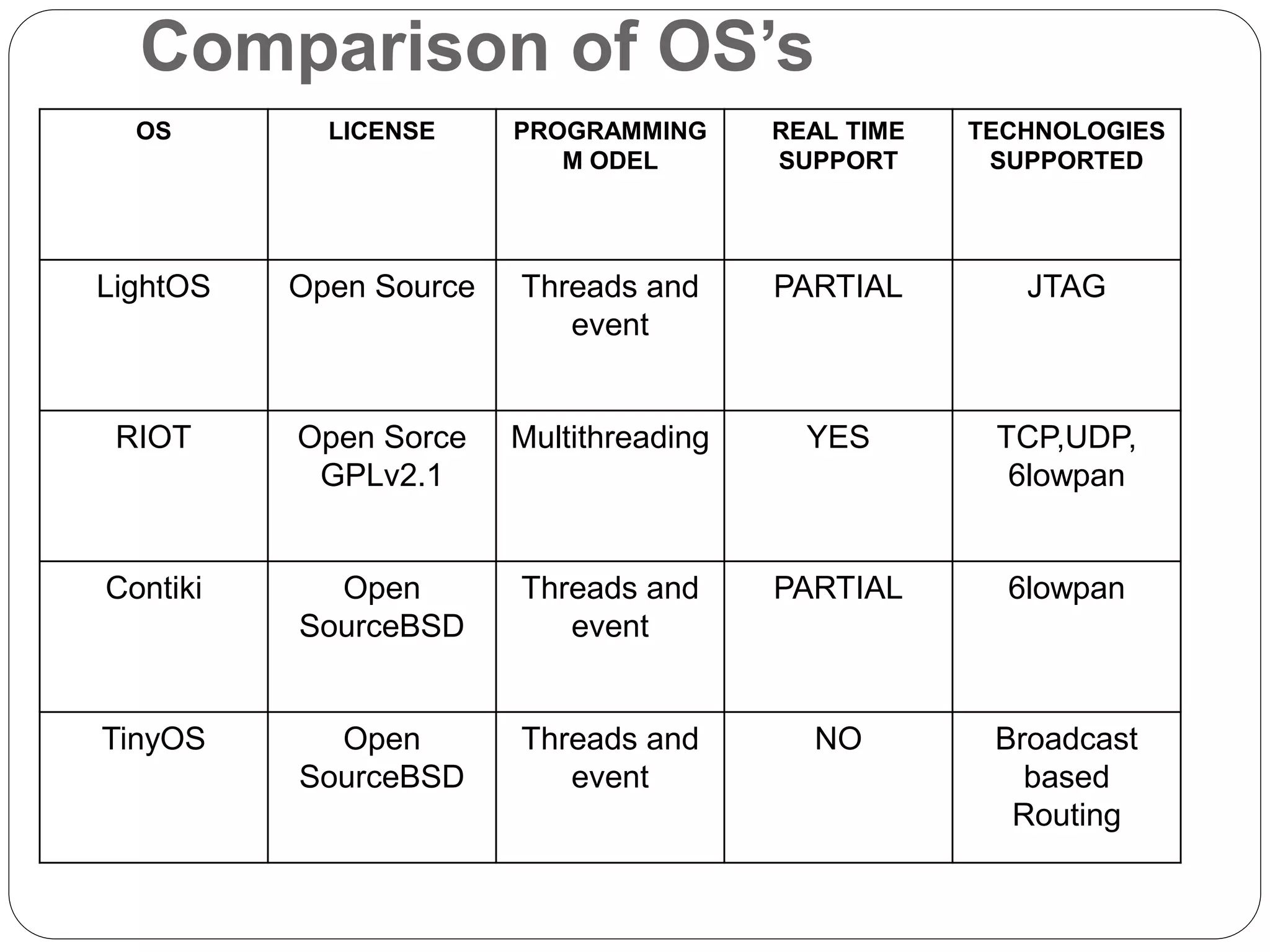
The document discusses requirements for an operating system for IoT devices and summarizes several popular IoT operating systems. The main requirements for an IoT OS are low memory usage, efficient use of limited resources, ability to handle concurrent tasks, flexibility to support different applications, low power usage, reliability, and support for various hardware platforms and protocols. It then summarizes LightOS, RIOT OS, Contiki OS, and TinyOS, comparing their key features such as licensing, programming models, real-time support, and supported technologies. RIOT OS stands out as offering the most support for communication technologies while also enabling multithreading and real-time capabilities under an open source license.