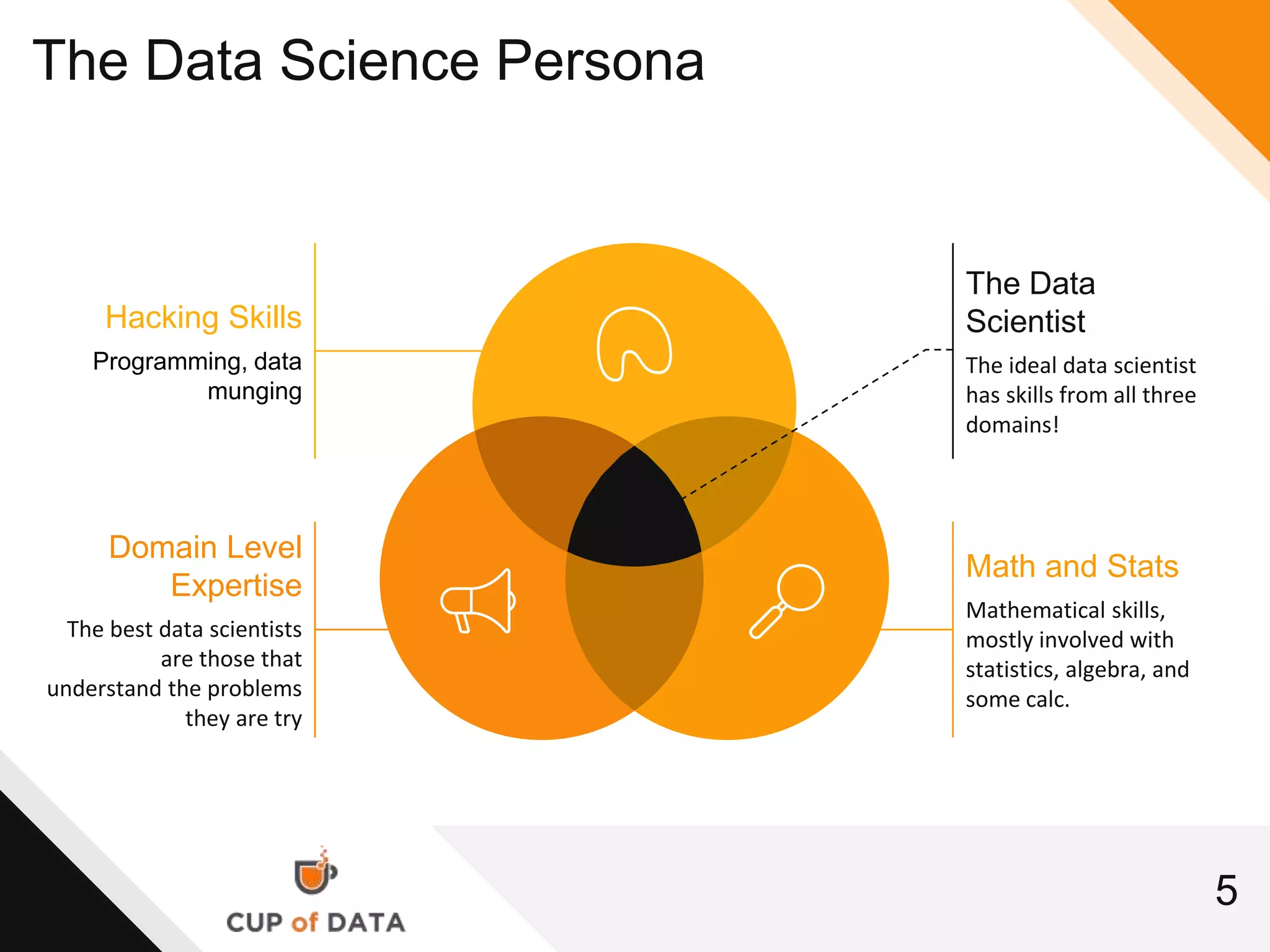
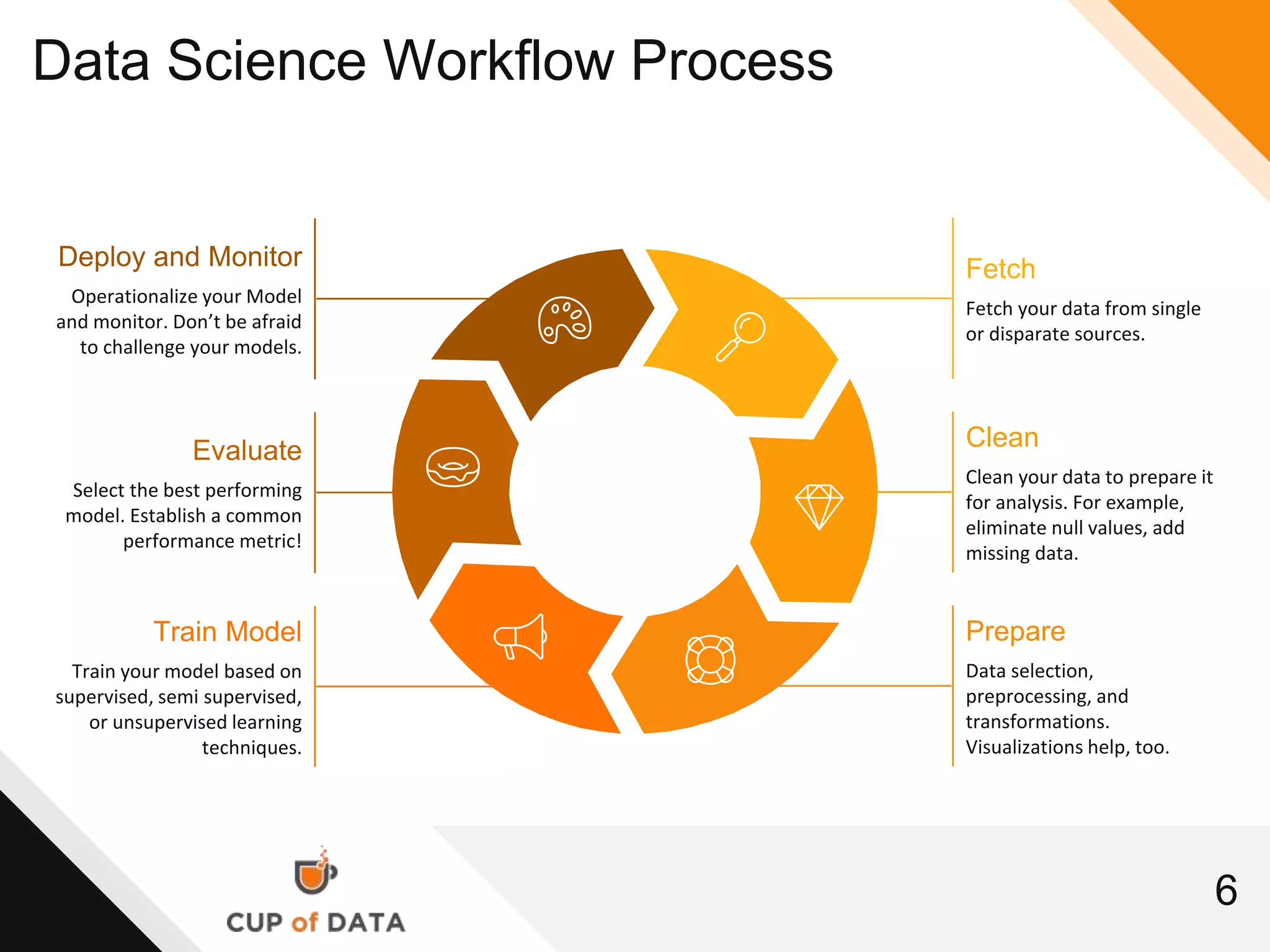
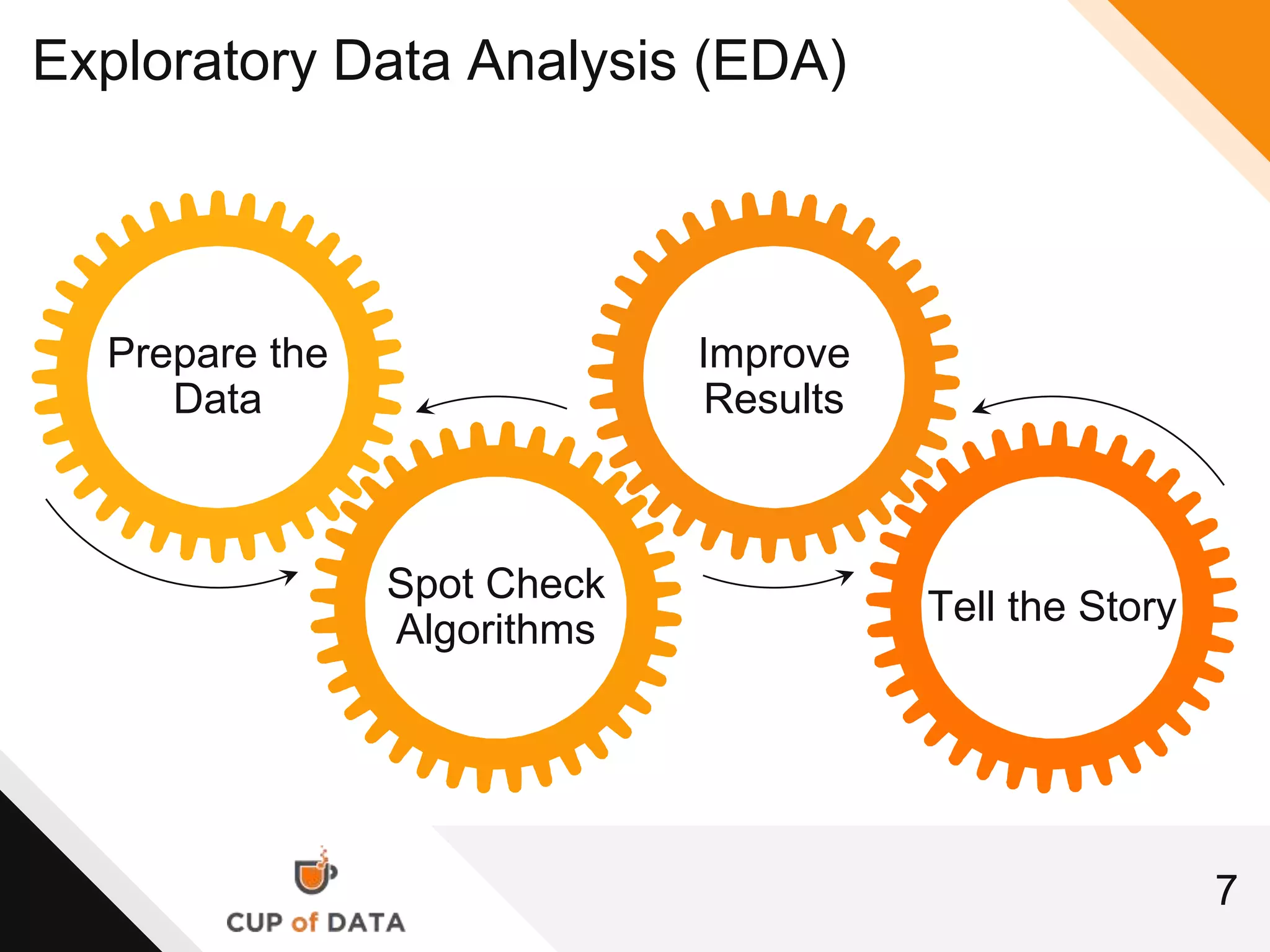
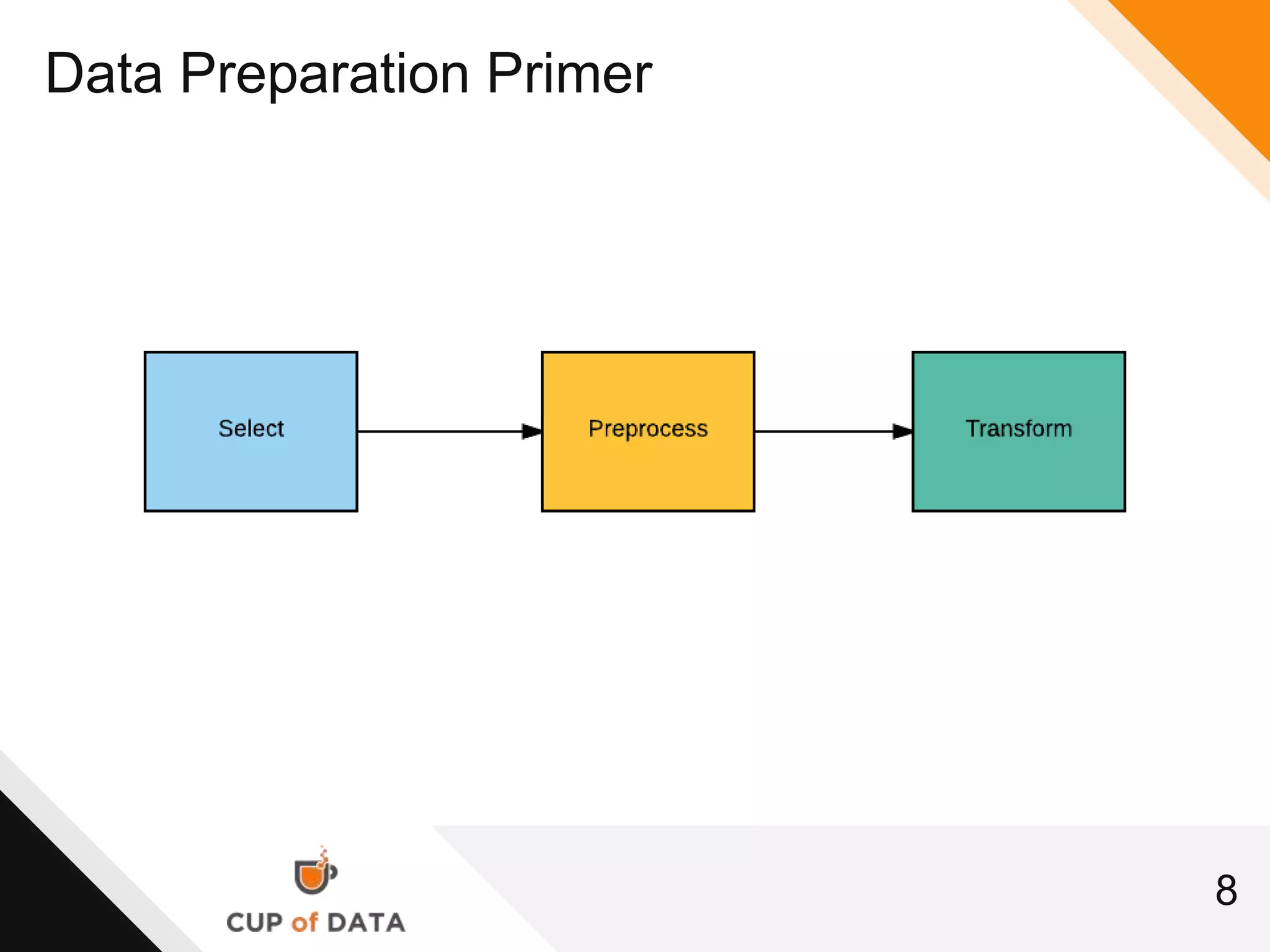
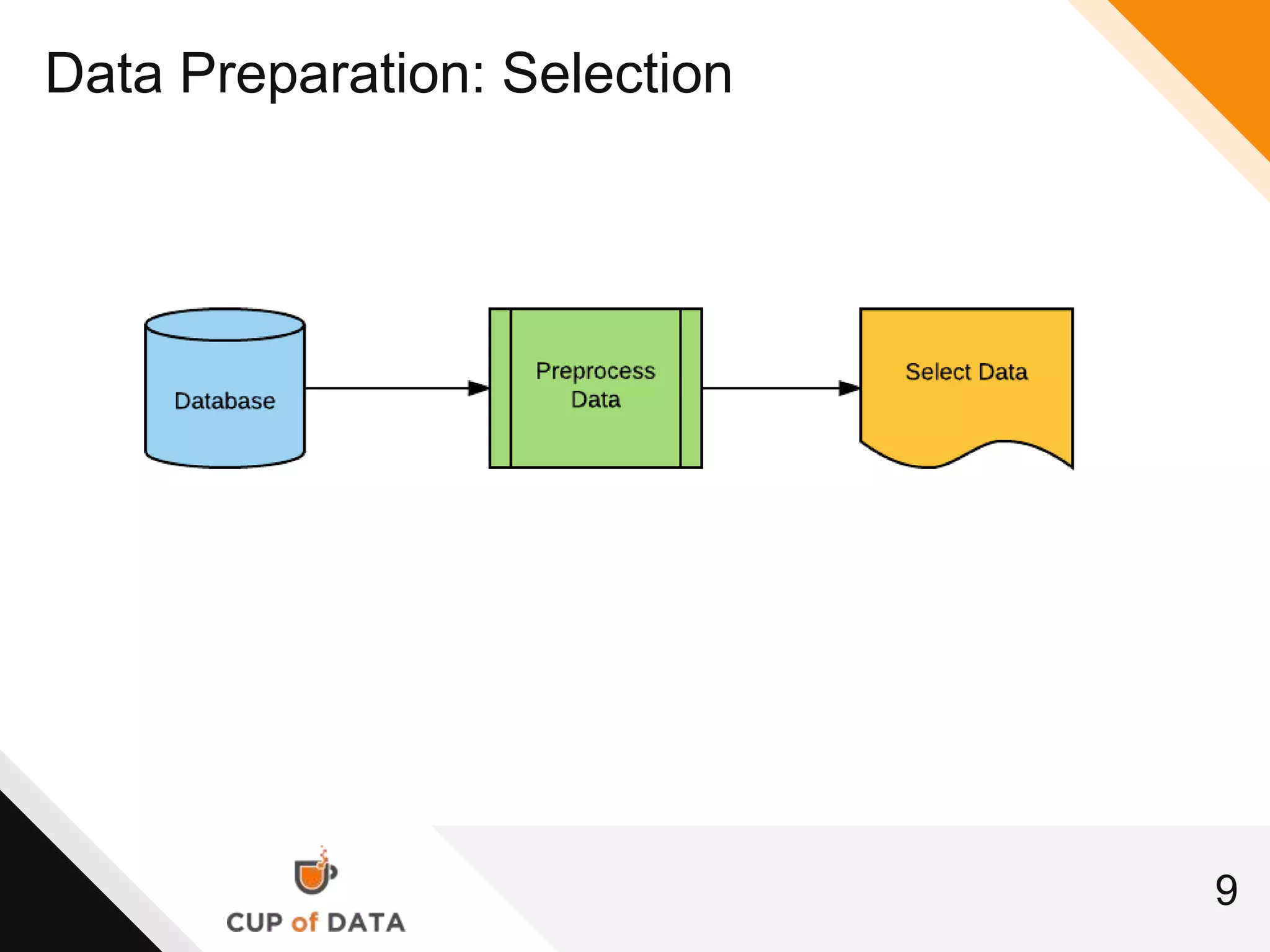
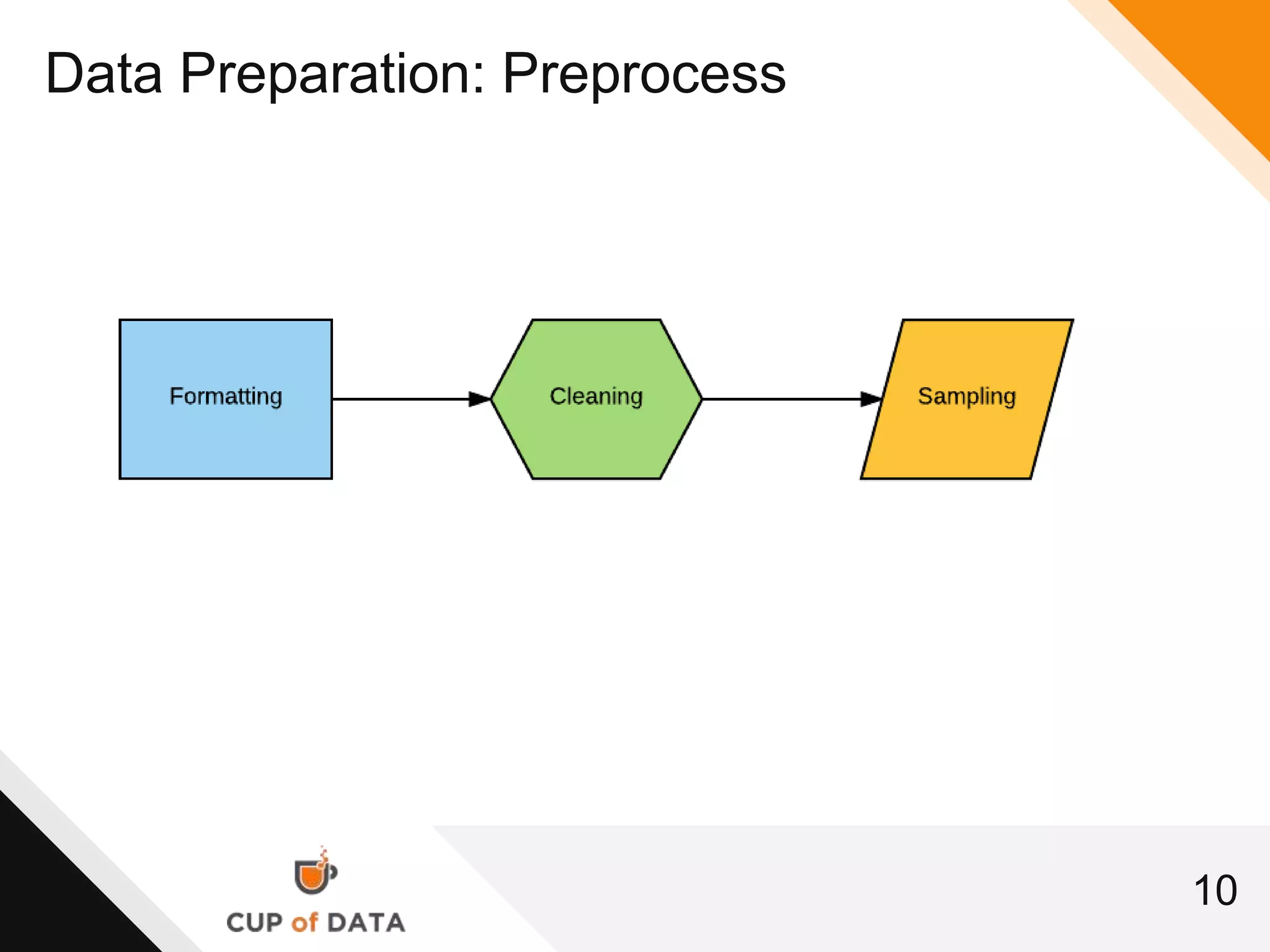
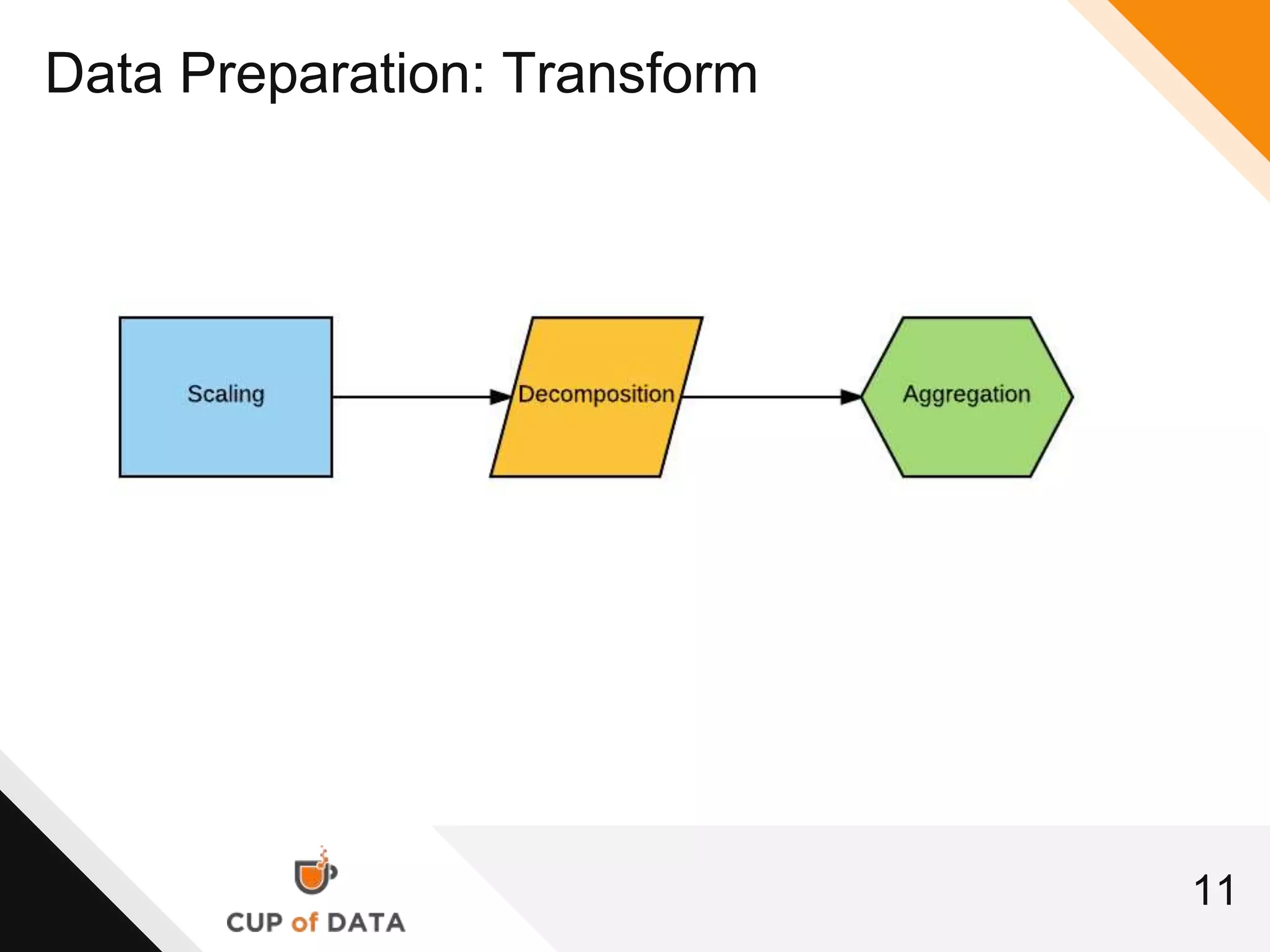
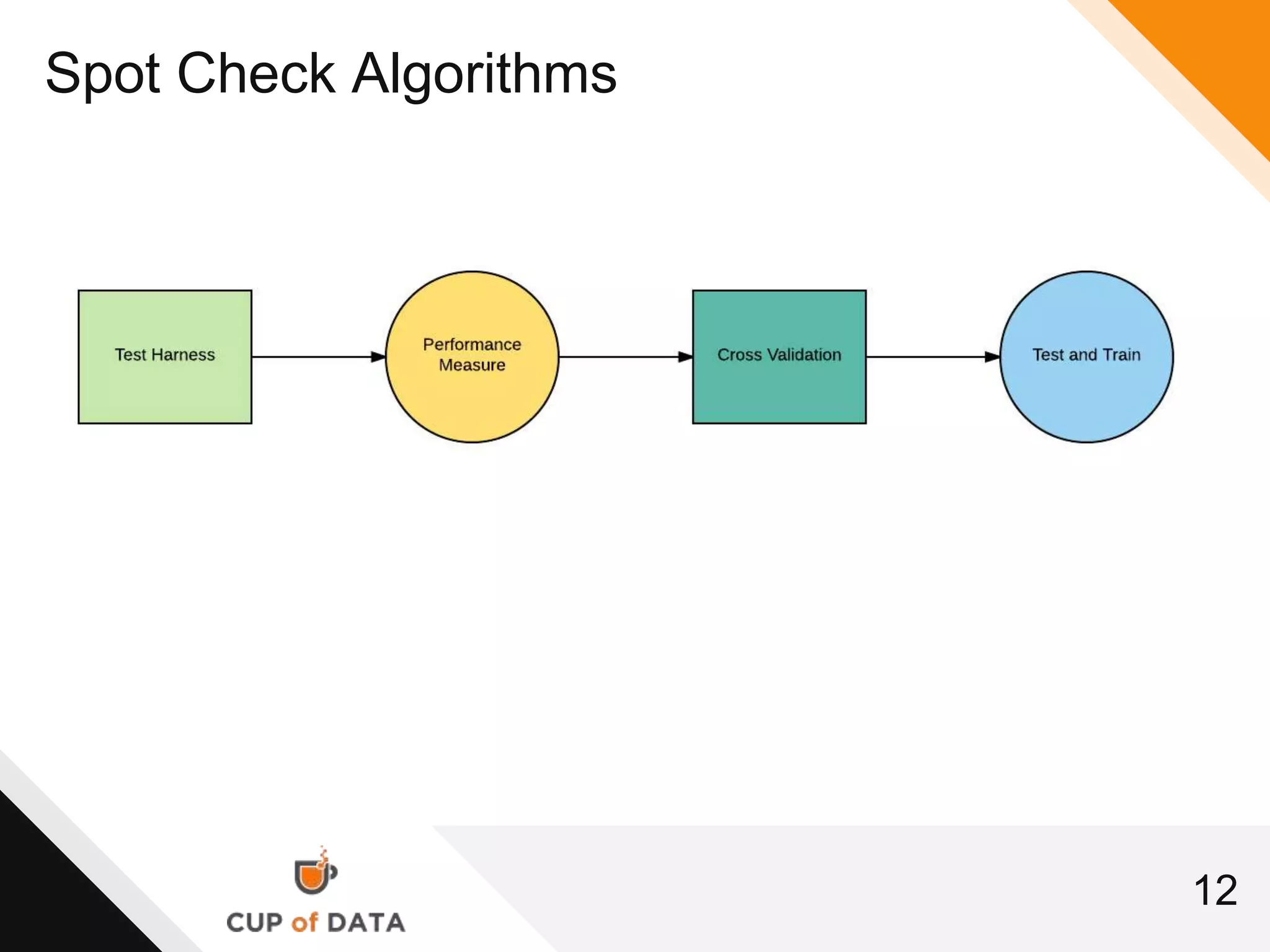
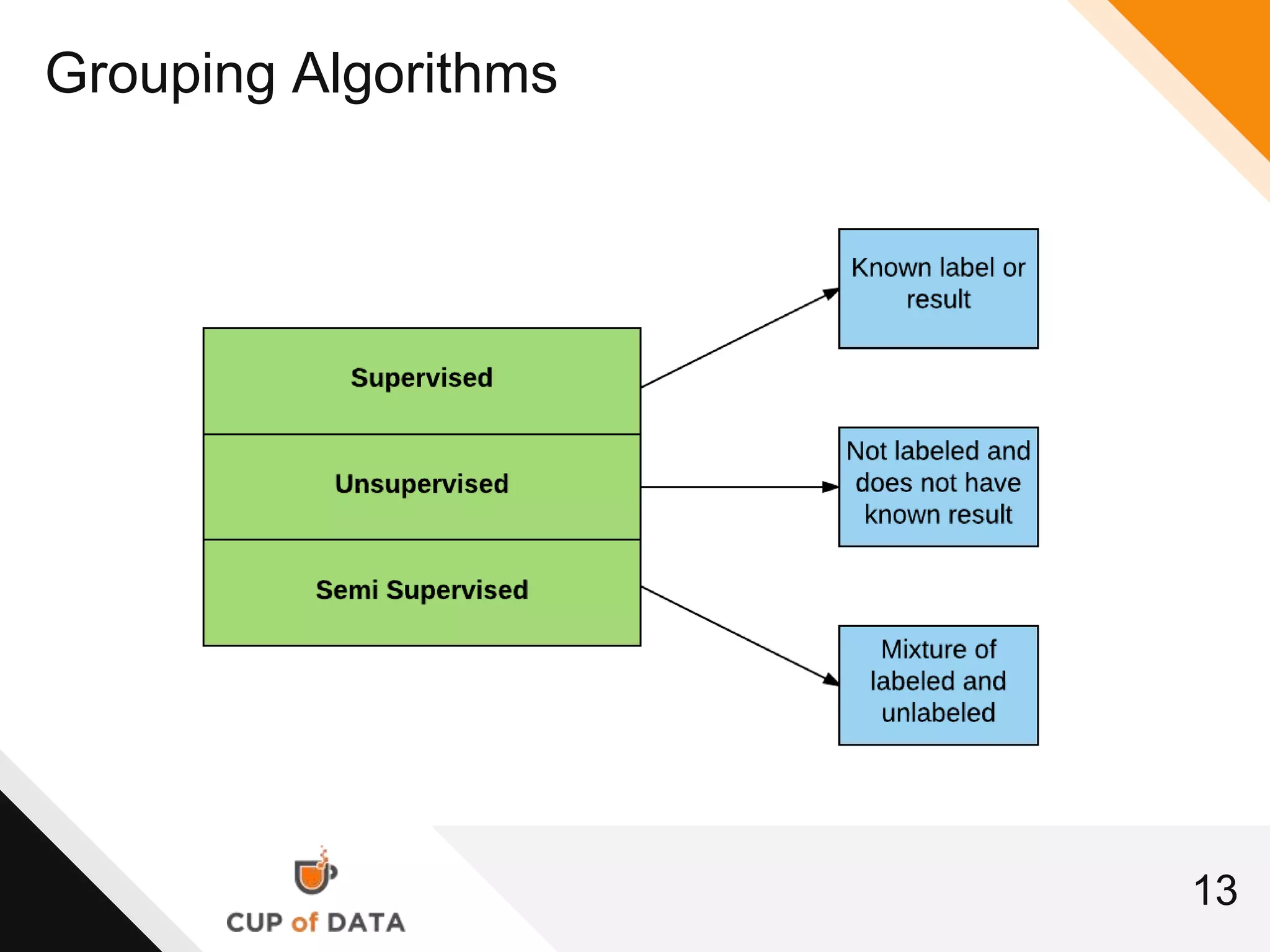
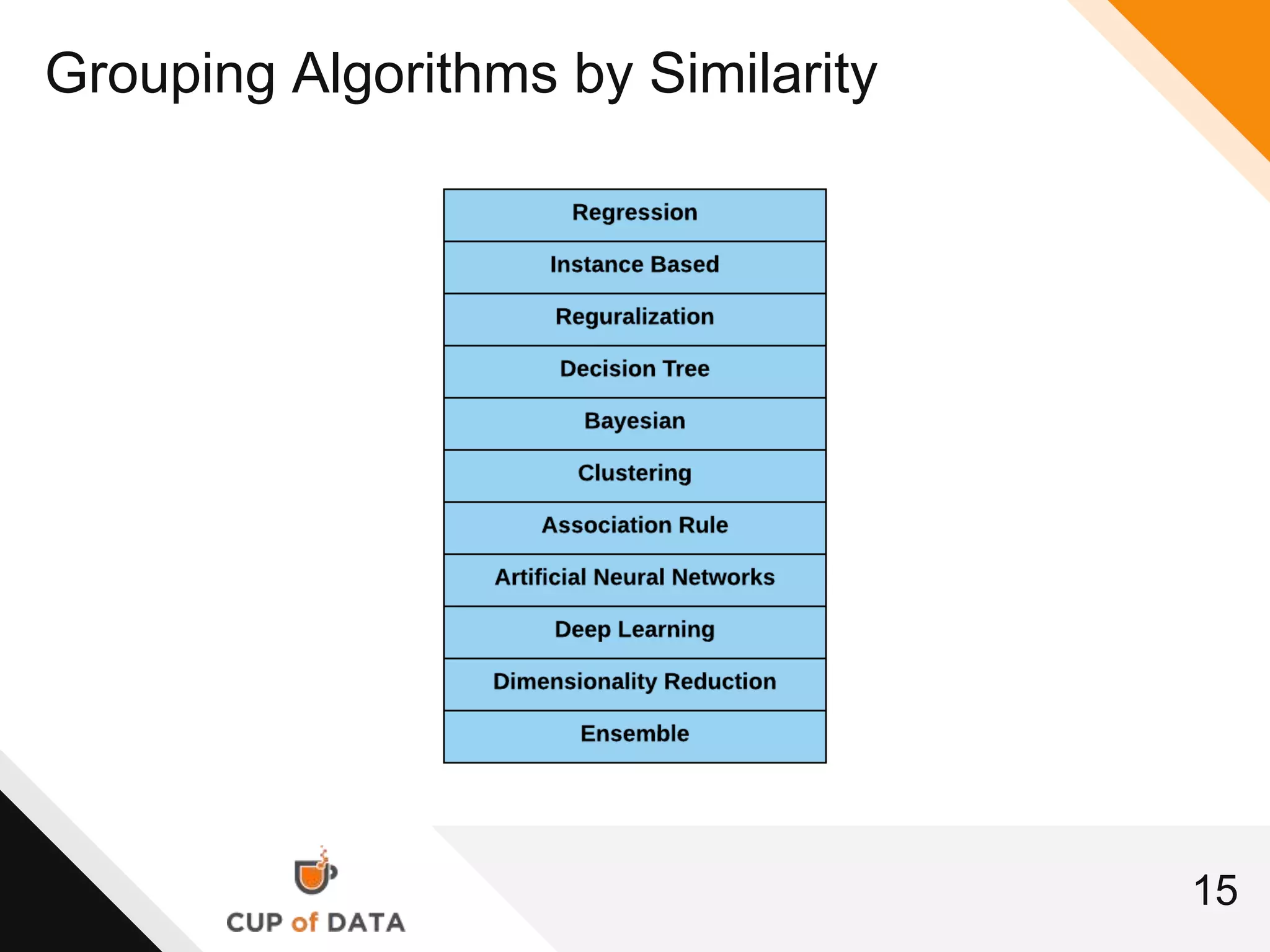
This document provides an introduction and agenda for a machine learning marketing use case presentation. It begins with introducing the presenter and their company Cup of Data, which is hiring data scientists. The basic agenda is then outlined, covering goals, the data science process, a machine learning primer, optimization techniques, and marketing examples. The remainder of the document dives deeper into each section of the agenda, providing overviews and explanations of topics like the data science workflow process, data preparation techniques, grouping algorithms, and deep learning.