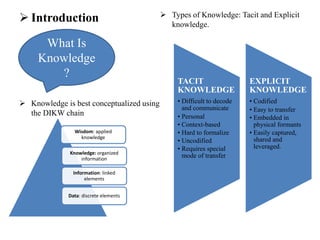
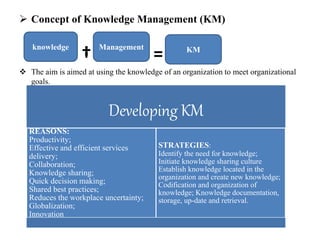
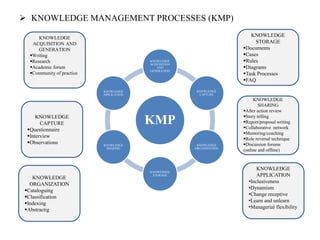
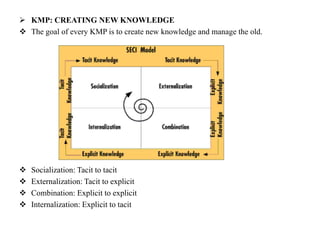
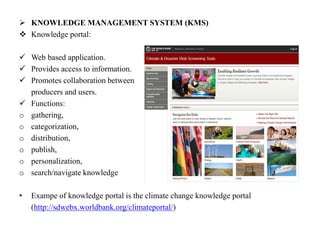
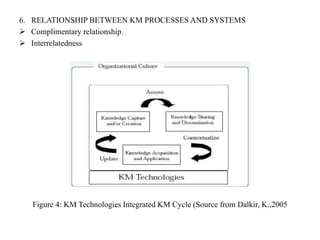
The document discusses the importance of knowledge management (KM) in organizations, emphasizing the interrelationship between people, processes, and systems in achieving organizational goals. It defines KM processes such as knowledge acquisition, sharing, storage, and application, while also highlighting technologies that facilitate these processes. It concludes with recommendations for fostering a knowledge-sharing culture and integrating technological systems to support KM practices.