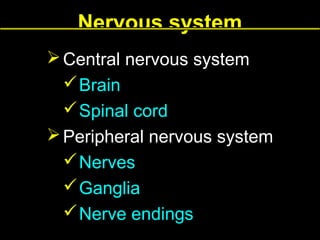
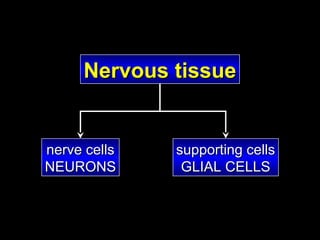
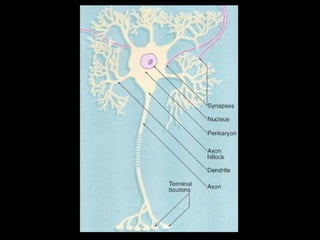
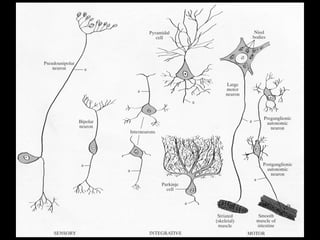
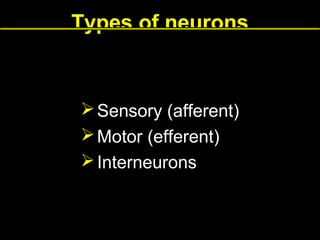
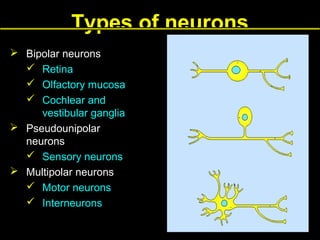
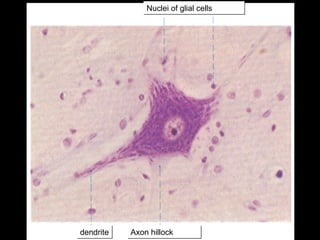
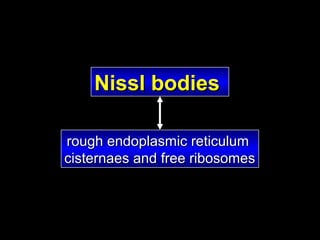
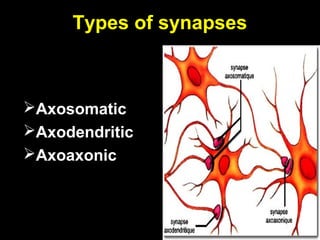
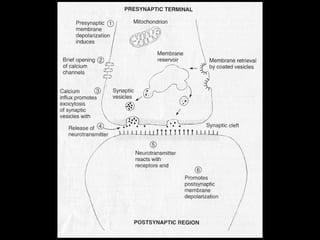
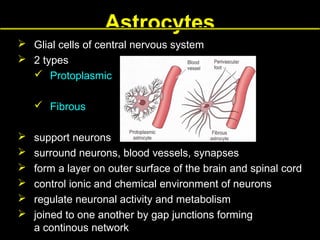
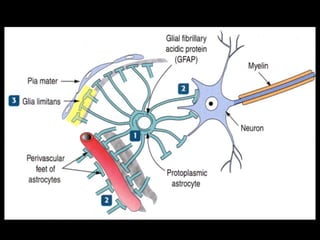
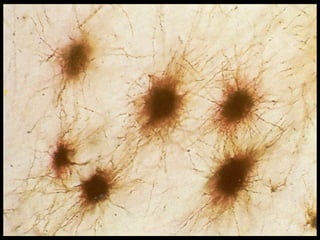
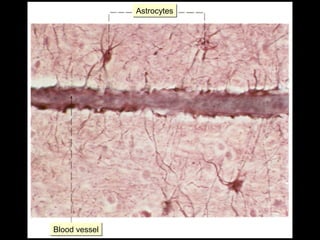
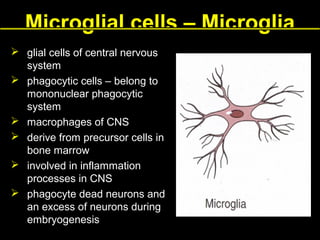
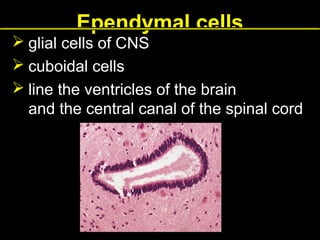
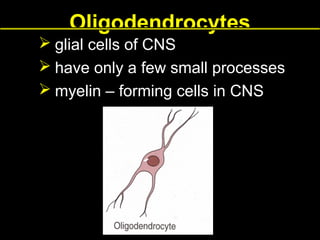
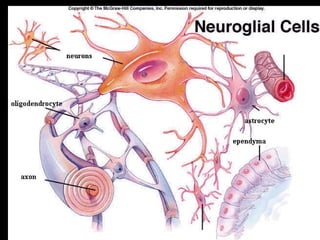
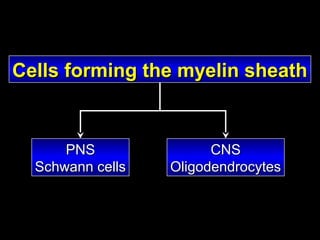
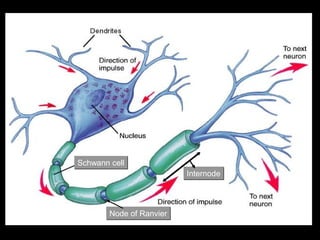
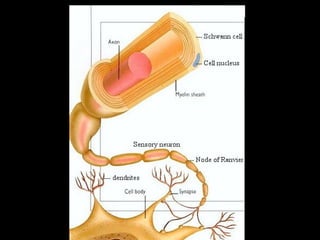
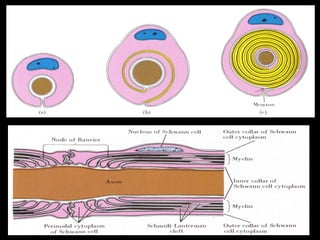
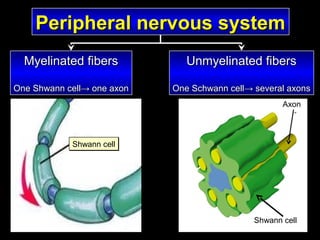
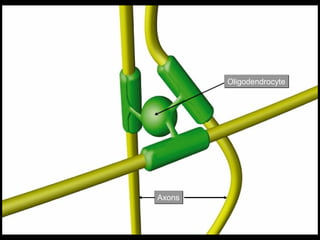
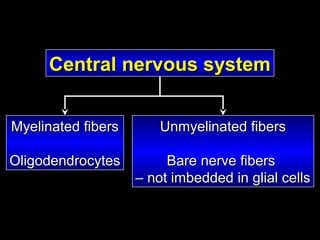
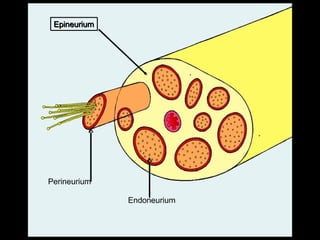
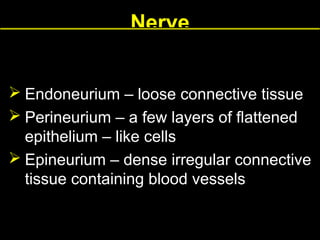
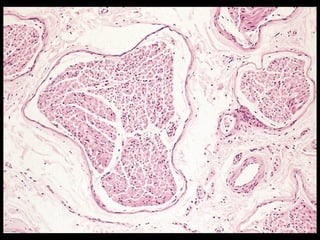
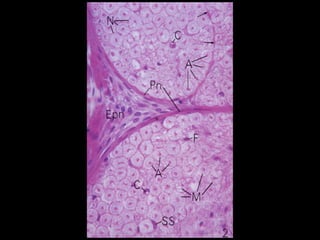
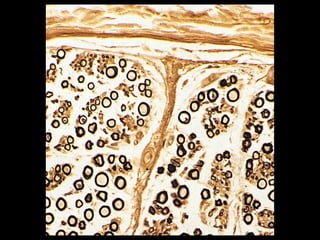
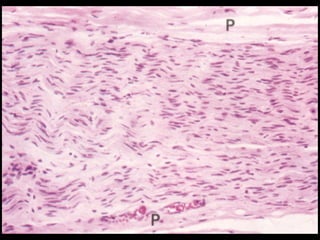
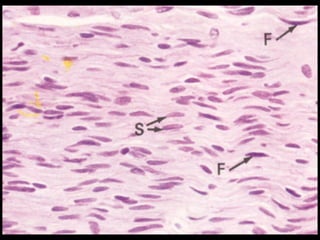
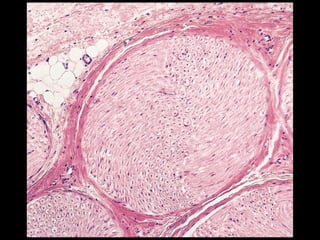
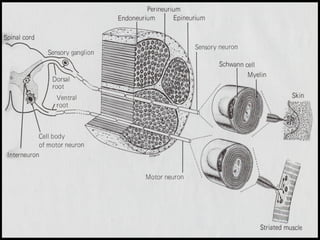
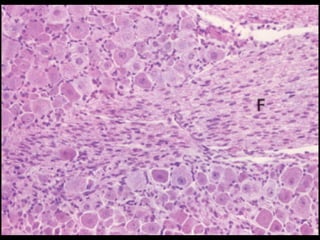
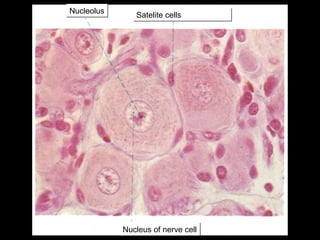
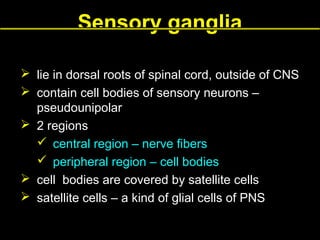
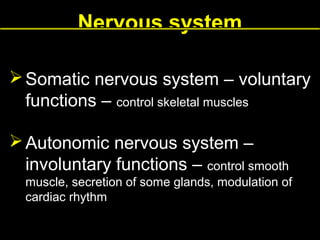
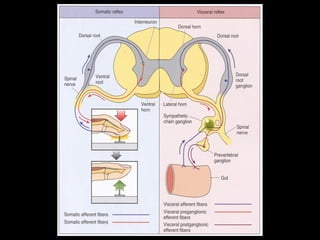
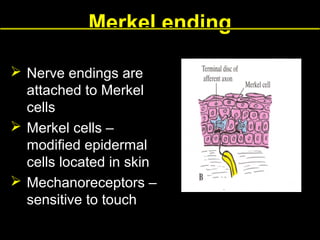
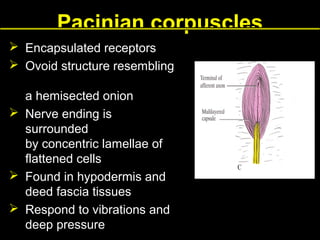
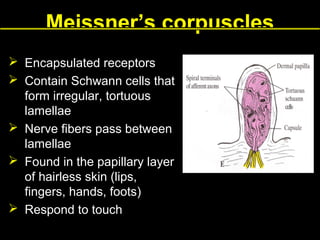
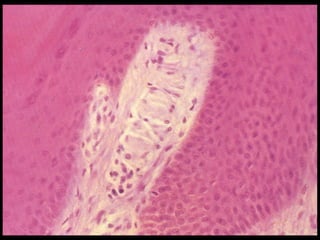
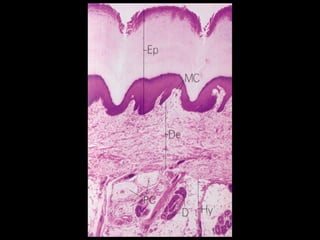
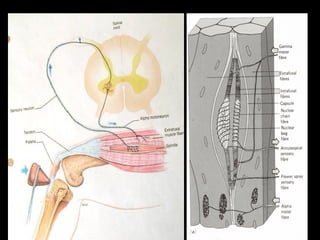
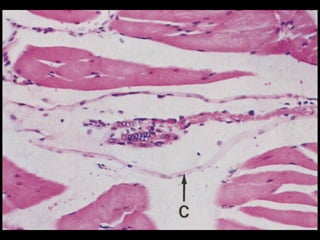
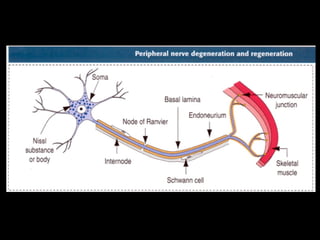
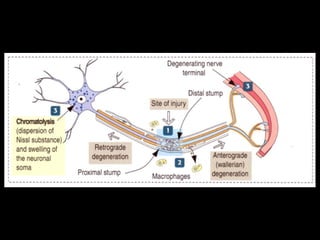
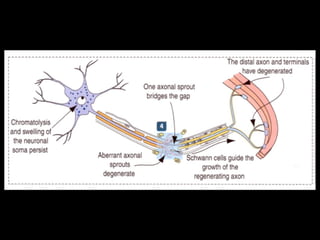
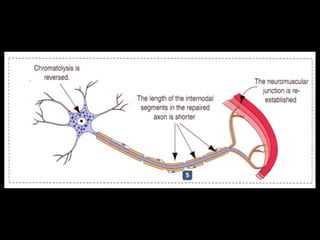
This document provides an overview of the nervous system, including its central and peripheral components. It describes the main cell types - neurons and glial cells. It discusses the key parts of neurons - dendrites, axons, axon hillock. It outlines the main types of neurons and glial cells in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. It provides details on how neurons communicate at synapses and how glial cells support neuronal function.