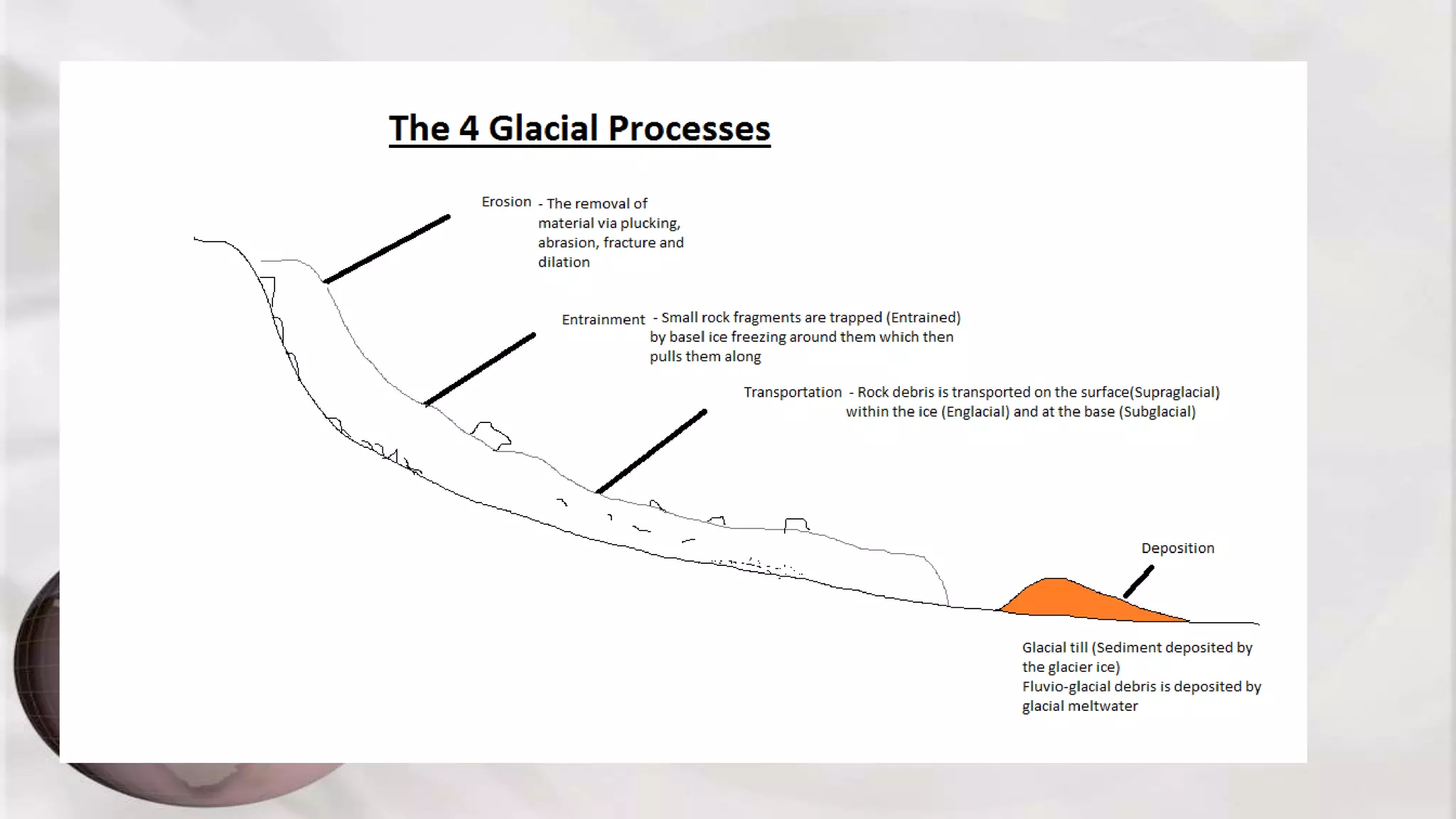
This document provides information about glacial processes and landforms at different scales. It discusses factors that influence glacial erosion rates like ice thickness, precipitation, ablation rates, and bedrock permeability. Landforms formed include cirques, arêtes, pyramidal peaks, truncated spurs, U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys, and ribbon lakes at the macro scale. Meso scale features include whalebacks, roches moutonnées, and crag and tail formations. Micro features provide evidence of ice flow direction through striations, chatter marks, and crescentic gouges. The document emphasizes that landforms result from multiple glacial periods and different glacial processes of erosion, entrainment, transport, and deposition