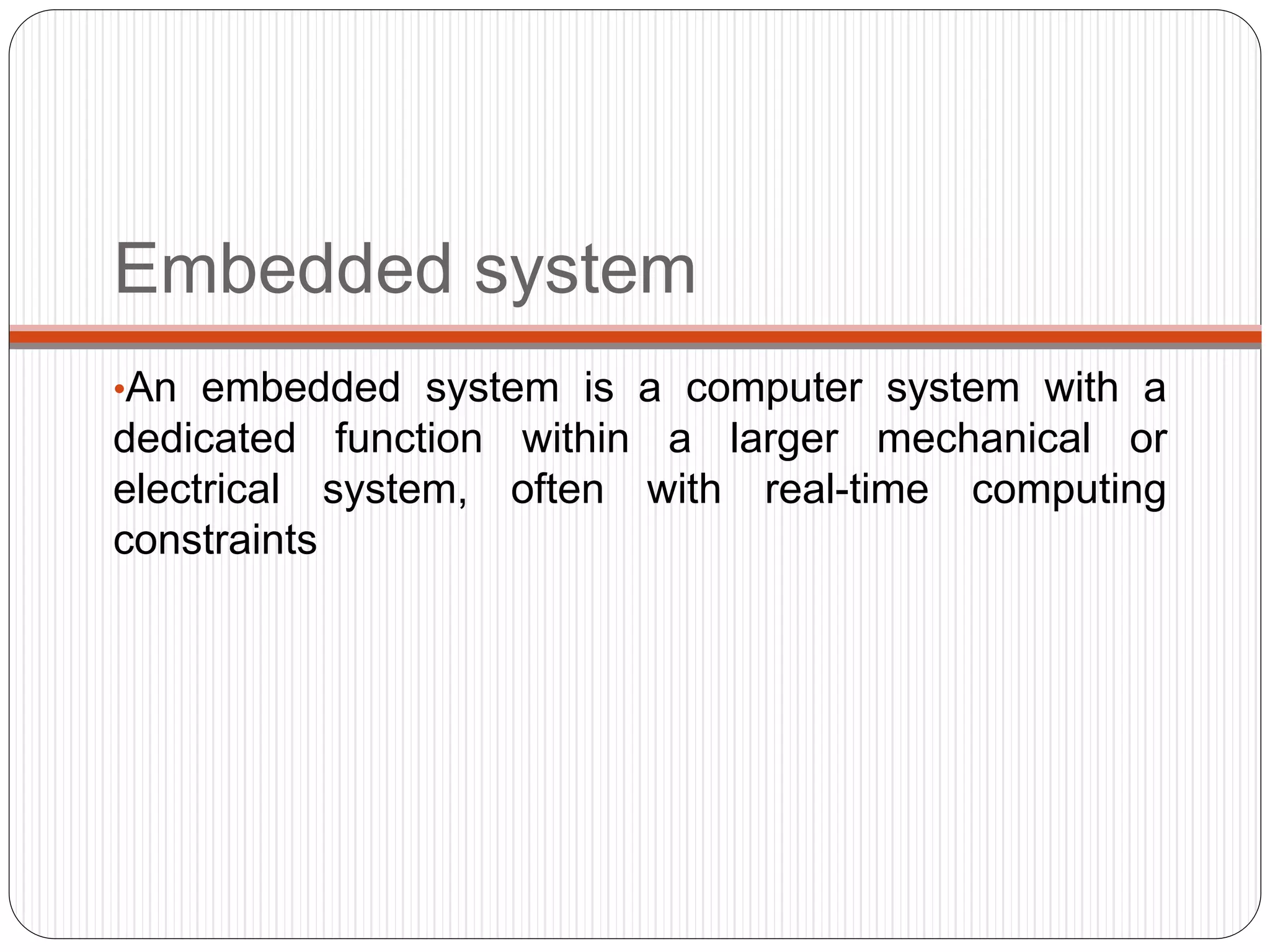
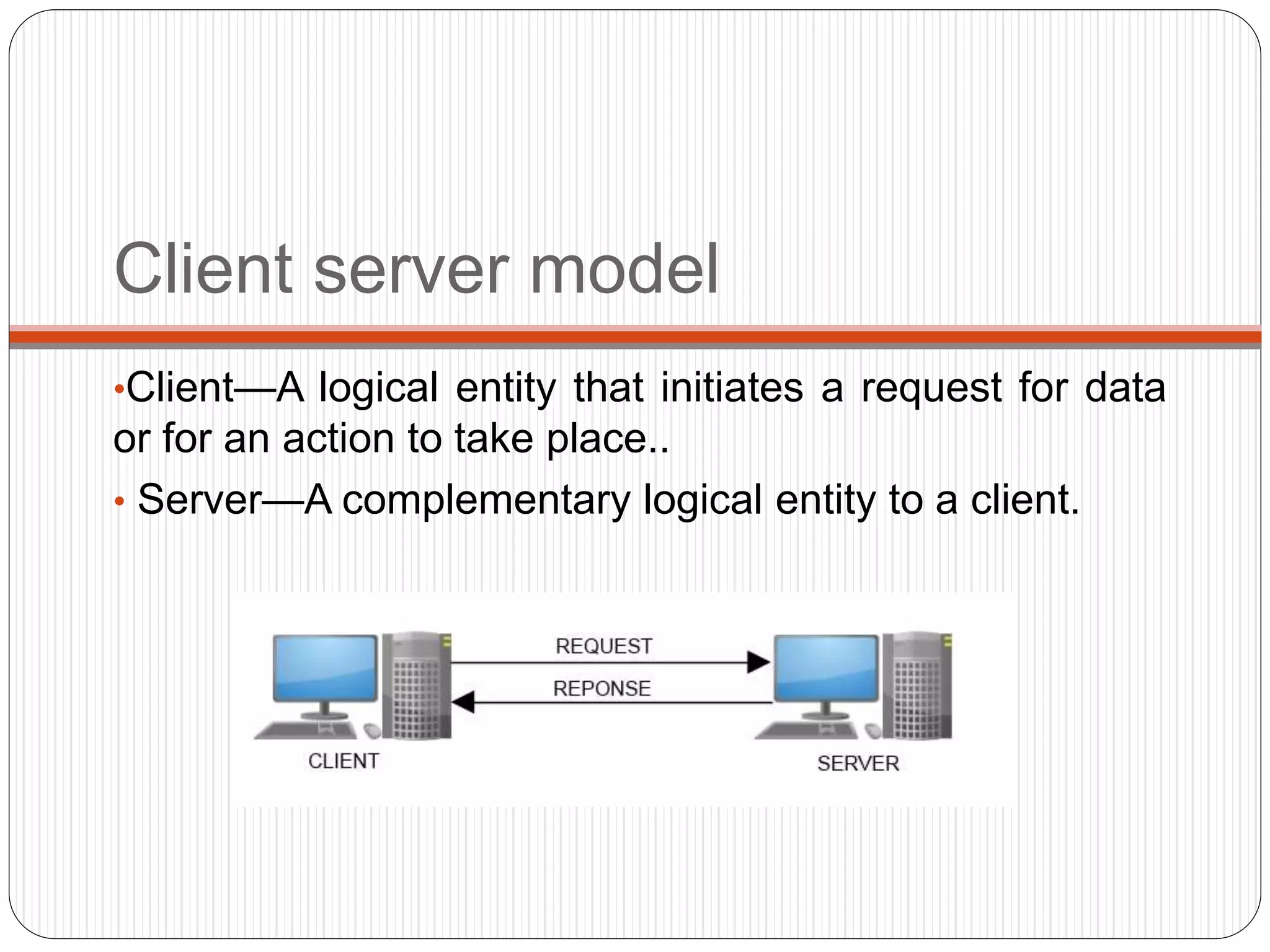
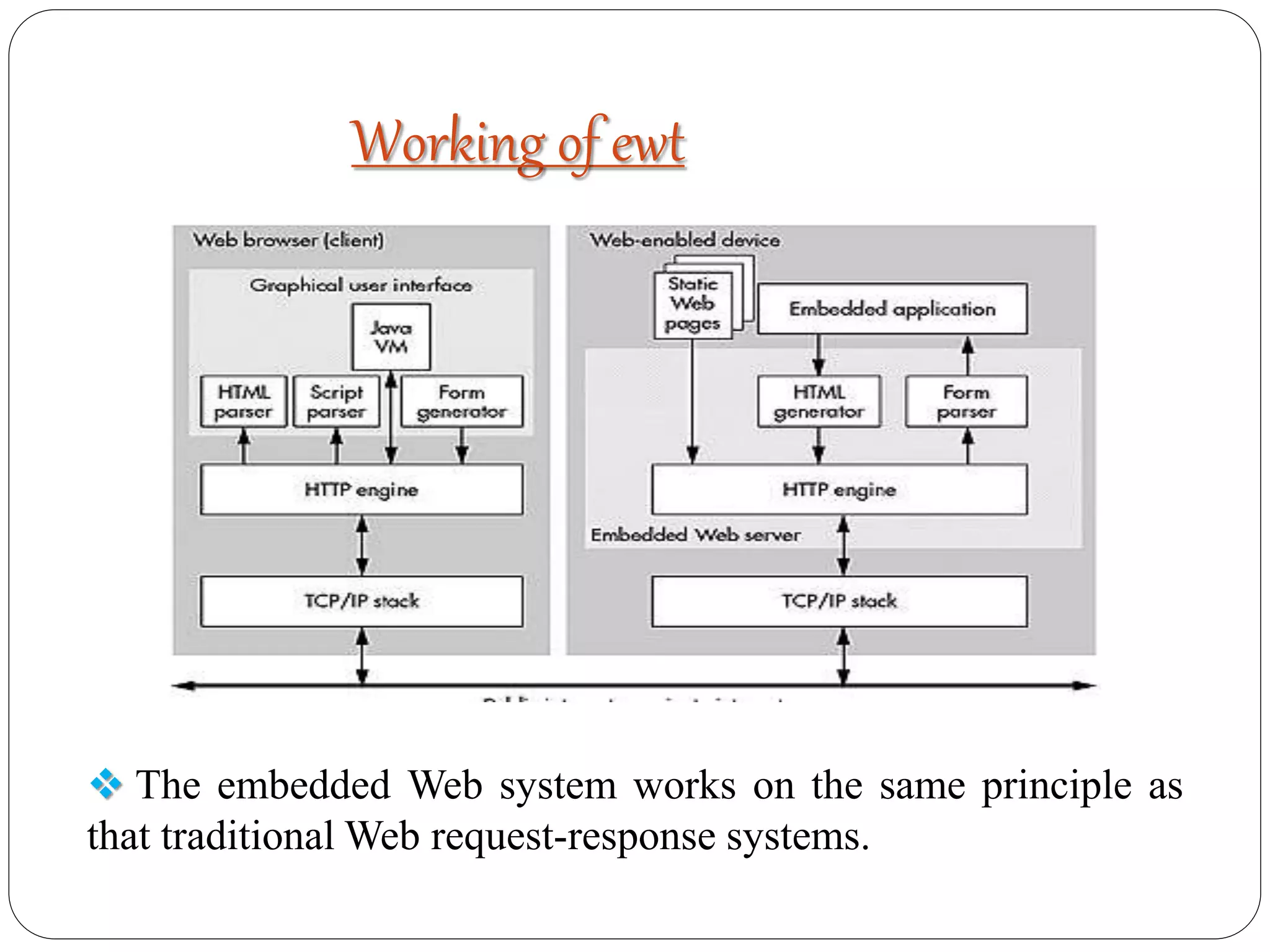
Embedded Web Technology (EWT) integrates embedded systems with the World Wide Web, facilitating real-time data transmission and user interface interaction via web servers and browsers. With advantages like scalability, security, and non-permanent applet storage, EWT is applicable in fields such as traffic and power infrastructure monitoring. Developed by NASA, EWT has evolved significantly and addresses various modern communication challenges.








![[1] “Embedded Web Technology: Applying World Wide Web Standards to Embedded
Systems”- Joseph G. Ponyik and David W. York Glenn Research Center, Cleveland,
Ohio; NASA/TM—2002-211199/March 2002/AIAA–2001–5107
[2] “Embedded web technology in traffic monitoring system”, International Journal of
Innovative Research in Advanced Engineering (IJIRAE) Volume 1 Issue 4 (May
2014 ISSN: 2349-2163 ) http://ijirae.com
[3] “Application Research of Embedded Web Technology in Traffic Monitoring System”
Proceedings of the Second Symposium International Computer Science and
Computational Technology(ISCSCT ’09) Huangshan, P. R. China, 26-28,Dec. 2009, pp.
094-097
[4] Dustdar, S.; Schreiner, W. (2005). "A survey on web services. composition". International
Journal of Web and Grid Services : Doi:10.1504/IJWGS.2005.007545
[5] “ Power infrastructure monitoring system on Embedded Web” International Journal of
Science and Engineering Volume 1, Number 2 - 2013 PP-71-76 ©IJSE
REFERENCES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarpresentationonembeddedwebtechnology-151011075345-lva1-app6892/75/Seminar-presentation-on-embedded-web-technology-16-2048.jpg)

![EXAMPLE
REQUEST
GET /index.html HTTP/1.0
Connection: Keep-Alive
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.7
[en] (WinNT; U)
Host: jgp6290.grc.nasa.gov
Accept: image/gif, image/x-
xbitmap, image/jpeg,
image/pjpeg, image/png, */*
Accept-Encoding: gzip
Accept-Language: en
Accept-Charset: iso-8859-
1,*,utf-8
RESPONSE
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Host:
jgp6290/139.88.219.70
Date: Mon, 020 Aug
2001 17:27:31 GMT
Server: TempestJava
1.2 (NASA/GRC Java
Version of Tempest)
Connection: Close
Content-Length: 293
293
Content-Type: text/html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarpresentationonembeddedwebtechnology-151011075345-lva1-app6892/75/Seminar-presentation-on-embedded-web-technology-18-2048.jpg)