Embed presentation
Download to read offline



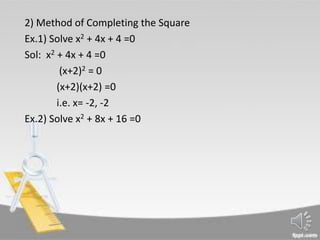


This document discusses quadratic functions and equations. A quadratic function is defined as f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, where a ≠ 0. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. A quadratic equation is an equation of degree 2 in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. There are three methods for solving quadratic equations: factorizing the equation, completing the square, and using the quadratic formula. Factorizing and completing the square are demonstrated through examples.




