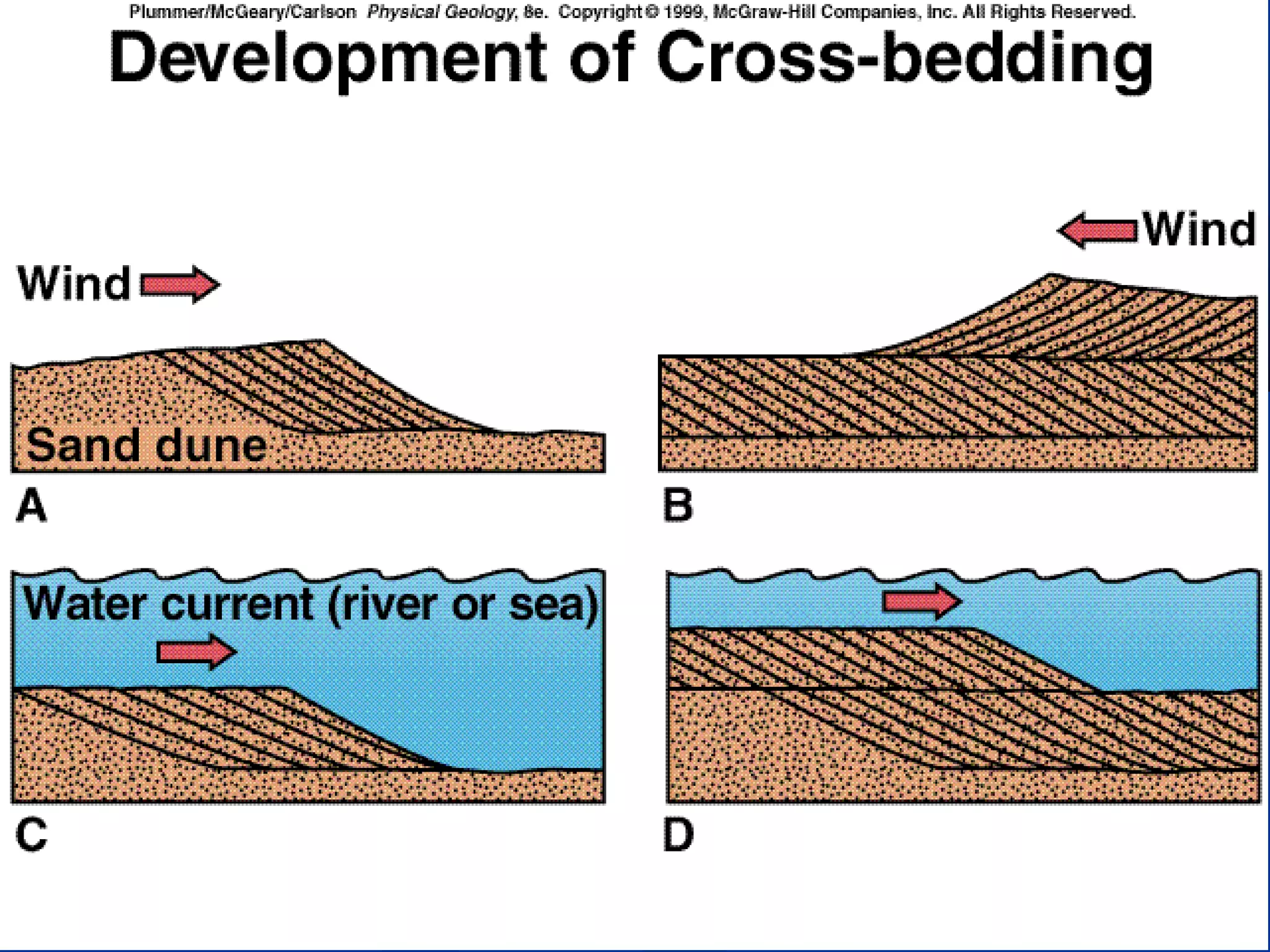
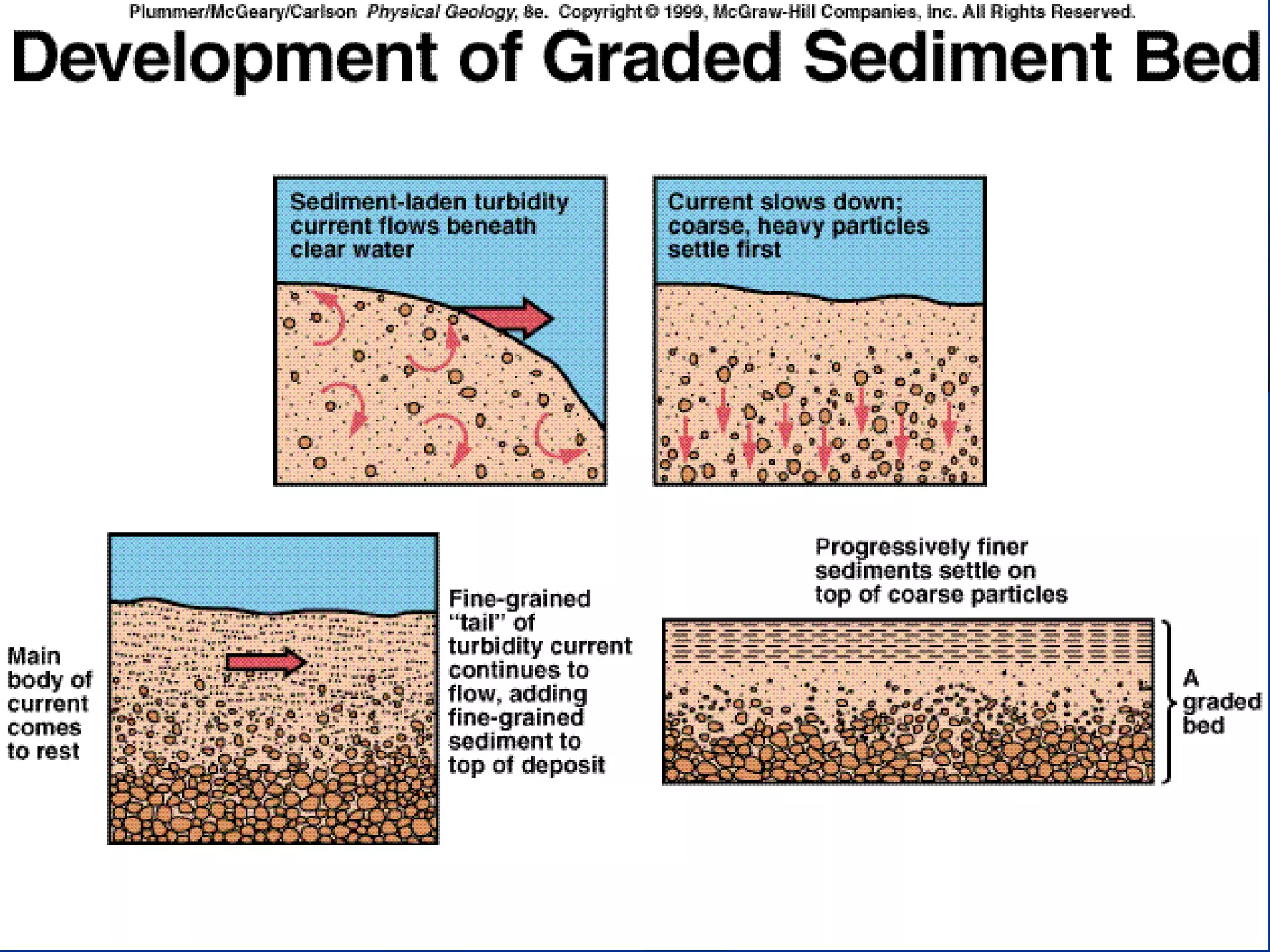
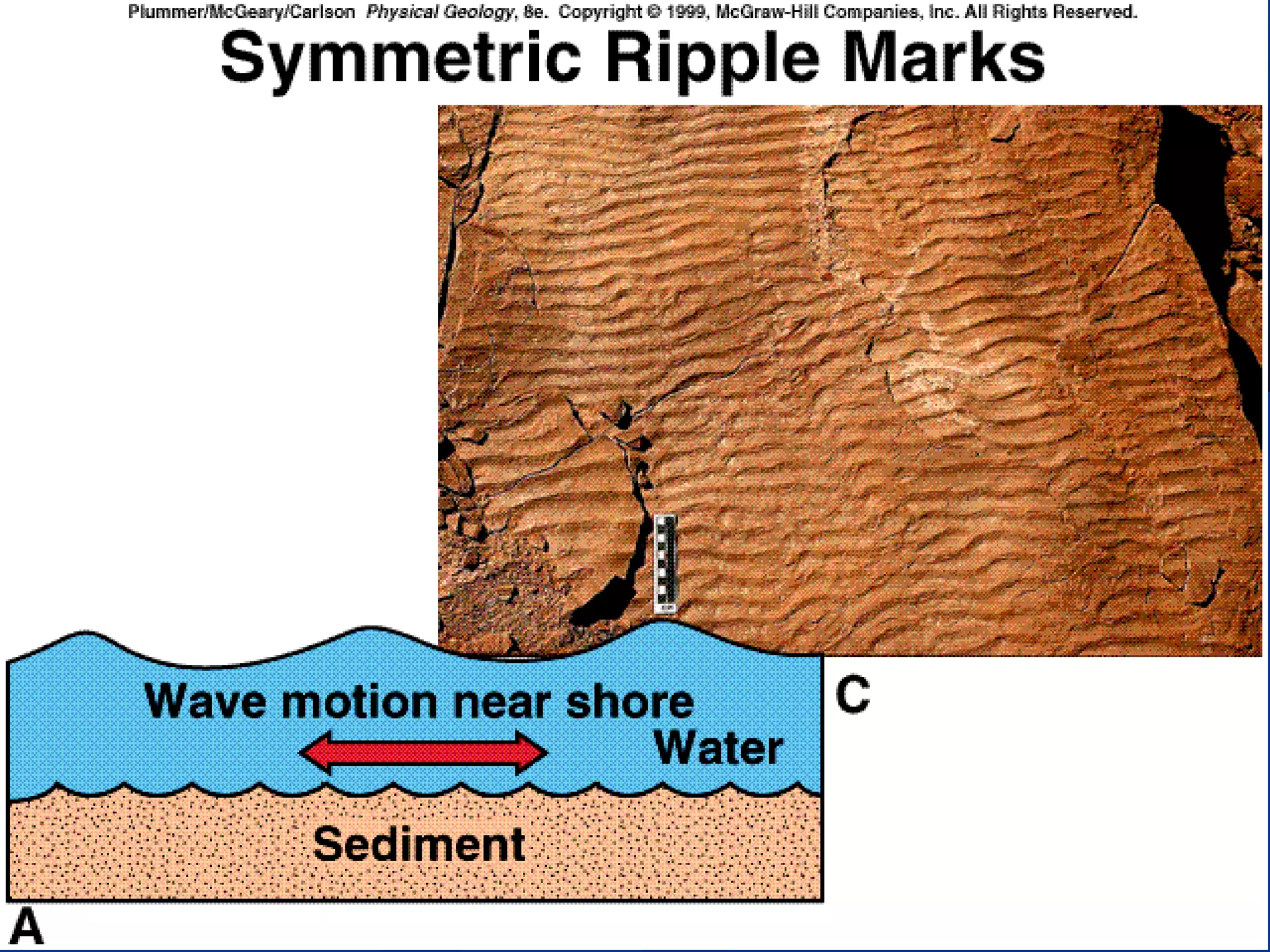
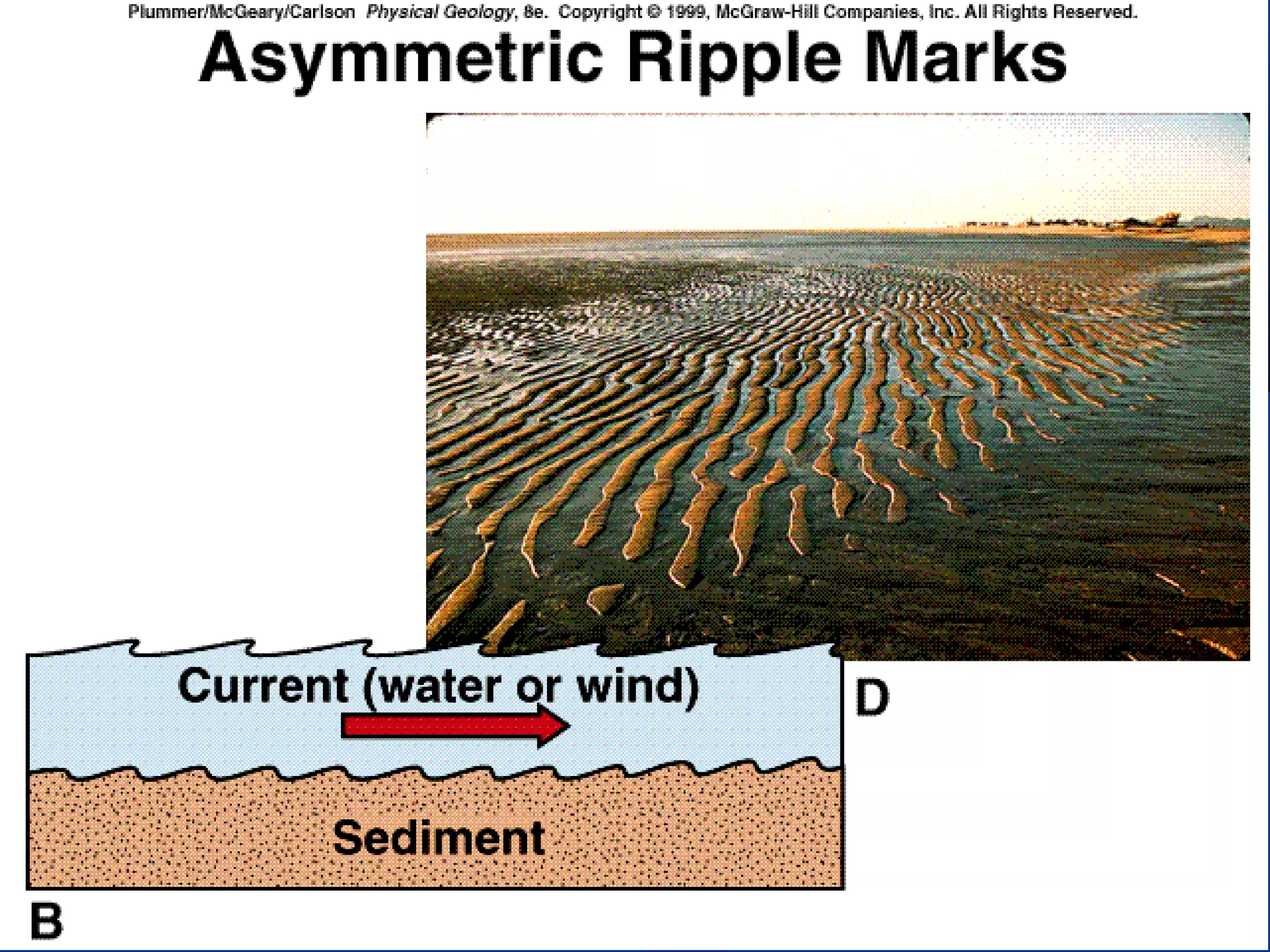
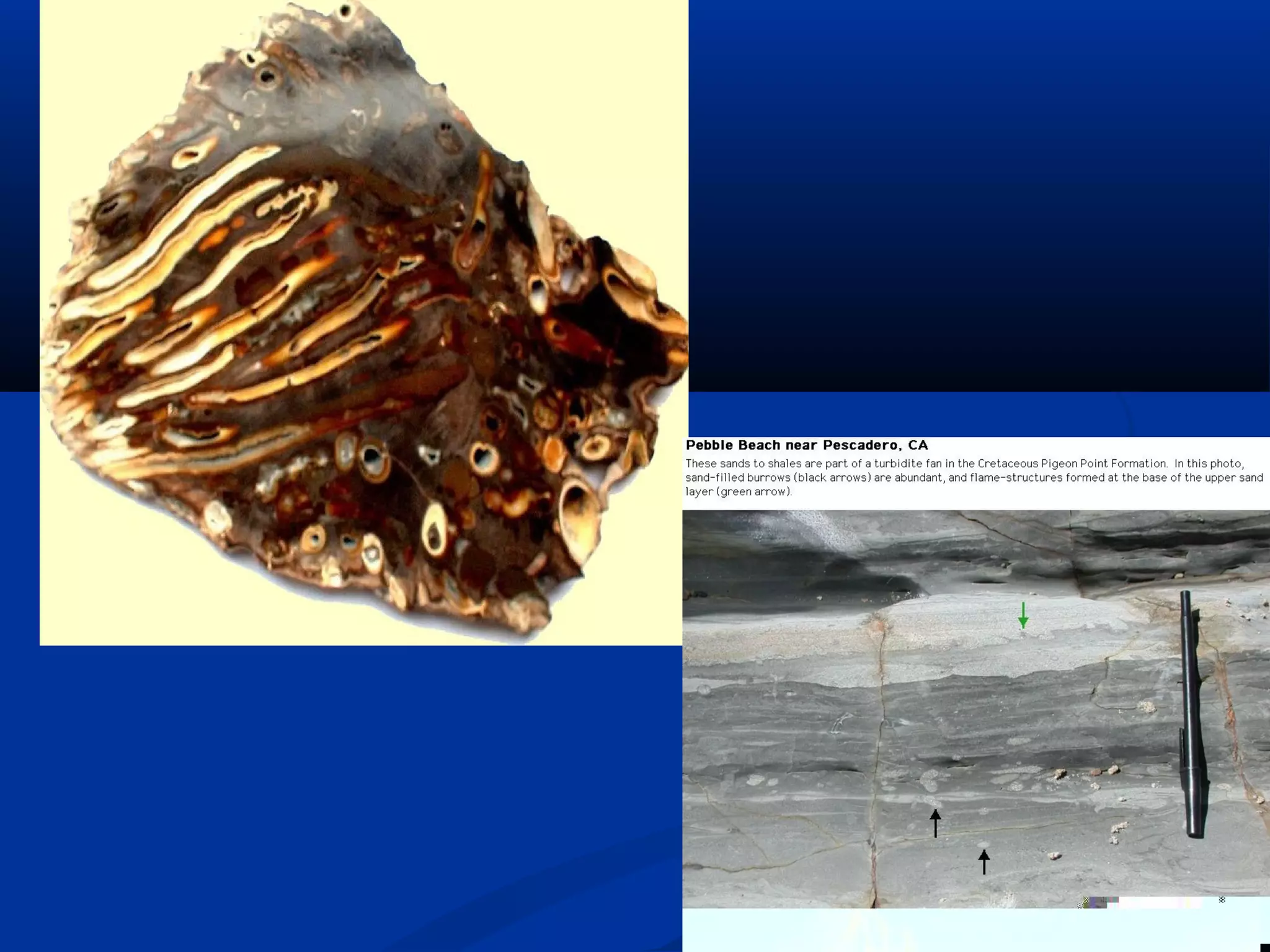
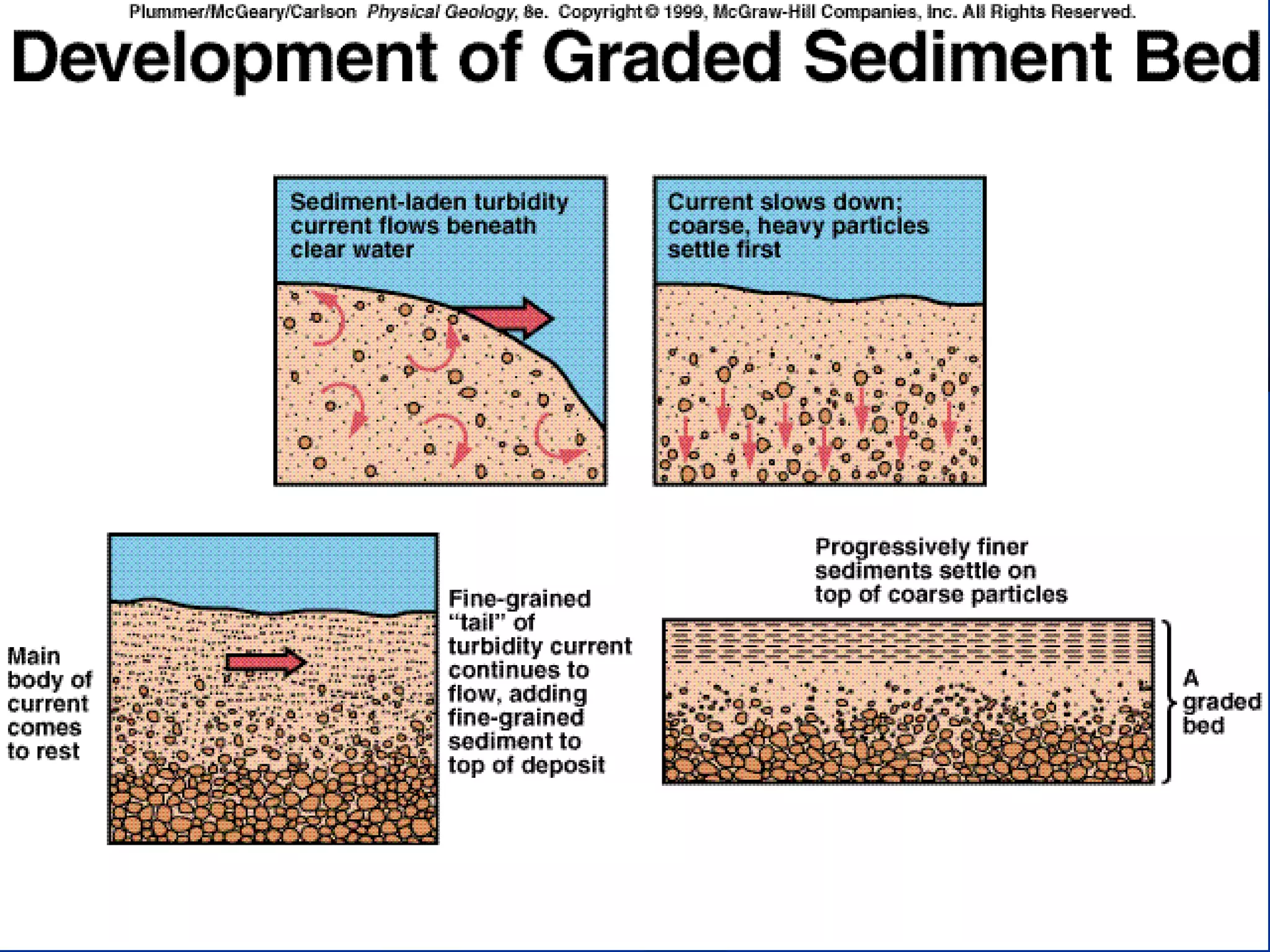
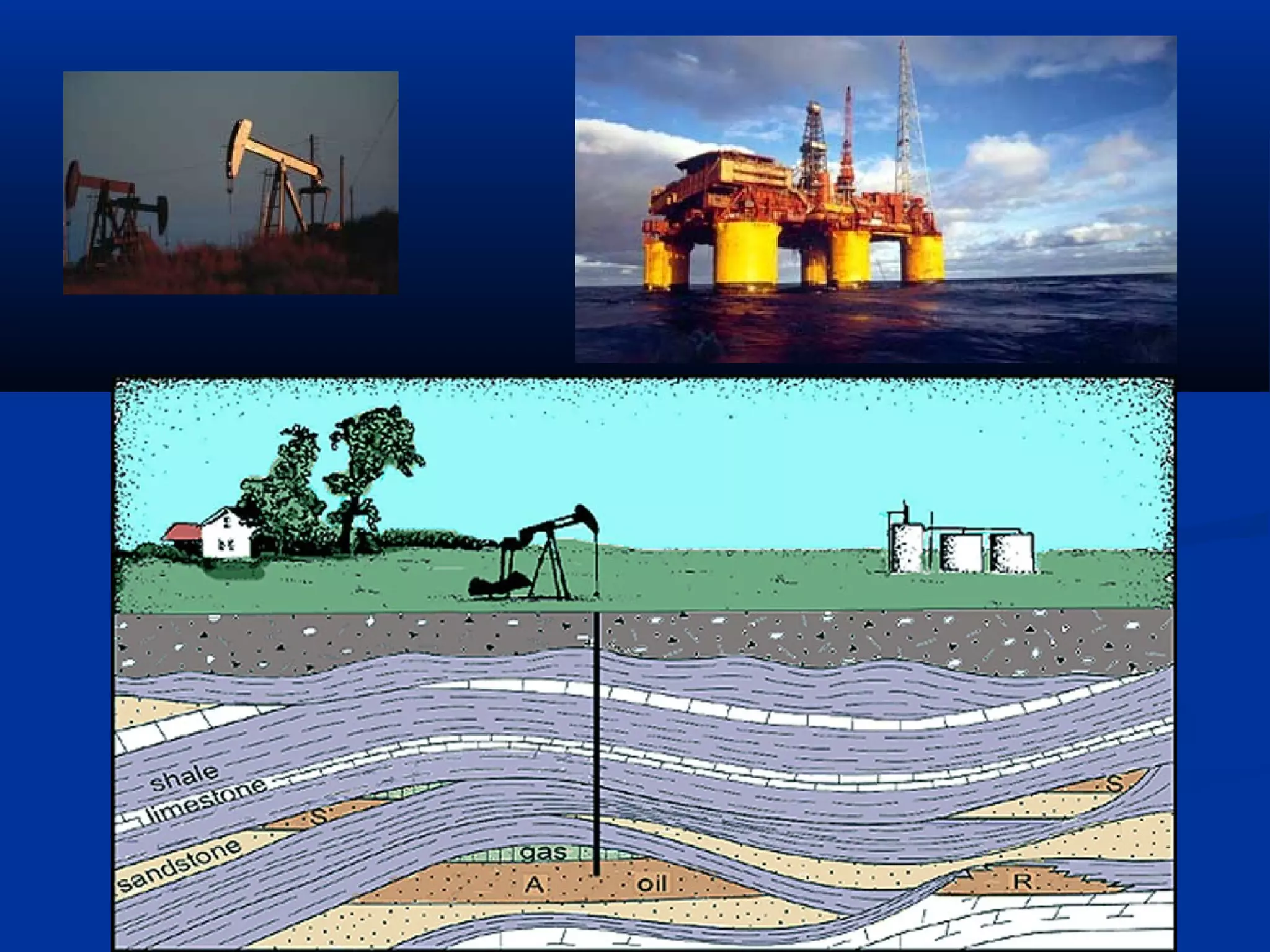
Sedimentary rocks form through the deposition of sediments or fragments by processes like erosion, transportation, and deposition. Sedimentary structures are classified based on how the sediments were deposited and include stratification, graded bedding, cross-bedding, ripple marks, mud cracks, rain drop marks, casts and molds, tool marks, tracks and trails, and burrow marks. Sedimentary rocks also include chemical rocks like limestone and dolomite formed from mineral precipitation, and biochemical rocks like coal and fossil-bearing limestone formed from organic materials.