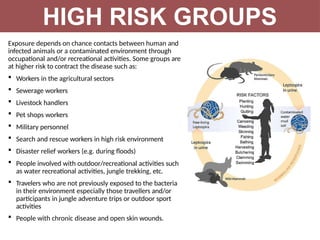
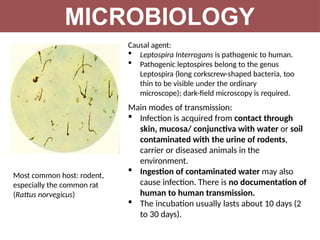
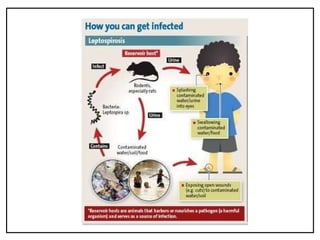
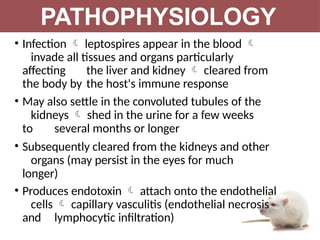
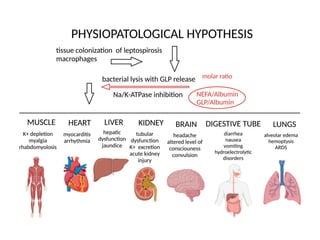
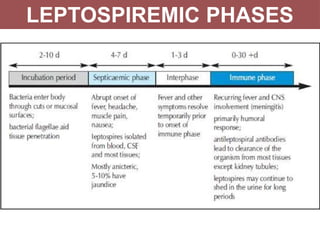
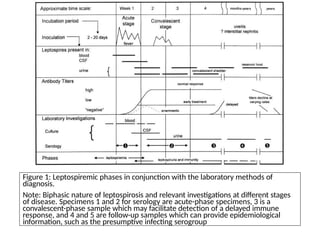
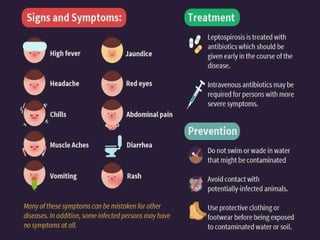
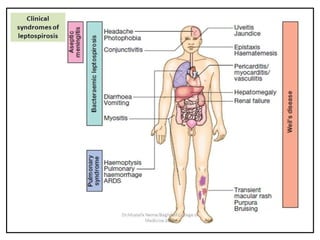
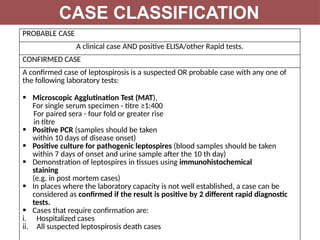
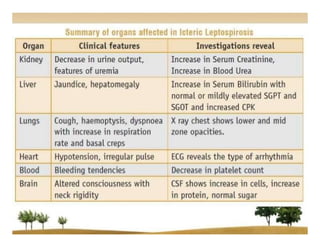
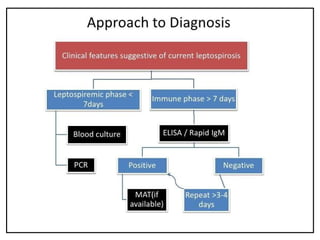
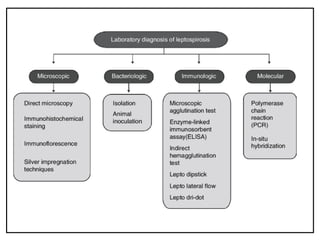
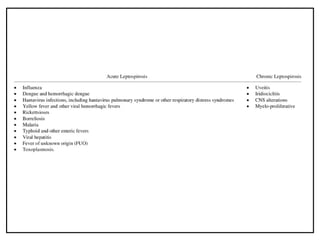
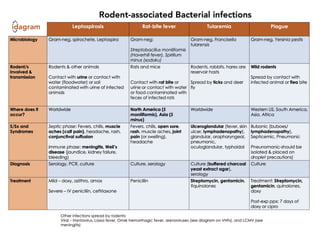
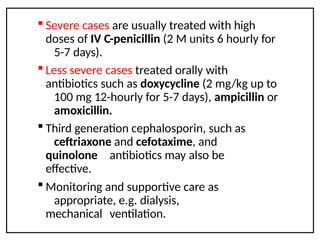
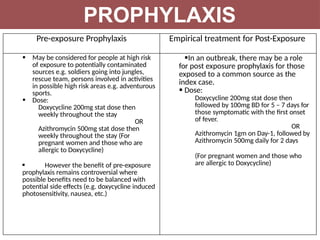
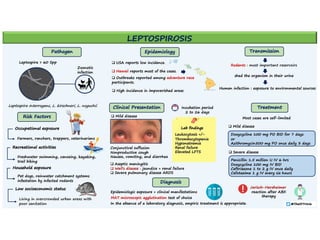
Leptospirosis is a zoonotic infectious disease caused by Leptospira bacteria, primarily transmitted through contact with contaminated environments or animal urine, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Clinical symptoms vary widely, ranging from mild flu-like symptoms to severe manifestations including renal failure and hemorrhage, complicating diagnosis and leading to underreporting. High-risk groups include agricultural workers and those involved in outdoor activities; treatment typically involves antibiotics, with pre-exposure and post-exposure prophylaxis recommended for at-risk populations.