Powerpoint presentation about peripheral nerve
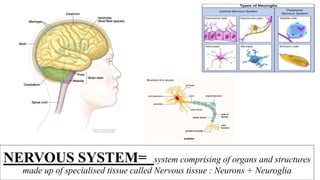
- 1. NERVOUS SYSTEM= system comprising of organs and structures made up of specialised tissue called Nervous tissue : Neurons + Neuroglia
- 2. •The Nervous System is the body’s main processing system for information •It is the most complex product of biological evolution ( complexity comes by the number of cells and not types)
- 3. NERVOUS SYSTEM Central Nervous System(CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) Somatic Nervous System(SNS) Autonomic Nervous system(ANS) Afferent & Efferent :Voluntary control over the skeletal muscle contraction Afferent & Efferent: Supply involuntary structures like heart, smooth muscle and glands Nervous tissue organised as :Brain, Spinal cord, Ganglia, Nerves Functionally :Afferent(Sensory) & Efferent system(Motor) Central Nervous System (CNS) – centres of nervous system, wide degree of effect if damaged Present at the centre of the body Sympathetic & Parasympathetic Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connect the CNS to the limbs and organs – Cranial(12 pairs) & spinal nerves(31 pairs 2 components: (Somatic- supply skeletal muscles & Autonomic)
- 4. Functions of CNS: • Integration, processing, co- ordinating sensory data and giving appropriate motor commands • Seat of higher functions such as intelligence, memory, learning and emotions Functions of PNS: • Provides sensory information to the CNS and carries its motor commands to the peripheral tissues and systems
- 5. AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: controls involuntary activities of the body, like sweating, salivation, peristalsis etc. • SYMPATHETIC(THORACO-LUMBAR OUTFLOW) & PARASYMPATHETIC(CRANIOSACRAL OUTFLOW)
- 6. • PRE- GANGLIONIC • POST GANGLIONIC
- 7. • 2 classes of cells: – Neurons or nerve cells – Glialcells(glia) • Glia surround neurons – from the Greek for ‘glue’ NERVOUS TISSUE:
- 8. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • Peripheral nerves- Cranial, Spinal • Ganglia
- 9. Glial Cells: • There are about 1 trillion glial cells in the brain – 10 - 50 x more than these are neurons • Types : IN THE CNS--- • Oligodendrocytes • Astrocytes • Ependymal cells • Microglia IN THE PNS --- • Satellite cells • Schwann cells
- 10. Types of Glial Cells: • Astrocytes: – Star shaped cells - Most numerous – Fill spaces between neurons – Form Blood-brain barrier • Oligodendroglia: – Wrap axons with myelin sheath in brain and spinal cord (Not all axons are myelinated) – Each oligodendrocyte wraps several axons in
- 11. • Microglia: - act as Phagocytes - clean debrisneur Satellite cells: • Capsular cells • Surround the neurons of sensory and autonomic ganglia FUNCTIONS: • supply nutrients to the surrounding neurons and also have some structural function • protective, cushioning cells
- 12. • Schwann Cells: – Wrap axons with myelin sheath outside the brain and spinal cord – Each Schwann cell wraps only one axon • Ependymal Cells: – Line the ventricles – Involved with secretion and absorption of cerebral spinal fluid – Also play a role in routing embryonic cells during development
- 13. Important functions of glial cells: – Act like a glue- hold the nervous tissue – Surround & support neurons – separate & insulate groups of neurons – some produce myelin ( Oligodendrocyte- CNS, Schwann cells- PNS) – some are scavengers- Microglia – some take up & remove chemical transmitters – some guide migration of neurons during development – some help form an impermeable lining in capillaries & venules, creating the blood-brain barrier:Astrocytes
- 14. Neurons: • Basic cells(functional units) of the nervous system • There are about 100 billion neurons in the brain – more in the spinal cord, peripheral nervous system and sensory organs • Neurons derive form the neural tube during development • 4 morphologically distinct regions: • Cell Body (soma) • Dendrites-carry impulses towards the cell body • Axon-single, carry impulses away from the cell body Axon divides into collateral branches and end in Axon Terminals with bulbous endings/ terminal buotons
- 15. IMPORTANT TERMINOLOGIES IN NEUROANATOMY: • NERVE CELL- Neuron • NERVE FIBER- Axon of a neuron • NEURO-TRANSMITTER: chemical messengers released at the nerve endings to effector organs like another nerve cell, a muscle cell or a gland • NERVE---Bundle of nerve fibers outside the CNS • TRACT--- A bundle of nerve fibres[axons] connecting neighbouring and distant nuclei of the CNS • NUCLEUS--- Collection of nerve cell bodies in the CNS • GANGLIA --- collection of cell bodies outside the CNS • The interior of the central nervous system is organized into gray and white matter • GRAY MATTER – Nerve cells embedded in neuroglia. • WHITE MATTER- nerve fibers (axons) embedded in neuroglia.
- 16. • UPPER MOTOR NEURON- cell bodies of neurons inside the cerebral/motor cortex • LOWER MOTOR NEURON- cell bodies of neurons in the spinal cord/ brain stem Upper motor neuron controls/ regulates the activity of lower motor neuron Lower motor neuron is in contact with the muscle and glands
- 17. PERIPHERAL NERVE
- 18. Peripheral Nerve : • Nerves in the Peripheral Nervous system • solid white cords composed of bundles of nerve fibers • Cranial nerves(12 pairs) & Spinal nerves(31 pairs)
- 19. • Each peripheral nerve consists of a large number of fine filaments- nerve fibers- arranged in the form of bundles/ fasciculi and surrounded by fibrous connective tissue: • Structure of of peripheral nerve(Cross section): 3 protective coverings of connective tissue: Endoneurium – loose, surrounds individual nerve fibers Perineurium – surrounds bundle of nerve fibers Epineurium – encloses the bundle of nerve fibers forming a trunk Importance – provide mechanical strength to the nerve fibers • Nerve fibers- Motor, sensory
- 20. • Non-myelinated - simply enveloped by the cytoplasm of Schwann cells • Myelinated - wrapped by concentric layers of schwann cell plasma membrane( Neurilemma) All peripheral nerves are enveloped by the schwann cells- some are myelinated and non-myelinated
- 21. CRANIAL NERVES: 12 pairs
- 22. SPINAL NERVES: • Nerves arise from the spinal cord and pass through the intervertebral foramina in the vertebral column • 31 pairs 8-cervical 12-thoracic 5-lumbar 5-sacral 1-coccygeal Spinal nerves emerging from the spinal cord by means of 2 roots Spinal nerves passing through the intervertebral foramina
- 23. SPINAL SEGMENT: A section of the spinal cord that gives rise to one pair of spinal nerve 31 pairs of spinal nerves
- 25. TYPICAL SPINAL NERVE (THORACIC) :
- 26. • Roots- anterior & Posterior • Trunk of spinal nerve • Ramus- Anterior & Posterior: Anterior ramus- divides into Anterior & Lateral cutaneous branches, connected to sympathetic ganglion by grey & white rami communicantes Posterior Ramus – small, divides into medial & lateral branches
- 27. • Spinal nerves (anterior primary ramii) ----- Except for T3 to T11 thoracic nerves, all form plexus(network of nerves)----branches from the plexuses Cervical plexus : C1 to C4 nerves Brachial plexus : C5 to T1 nerves Lumbosacral plexus : L1 to S5 nerves Importance of Plexus formation: Redistribution of the nerve fibers
- 28. DERMATOME: Area of skin supplied/innervated by a single segment of spinal cord giving origins to one pair of spinal nerves
- 29. MYOTOME: group of muscles which is innervated by single spinal nerve root Each muscle in the body is supplied by one or more levels or segments of the spinal cord and by their corresponding spinal nerves. A group of muscles innervated by the motor fibres of a single nerve root is known as a myotome
- 30. • important diagnostic tool to localize neurologic levels • Symptoms that follow a dermatome (e.g. like pain or a rash) may indicate a pathology that involves the related nerve root. • Herpes Zoster( Shingles)- follow one or two adjacent dermatomes DERMATOME TESTING
- 31. • Testing of myotomes, in the form of isometric resisted muscle testing, provides the clinician with information about the level in the spine where a lesion may be present. • During myotome testing, the clinician is looking for muscle weakness of a particular group of muscles. Results may indicate lesion to the spinal cord nerve root, or intervertebral disc herniation pressing on the spinal nerve roots.
- 33. GANGLIA: • Collection of nerve cell bodies outside the central nervous system – ganglion • Sensory ganglia - Dorsal root ganglia of spinal & on the trunks of cranial nerves • Autonomic ganglia- Sympathetic & Parasympathetic DORSAL ROOT GANGLION
- 34. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • Brain & Spinal cord • Delicate CNS is well protected as it is enclosed by the skull and vertebral canal and meninges and is bathed in cerebrospinal fluid
- 35. • Sections through the CNS presents grey matter: nerve cell bodies, dendrites white matter: Predominantly made up of myelinated nerve fibers Sub-cortical grey matter- brain( basal nuclei)
- 36. BRAIN: • Lies within the cranial cavity • 6 major parts : a) Cerebrum b)Diencephalon c)Midbrain d) Pons e) Medulla oblongata f) Cerebellum BRAINSTEM