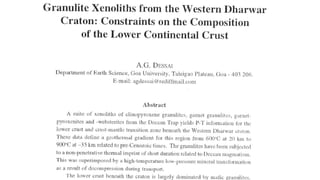
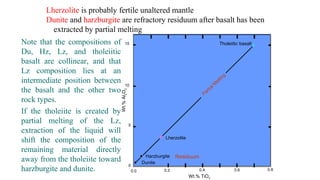
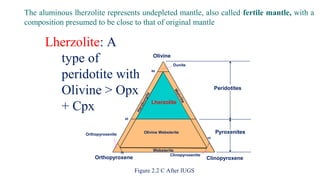
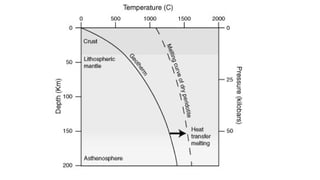
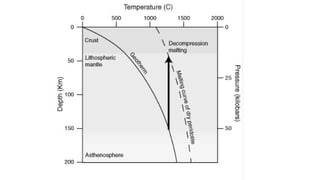
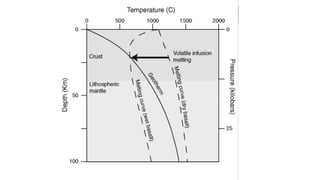
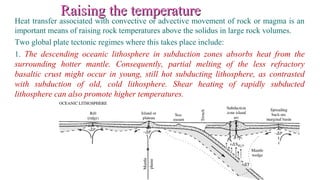
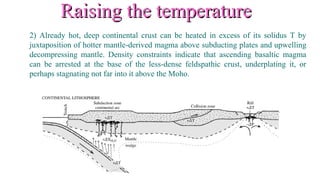
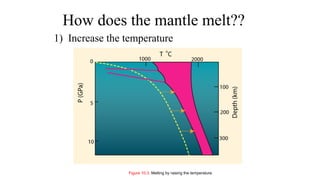
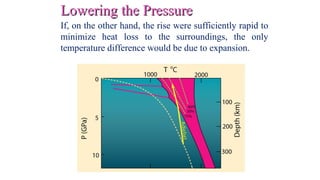
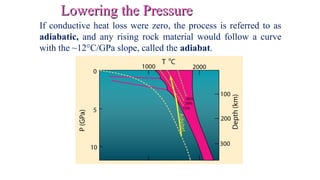
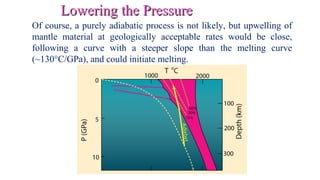
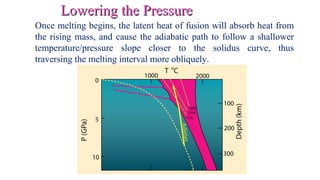
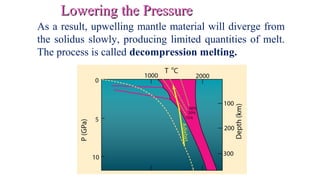
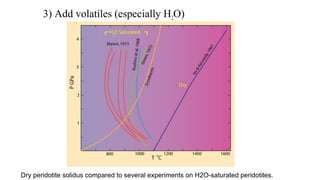
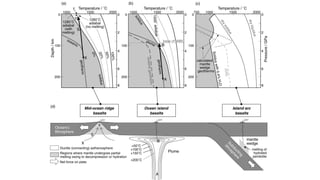
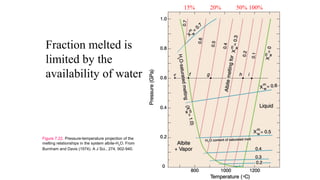
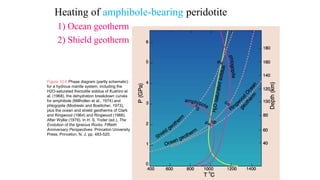
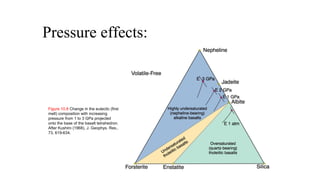
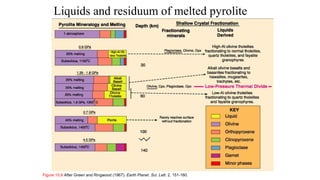
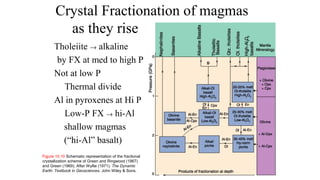
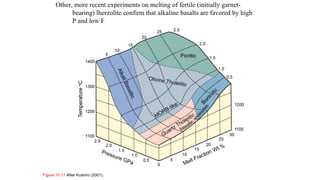
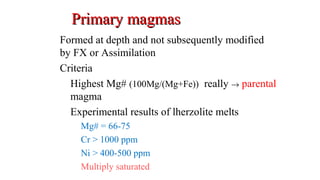
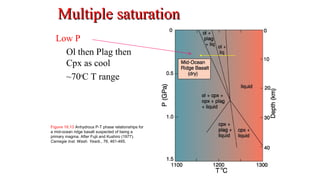
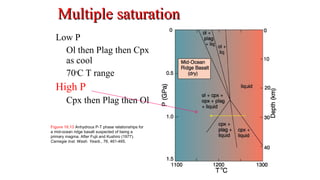
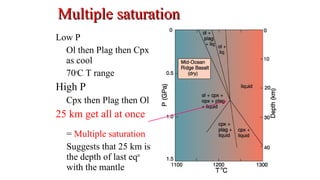
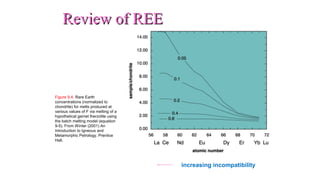
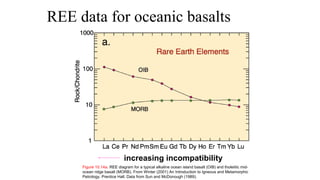
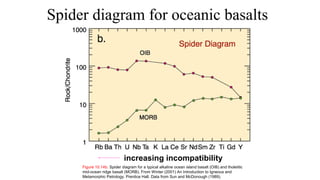
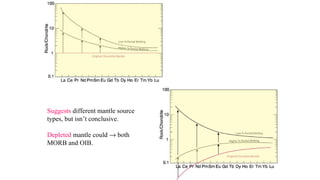
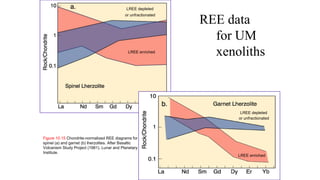
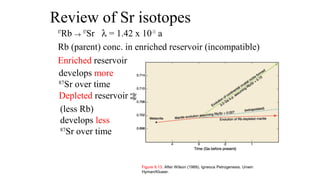
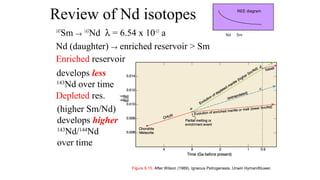
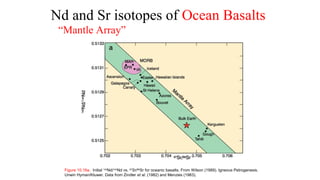
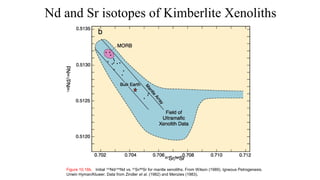
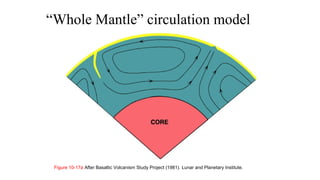
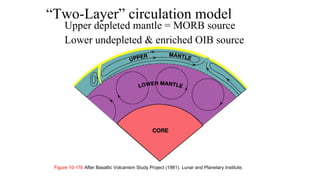
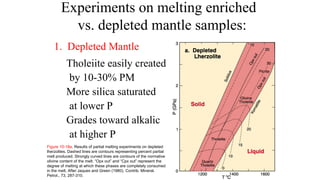
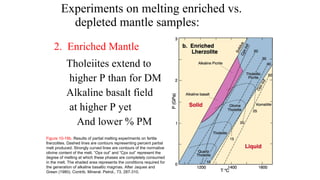
Mantle melting occurs when heat and pressure cause partial melting of the mantle, producing basaltic magma. Basalt is the most common volcanic rock on Earth and can be further differentiated to form other igneous rock types. Evidence for the composition and processes of the mantle comes from ophiolites, dredged samples from ocean floors, nodules contained in basalts, and xenoliths brought up from deep in the mantle via kimberlite eruptions. Together this evidence indicates that the upper mantle is composed predominantly of the minerals olivine, orthopyroxene, and clinopyroxene which make up the rocks dunite, harzburgite, and lherzol