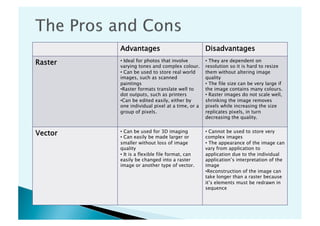
This document discusses different types of digital images. Raster images are made up of pixels and lose quality when resized, while vector images use paths and shapes so maintain quality when resized. It provides details on raster and vector images, comparing their advantages and disadvantages. Common file formats like JPEG, GIF and TIFF are also explained, including when each format is best used.