An array is a data structure that stores a collection of related data items of the same type in contiguous memory locations that can be individually referenced by adding an index to the array name. Arrays allow storing multiple values in one variable and are useful for organizing related data in an ordered way so that values can be easily sorted, searched, and accessed using their index position in the array.

![Array
• element
arrayname[position-number]
-45
6
0
72
1543
-89
0
62
-3
1
6453
78
c[6]
c[0]
c[1]
c[2]
c[3]
c[11]
c[10]
c[9]
c[8]
c[7]
c[5]
c[4]
c
Array
Name](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-3-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
Array
-45
6
0
72
1543
-89
0
62
-3
1
6453
78
c[6]
c[0]
c[1]
c[2]
c[3]
c[11]
c[10]
c[9]
c[8]
c[7]
c[5]
c[4]
c
c[0] = 3;
scanf(“%d”, &c[1]);
printf(“%d”, c[1]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-4-2048.jpg)
![Defining Arrays
arrayType arrayName[numberOfElements]
#define MAX 200;
int c[12];
float f[1000];
int a[MAX], b[MAX*10];
int n, m=5, x[m];
scanf(“%d”,&n);
int y[n];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-5-2048.jpg)
![Arrays Inilialization
arrayType arrayName[numberOfElements] = {valueList};
int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int a[5] = {1};
int a[ ] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-6-2048.jpg)
![Using Arrays
Example:Using Arrays
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10
void main() {
int n[SIZE] = {19, 2, 15, 7, 11, 9, 13, 5, 17, 1};
int i ,j;
printf("%s%13s%17sn", "Element", "Value", "Histogram");
for (i=0; i<=SIZE-1; i++) {
printf("%7d%13d", i, n[i]);
for (j=1; j<=n[i]; j++)
printf("%c", '*');
printf("n");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-8-2048.jpg)
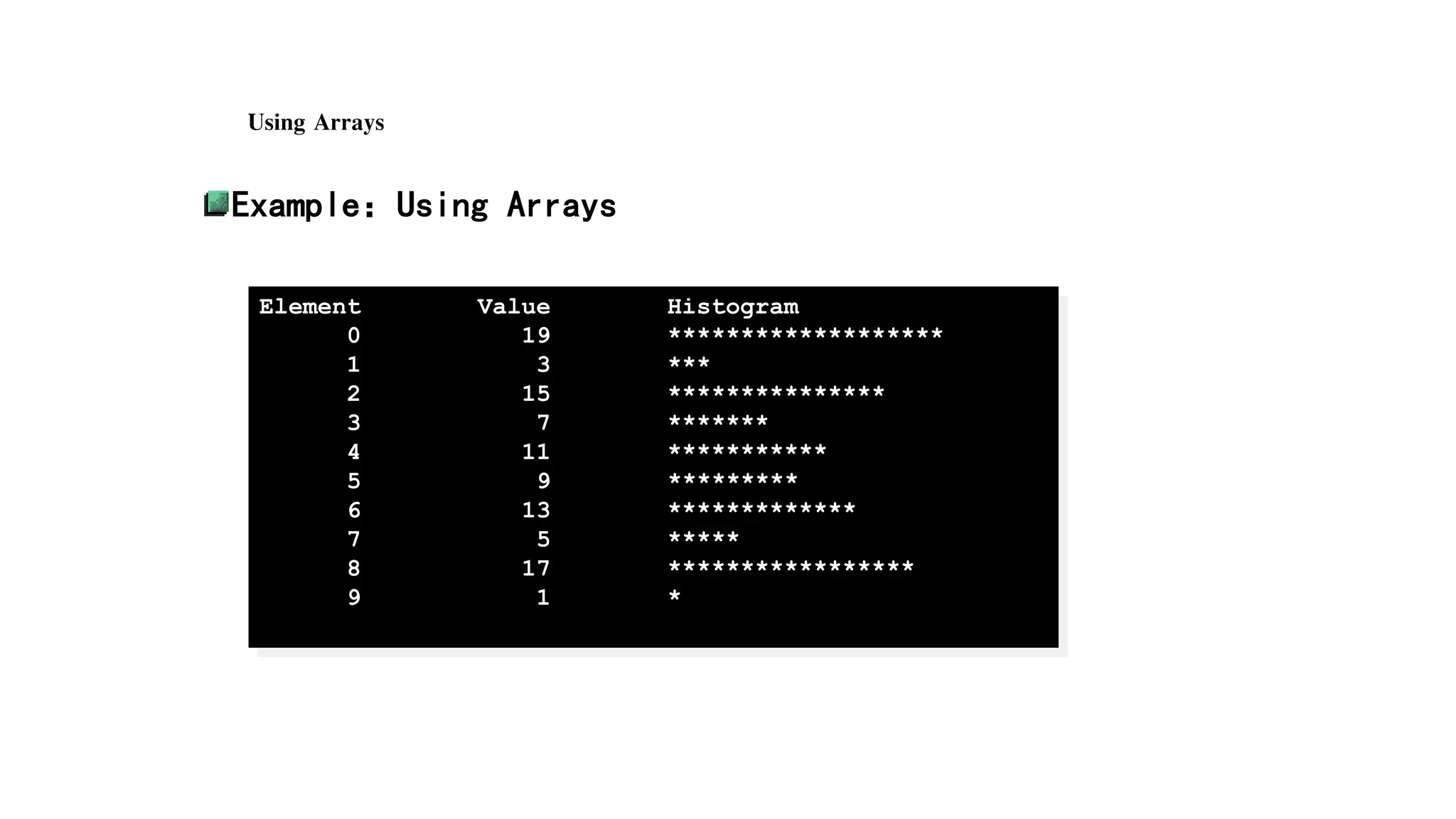
![Using Arrays
Example:Using Arrays
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 32
void main()
{ float score[MAX], sum, best;
int i;
printf("Input %d scores:n",MAX);
for (i=0; i<MAX; i++)
scanf("%f", &score[i]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-10-2048.jpg)
![Using Arrays
Example:Using Arrays
sum=best=score[0];
for (i=1;i<MAX;i++)
{ sum+=score[i];
if (best<score[i])
best=score[i];
}
printf("The average:%.1fn", sum/MAX);
printf("The best:%.1fn", best);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-11-2048.jpg)
![#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 32
void main()
{ float score[MAX], sum;
int i, best;
printf("Input %d scores:n",MAX);
for (i=0; i<MAX; i++)
scanf("%f", &score[i]);
Using Arrays
Example:Using Arrays
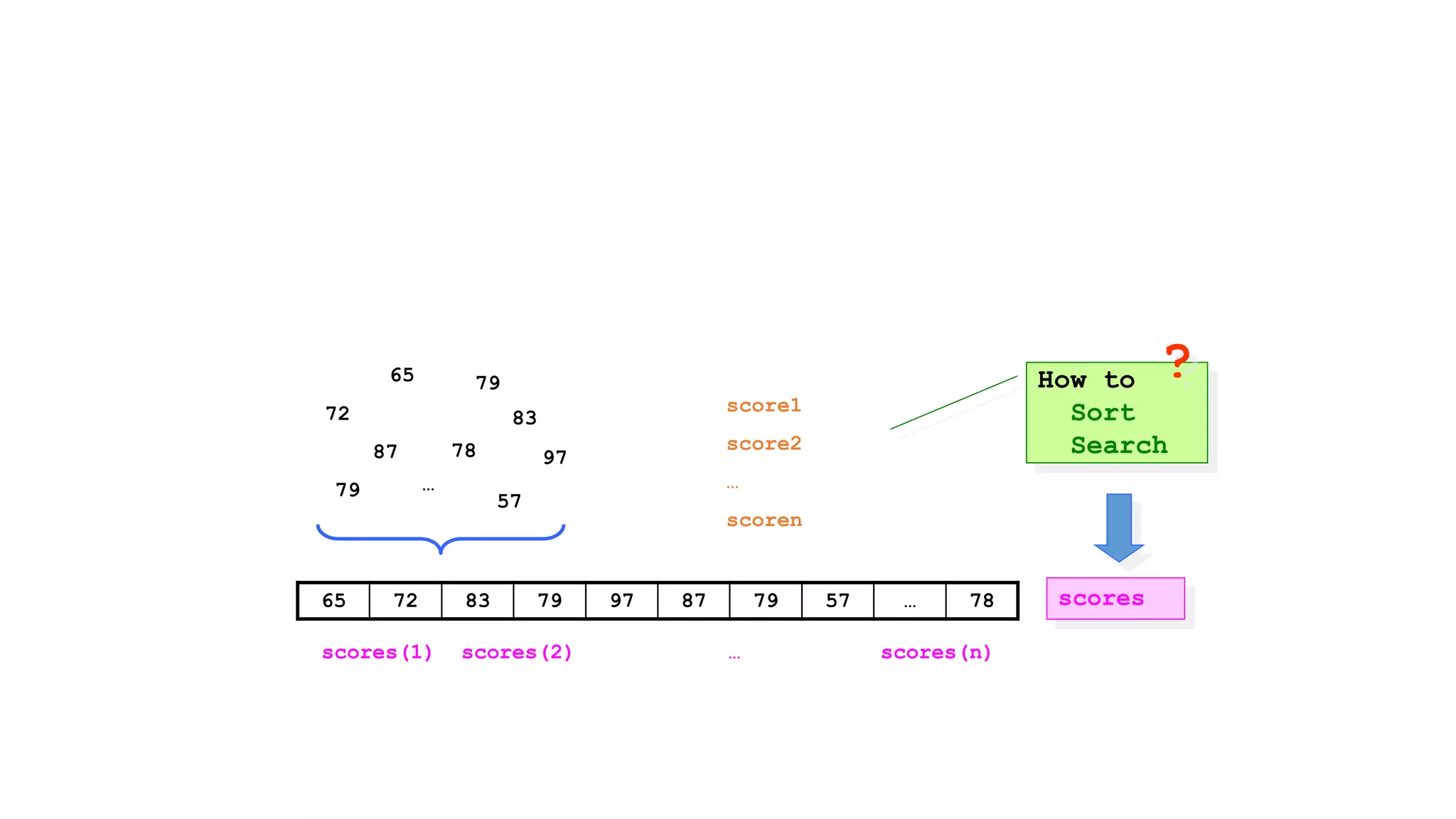
65 72 83 79 97 87 79 57 91 78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-12-2048.jpg)
![Using Arrays
Example:Using Arrays
sum=score[0];
best=0;
for (i=1; i<MAX; i++)
{ sum+=score[i];
if (score[best]<score[i])
best=i;
}
printf("The average:%.1fn", sum/MAX);
printf("The best:%.1fn", score[best]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-13-2048.jpg)
![#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define SIZE 7
void main() {
int face, roll, frequency[SIZE]={0};
srand(time(NULL));
Using Arrays
Example:Using Arrays
frequency[1], …, frequency[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session11singledimarrays-210602100458/75/Session11-single-dimarrays-14-2048.jpg)