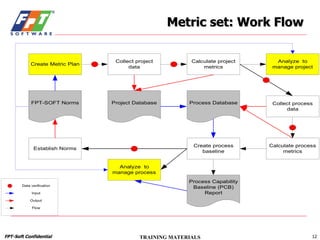
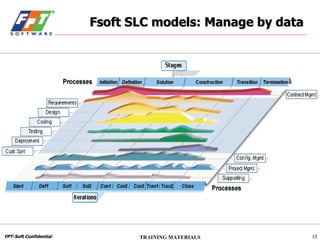
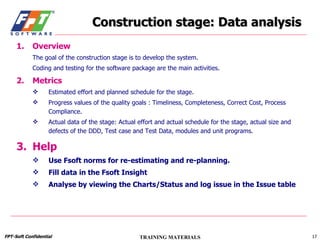
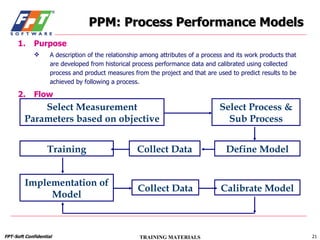
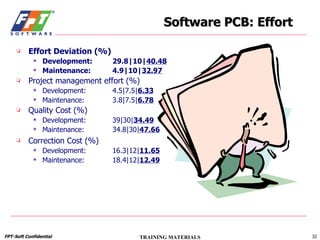
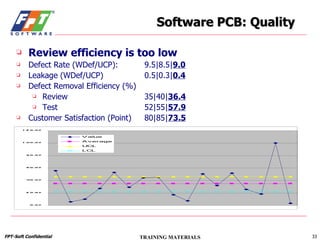
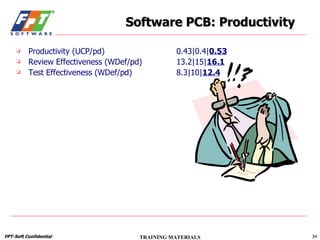
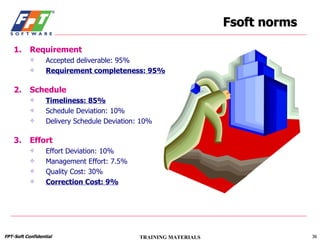
The document outlines a course for project management using data, aimed primarily at team leaders and project managers, lasting 1 hour and 45 minutes. It covers the Fsoft metric system, project management standards, and structured stages of the software life cycle (SLC), detailing how to effectively use data to manage projects, while evaluating and predicting project performance through metrics. Course objectives include understanding Fsoft norms and metrics, and applying these tools to enhance project planning, execution, and closure.