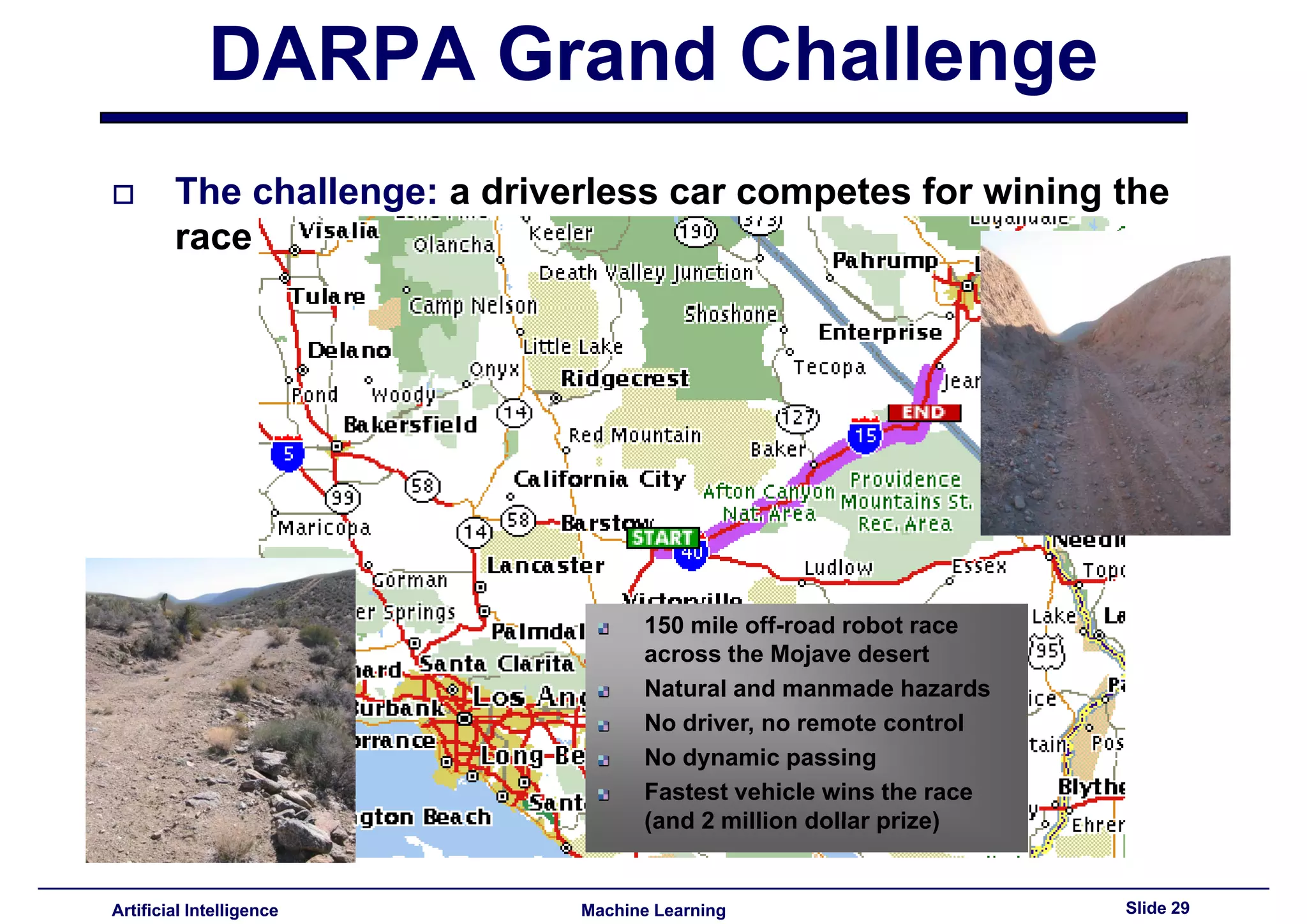
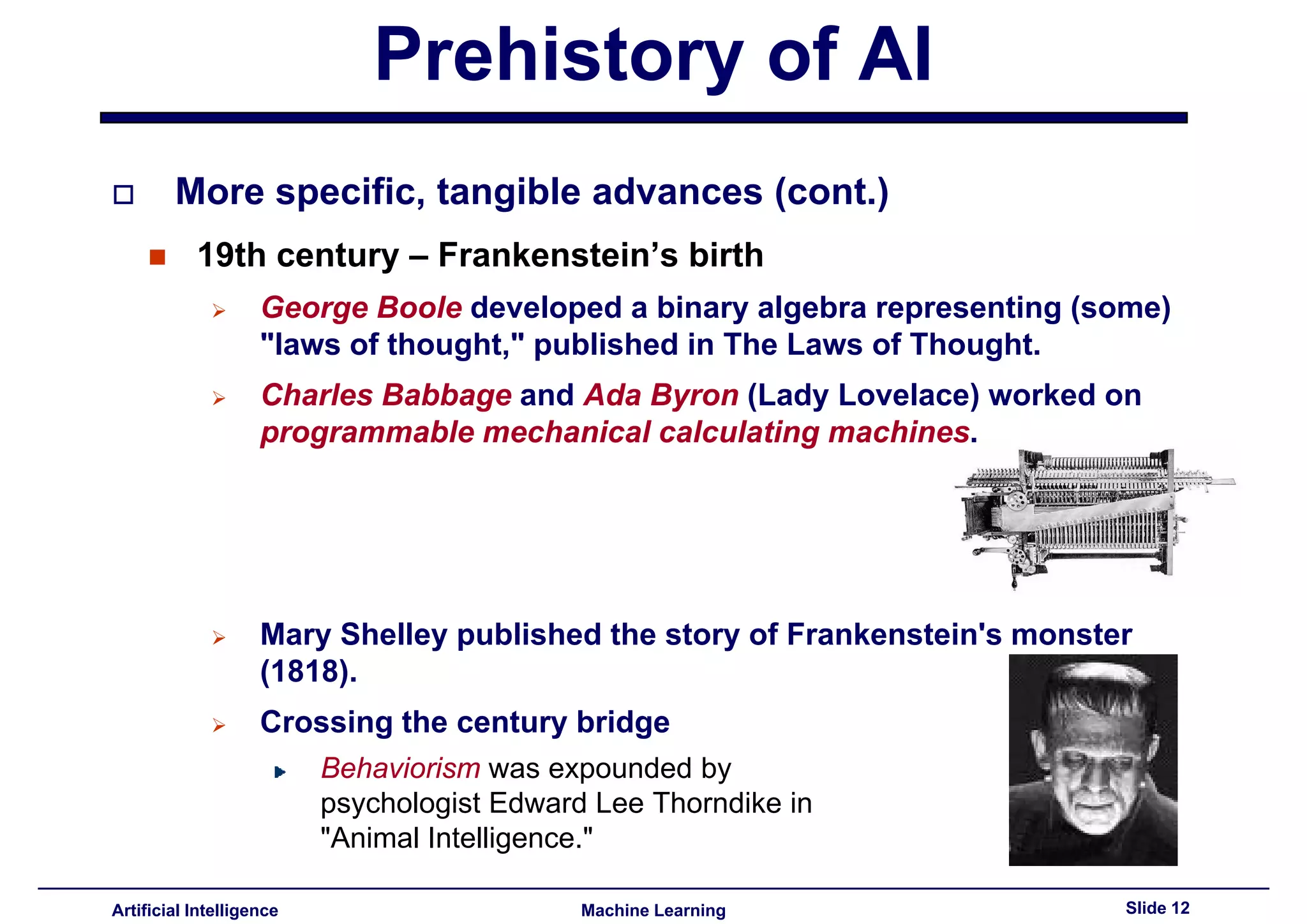
This document provides an overview of the history and development of artificial intelligence, beginning with early concepts of artificial beings and progressing through milestones like the Dartmouth Conference, development of expert systems in the 1970s-80s, advances in the 1990s with things like Deep Blue and robotics, and examples of modern applications like robotic vacuums and self-driving cars through challenges like DARPA's Grand Challenge.






![The Turing Test
More on Turing test
g
Objective: The machine needs to fool the machine
[INT] I heard that a striped rhinoceros flow on the
Mississippi in a pink balloon this morning. What do
you think about?
[COMP] That sound rather ridiculous to me
[INT] Really? My uncle did this one... Why this sound
ridiculous?
[COMP] Option 1: Rhinoceros don't have stripes
don t
[COMP] Option 2: Rhinoceros can't fly
Try
Tr to change ON for UNDER the Mississipi
Is this unfair for the computer?
[INT] What’s the result of 324 x 678?
[COMP] This is too difficult. I’m not a calculator!
Needs to seem more foolish than it actually is (has to lie!)
Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning Slide 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-ai1-introductionai-090922155953-phpapp02/75/Lecture1-AI1-Introduction-to-artificial-intelligence-16-2048.jpg)