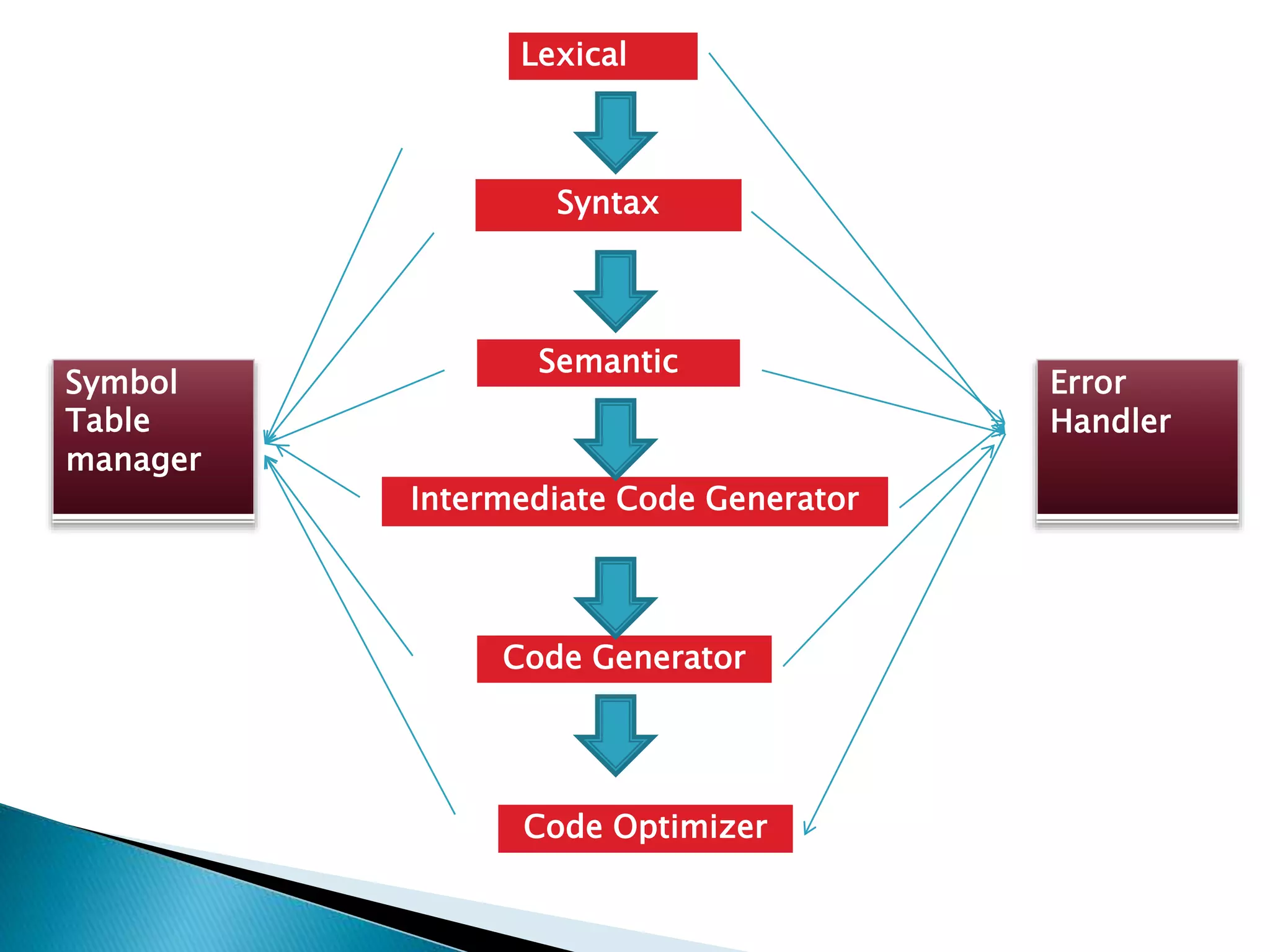
The document discusses the different phases of a compiler:
1) The front end checks the syntax and semantics of the source code and the back end translates it to assembly code.
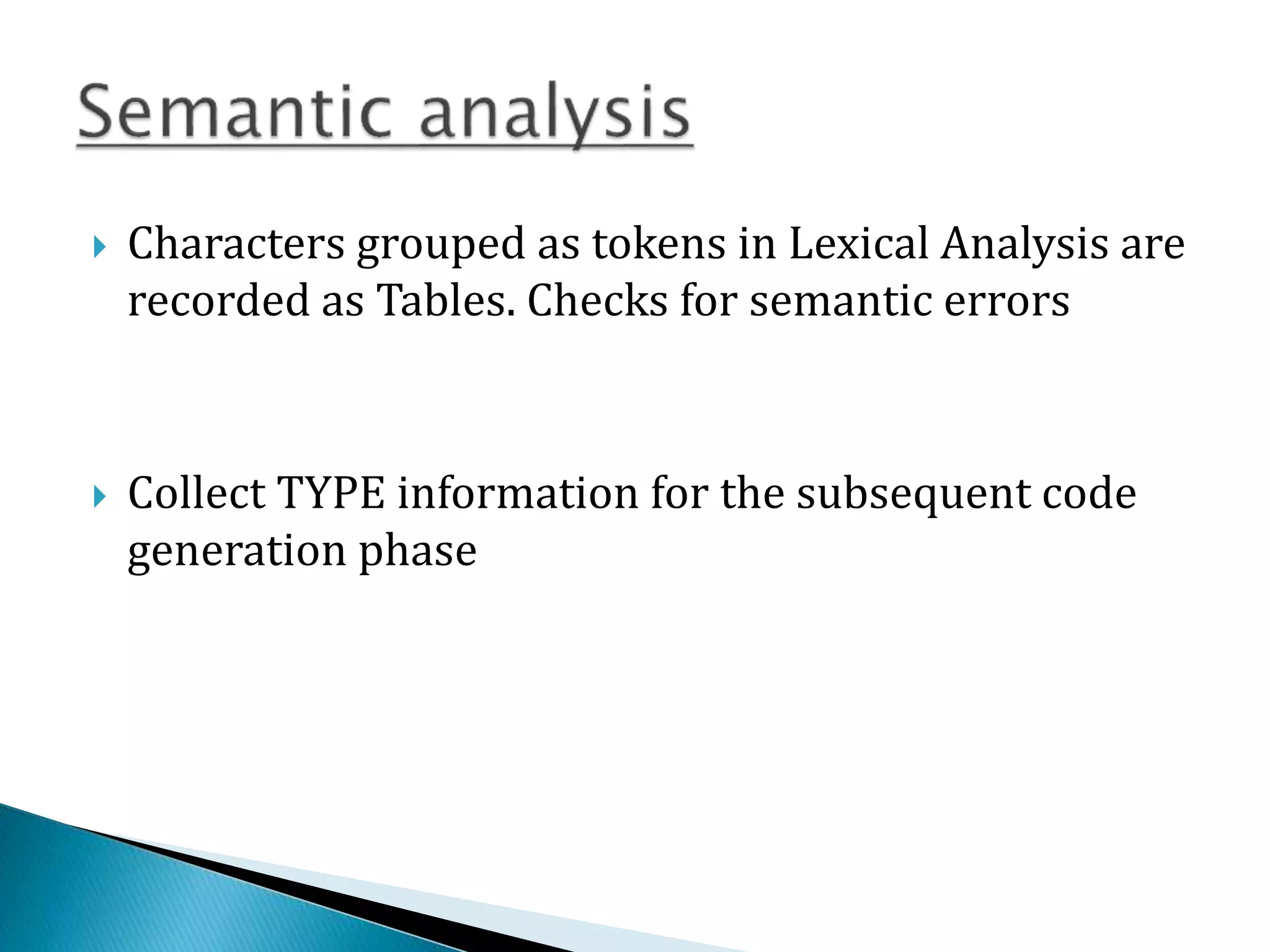
2) The front end contains lexical analysis, preprocessing, syntax analysis, and semantic analysis. The back end contains analysis, optimization, and code generation.
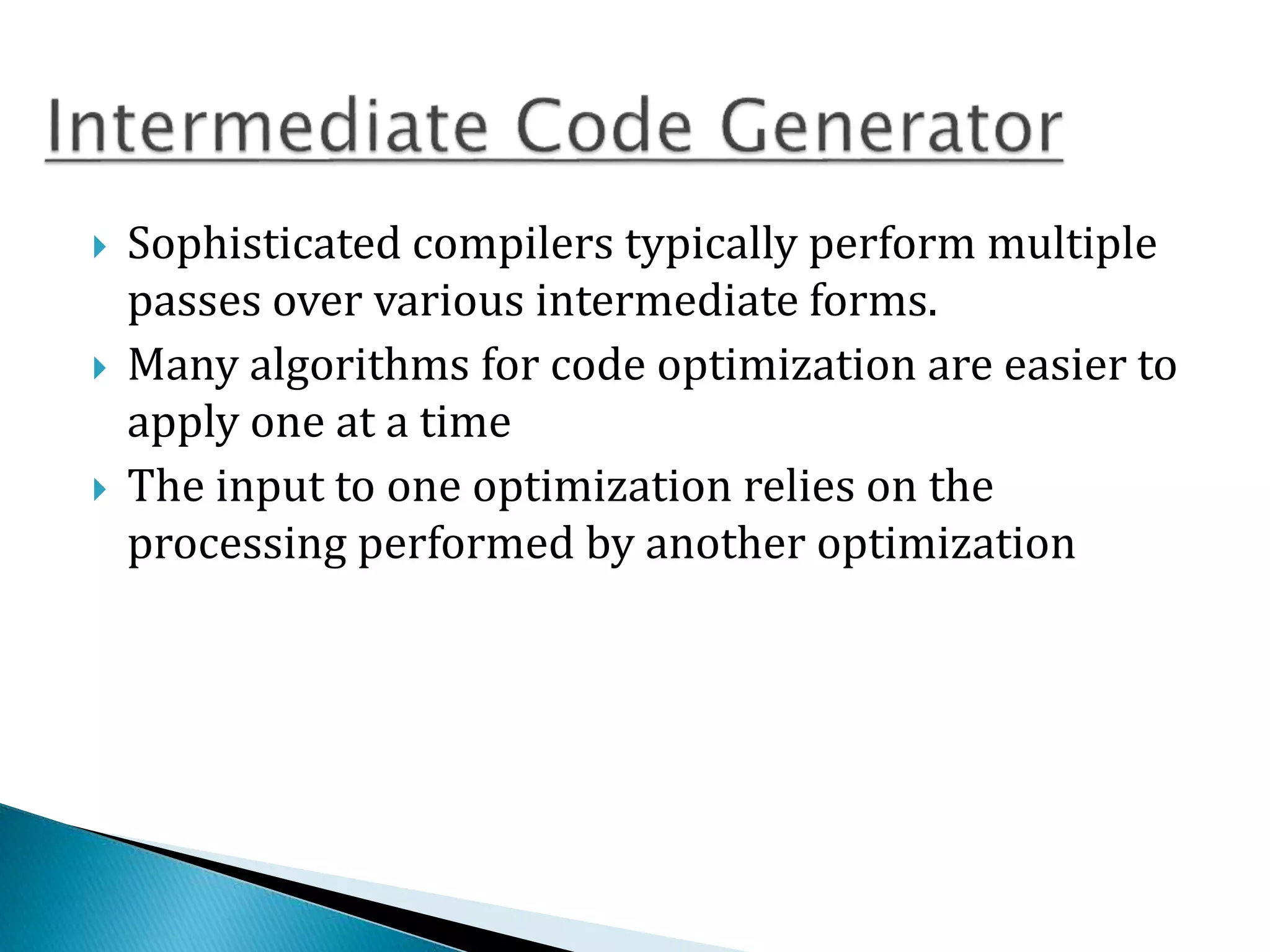
3) Optimization aims to improve the intermediate code to increase performance by reducing complexity and leading to faster execution.


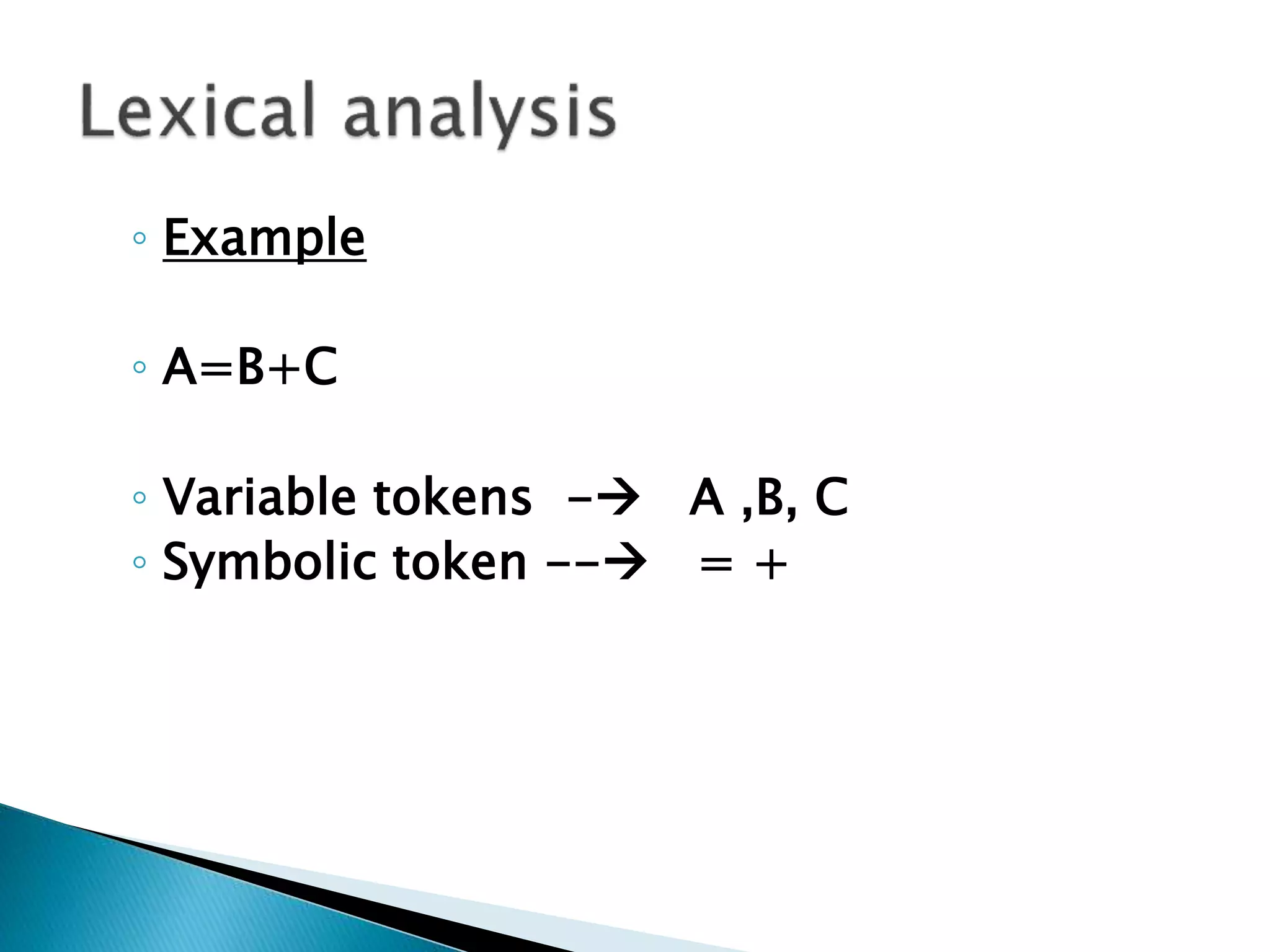


![ Declarations of ordinary C variables
,constants and Libraries.
%{
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
%}
flex definitions :- name definition
Digit [0-9] (Regular Definition)
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compilerdesign-170426184632/75/Compiler-design-and-lexical-analyser-14-2048.jpg)
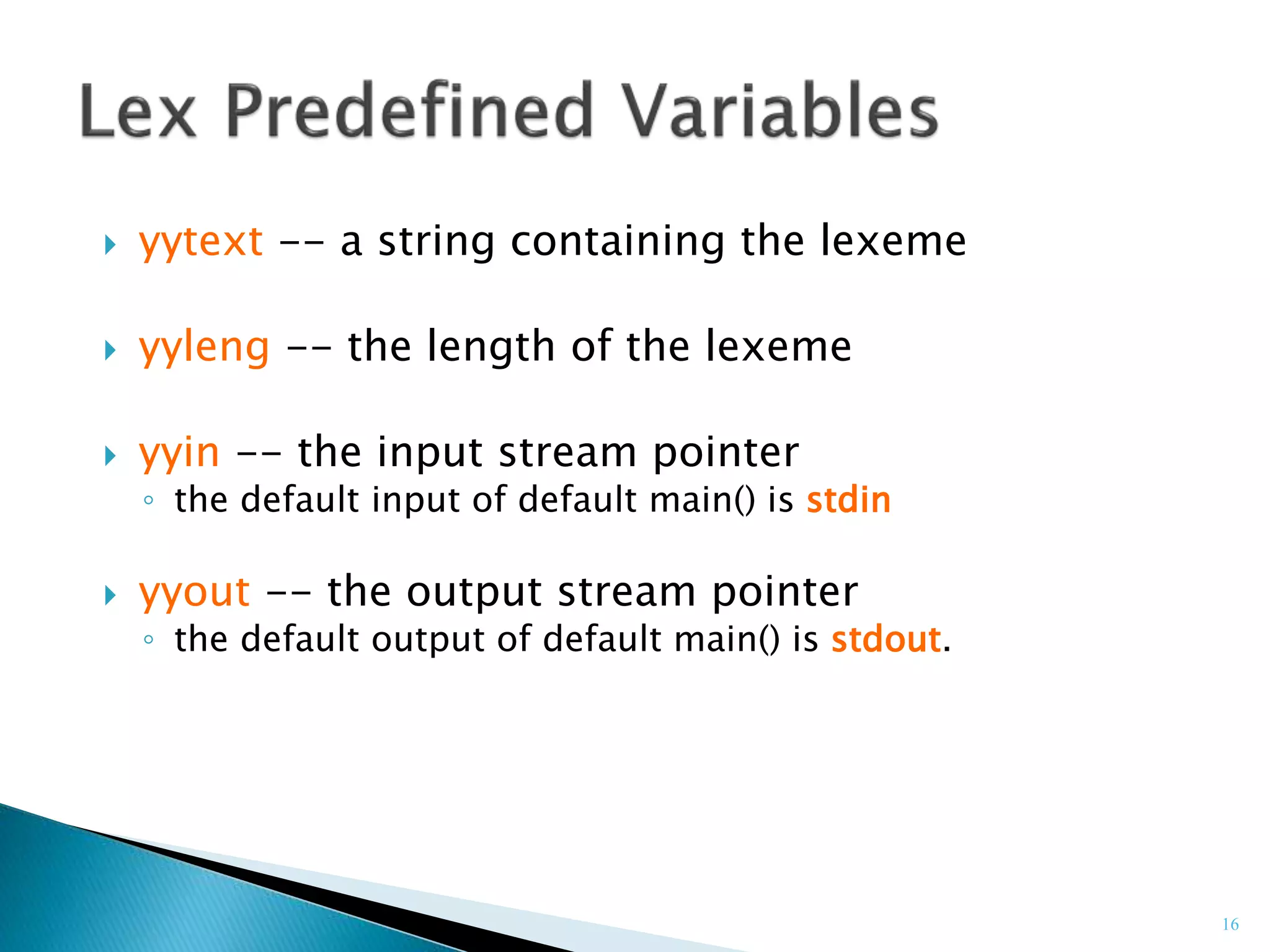

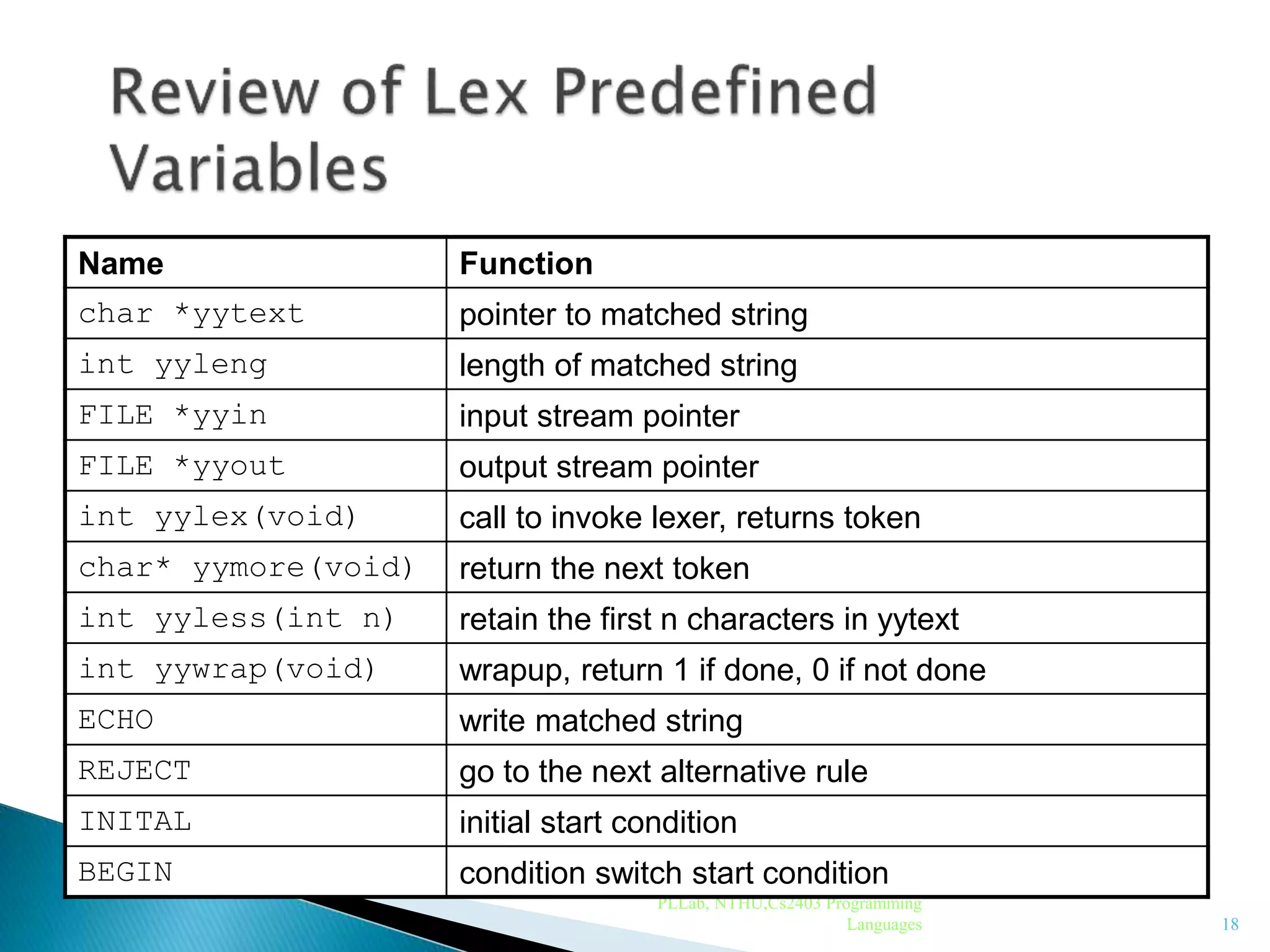
![ Also called as Hierarchial Analysis
A syntax tree[also called as parse tree] is generated
where
◦ Operators Interior nodes
◦ Operands Children of node for operators.
=
A + Interior
B C Children](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compilerdesign-170426184632/75/Compiler-design-and-lexical-analyser-19-2048.jpg)
![Concrete Parse tree
Abstract syntax tree
Converted into a linear sequence of instructions
Results in 3AC [ 3 Address Code]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compilerdesign-170426184632/75/Compiler-design-and-lexical-analyser-22-2048.jpg)