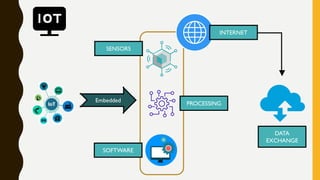
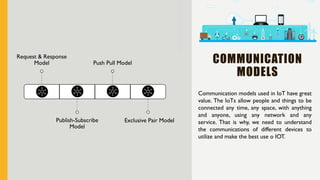
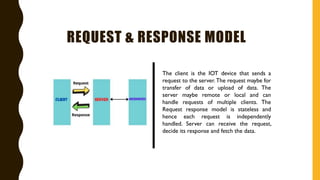
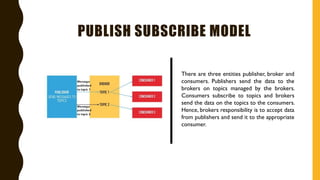
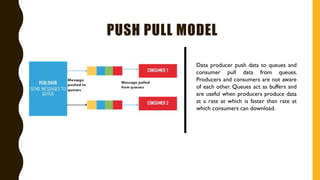
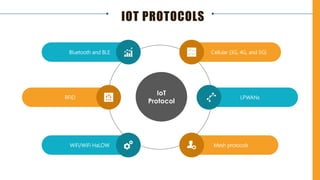
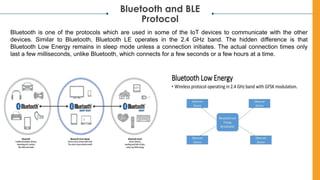
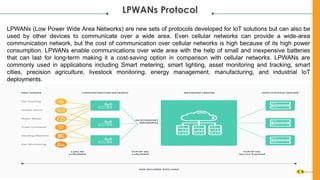
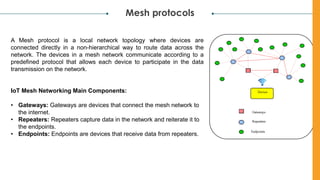
The document discusses various Internet of Things (IoT) communication models and protocols, such as request-response, publish-subscribe, and push-pull models. It explores IoT protocols including cellular networks, LPWANs, and mesh protocols, highlighting their specific applications and characteristics. The text emphasizes understanding these models and protocols to effectively utilize IoT technologies across different domains.