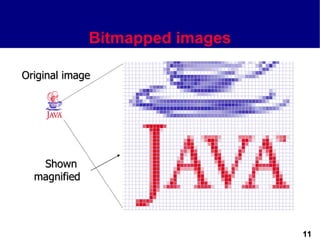
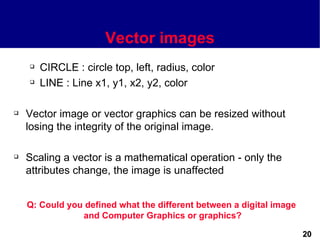
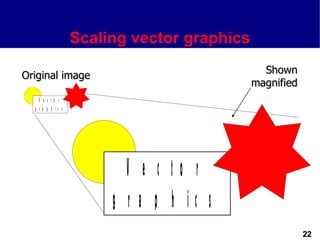
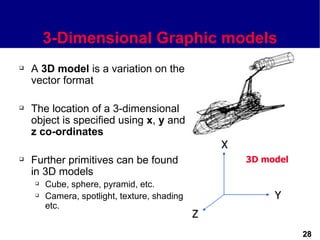
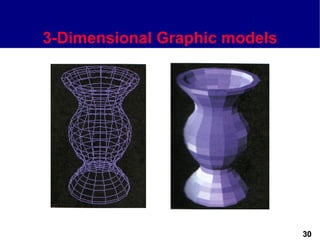
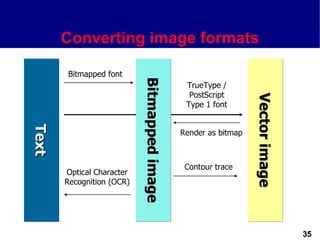
This document discusses different types of images used in multimedia. It describes bitmapped images, which are composed of pixels and have attributes like resolution and color depth that determine file size. Vector images are composed of graphic primitives defined by mathematical equations and can be resized without quality loss. The document outlines popular file formats for bitmaps and vectors as well as software used to create and edit different image types. Hardware and file conversion are also mentioned.