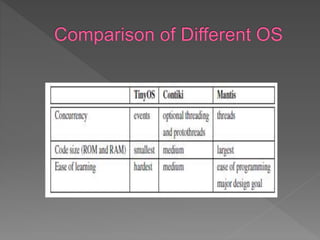
This document discusses system architecture and operating systems for wireless sensor networks and embedded devices. It defines system architecture as the structure and organization of a computing system consisting of hardware and software modules that enable data exchange. It then describes several operating systems used for wireless sensor networks and embedded devices, including TinyOS, Contiki, Mantis, Windows CE, eCos, QNX, and XMK. It explains key aspects of each operating system such as scheduling, concurrency, programming models, and dynamic reprogramming capabilities.
![S.VARUN
M.Tech[EST]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wsn-160413155230/75/Wireless-Sensor-System-Architecture-1-2048.jpg)














![S.VARUN
M.Tech[EST]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wsn-160413155230/85/Wireless-Sensor-System-Architecture-22-320.jpg)