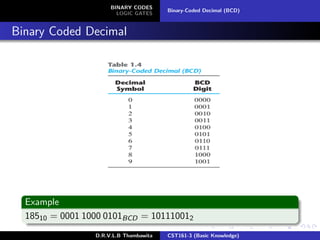
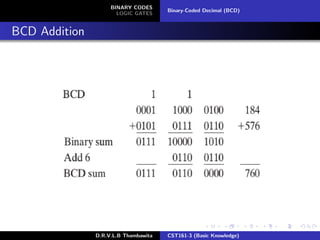
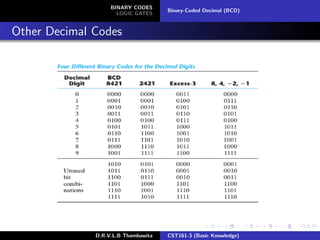
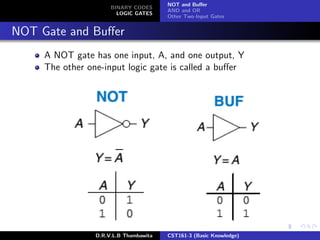
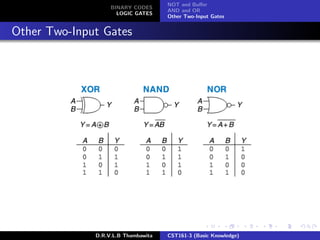
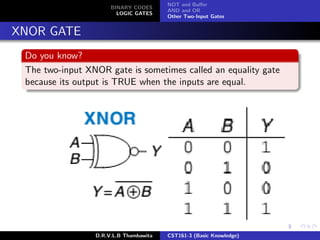
The document provides an overview of binary codes and logic gates, focusing on binary-coded decimal (BCD) representation and its applications in digital systems. It explains the fundamentals of binary codes, such as how n-bit binary codes can represent distinct elements, and discusses various logic gates and their functions. Additionally, the document includes examples of BCD representation and emphasizes the differences between decimal and BCD numbers.