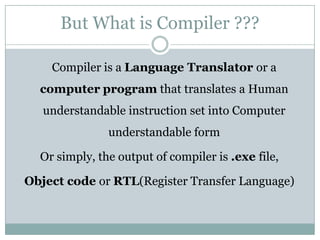
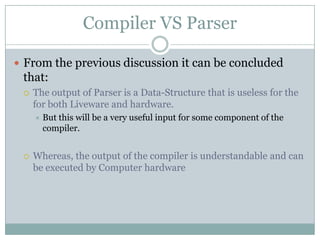
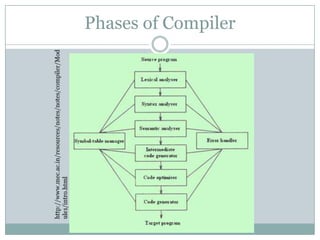
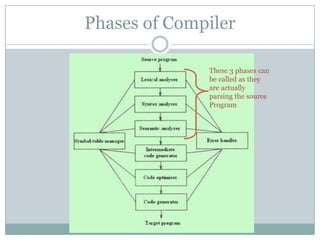
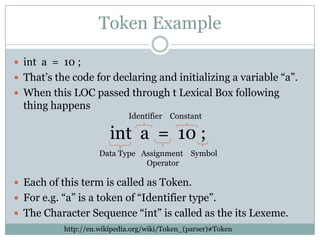
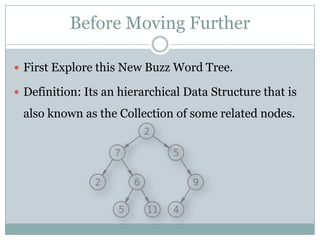
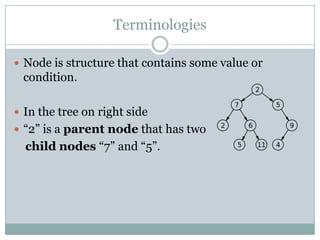
The document explains the concepts of parsers and compilers in computer science, emphasizing that a parser evaluates scripts to determine their grammatical correctness by breaking them into tokens and producing a hierarchical data structure, typically a tree. It distinguishes between parsing and evaluating, noting that parsers do not execute code or summarize text but are essential in the compilation process. It also describes the phases of a compiler, particularly focusing on lexical analysis and syntax analysis.