Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX









C4.5 enhances ID3 by making it more robust to noise, able to handle continuous attributes, deal with missing data, and convert decision trees to rules. It avoids overfitting through pre-pruning and post-pruning techniques. When dealing with continuous attributes, it evaluates all possible split points and chooses the optimal one. It treats missing data as a separate value but this is not always appropriate. It generates rules from trees in a greedy manner by pruning conditions to reduce estimated error. The next topic will be on instance-based classifiers.
Introduced ID3 decision tree, its ability to handle noisy data, drawbacks like dealing only with nominal data and issues with noise.
Discussed moving from ID3 to C4.5, enhancing robustness against noise, managing continuous attributes, and handling missing data.
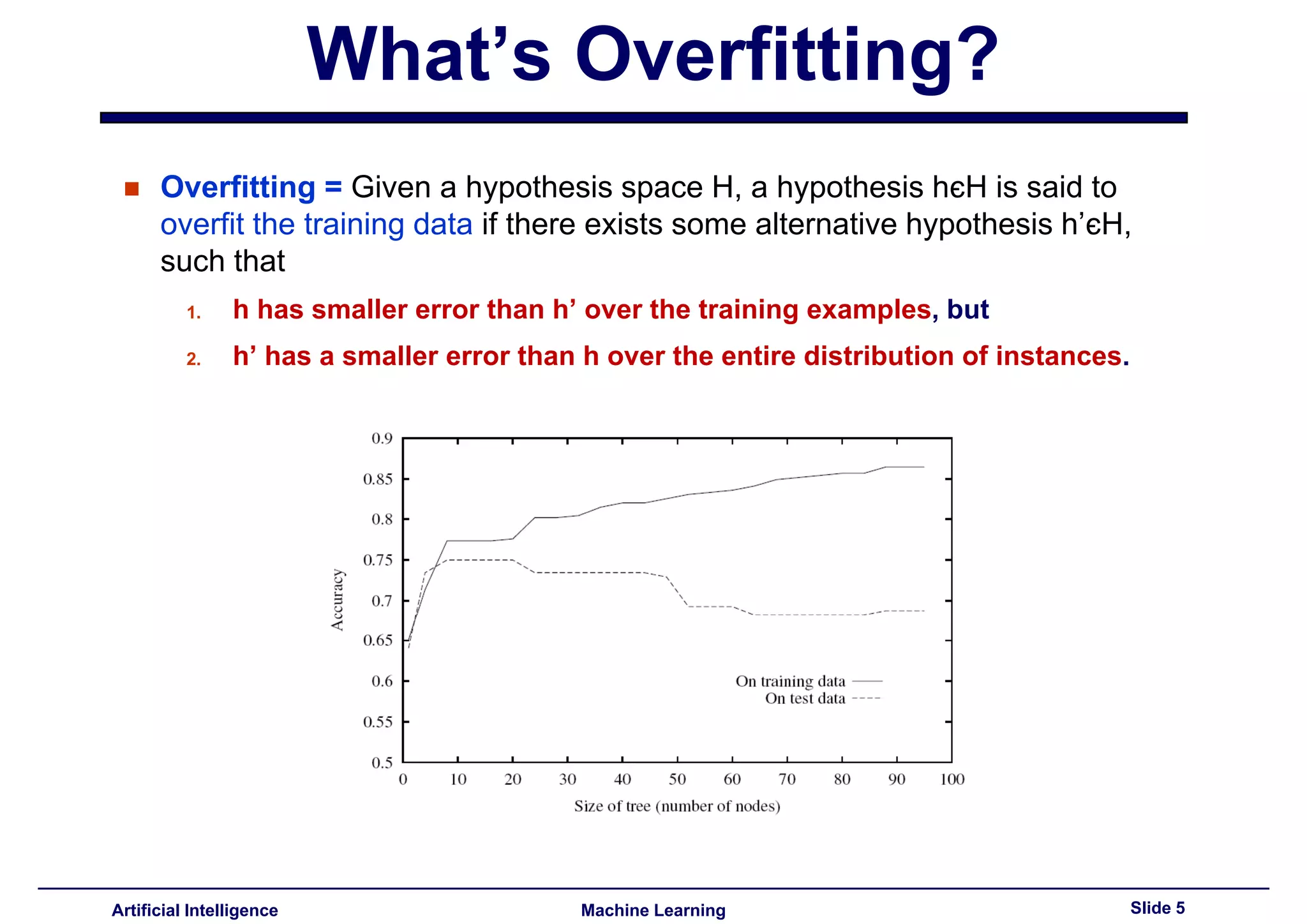
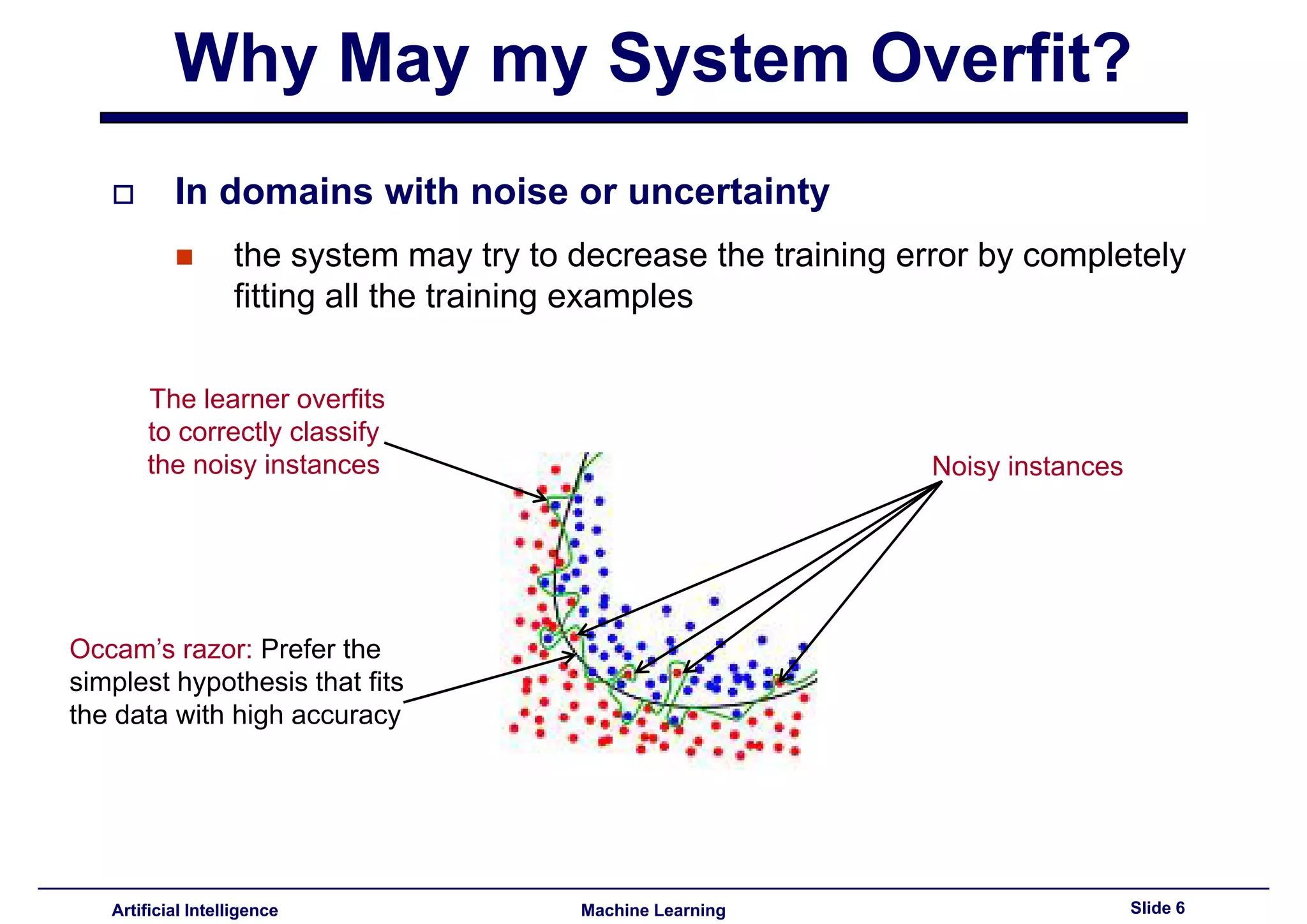
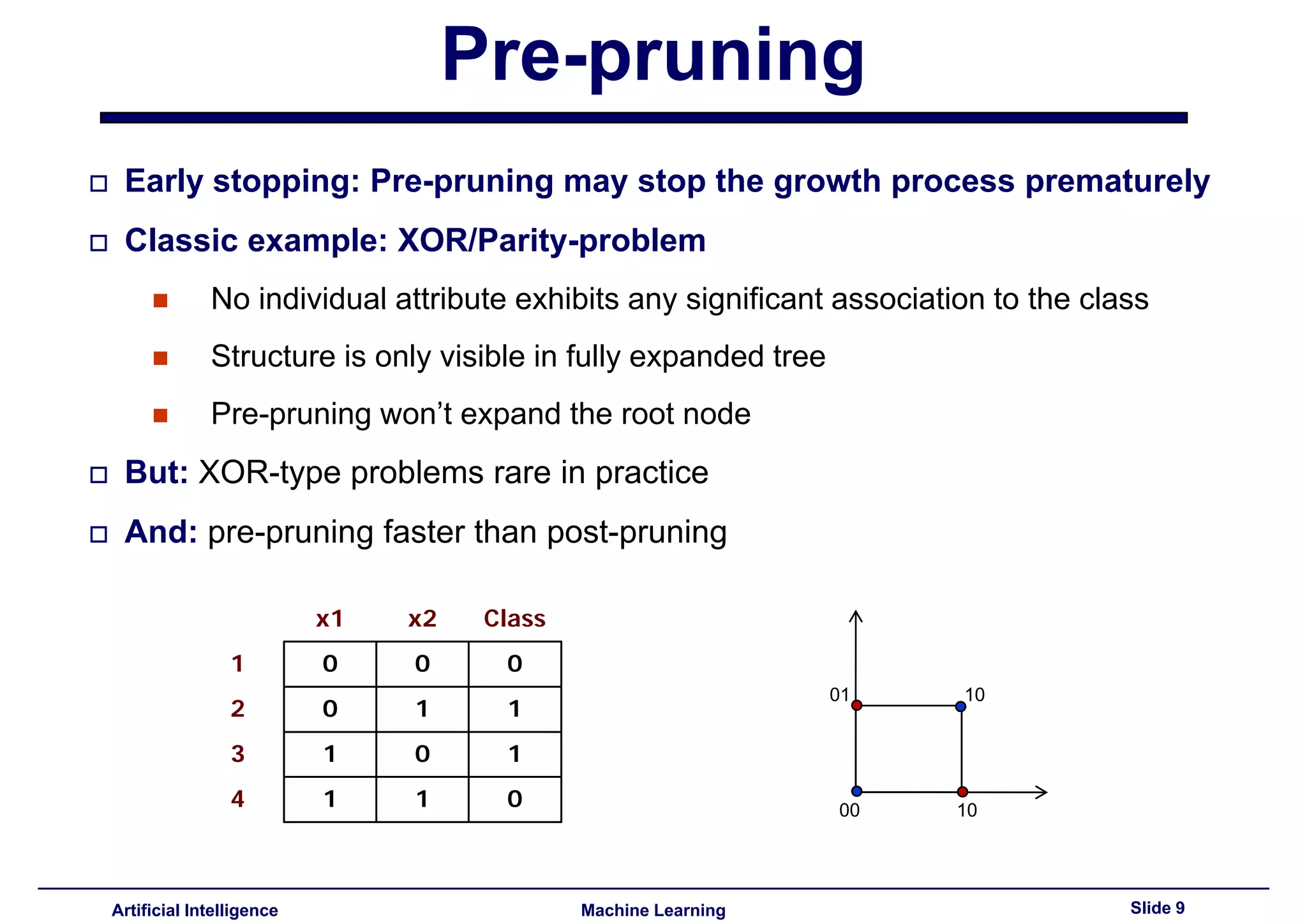
Defined overfitting and reasons systems may overfit in noisy domains. Introduced Occam's razor to simplify hypotheses.
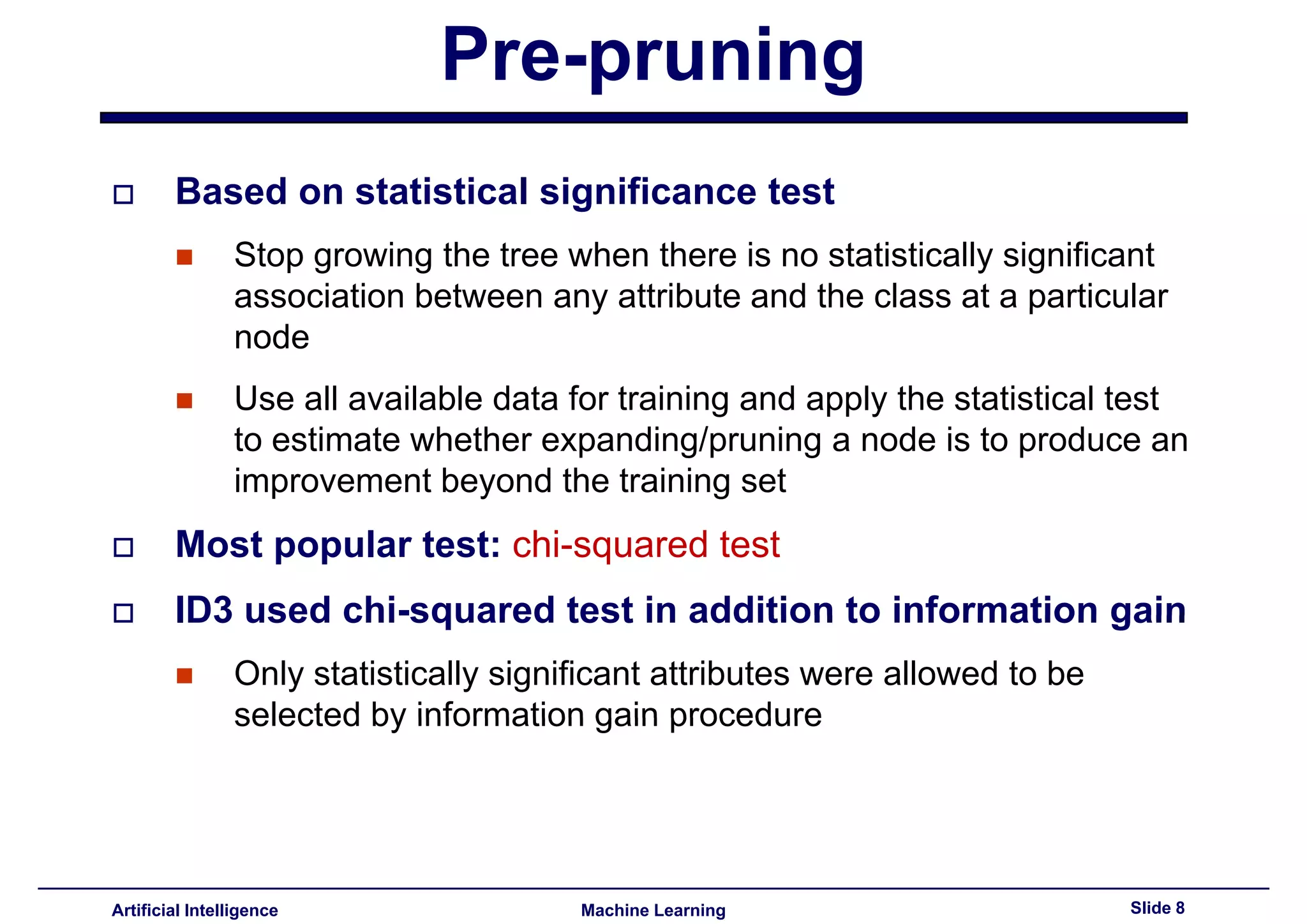
Techniques like pre-pruning and post-pruning to prevent overfitting. Discussed reliance on statistical tests for pruning decisions.
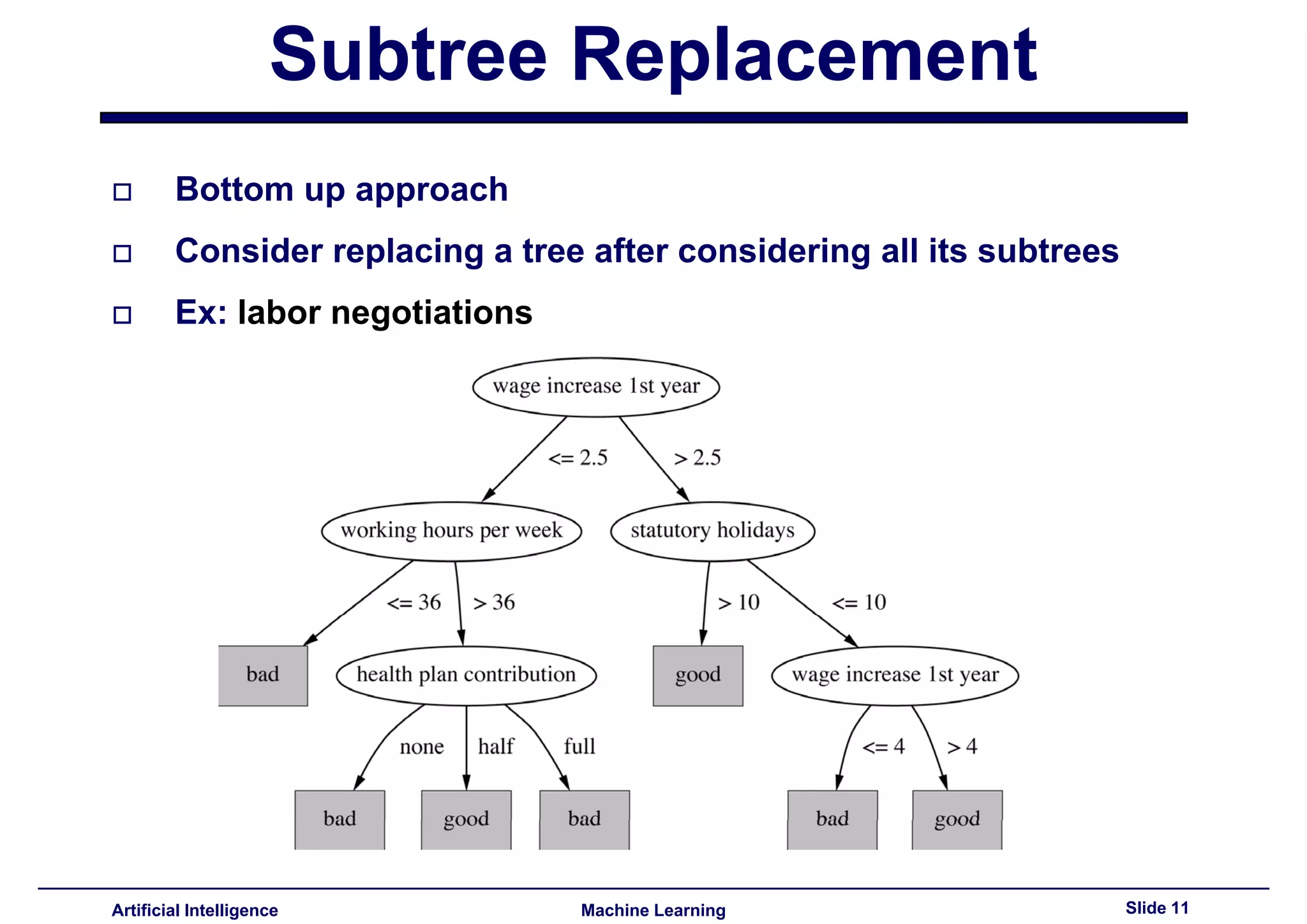
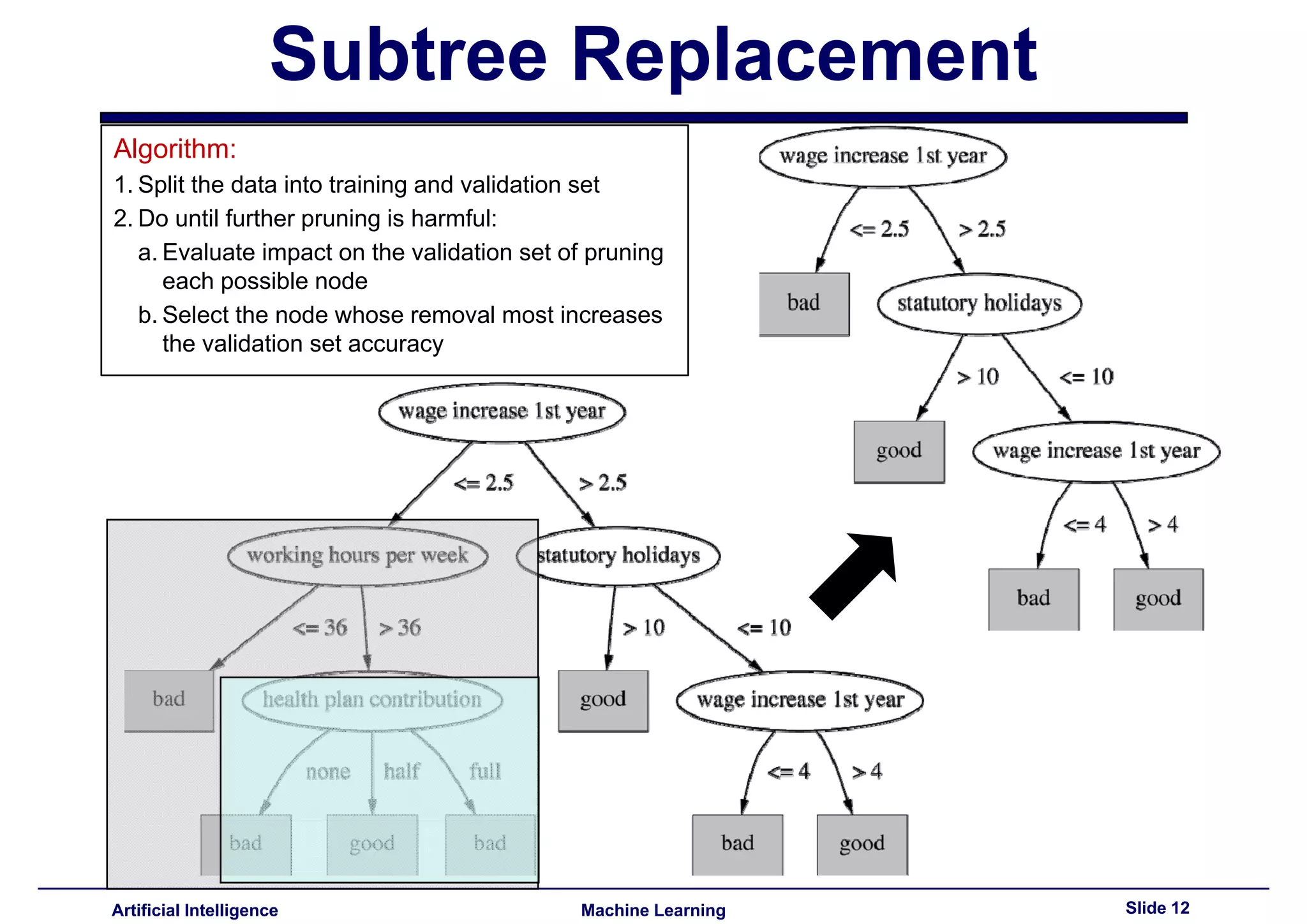
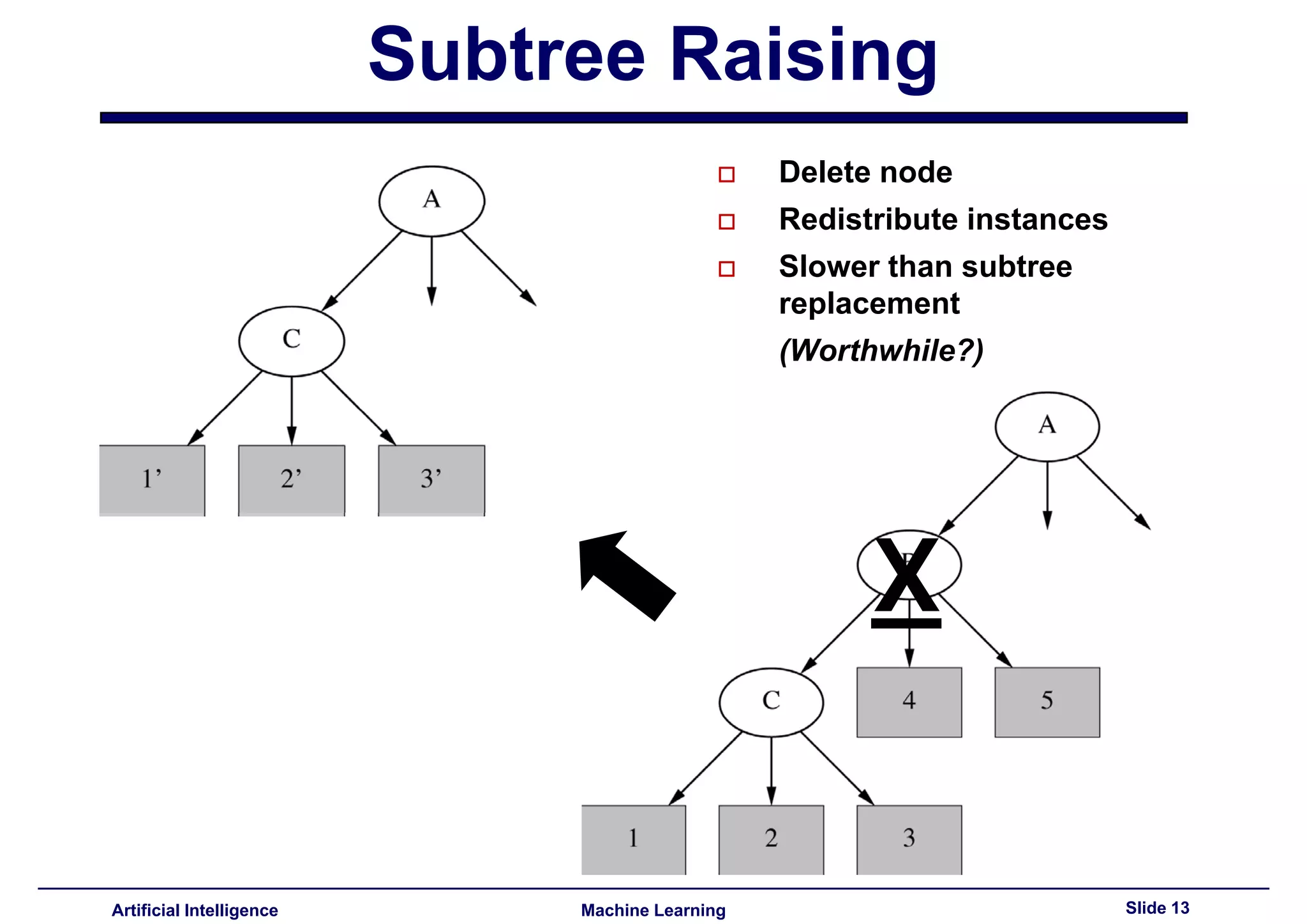
Explained post-pruning and subtree replacement/raising methods, considering their strengths and weaknesses.
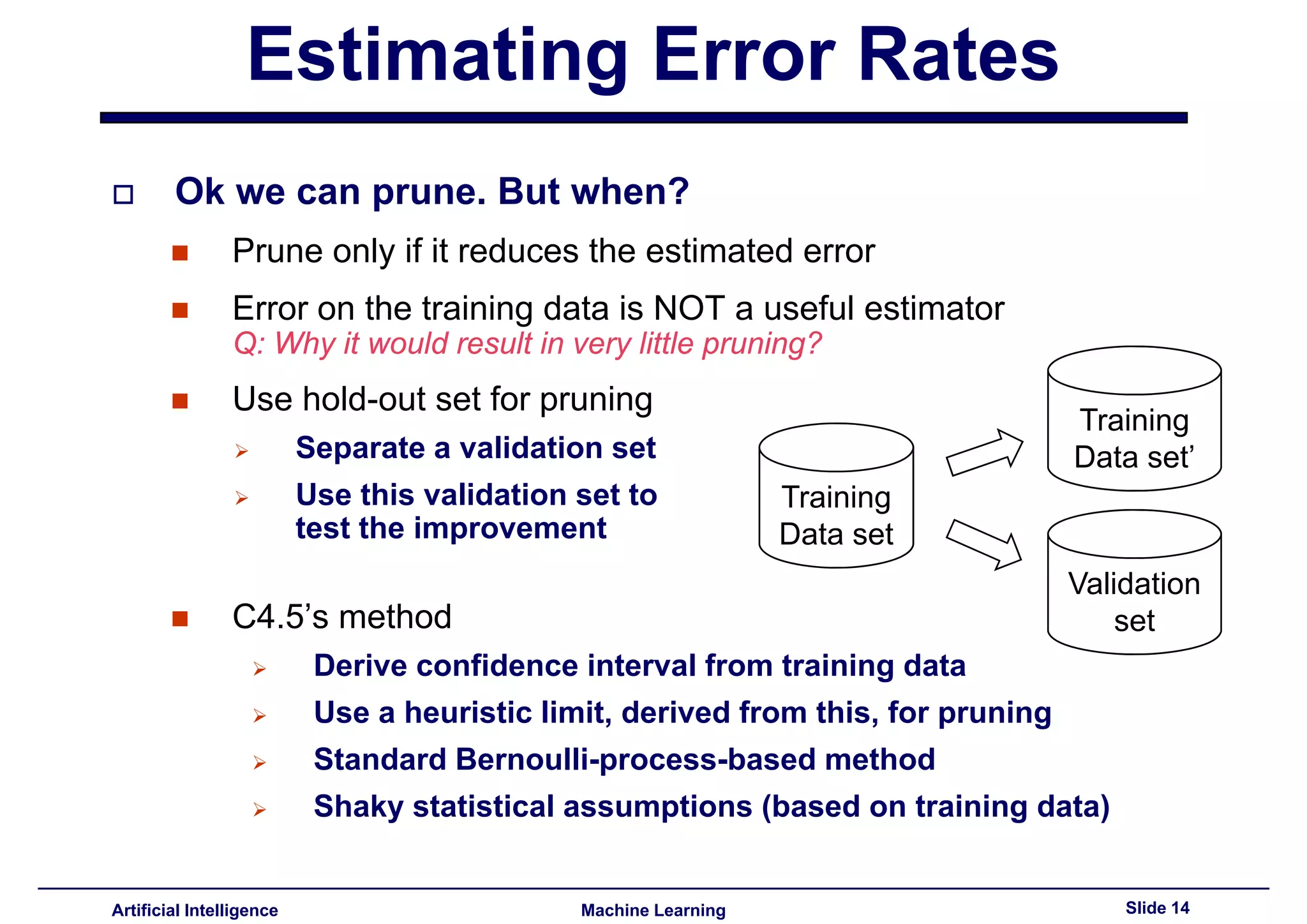
Stated methods for estimating error rates for pruning decisions, emphasizing validation sets over training data.
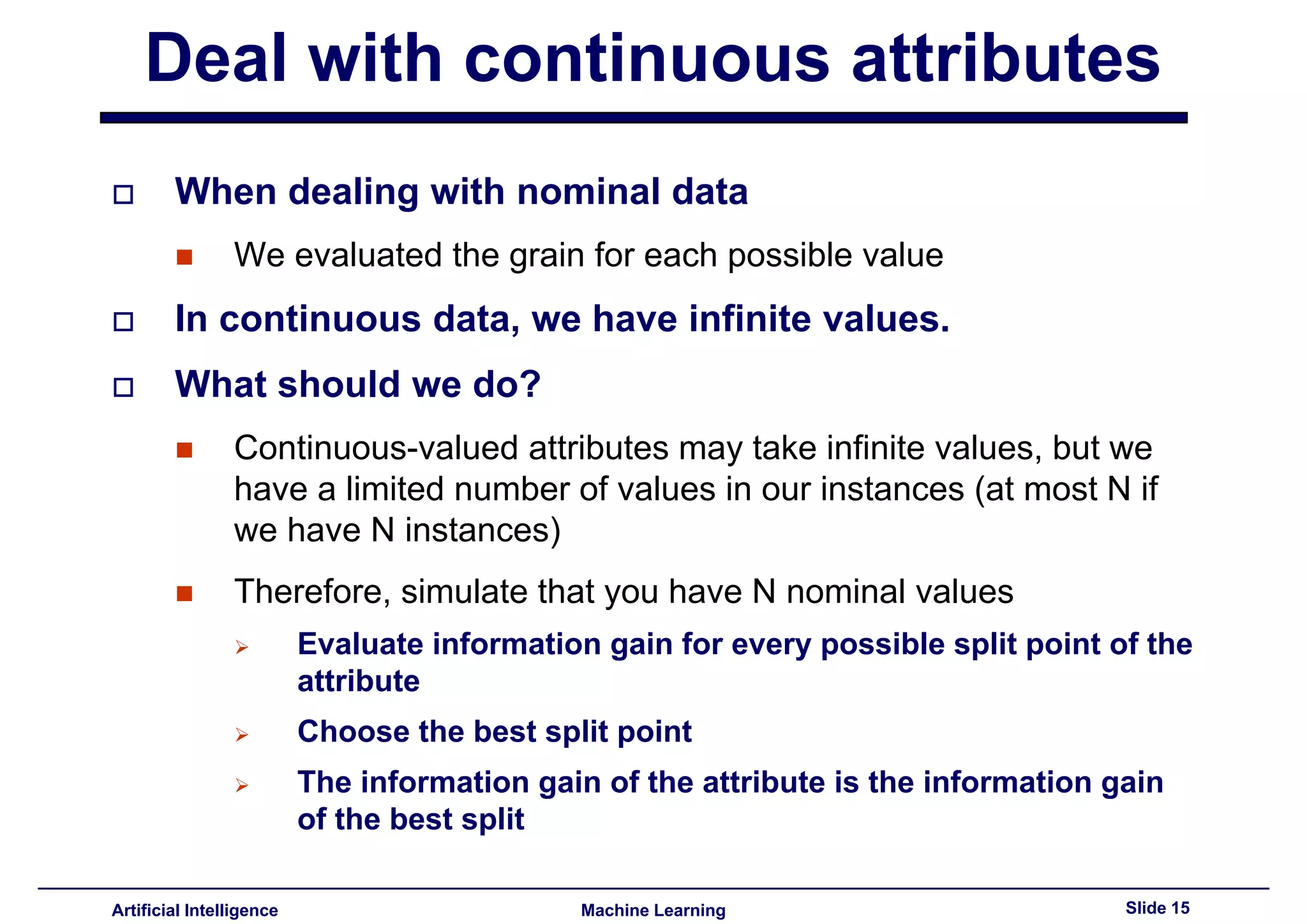
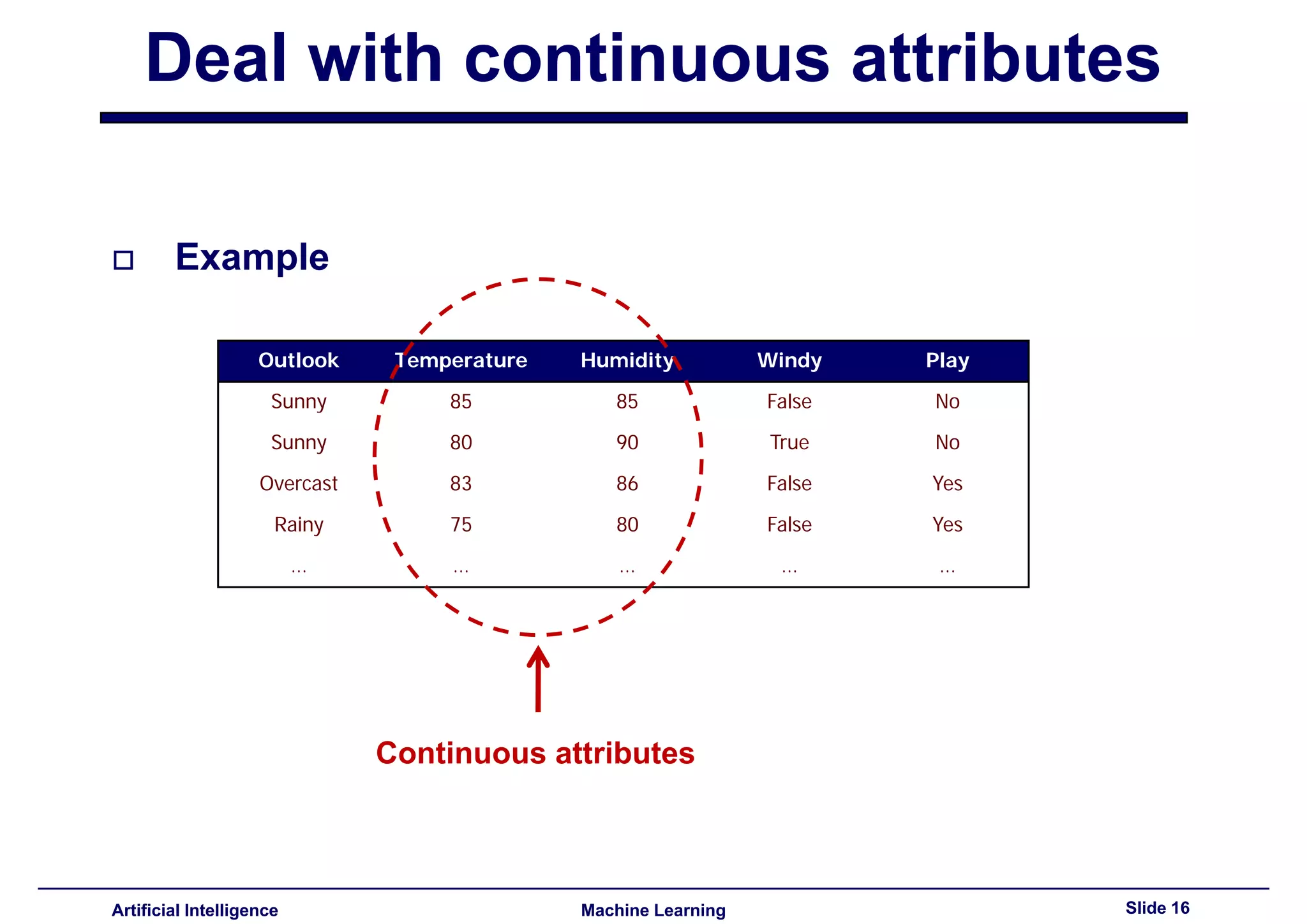
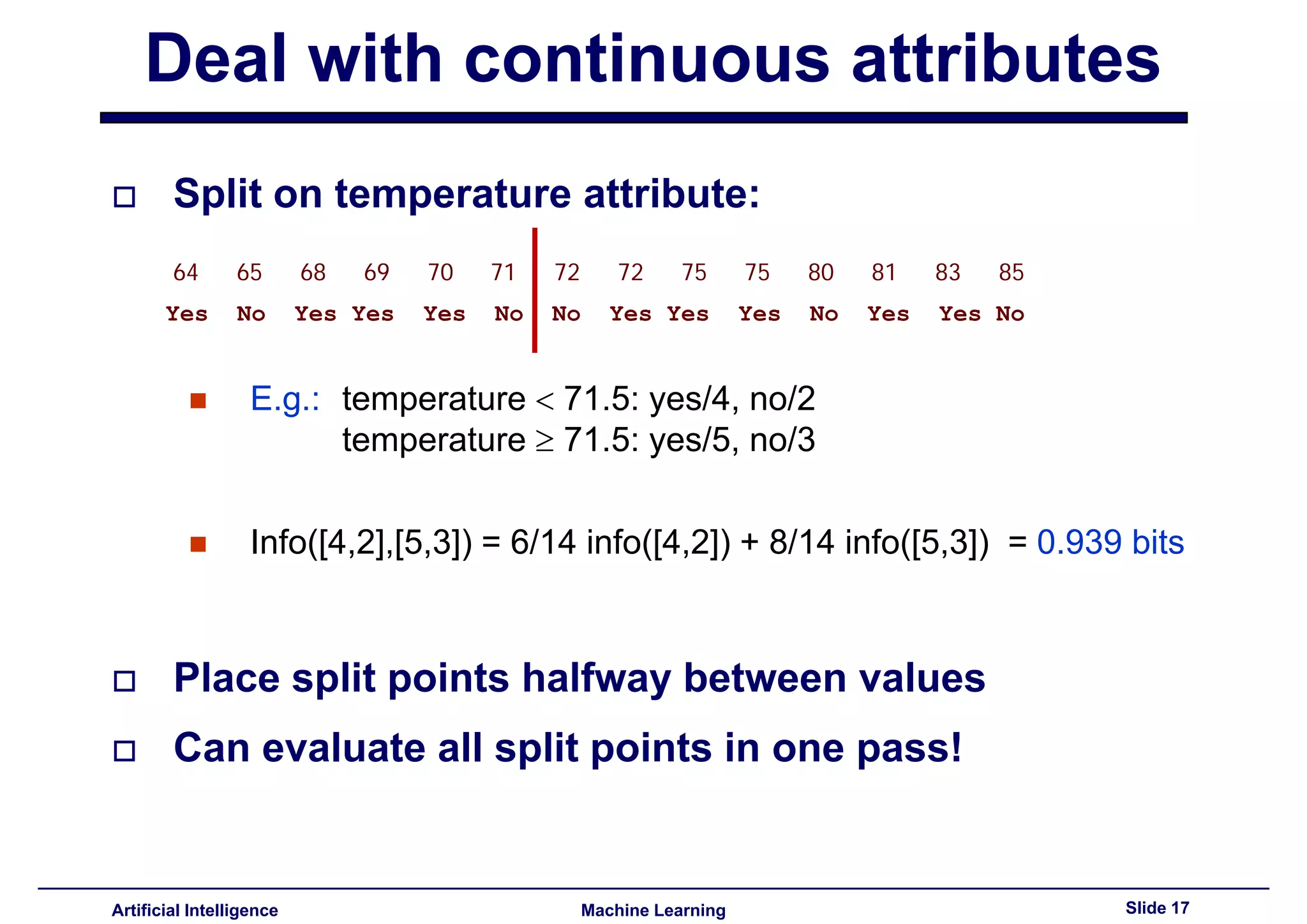
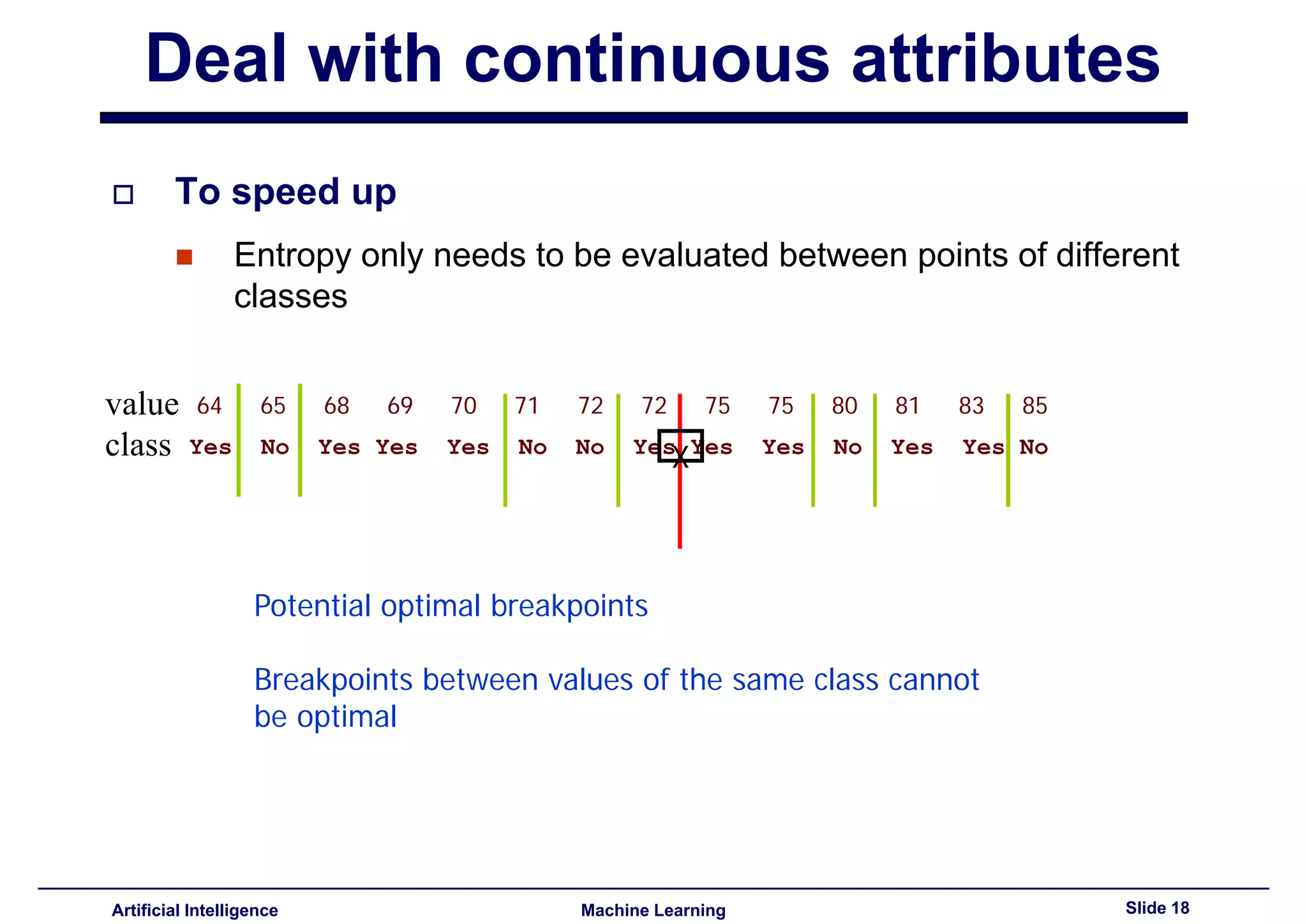
Methods to deal with continuous data, including finding optimal split points and using entropy for evaluation.
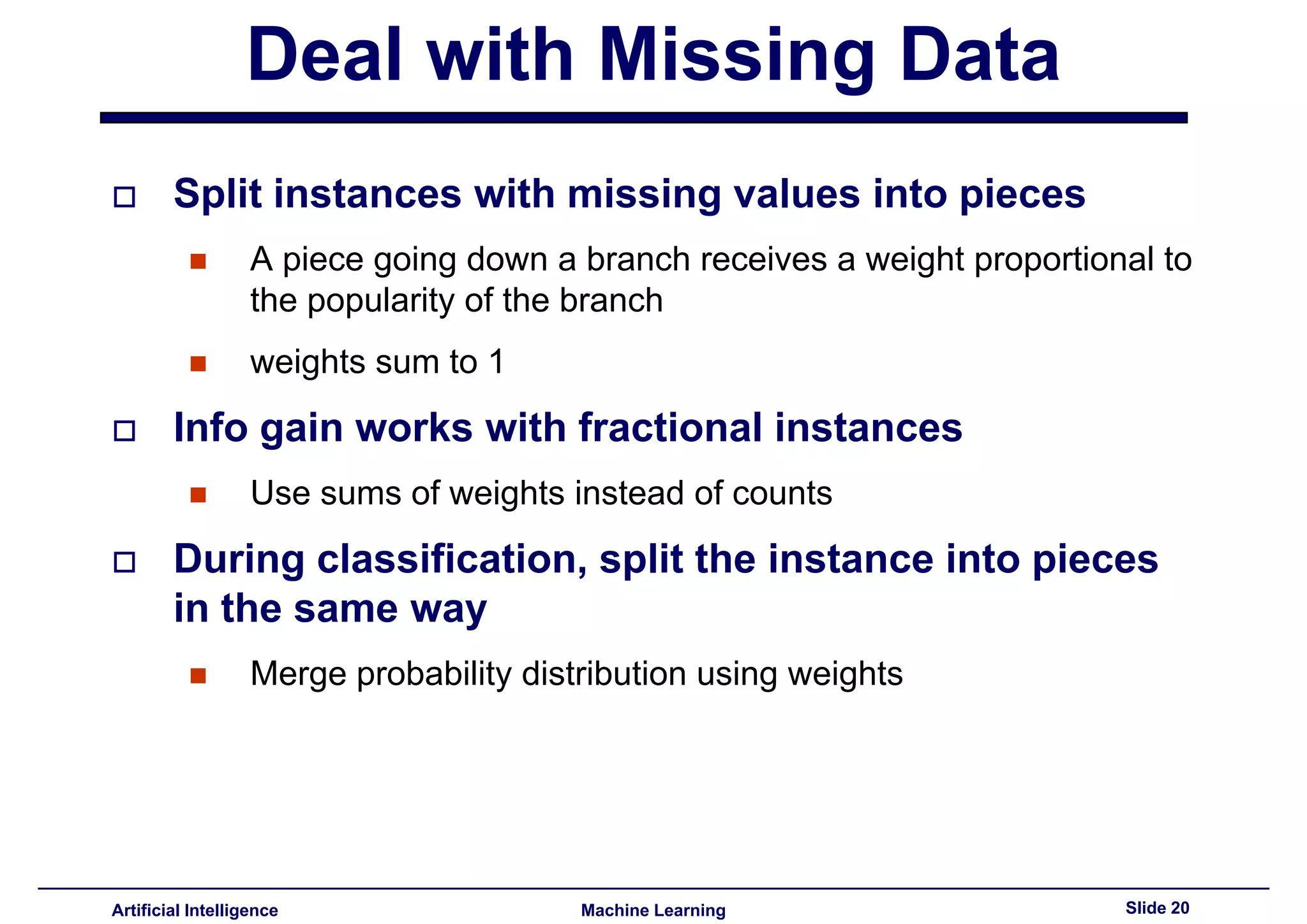
Methods for treating missing data values and splitting instances accordingly for effective classification.
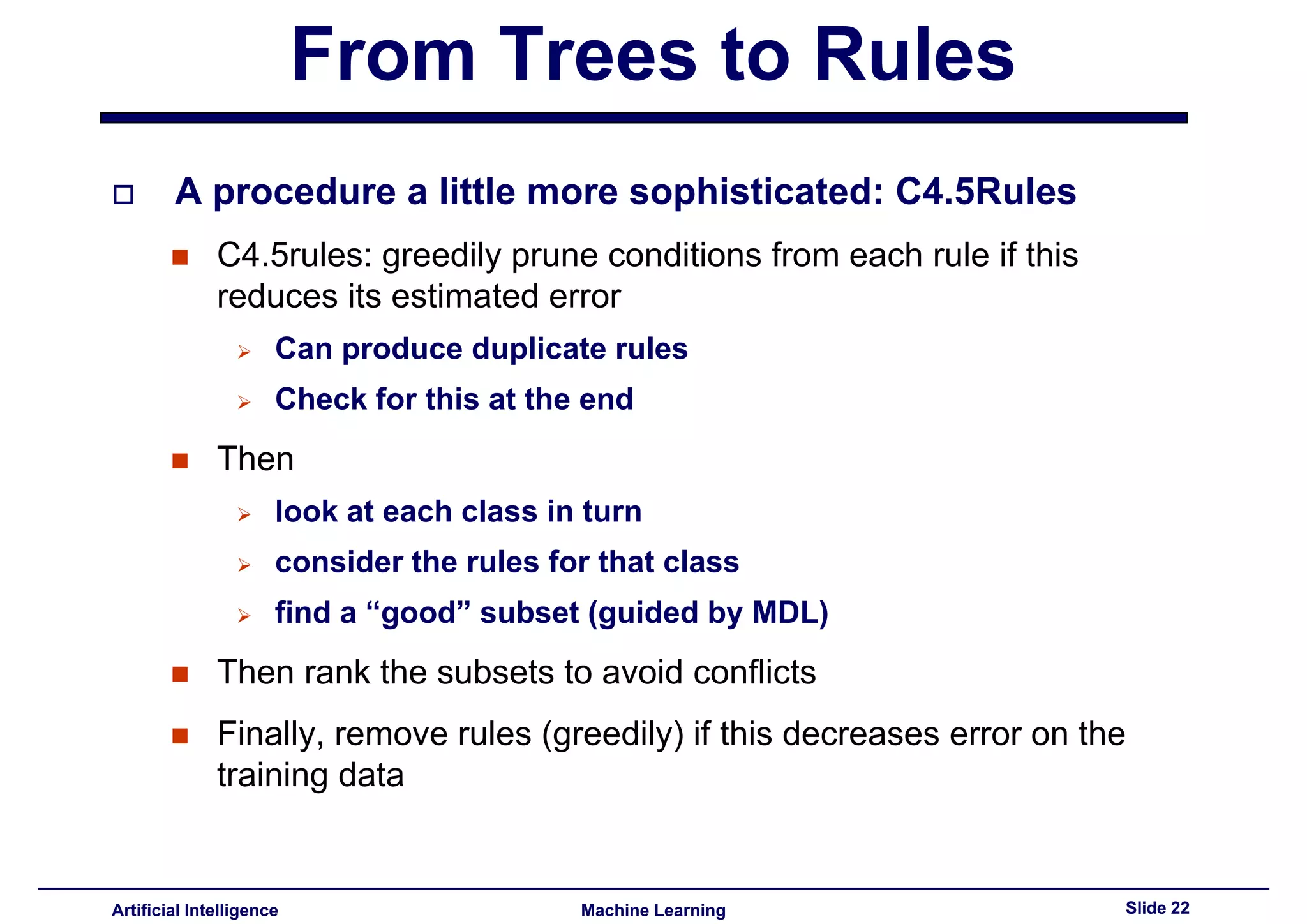
Described the conversion of decision trees to rules, emphasizing benefits like simplicity and independence from context.
Introduced the topic of instance-based classifiers for the next class, reiterating the presentation's theme.























