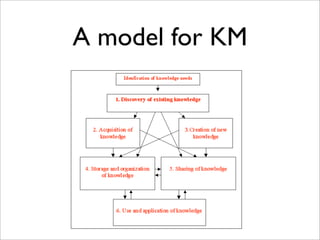
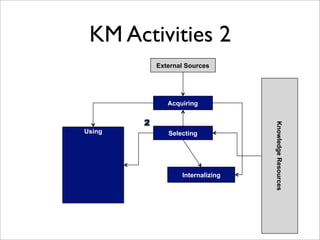
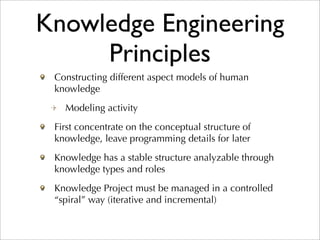
The document provides an overview of knowledge management and knowledge engineering. It discusses the differences between tacit and explicit knowledge. It also summarizes several models for knowledge management processes and activities, including acquiring, selecting, using, internalizing, and generating knowledge. Key frameworks covered include the SECI model, Frapaiolo's KM processes, and CommonKADS, a methodology for knowledge management system development.