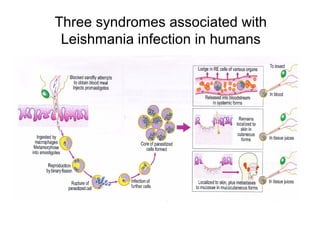
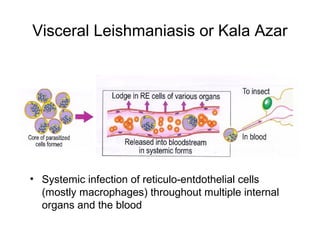
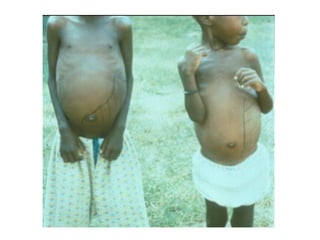
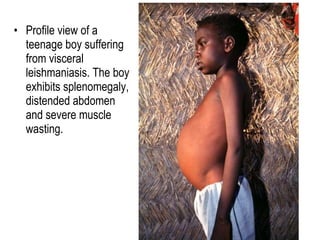
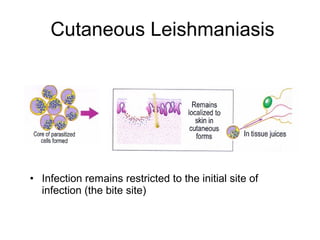
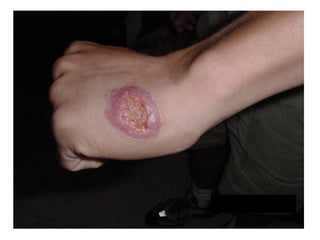
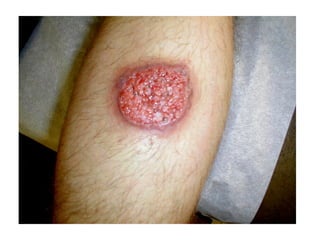
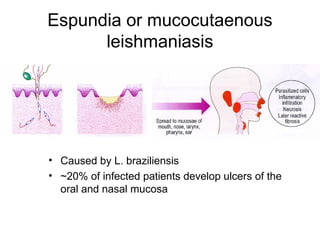
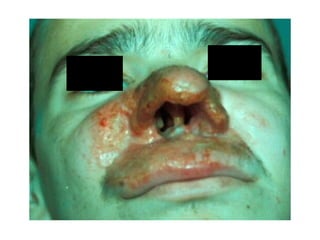
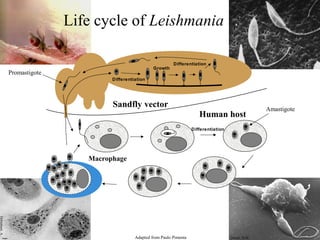
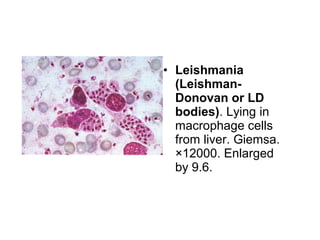
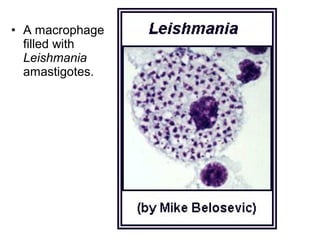
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Leishmania transmitted by sandflies. There are three main clinical syndromes: visceral leishmaniasis, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Visceral leishmaniasis is the most severe form and affects internal organs if left untreated, potentially causing fever, enlarged liver and spleen, weight loss, and death. Cutaneous leishmaniasis causes skin lesions at the site of infection. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis occurs in some cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis and can spread to cause ulcers in the mouth and nose. Prevention efforts