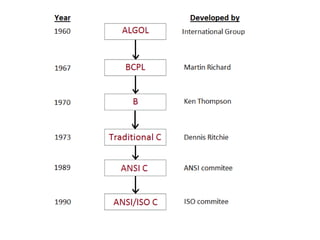
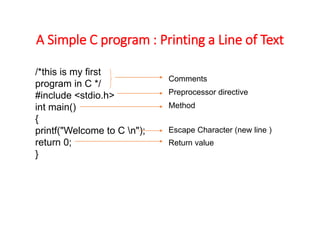
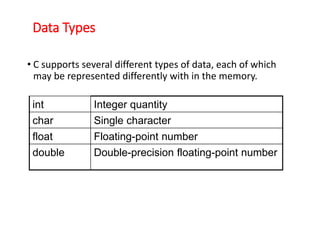
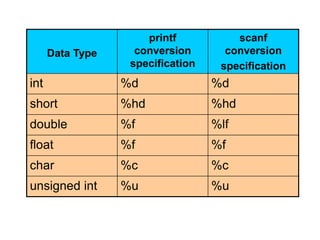
C was developed by Dennis Ritchie and evolved from BCPL and B programming languages. C is a hardware-independent language that allows for portable code across different computer systems. A simple C program prints text by using comments, preprocessor directives, and escape characters. Memory in C is represented by variables that have names, types, sizes, and values corresponding to computer memory locations. Data types in C include integers, characters, floating-point numbers, and more.