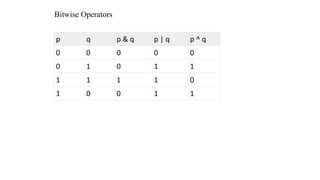
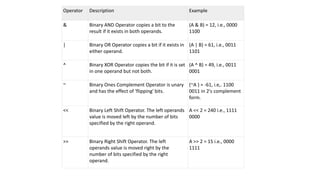
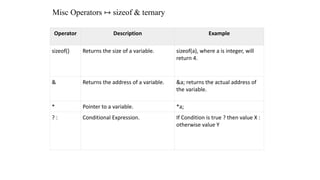
The document describes the different types of operators in C language including arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, and other operators. It provides examples of each operator and explains their functions such as adding, subtracting, comparing, assigning values, and more. C language contains a rich set of built-in operators that allow various mathematical, logical, and bitwise operations to be performed.