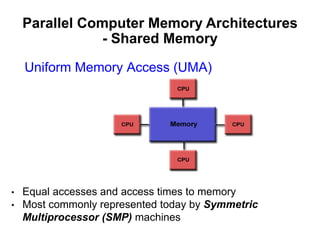
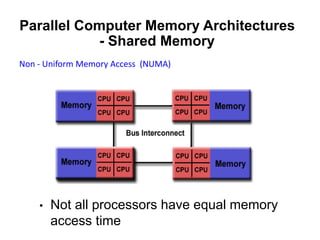
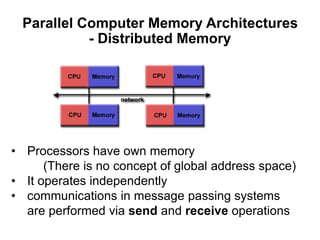
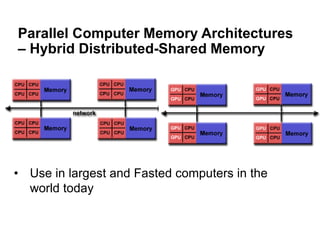
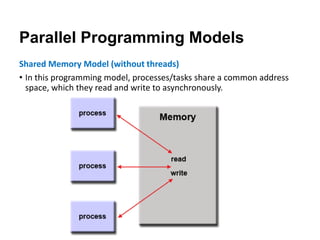
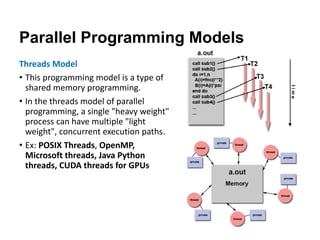
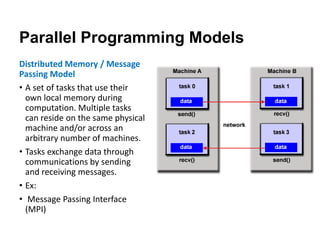
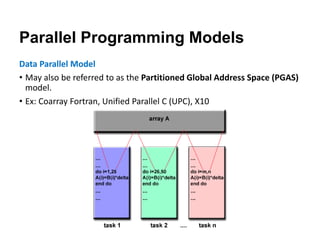
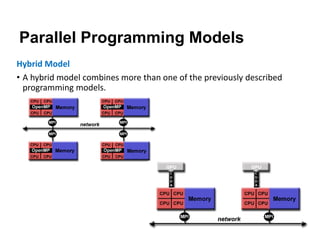
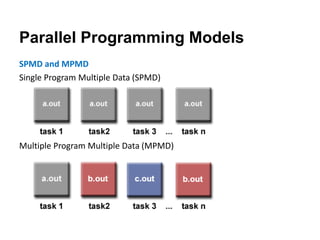
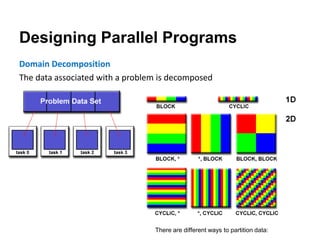
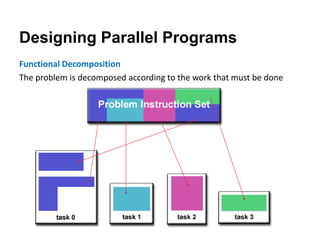
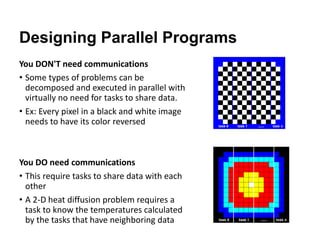
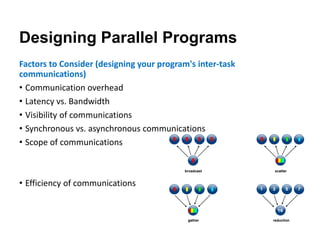
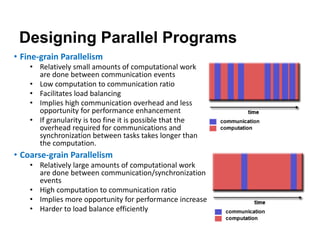
The document discusses parallel computing and memory architectures, specifically distinguishing between shared memory, distributed memory, and hybrid systems. It also covers various parallel programming models such as shared memory without threads, distributed memory/message passing, and hybrid approaches, along with key design considerations like partitioning, granularity, and I/O efficiency. Additionally, it highlights debugging and performance analysis tools used in parallel program development.