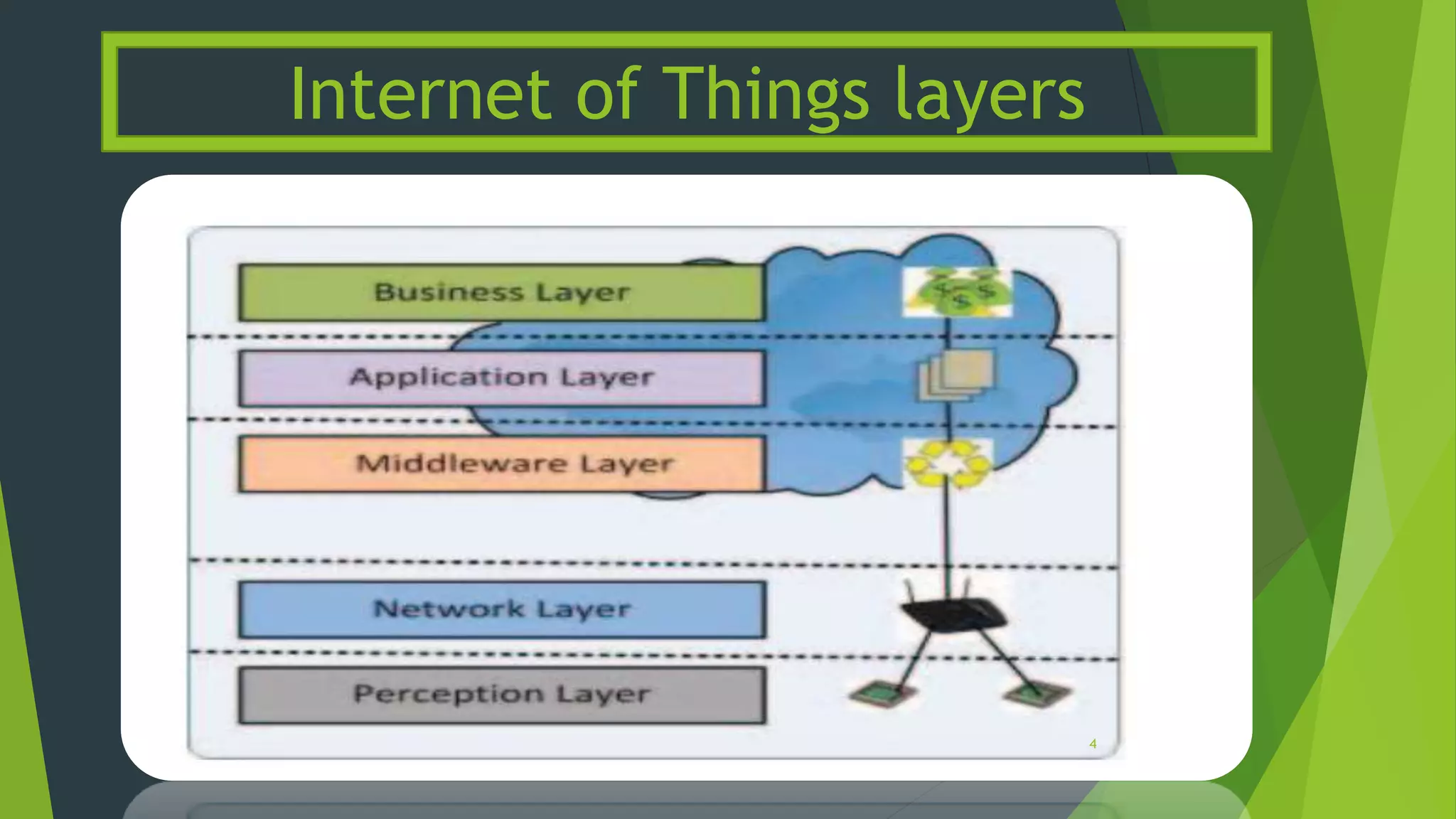
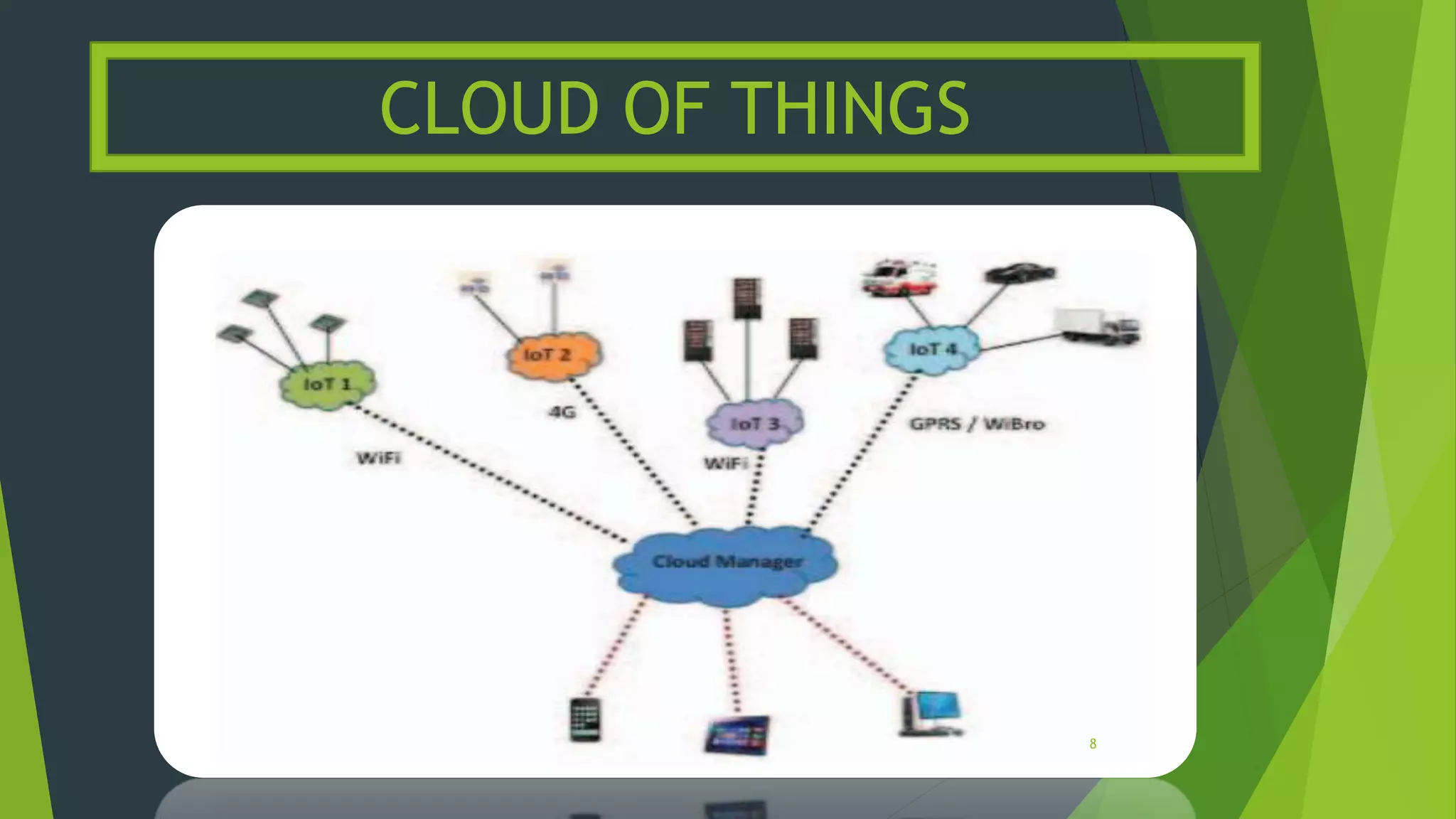
The document discusses the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing, referred to as Cloud of Things. It identifies several key issues with this integration, such as protocol support, energy efficiency, resource allocation, identity management, and security/privacy. Potential solutions are provided for some of the issues. The conclusion discusses the need for more study on the impact of these issues based on the specific IoT application and services provided.


![[1] Yen-Kuang Chen, “Challenges and Opportunities of Internet of Things”,in the proceedings of 17th Asia and South
Pacific Design Automation Conference, , 30 Jan. – 02 Feb., 2012, Santa Clara, CA, USA.
[2] Miao Wu et. al., “Research on the architecture of Internet of things”, in the proceedings of 3rd International
Conference on Advanced Computer Theory and Engineering, 20-22 August, 2012,Beijing, China,
[3] Gerd Kortuem, Fahim Kawsar, Daniel Fitton, and Vasughi Sundramoorthi, “Smart Objects and Building Blocks of
Internet of Things”, IEEE Internet Computing Journal, volume 14, issue 1, pp. 44- 51, Jan.-Feb., 2010
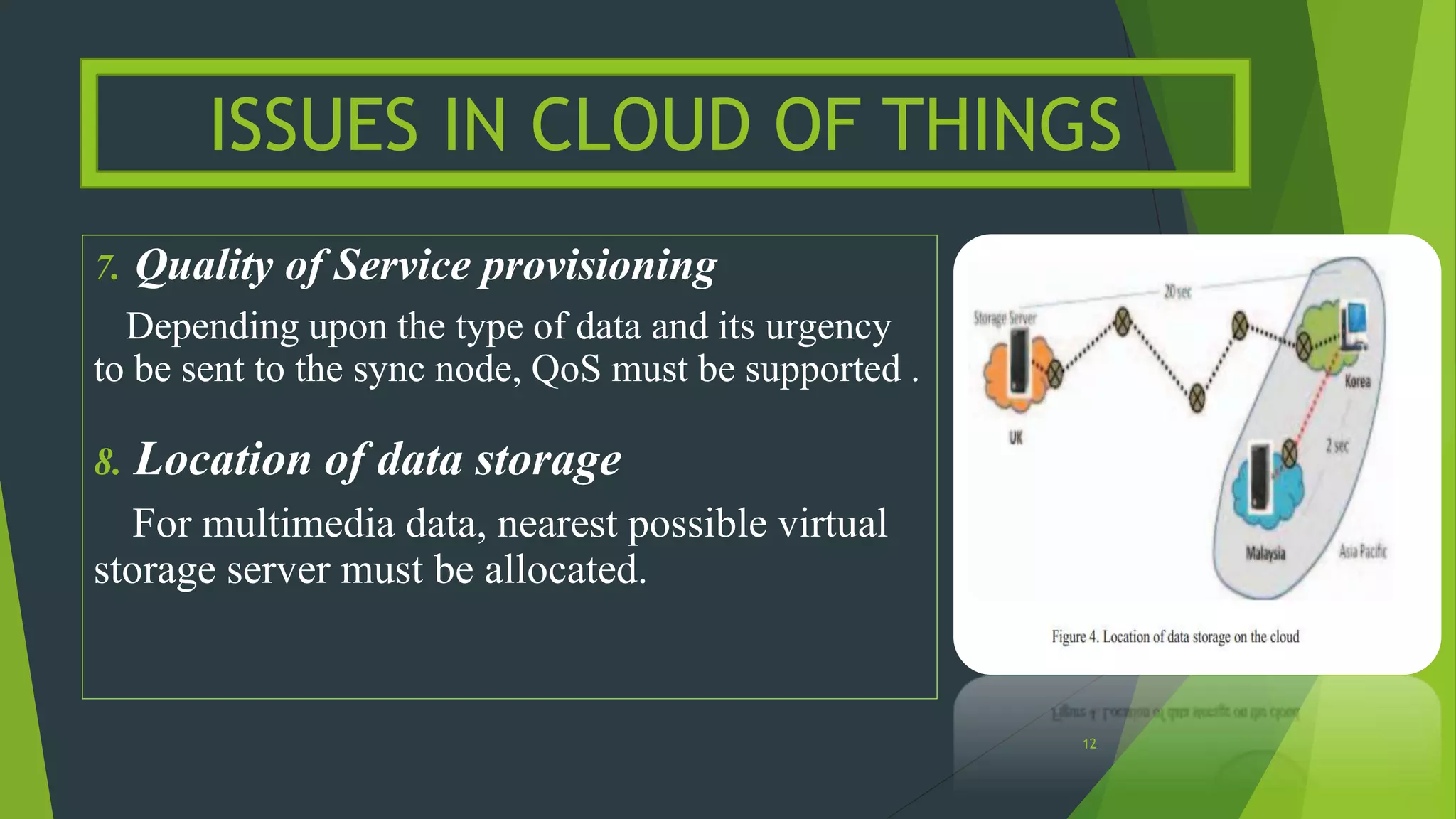
[4] Rafiullah Khan, Sarmad Ullah Khan, Rifaqat Zaheer, and Shahid Khan, “Future Internet: The Internet of Things
Architecture,Possible Applications and Key Challenges”, in the proceedings of 10th International Conference on
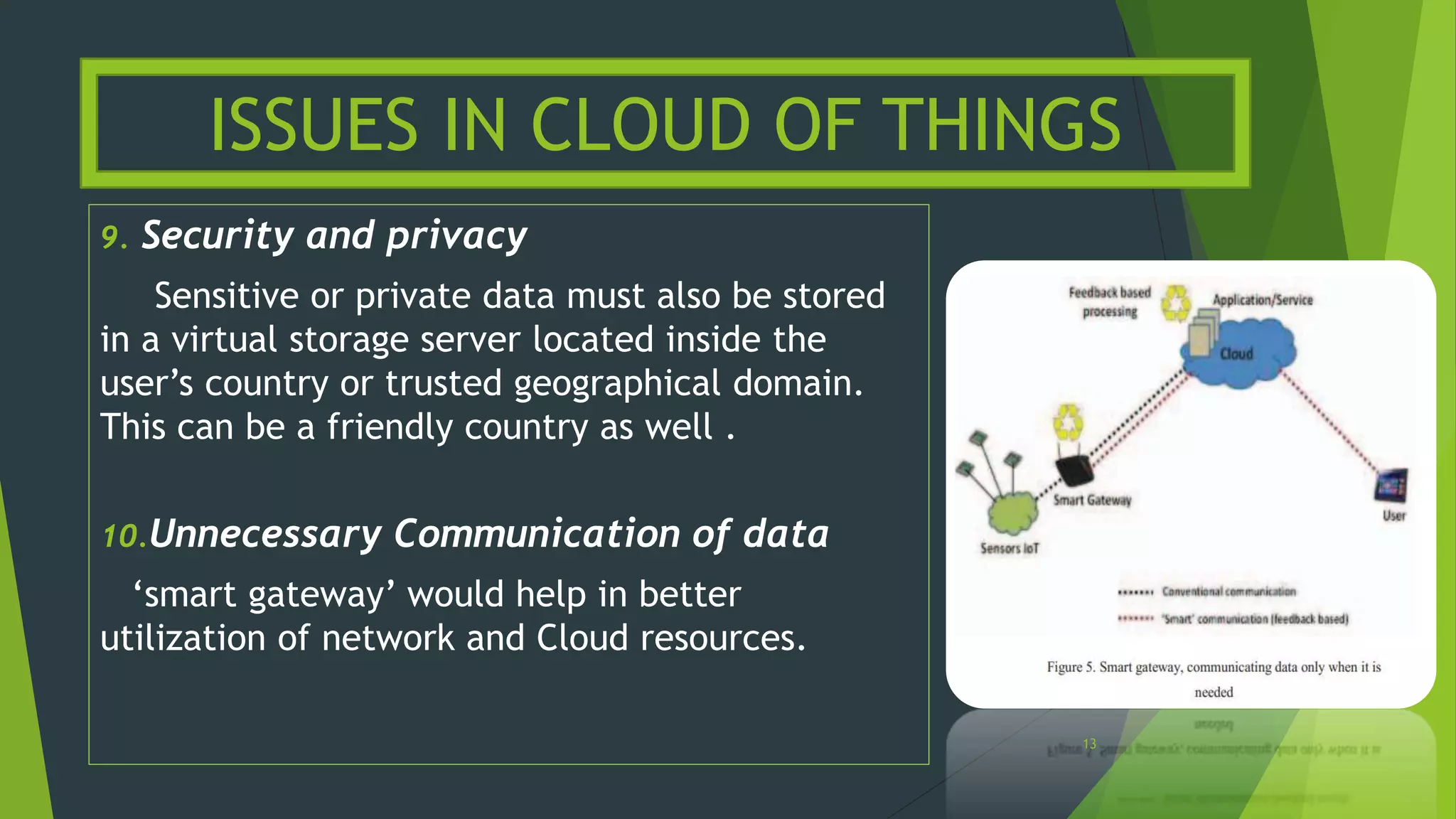
Frontiers of Information Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, 17-19 December, 2012.
[5] Dieter Uckelamann, Mark Harrison, and Floria Michahelles, “Architecting the Internet of Things,” Springer-
Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2011.
[6] Shuai Zhang et. al., “Cloud Computing Research and Development Trend”, in the proceedings of International
Conference on Future Networks, 22-24 Jan., 2010, Sanya, China.
[7] W Ma et. al., “The Survey and Research on Application of Cloud Computing”, in the proceedings of 7th
International Conference on Computerl Science and Education, 02-04 November, 2012, Wuyishan Mountain, China.
[8] Y. Jadeja, et. al., “Cloud Computing - Concepts, Architecture and Challenges”, in the proceedings of
International Conference on Computing Electronics and Electrical Technologies, 21-22 March, 2012, Nagercoil,
India.
[9] Minqi Zhou et. al., “Services in the Cloud Computing Era: A Survey”, in the proceedings of 4th International
Universal Communications Symposium, 18-19 October, 2010, Beijing, China.
Used References
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudofthings-180718145026/75/Cloud-of-things-IoT-Cloud-Computing-15-2048.jpg)
