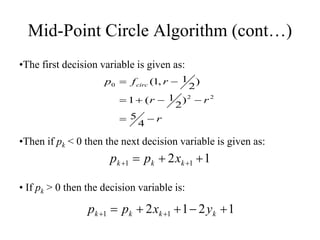
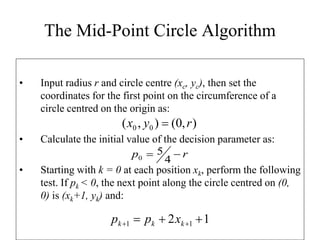
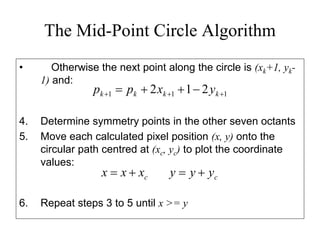
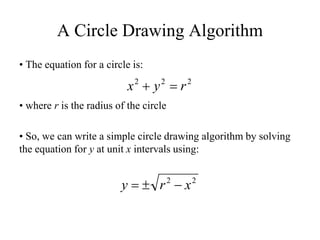
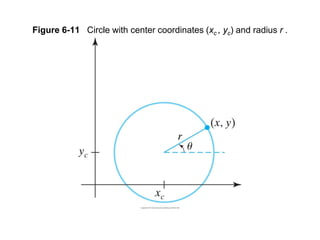
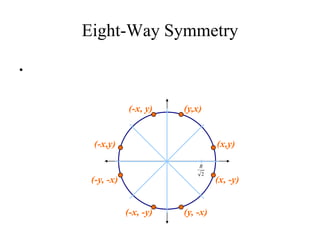
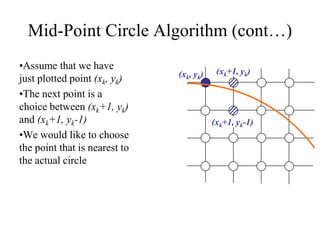
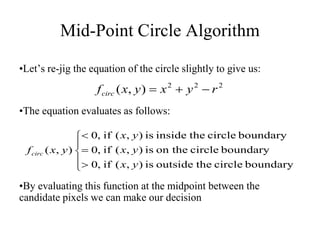
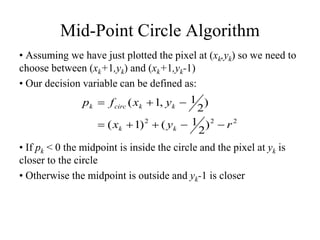
The document describes the mid-point circle algorithm for drawing circles. It uses eight-way symmetry to only calculate points for one octant of the circle, then uses symmetry to get the remaining points. At each x-coordinate, it must choose between two possible y-coordinates by calculating the mid-point between them and determining which side of the circle it falls on based on comparing the mid-point to the circle equation. It iterates this process, incrementally updating values for efficiency, until all points along the top-right octant are drawn, then uses symmetry to plot the full circle.

![Mid-Point Circle Algorithm (cont…)
• To ensure things are as efficient as possible we can do all of our
calculations incrementally
• First consider:
or:
where yk+1 is either yk or yk-1 depending on the sign of pk
( )
( ) 2
2
1
2
1
1
1
2
1
]
1
)
1
[(
2
1
,
1
r
y
x
y
x
f
p
k
k
k
k
circ
k
−
−
+
+
+
=
−
+
=
+
+
+
+
1
)
(
)
(
)
1
(
2 1
2
2
1
1 +
−
−
−
+
+
+
= +
+
+ k
k
k
k
k
k
k y
y
y
y
x
p
p](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/midpointalgorithm-230712130538-2ebc1cee/85/mid-point-algorithm-pdf-10-320.jpg)