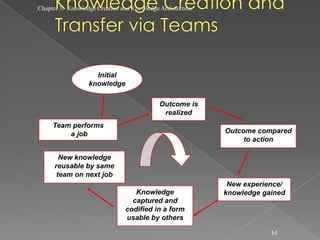
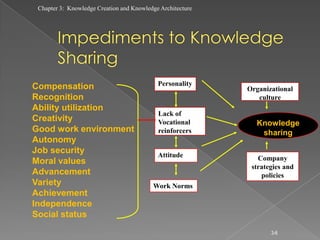
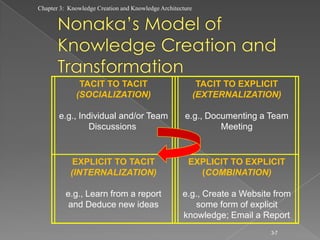
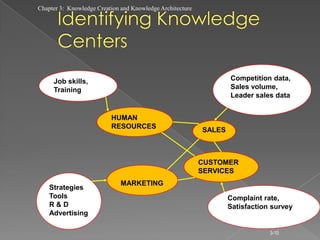
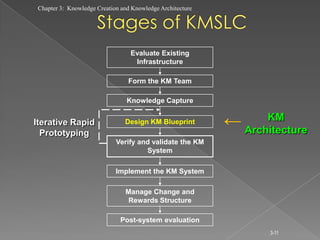
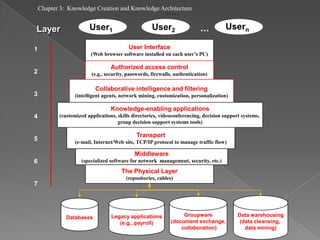
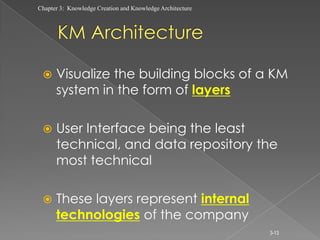
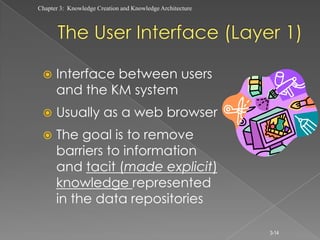
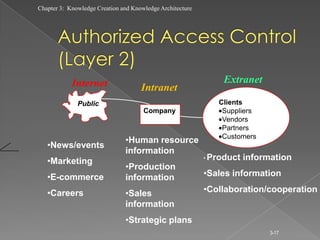
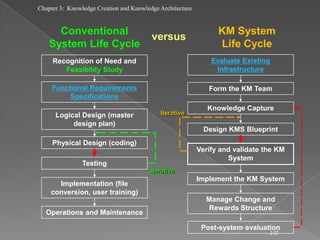
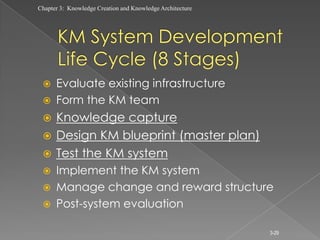
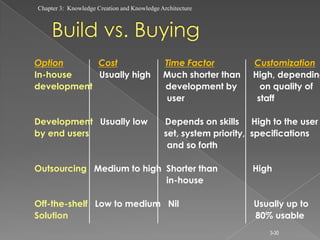
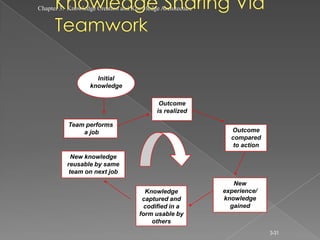
The document discusses knowledge creation and knowledge architecture. It covers challenges in building knowledge management systems, compares knowledge management system life cycles, and outlines an 8 stage knowledge management system life cycle. It also discusses knowledge creation, infrastructure, architecture, and whether to build or buy a knowledge management system. Finally, it presents models for knowledge conversion and a 7 layer knowledge management system architecture.