Embed presentation
Downloaded 115 times








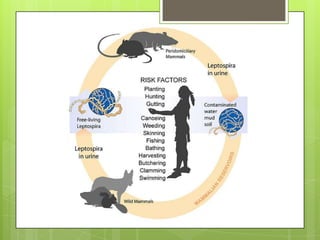












Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection caused by Leptospira bacteria found in the urine of infected animals like cattle, pigs, horses, dogs, and rodents. It can be transmitted to humans via contact with water or soil contaminated by animal urine. Common symptoms include high fever, severe headache, chills, vomiting, jaundice, and muscle aches. If not treated, it can lead to kidney damage, meningitis, liver failure or respiratory distress. Doxycycline or penicillin antibiotics are used for treatment if given early in the infection. Prevention involves avoiding swimming in contaminated water and wearing protective clothing when exposed to contaminated soil or water.

























