Embed presentation
Downloaded 157 times









This document summarizes a lecture on reinforcement learning and the Q-learning algorithm. Q-learning is a temporal difference learning method that allows an agent to learn optimal policies without needing a model of the environment's dynamics. The algorithm works by learning an action-value function (Q-function) that directly approximates the optimal Q-function through Q-backups without requiring a model of the environment. Pseudocode is provided for the basic Q-learning algorithm. Examples are also given showing how Q-learning can be used to learn an optimal policy for navigating a maze.
































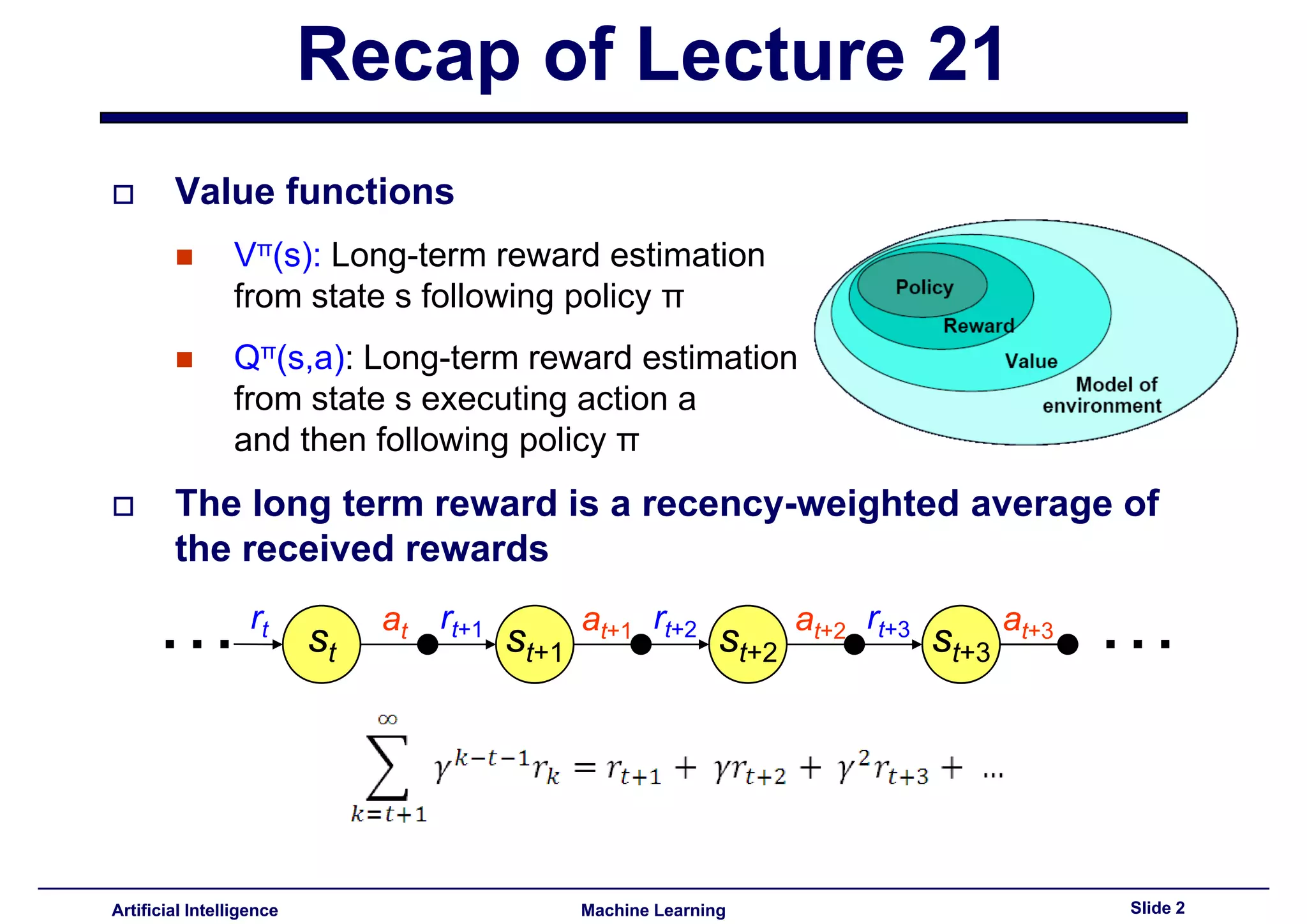
Overview of lecture series; Introduction of reinforcement learning and recap of previous concepts, including the state and action value functions.
Definition of policy as a mapping from states to actions based on probabilities.
Outline of the main topics to be covered including Bellman equations, optimal policy, Q-learning.
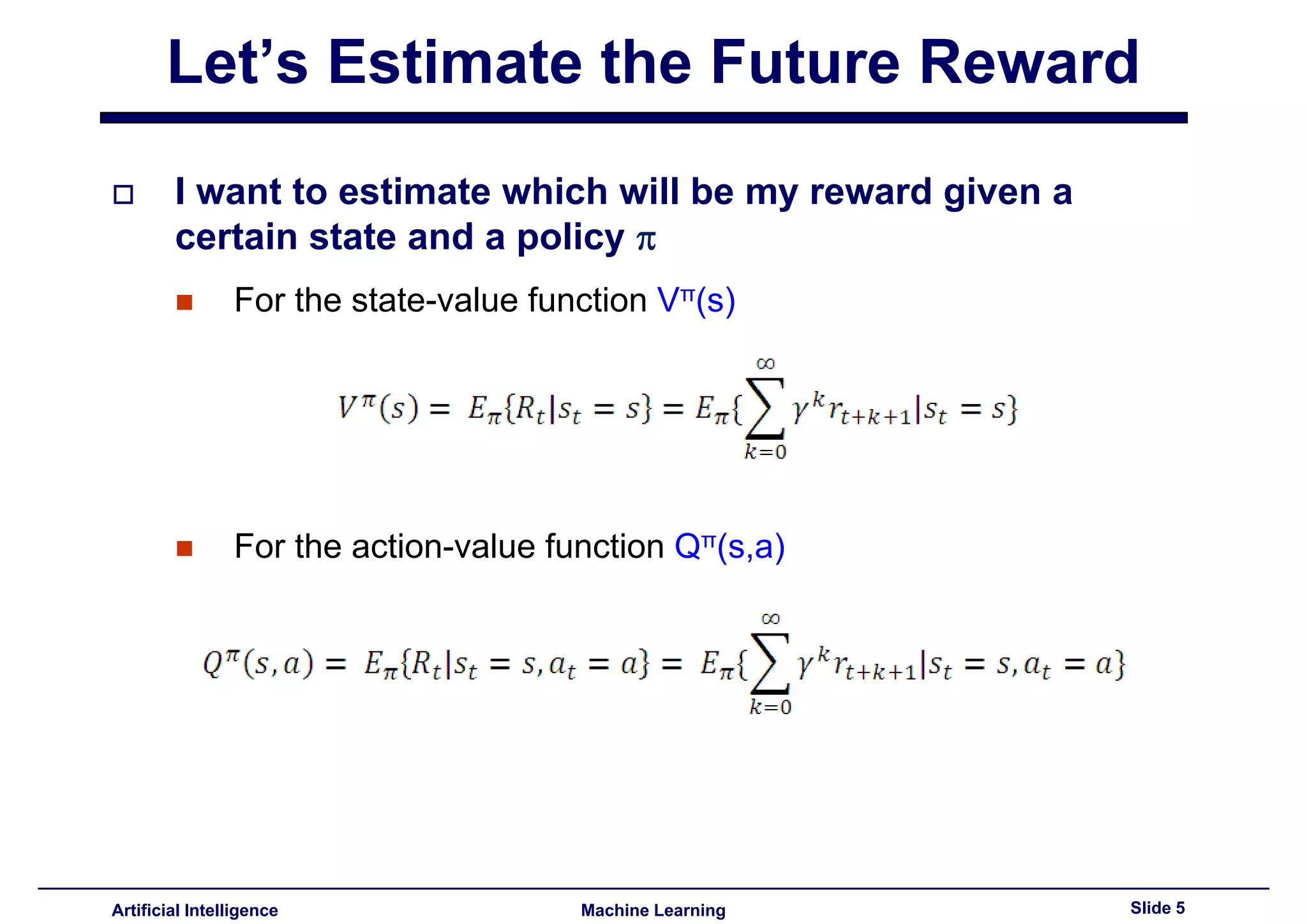
Introduction to estimating rewards based on states using state-value and action-value functions.
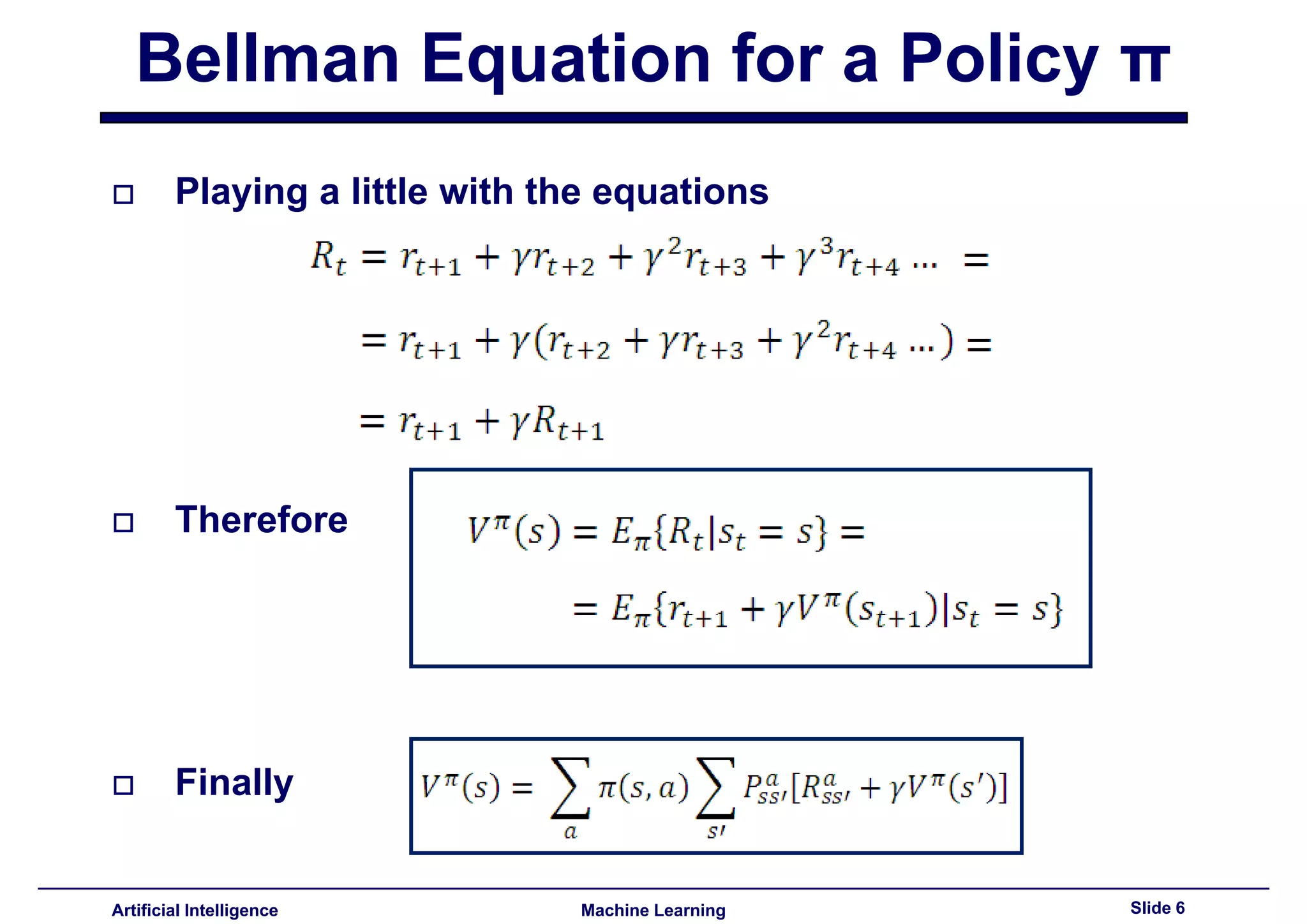
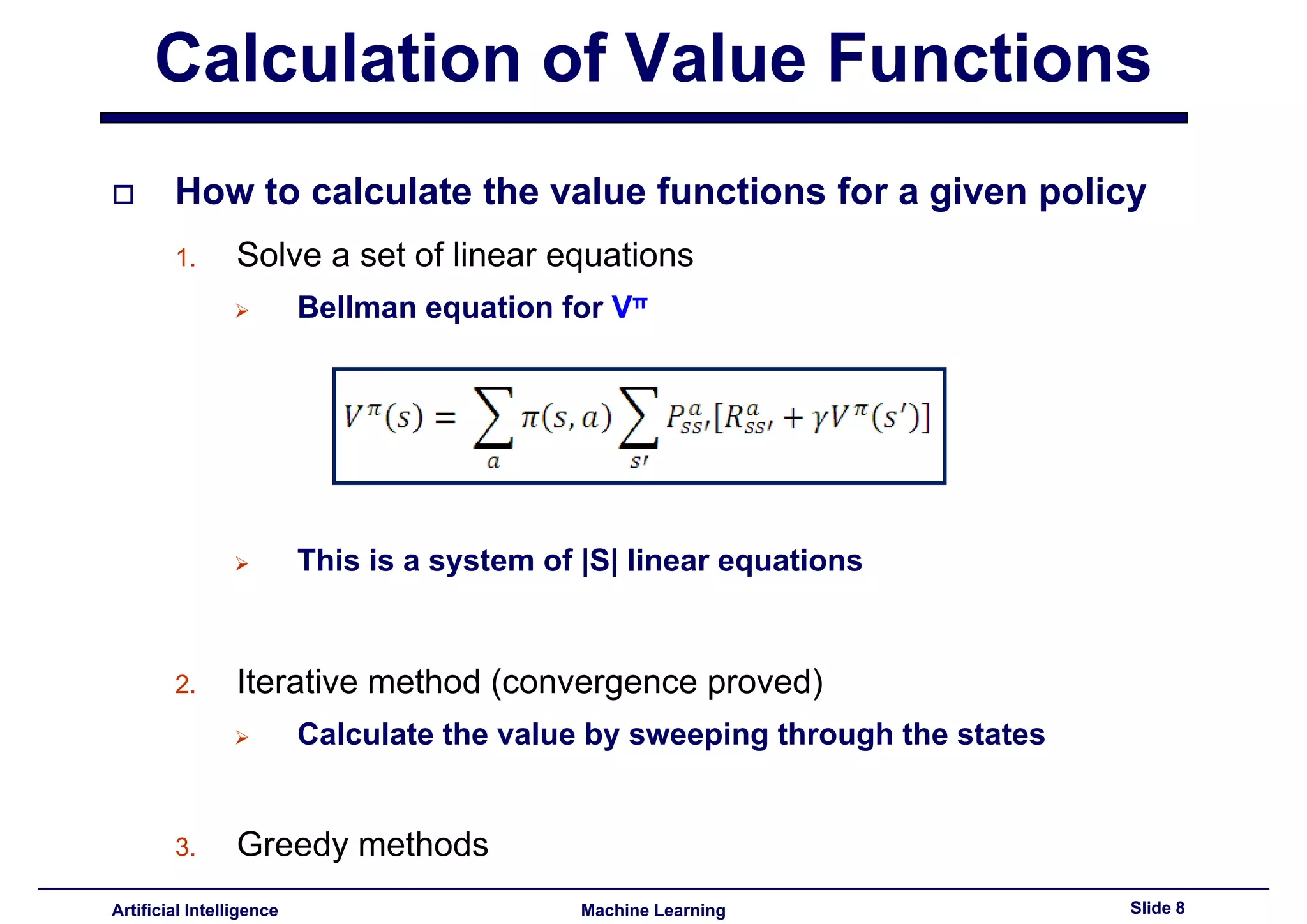
Introduction and manipulation of the Bellman equation relevant for policy evaluation.
Discussion of the Q-value Bellman equation as part of evaluating action-value functions.
Methods for calculating value functions including solving linear equations and iterative methods.
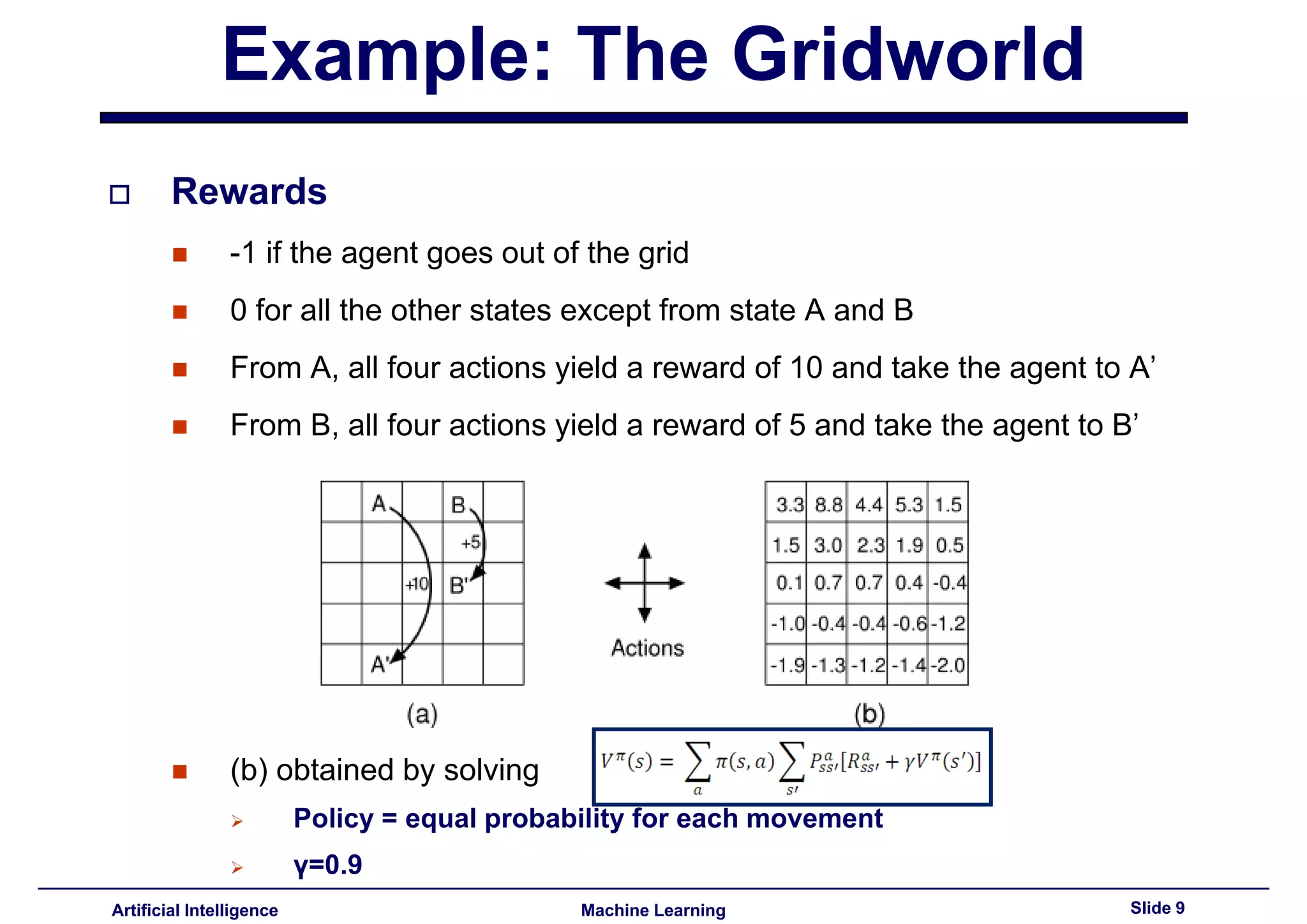
Example environment (Gridworld) to illustrate concepts of rewards in reinforcement learning.
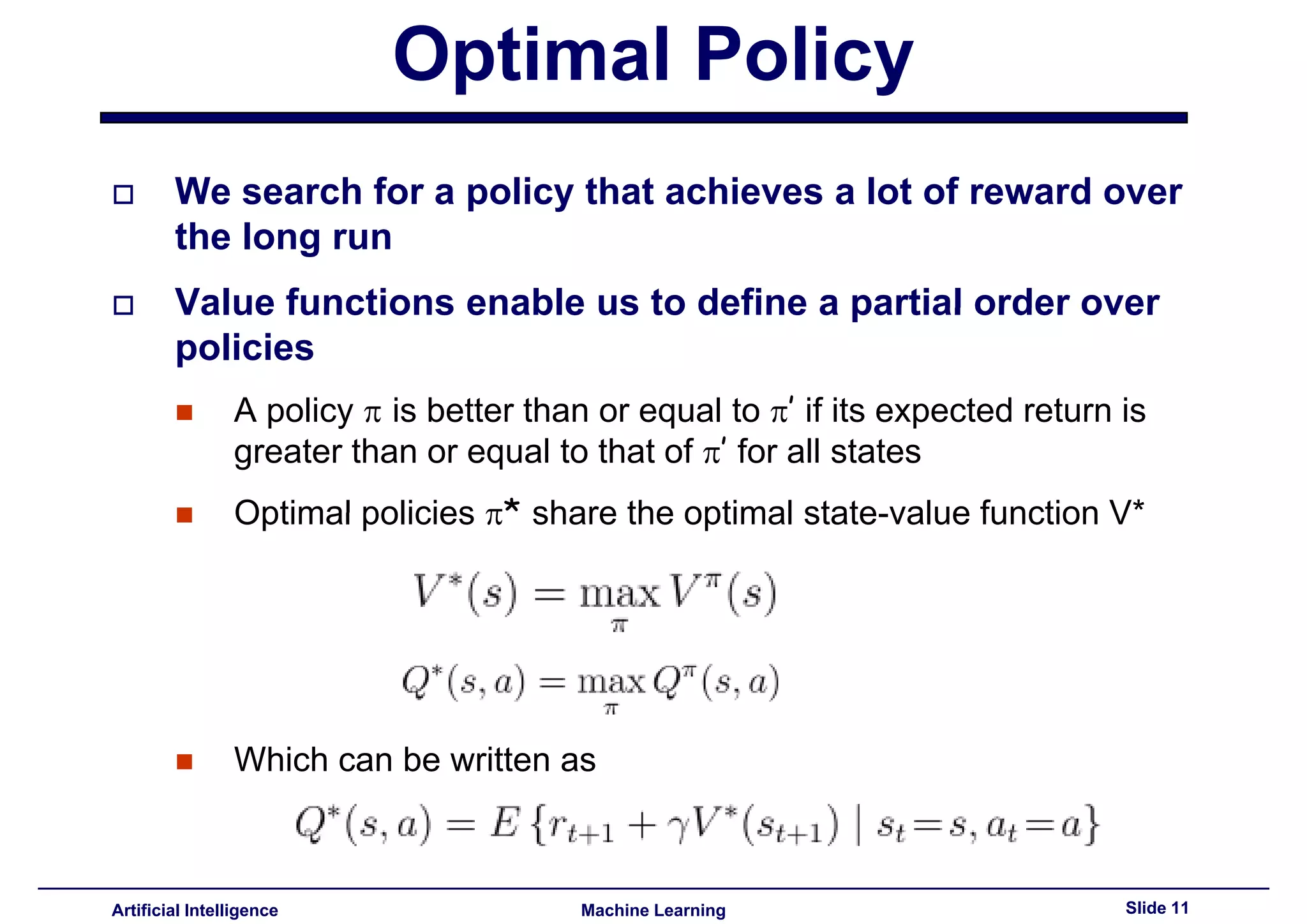
Introduction to the approach of identifying the optimal policy in reinforcement learning.
Criteria for optimal policies based on their expected returns compared to other policies.
Exploration of techniques to discover optimal policies within reinforcement learning.
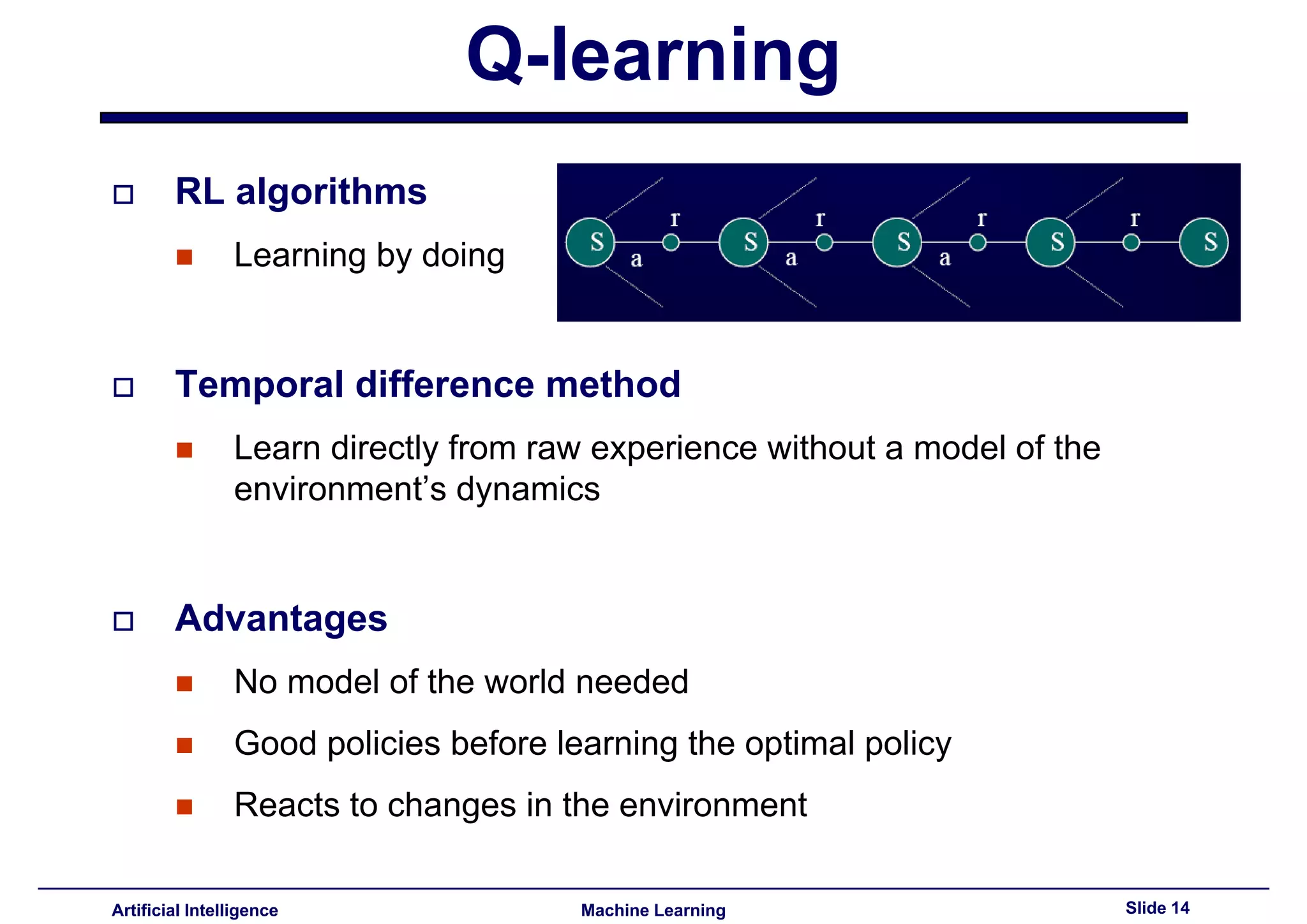
Introduction to Q-learning, emphasizing learning through experience without needing a model.
Benefits of Q-learning, including adaptability and applicability without environment models.
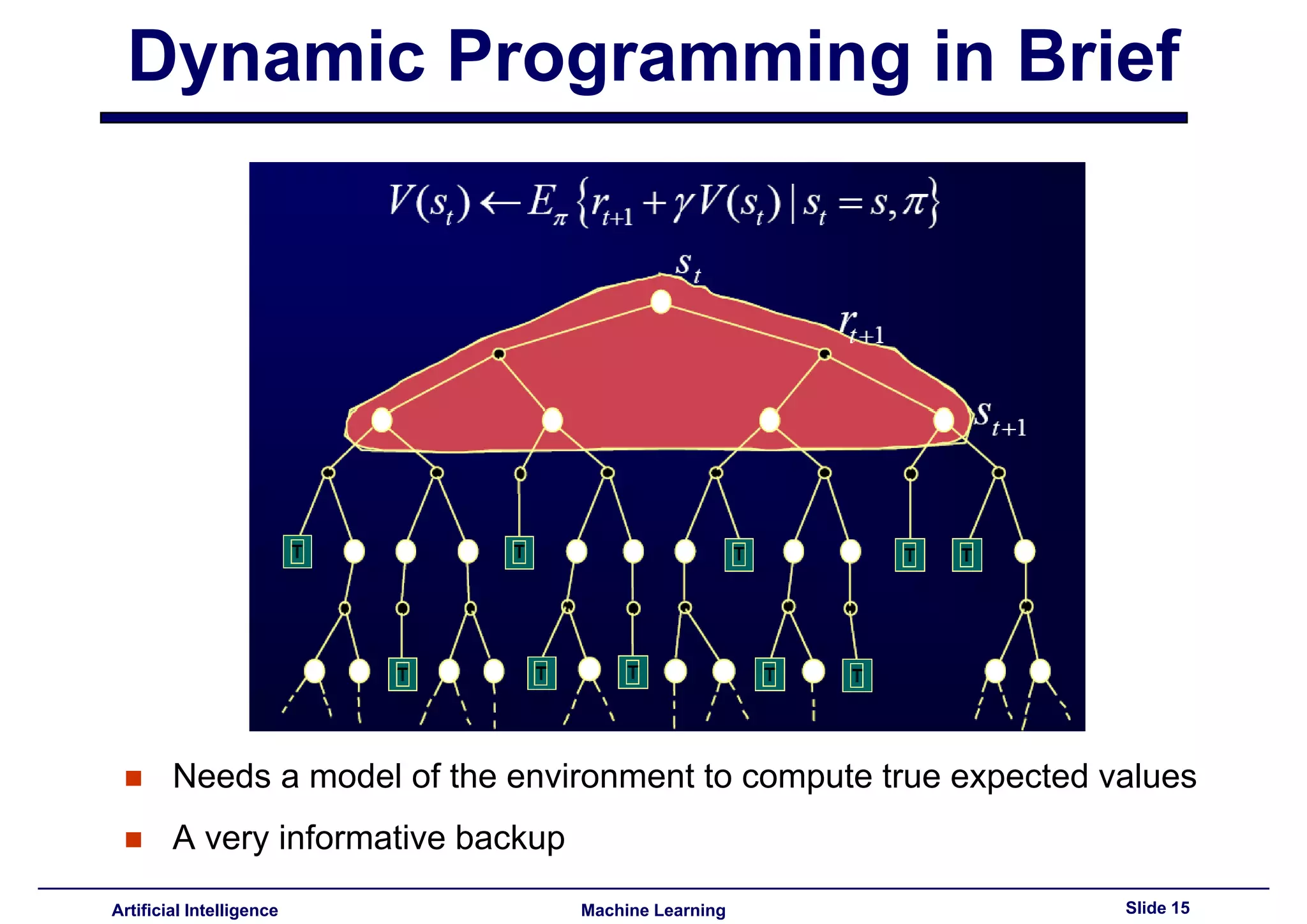
Brief discussion on dynamic programming and its need for an accurate environment model.
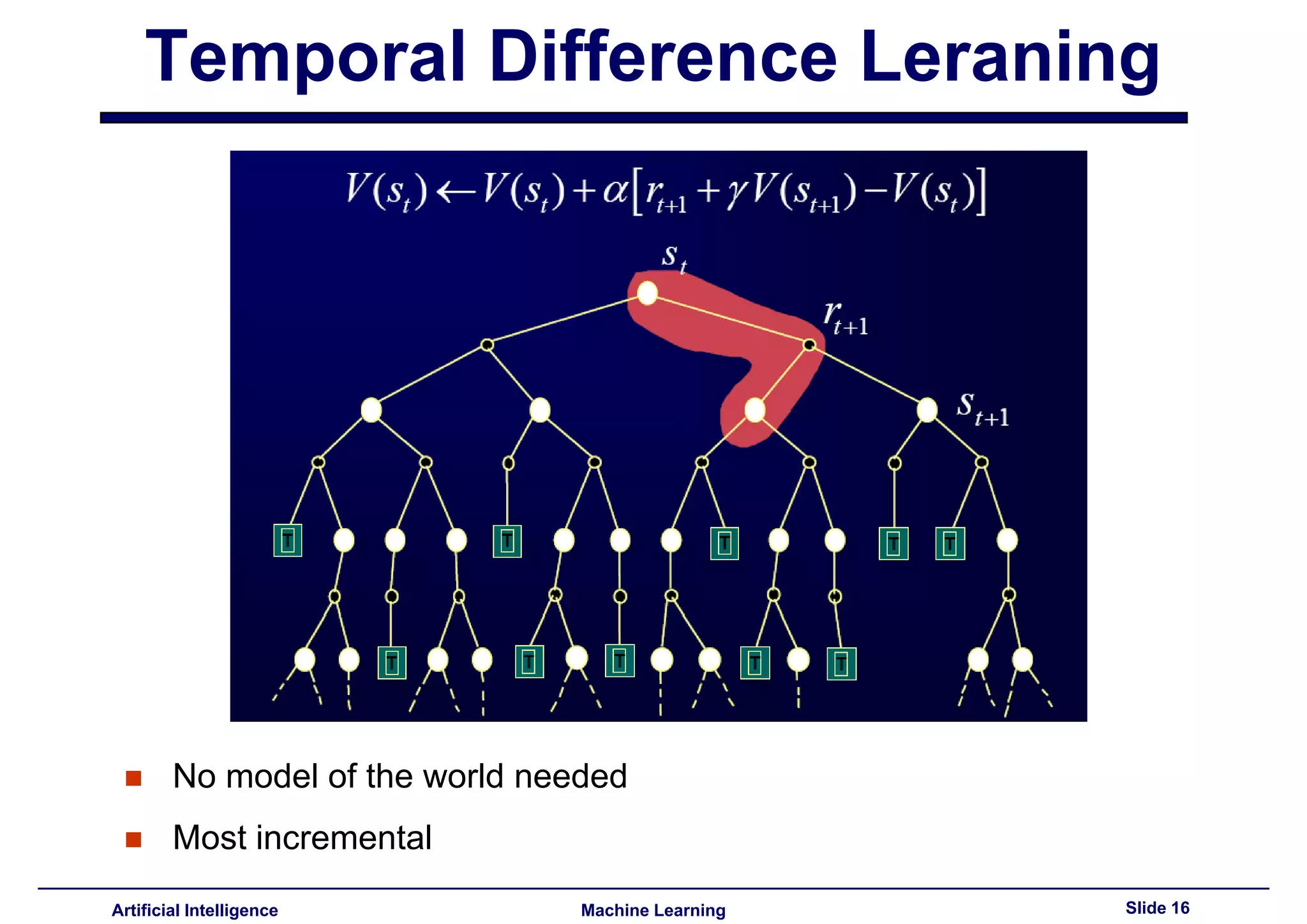
Introduction to Temporal Difference learning, emphasizing its incremental updates without models.
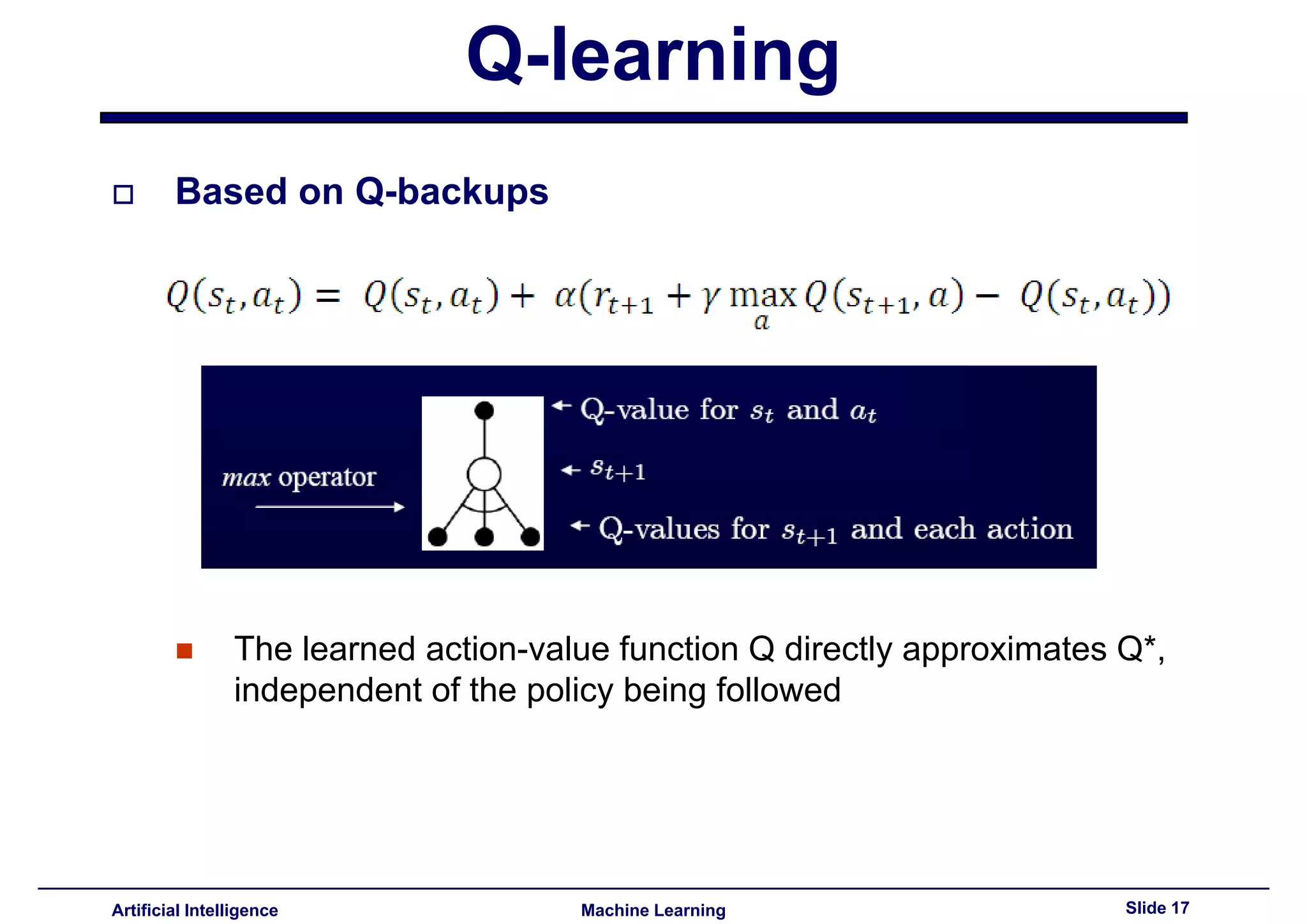
Description of Q-backups in Q-learning; the learned action-value function approximate Q*.
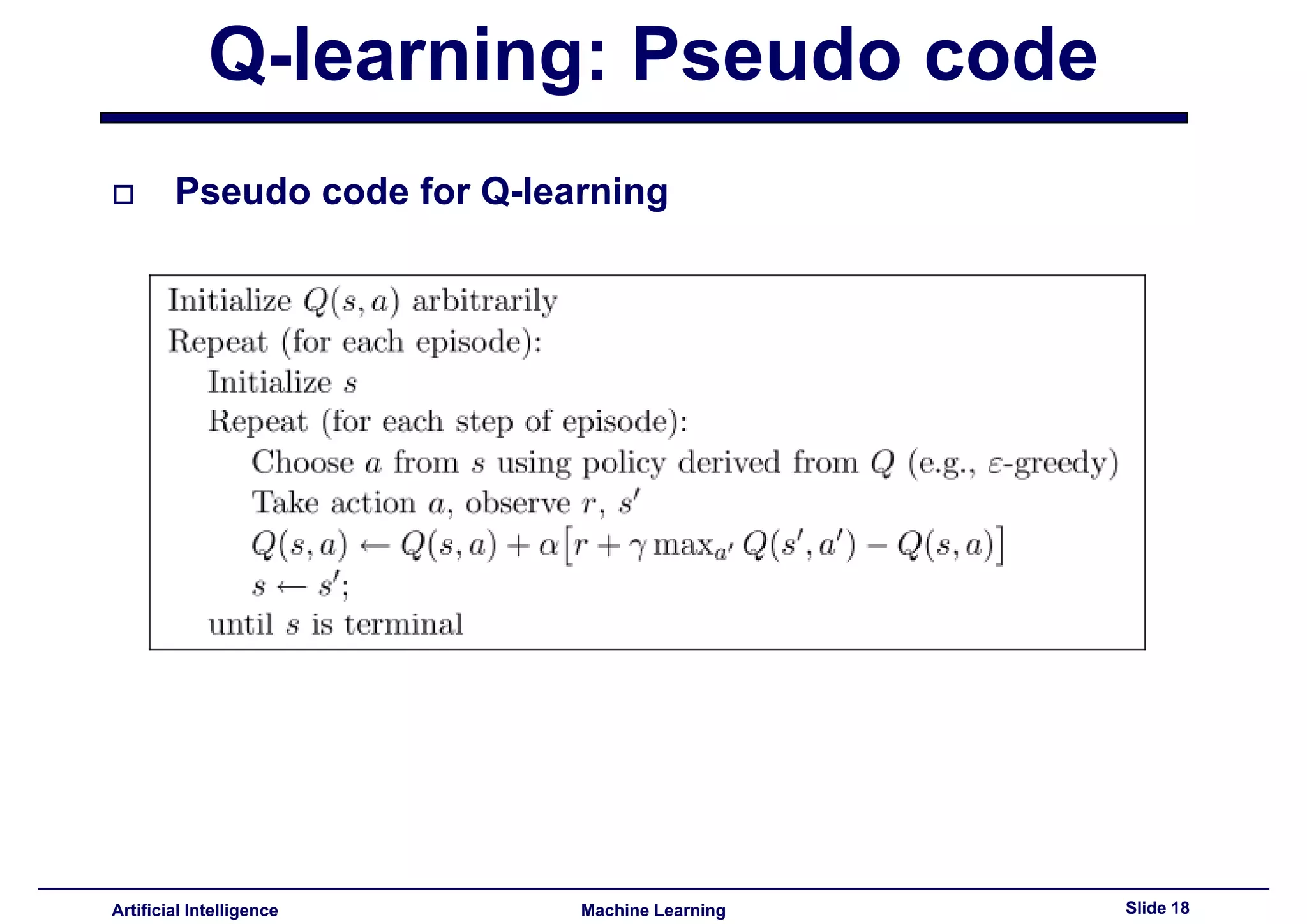
Presentation of pseudo code for implementing Q-learning in reinforcement learning frameworks.
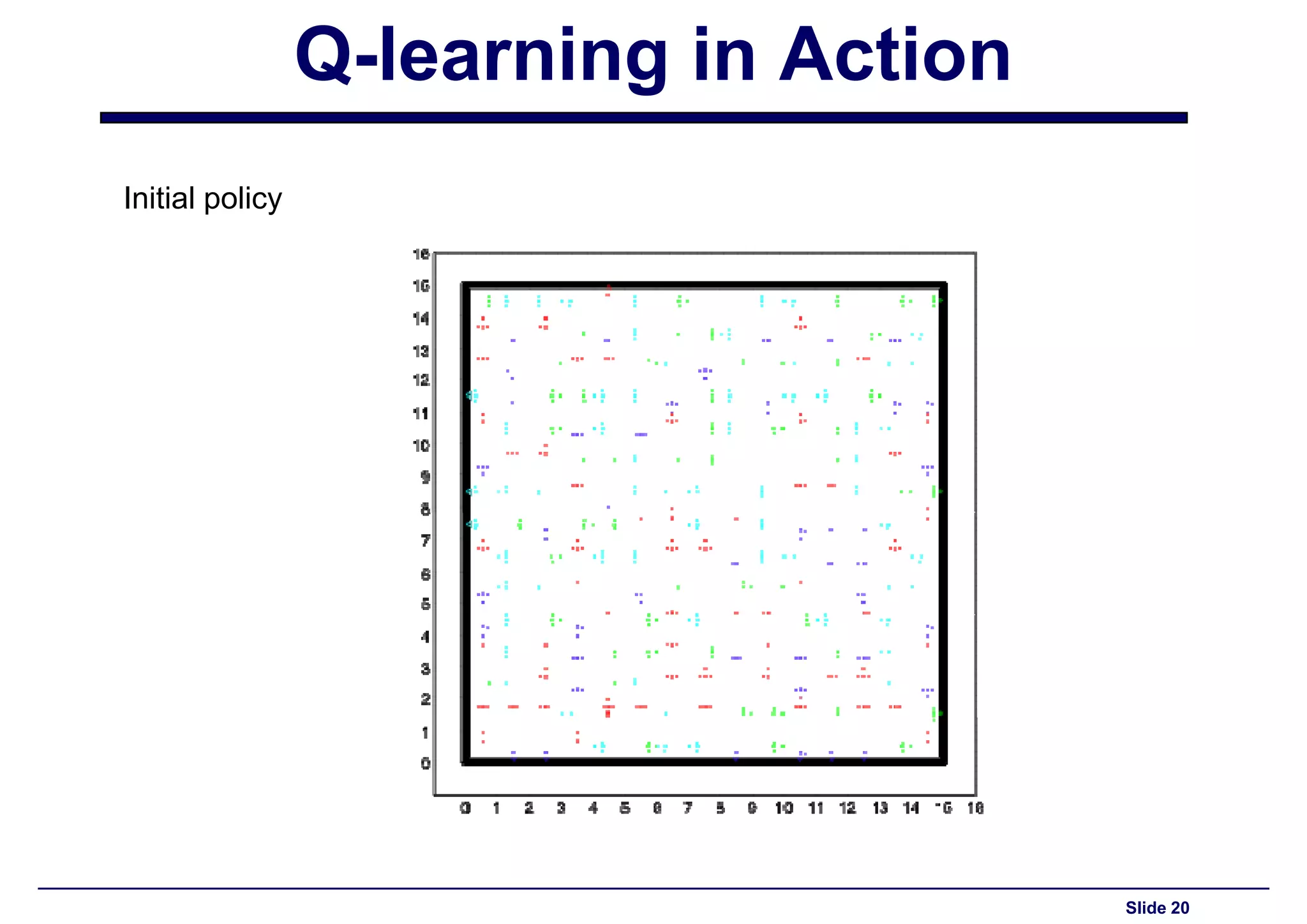
Demonstration of Q-learning application in a 15x15 maze world with defined rewards.
Display of the initial policy used in Q-learning implementation for the maze.
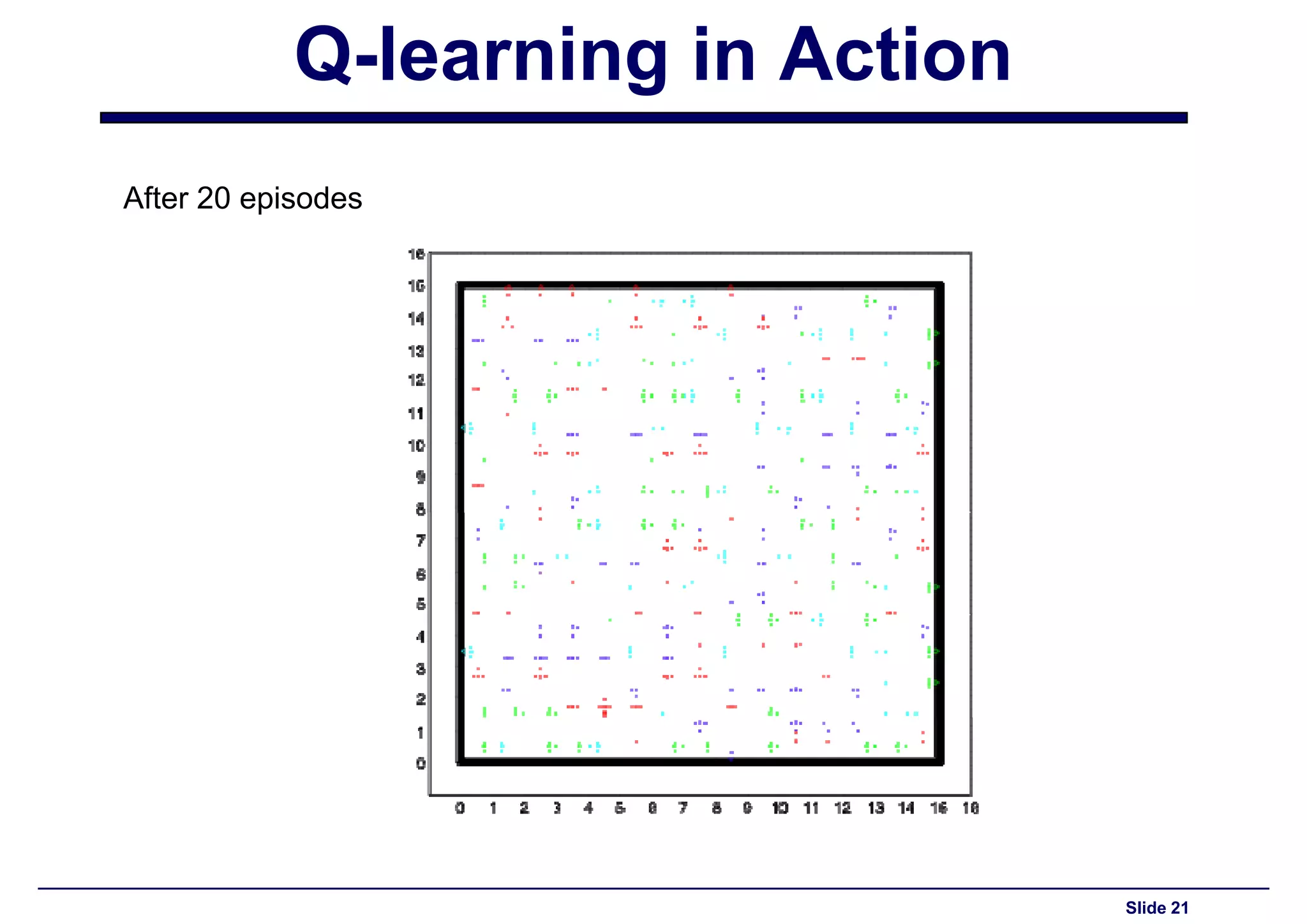
Results of Q-learning after 20 episodes showing changes in agent's performance.
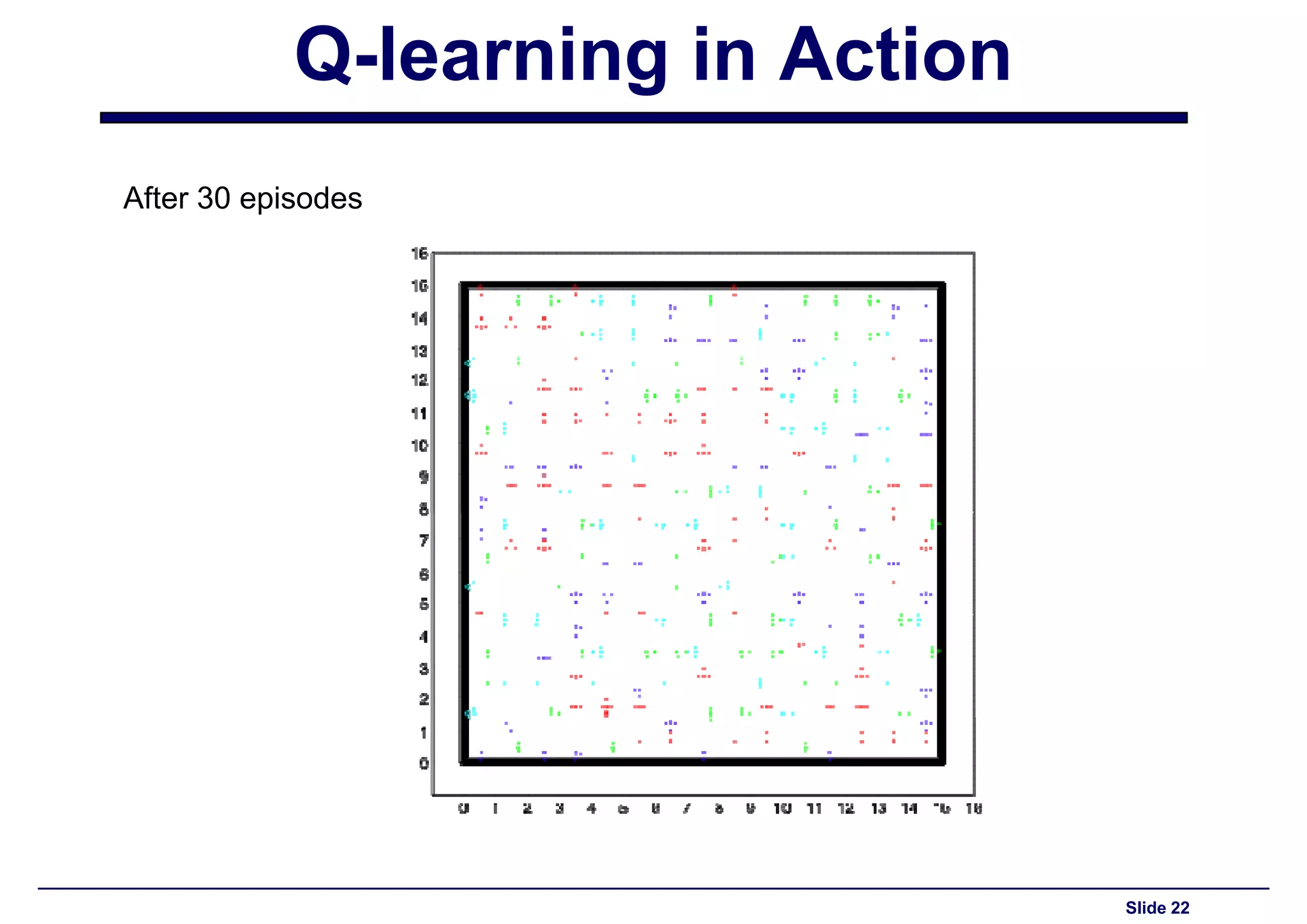
Observations and results from the Q-learning application after 30 episodes.
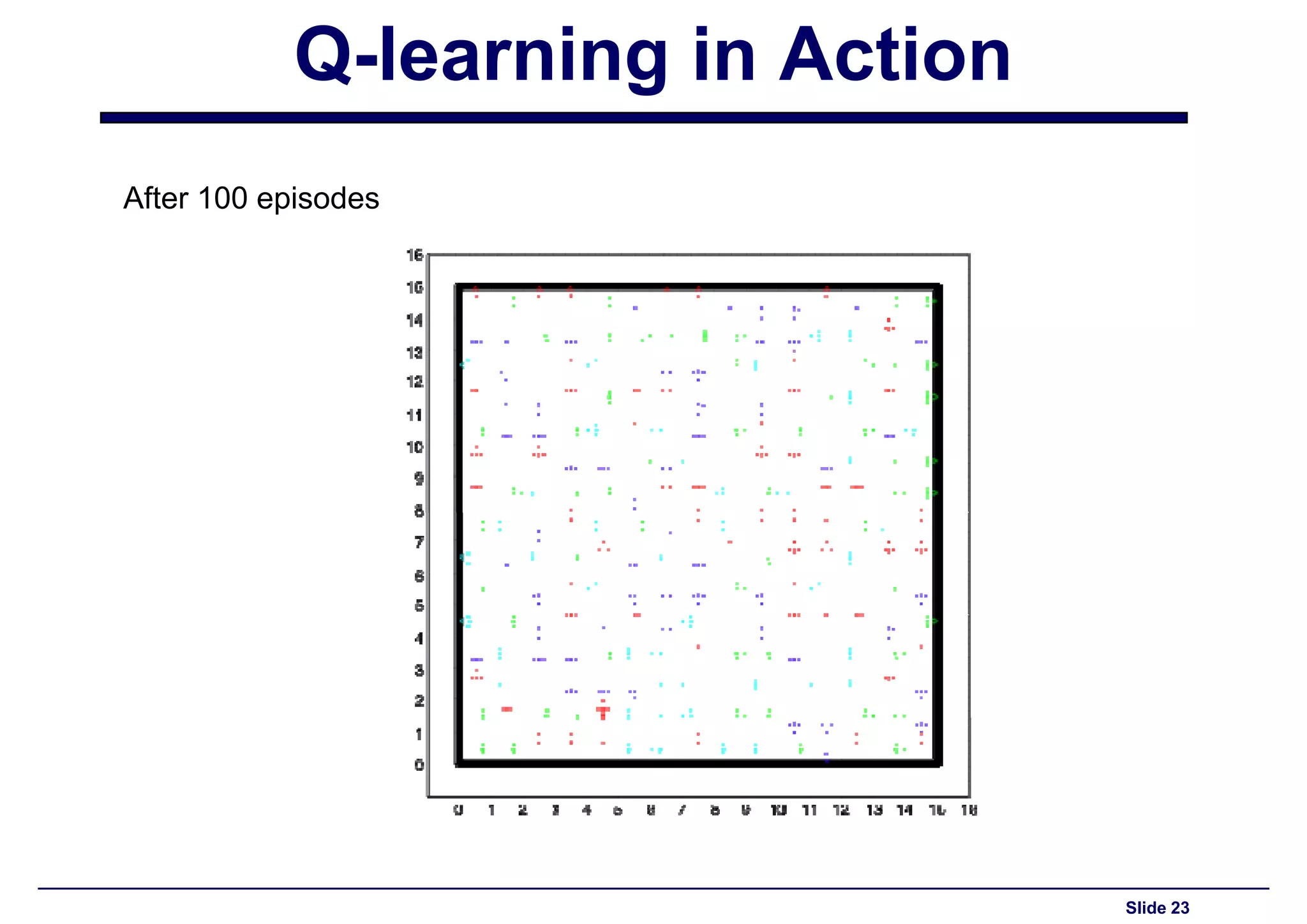
Analysis and output of Q-learning's performance after 100 training episodes.
Performance evaluation of the Q-learning agent following 150 episodes of learning.
Assessment of Q-learning outcomes after 200 episodes, gauging improvements in policy.
Performance metrics from Q-learning after 250 episodes showcasing learned strategies.
Analysis of the agent's performance and learned behavior after training for 300 episodes.
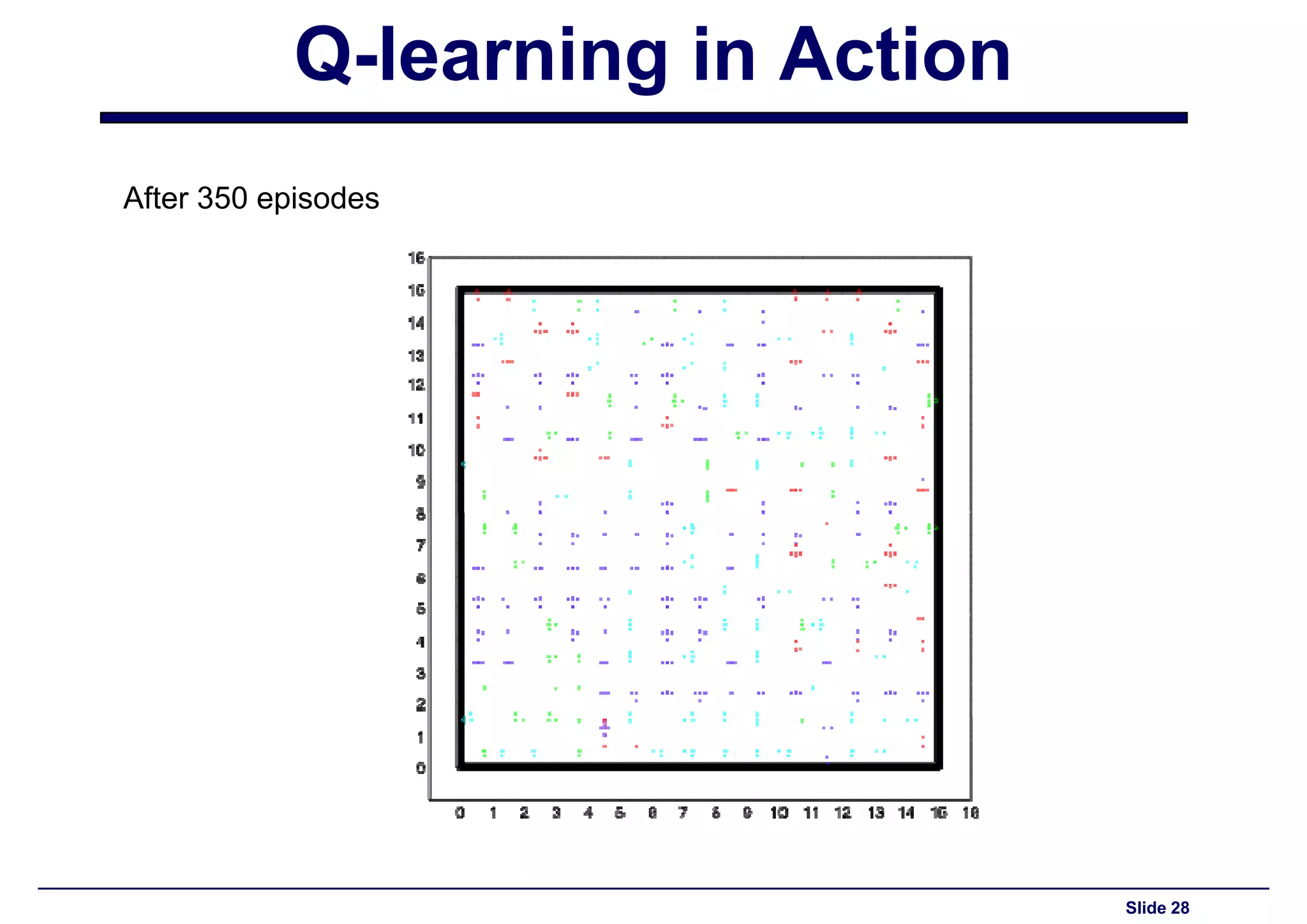
Ongoing performance assessment of the Q-learning agent after 350 episodes.
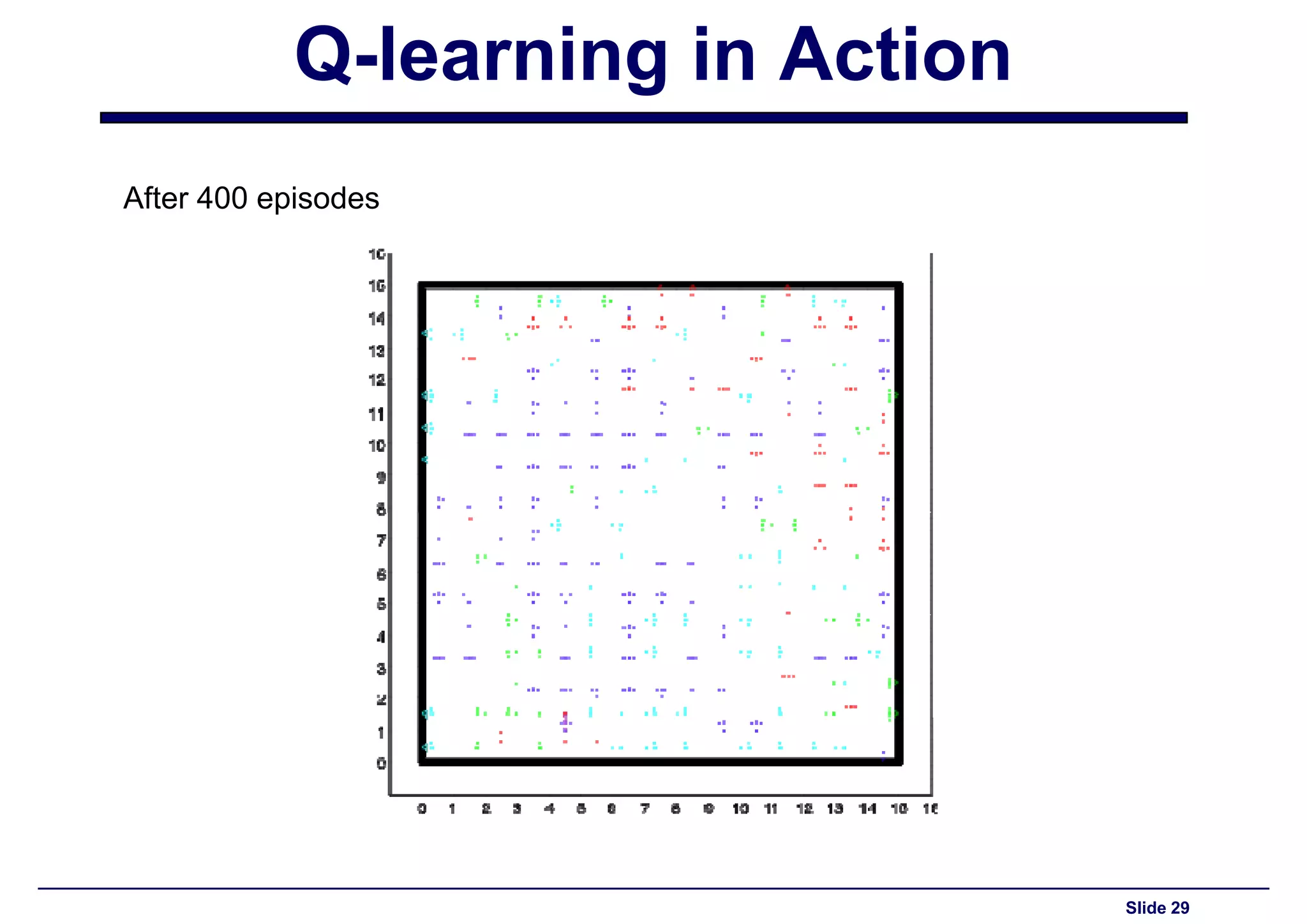
Final performance insights from Q-learning after 400 episodes of training.
Discussion on the balance of exploration techniques in learning optimal policies and values.
Preview of the next lecture focusing on reinforcement learning with Learning Classifier Systems.
Findings and reinforcement of concepts discussed in the course on reinforcement learning.